
Photo of the Day


LIFE IN THE LOWER SUSQUEHANNA RIVER WATERSHED
A Natural History of Conewago Falls—The Waters of Three Mile Island

Let us travel through time for just a little while to recall those sunny, late-spring days down on the farm—back when the rural landscape was a quiet, semi-secluded realm with little in the way of traffic, housing projects, or industrialized agriculture. Those among us who grew up on one of these family homesteads, or had friends who did, remember the joy of exploring the meadows, thickets, soggy springs, and woodlots they protected.

For many of us, farmland was the first place we encountered and began to understand wildlife. Vast acreage provided an abundance of space to explore. And the discovery of each new creature provided an exciting experience.

Today, high-intensity agriculture, relentless mowing, urban sprawl, and the increasing costs and demand for land have all conspired to seriously deplete habitat quality and quantity for many of the species we used to see on the local farm. Unfortunately for them, farm wildlife has largely been the victim of modern economics.
For old time’s sake, we recently passed a nostalgic afternoon at Middle Creek Wildlife Management Area examining what maintenance of traditional farm habitat has done and can do for breeding birds. Join us for a quick tour to remember how it used to be at the farm next door…

















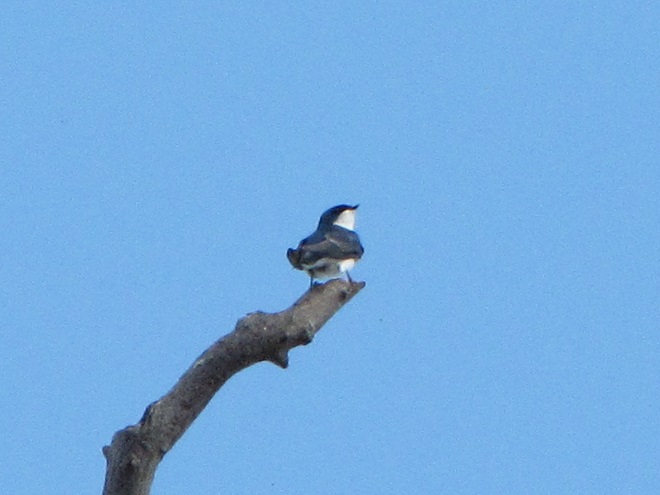
For many animals, an adequate shelter is paramount for their successful reproduction. Here’s a sample of some of the lower Susquehanna valley’s nest builders in action…
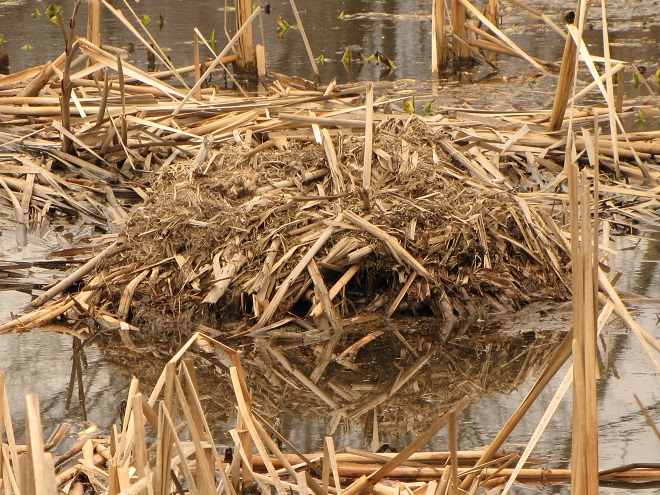




















Despite what seemed to be a chilly early spring, the bright green leaves that unfold to close the canopy of our deciduous forests were dense and casting shade by the last days of April. For northbound migrants, this fresh foliage provides the cover they need for foraging, resting, and, for those that will stick around to breed in the lower Susquehanna valley, nesting.
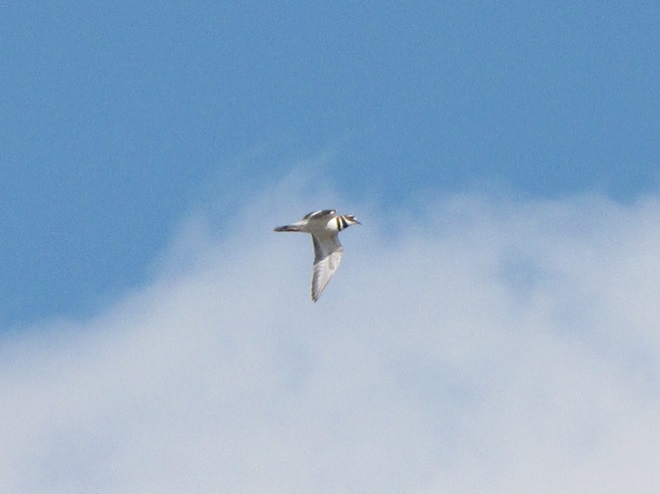
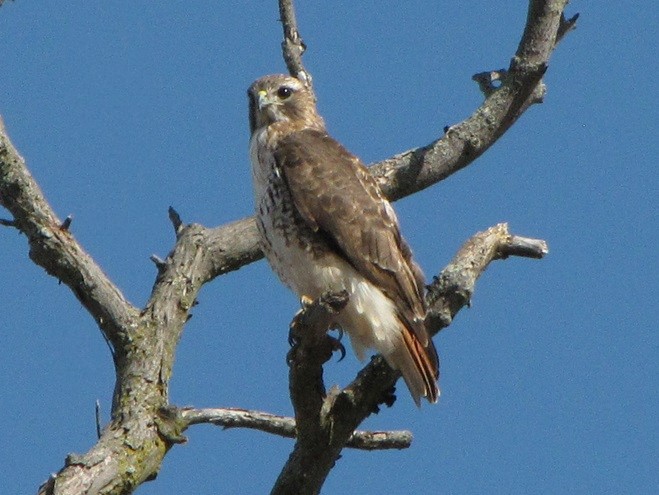
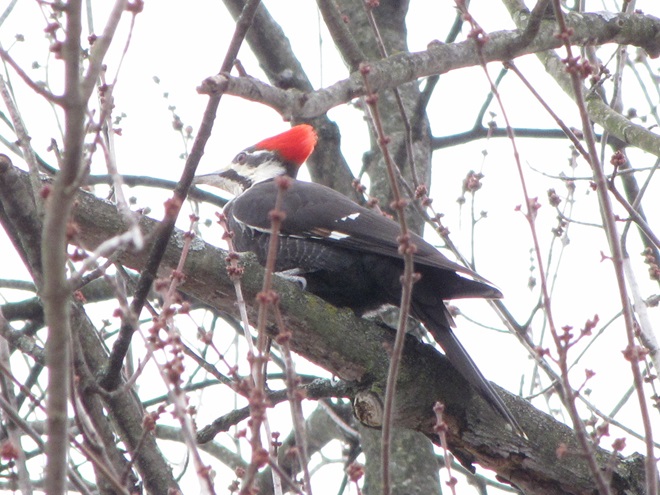
We recall many occasions when sparse foliage during the first days of May seemed to delay the big push of Neotropical species, but the seasonal arrival of these birds in 2025 is thus far mostly ahead of schedule. This absence of delay is due in part to the lushness of the oaks. Some stands have not only leafed out, but are finished flowering and have added up to 12 inches of new branch growth. We spent these early hours of May among the oaks. Here’s a look at the Neotropical migrants and other species we found…








The movements of our migratory birds typically continue through much of the month of May. And peak numbers of Neotropical species often occur sometime during the second week of the month. But with habitat at the ready, favorable flight conditions could facilitate quick arrival and/or passage of the bulk of the remaining migrants during the coming week. You may want to venture out sooner rather than later—but watch your step!



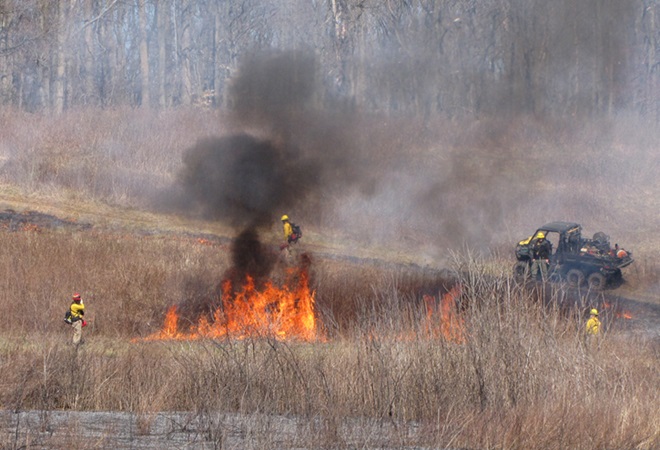
During Saturday’s Prescribed Fire Demonstration at the Pennsylvania Game Commission’s Middle Creek Wildlife Management Area, we noticed just how fast some species of wildlife return to areas subjected to burns administered to maintain grassland habitat and reduce the risk of high-intensity blazes.







Following the Prescribed Fire Demonstration, we decided to pay a visit to some of the parcels where burns had been administered one week earlier on the north side of Middle Creek’s main impoundment. We found a surprising amount of activity.







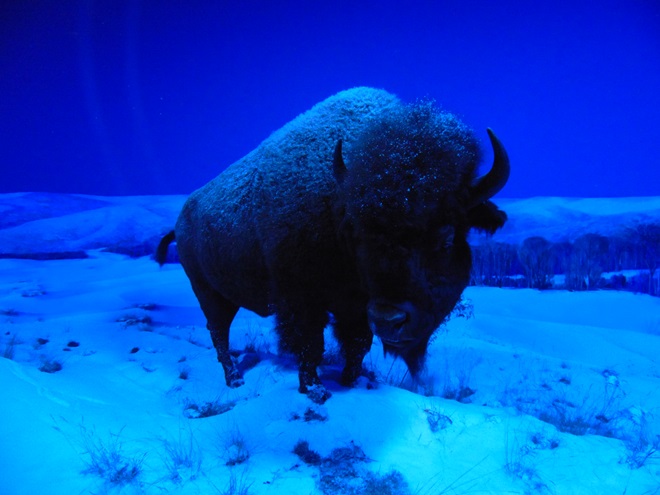
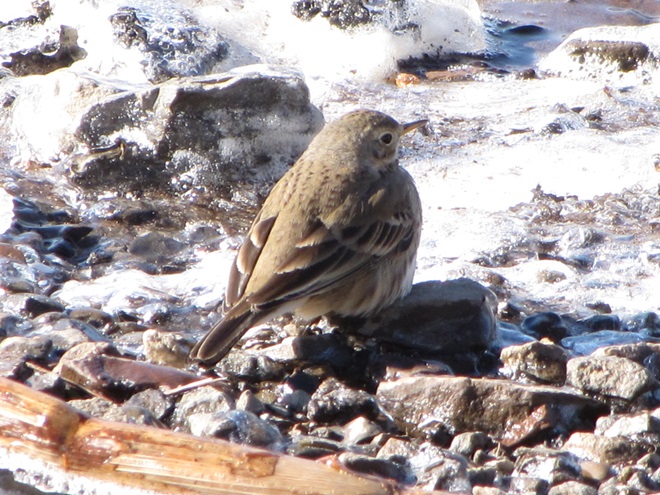
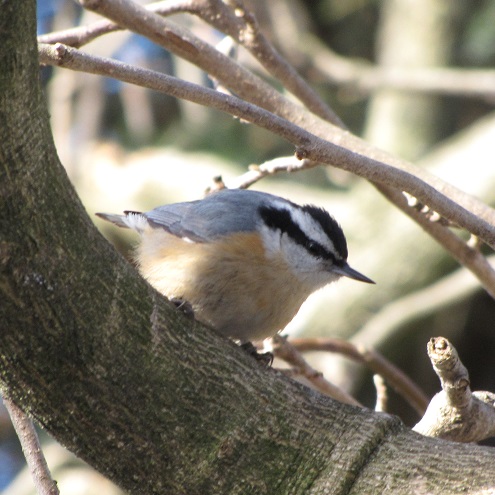
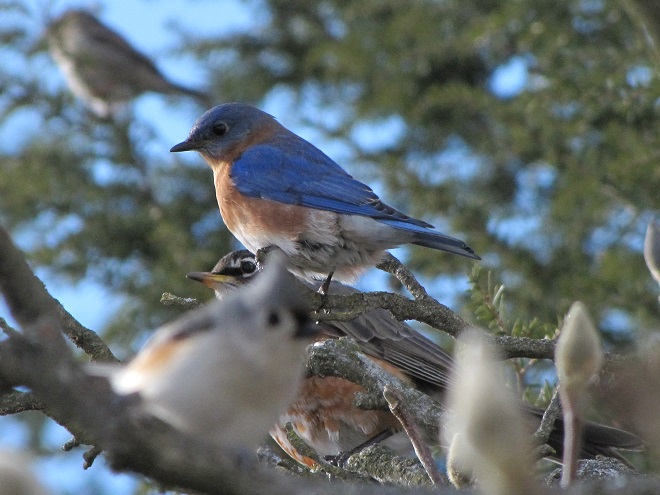
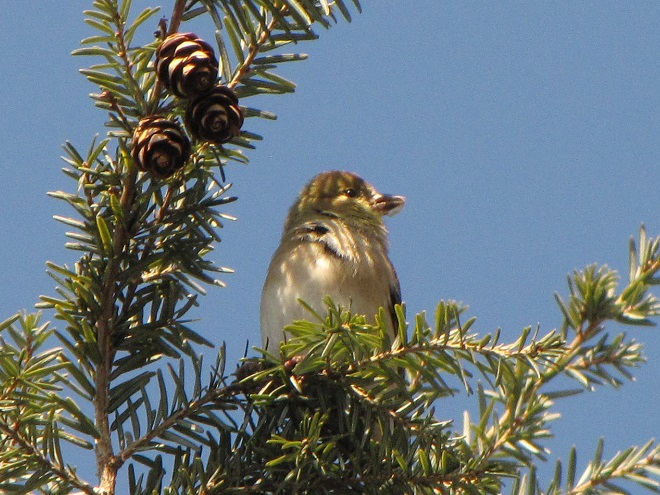
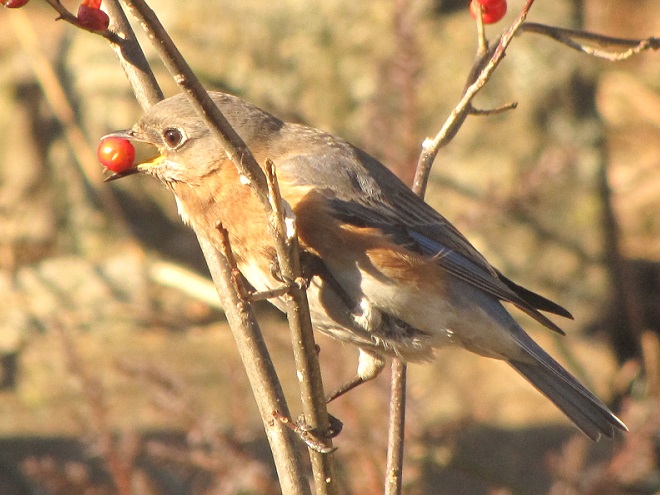
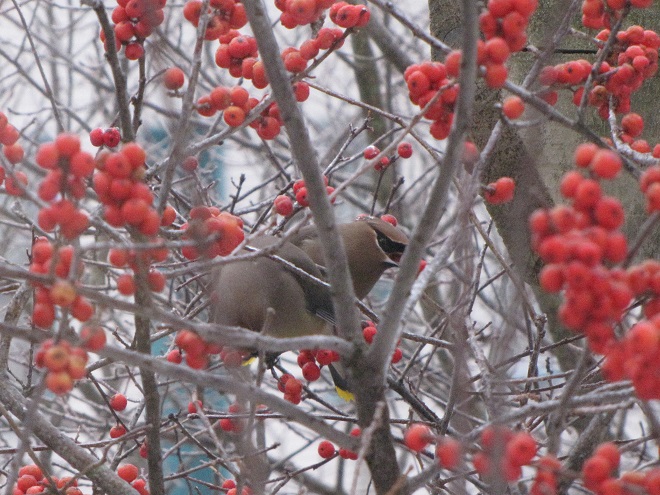
We’ve seen worse, but this winter has been particularly tough for birds and mammals in the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed. Due to the dry conditions of late summer and fall in 2024, the wild food crop of seeds, nuts, berries, and other fare has been less than average. The cold temperatures make insects hard to come by. Let’s have a look at how some of our local generalist and specialist species are faring this winter.





















Wildlife certainly has a tough time making it through the winter in the lower Susquehanna valley. Establishing and/or protecting habitat that includes plenty of year-round cover and sources of food and water can really give generalist species a better chance of survival. But remember, the goal isn’t to create unnatural concentrations of wildlife, it is instead to return the landscape surrounding us into more of a natural state. That’s why we try to use native plants as much as possible. And that’s why we try to attract not only a certain bird, mammal, or other creature, but we try to promote the development of a naturally functioning ecosystem with a food web, a diversity of pollinating plants, pollinating insects, and so on. Through this experience, we stand a better chance of understanding what it takes to graduate to the bigger job at hand—protecting, enhancing, and restoring habitats needed by specialist species. These are efforts worthy of the great resources that are sometimes needed to make them a success. It takes a mindset that goes beyond a focus upon the welfare of each individual animal to instead achieve the discipline to concentrate long-term on the projects and processes necessary to promote the health of the ecosystems within which specialist species live and breed. It sounds easier than it is—the majority of us frequently become distracted.


On the wider scale, it’s of great importance to identify and protect the existing and potential future habitats necessary for the survival of specialist species. And we’re not saying that solely for their benefit. These protection measures should probably include setting aside areas on higher ground that may become the beach intertidal zone or tidal marsh when the existing ones become inundated. And it may mean finally getting out of the wetlands, floodplains, and gullies to let them be the rain-absorbing, storm-buffering, water purifiers they spent millennia becoming. And it may mean it’s time to give up on building stick structures on tinderbox lands, especially hillsides and rocky outcrops with shallow, eroding soils that dry to dust every few years. We need to think ahead and stop living for the view. If you want to enjoy the view from these places, go visit and take plenty of pictures, or a video, that’s always nice—then live somewhere else. Each of these areas includes ecosystems that meet the narrow habitat requirements of many of our specialist species, and we’re building like fools in them. Then we feign victimhood and solicit pity when the calamity strikes: fires, floods, landslides, and washouts—again and again. Wouldn’t it be a whole lot smarter to build somewhere else? It may seem like a lot to do for some specialist animals, but it’s not. Because, you see, we should and can live somewhere else—they can’t.


Here are 7 reasons why you, during the coming week or so, should consider spending some time at Willow Point overlooking the lake at the Pennsylvania Game Commission’s Middle Creek Wildlife Management Area.
REASON NUMBER ONE— Wildlife is at close quarters along the trail leading from the parking lot to Willow Point…




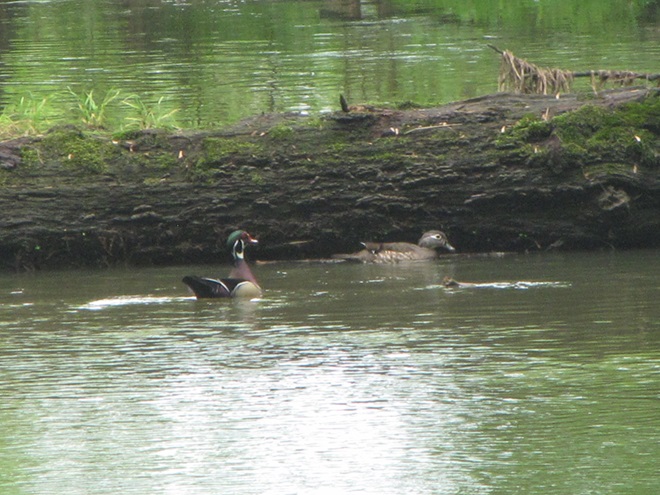
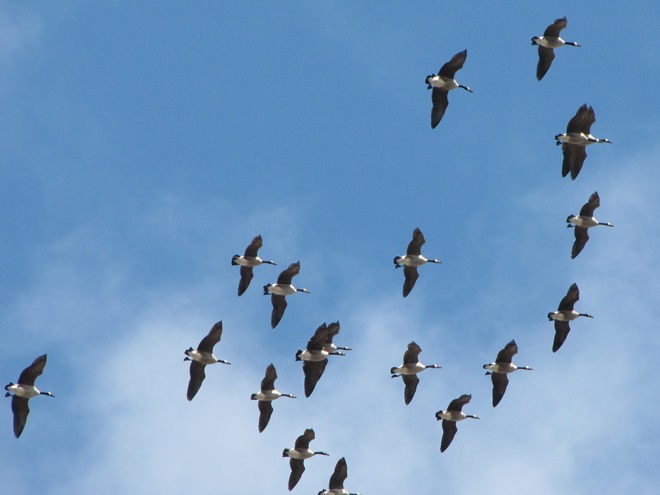
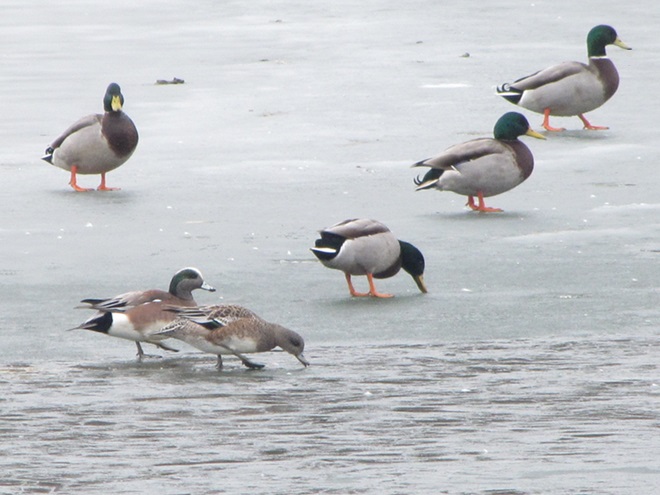
REASON NUMBER TWO— A variety of waterfowl species are lingering on ice-free sections of the lake surrounding Willow Point…






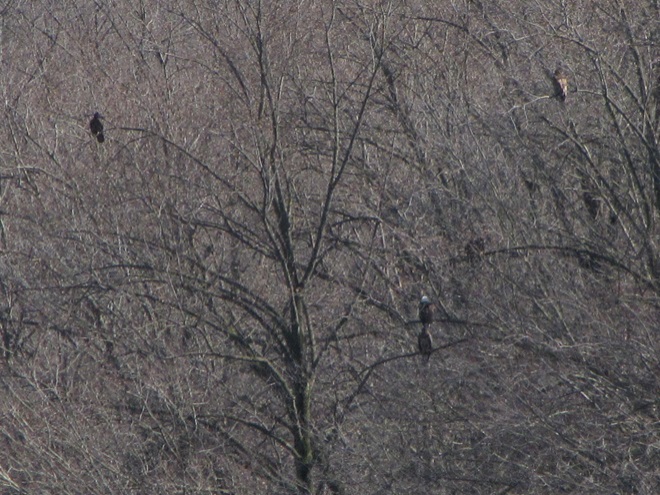
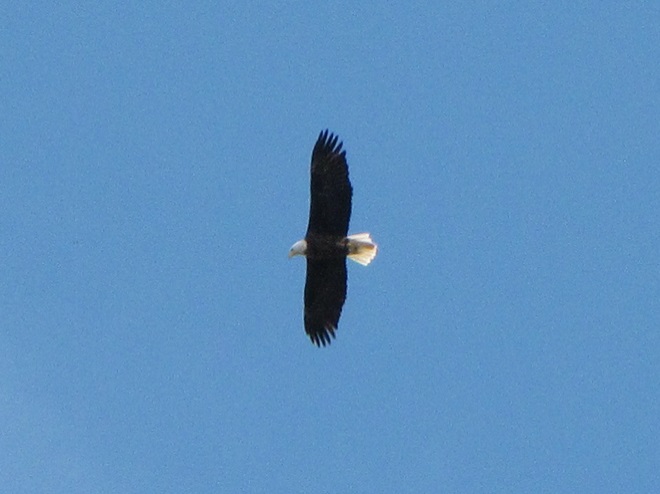
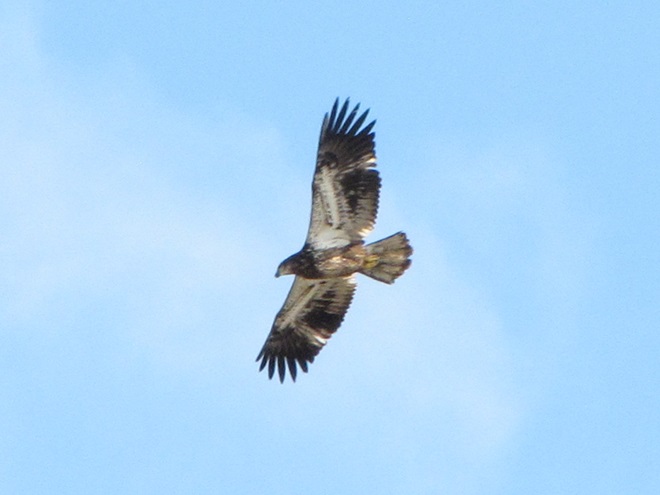
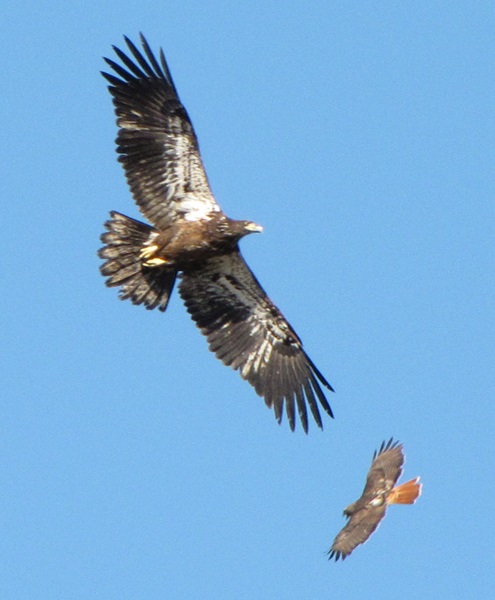
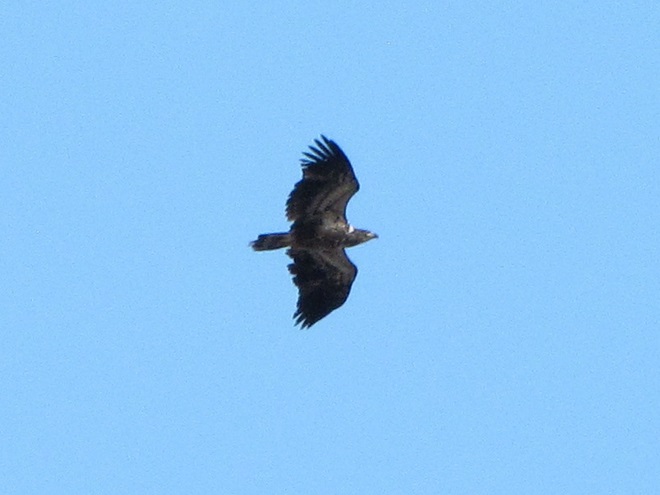
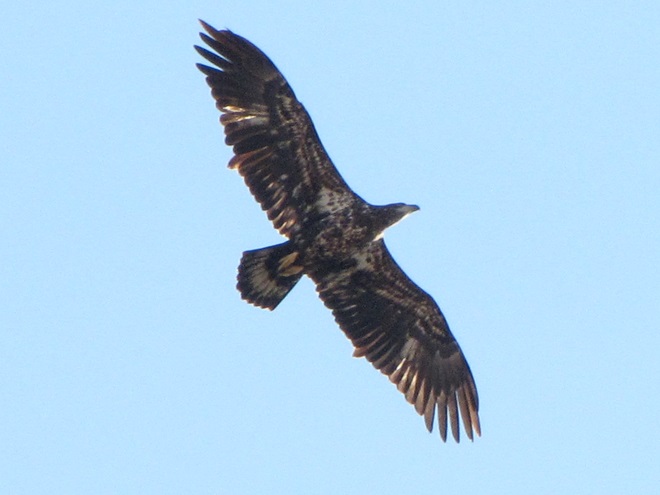
REASON NUMBER THREE— Bald Eagles are conspicuous, easily seen and heard…


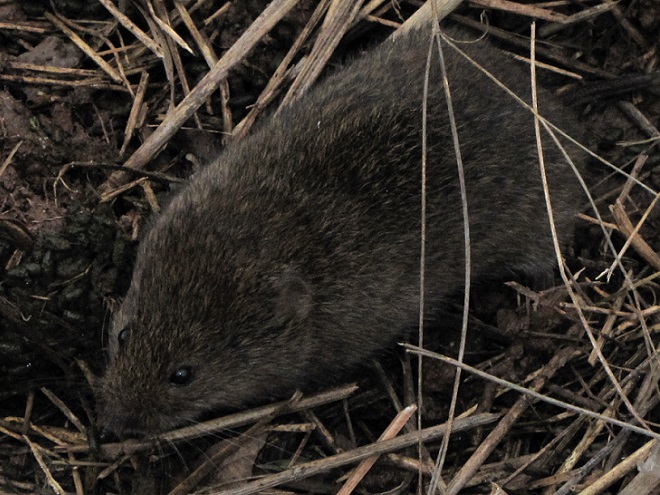
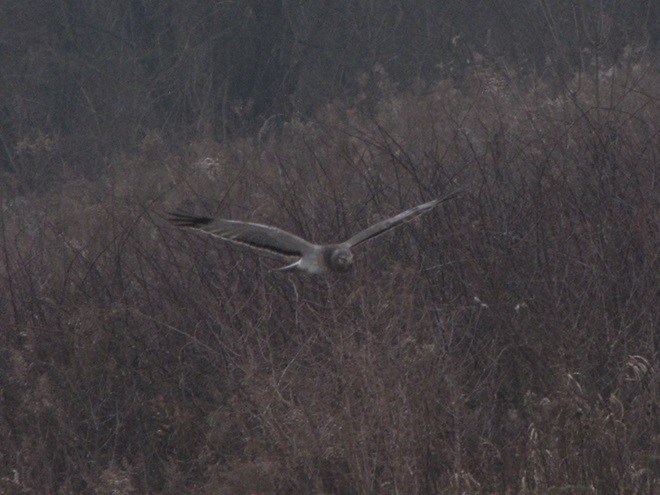
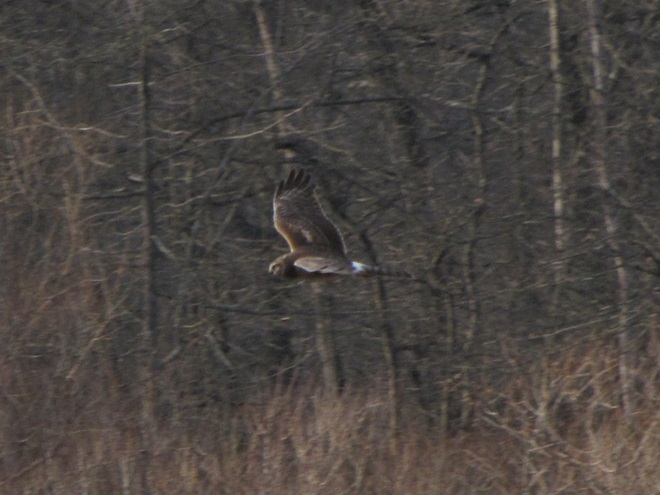
REASON NUMBER FOUR— Northern Harriers have been making close passes over Willow Point as they patrol Middle Creek’s grasslands while hunting voles…




REASON NUMBER FIVE— The annual observance of the White-tailed Deity holidays may be drawing to a close for the gasoline and gunpowder gang, but for the supreme ungulates, the rituals that lead to consummation of their unions are still ongoing…



REASON NUMBER SIX— Sandhill Cranes are still being seen from Willow Point…


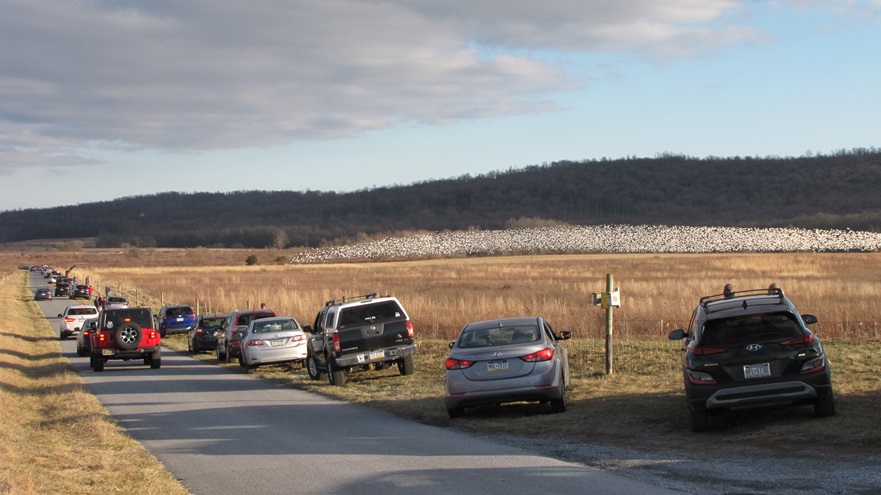
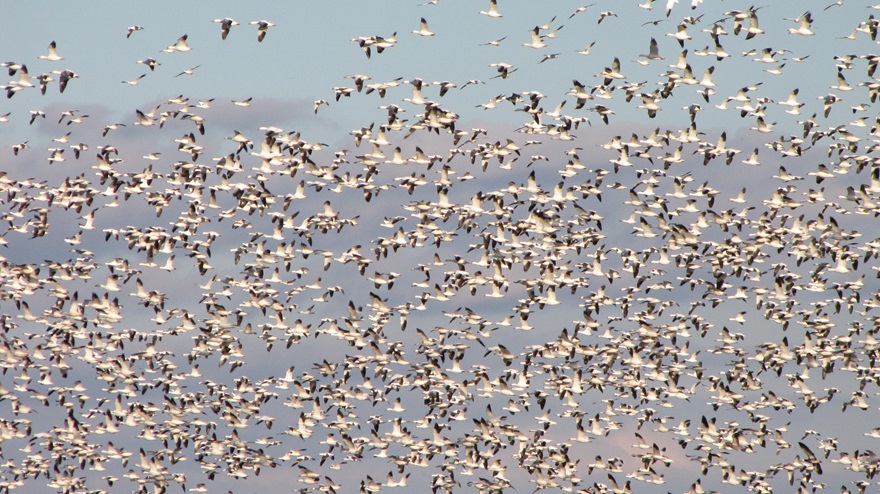
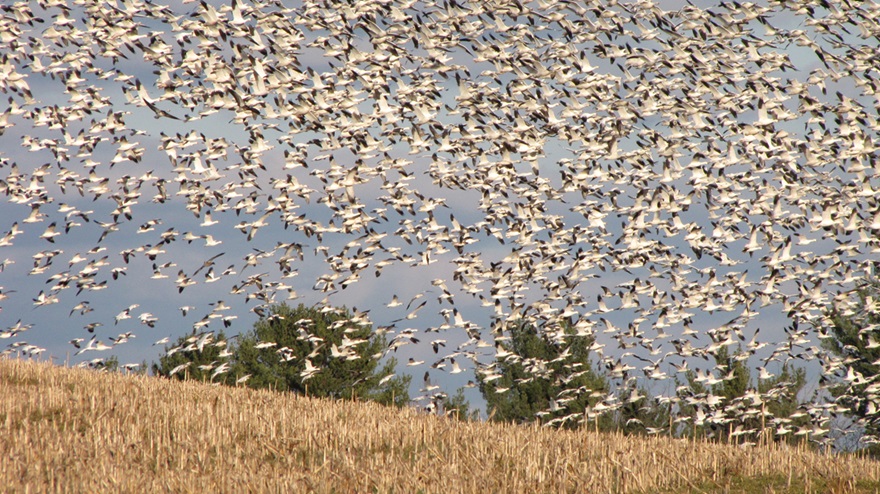
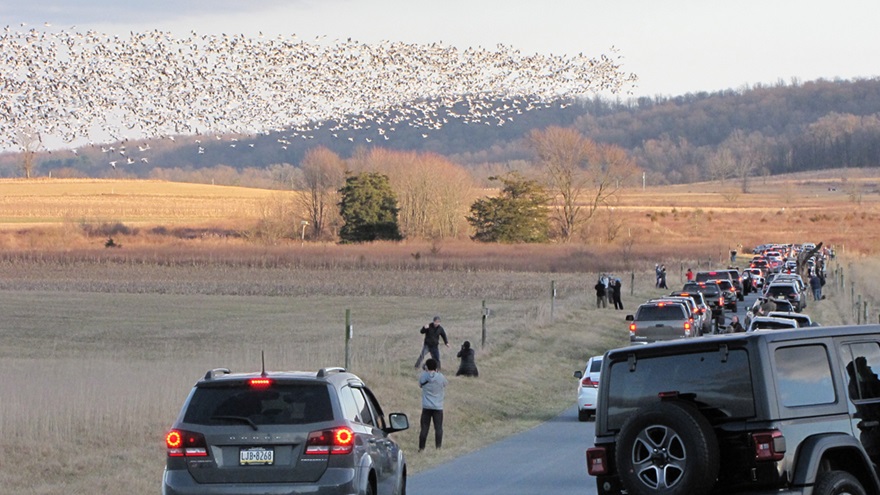
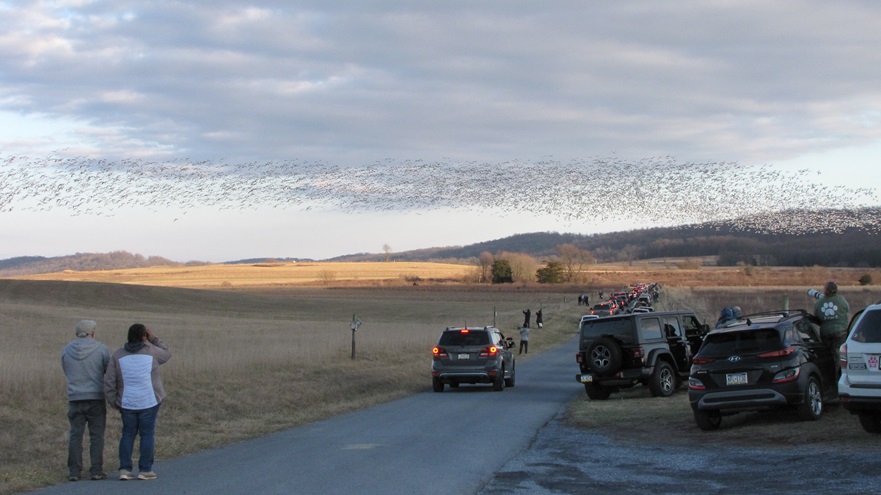
REASON NUMBER SEVEN— The crowds that will accompany the arrival of thousands of Snow Geese in early 2025 can make visiting Willow Point a stressful experience. Visit now to see these birds and mammals at Willow Point and you might just have the place all to yourself. Then you can spend your time looking through the flocks of waterfowl and other birds for unusual new arrivals instead of wading through a sea of humanity.

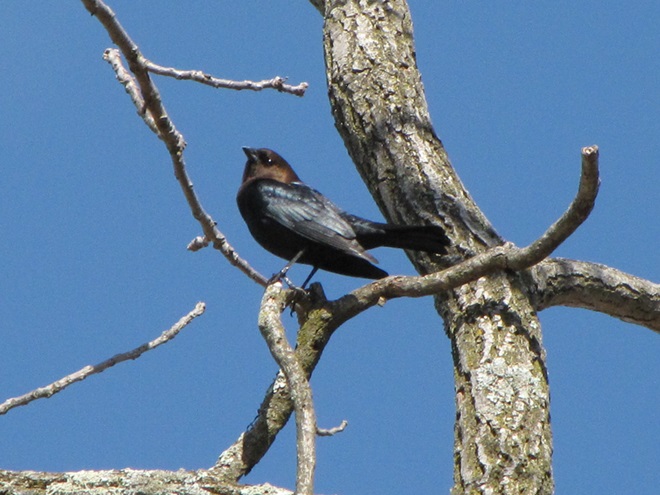
Each spring and fall, Purple Finches are regular migrants through the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed. Northbound movements usually peak in April and early May. During the summer, these birds nest primarily in cool coniferous forests to our north. Then, in October and November each year, they make another local appearance on their way to wintering grounds in the southeastern United States. A significant population of Purple Finches remains to our north through the colder months, inhabiting spruce-pine and mixed forests from the Great Lakes east through New England and southeastern Canada. This population can be irruptive, moving south in conspicuous numbers to escape inclement weather, food shortages, and other environmental conditions. Every few years, these irruptive birds can be found visiting suburbs, parks, and feeding stations—sometimes lingering in areas not often visited by Purple Finches. Right now, Purple Finches in flocks larger than those that moved through earlier in the fall are being seen throughout the lower Susquehanna valley. Snow and blustery weather to our north may be prompting these birds to shift south for a visit. Here are some looks at members of a gathering of more than four dozen Purple Finches we’ve been watching in Lebanon County this month…







As the autumn bird migration draws to a close for 2024, we’re delighted to be finding five of our favorite visitors from the coniferous and mixed forests of Canada and the northernmost continental United States.






While right now is the best time to get out and look for these species from the northern forests, any or all of them could linger into the winter months, particularly where the food supply is sufficient and conifers and other evergreens provide cover from the blustery weather.
During your foray to view the colorful foliage of the autumn landscape, a little effort will reveal much more than meets the eye of the casual observer.






















You too can experience the joys of walking and chewing gum at the same time, so grab your field glasses, your camera, and your jacket, then spend lots of time outdoors this fall. You can see all of this and much more.
Don’t forget to click the “Hawkwatcher’s Helper: Identifying Bald Eagles and other Diurnal Raptors” tab at the top of this page to help you find a place to see both fall foliage and migrating birds of prey in coming weeks. And click the “Trees, Shrubs, and Woody Vines” tab to find a photo guide that can help you identify the autumn leaves you encounter during your outings.
Back on March 24th, we took a detailed look at the process involved in administering prescribed fire as a tool for managing grassland and early successional habitat. Today we’re going turn back the hands of time to give you a glimpse of how the treated site fared during the five months since the controlled burn. Let’s go back to Middle Creek Wildlife Management Area for a photo tour to see how things have come along…
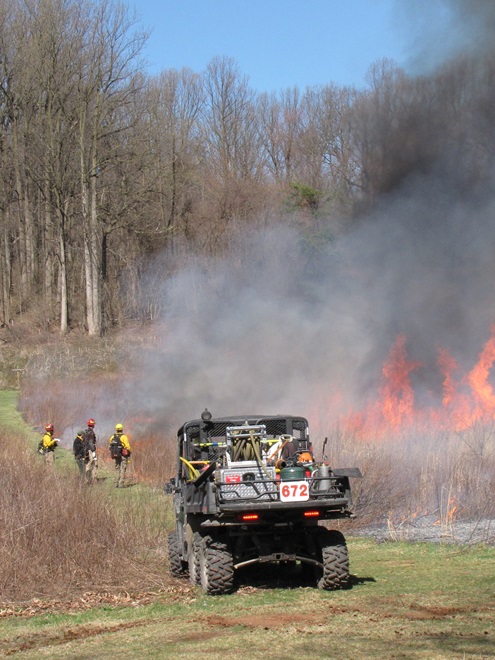















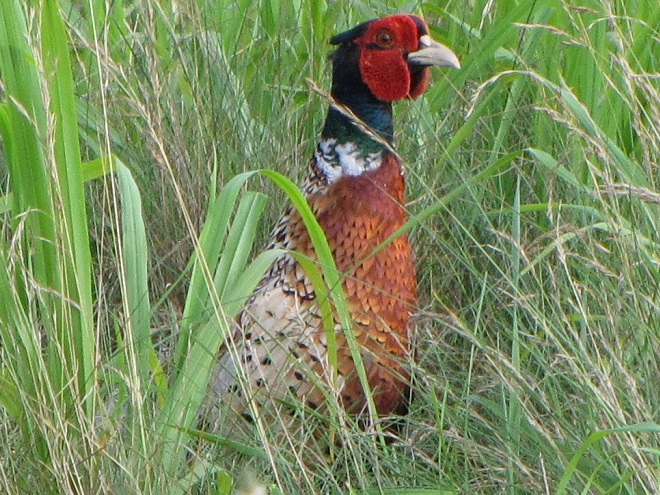
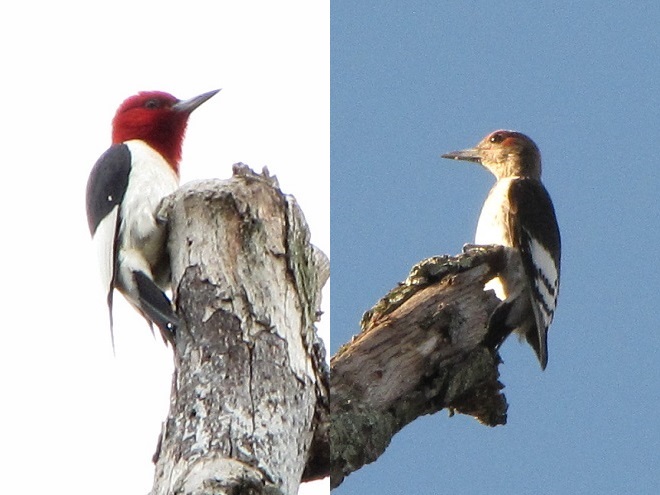
Elsewhere around the refuge at Middle Creek, prescribed fire and other management techniques are providing high-quality grassland habitat for numerous species of nesting birds…



We hope you enjoyed this short photo tour of grassland management practices. Now, we’d like to leave you with one last set of pictures—a set you may find as interesting as we found them. Each is of a different Eastern Cottontail, a species we found to be particularly common on prescribed fire sites when we took these images in late May. The first two are of the individuals we happened to be able to photograph in areas subjected to fire two months earlier in March. The latter two are of cottontails we happened to photograph elsewhere on the refuge in areas not in proximity to ground treated with a prescribed burn or exposed to accidental fire in recent years.


These first two rabbits are living the good life in a warm-season grass wonderland.


Oh Deer! Oh Deer! These last two rabbits have no clock to track the time; they have only ticks. Better not go for a stroll with them Alice—that’s no wonderland! I know, I know, it’s time to go. See ya later.
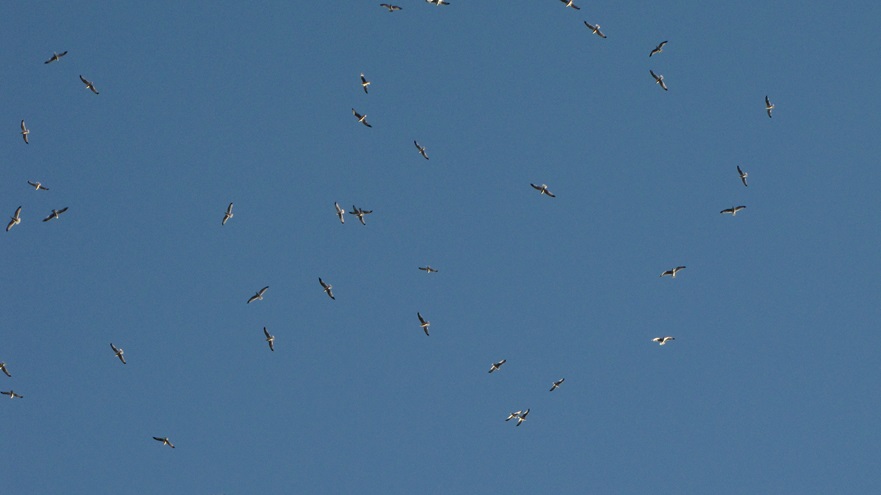
As waves of wet weather persistently roll through the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed, the tide of northbound migrants continues. Here are few of today’s highlights…





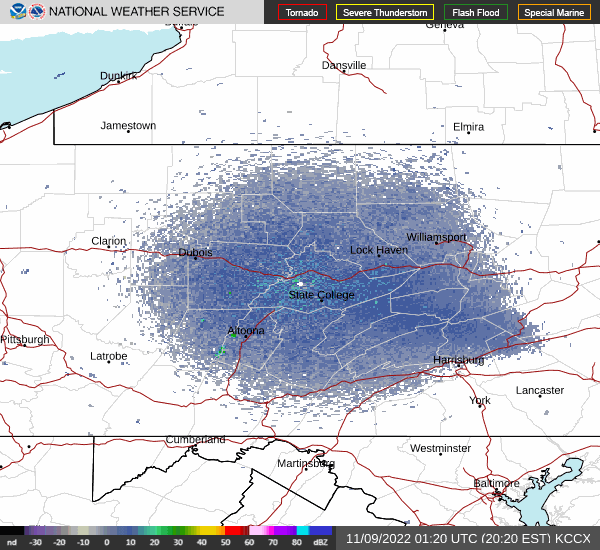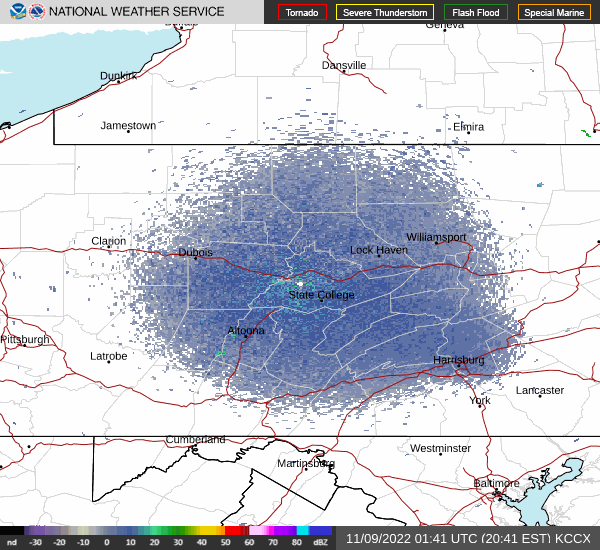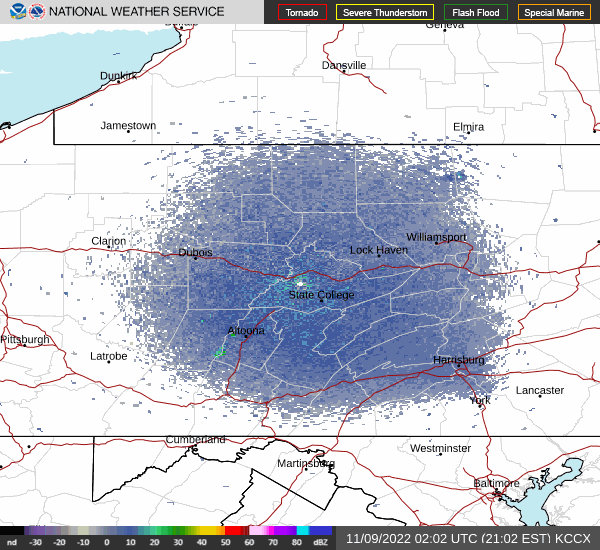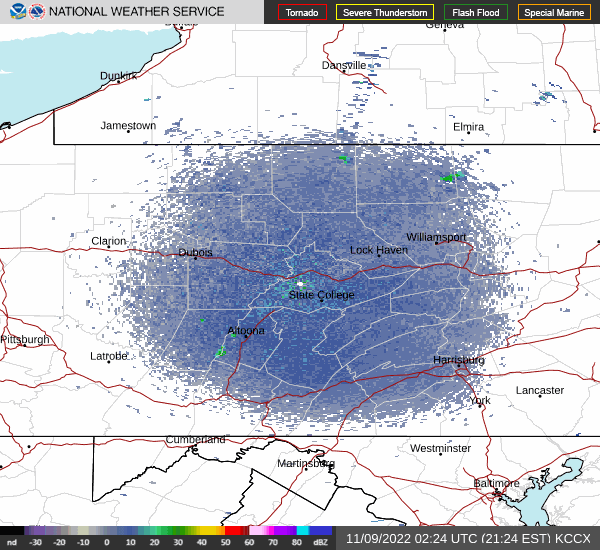
In recent days, the peak northbound push of migratory birds that includes the majority of our colorful Neotropical species has been slowed to a trickle by the presence of rain, fog, and low overcast throughout the Mid-Atlantic States. Following sunset last evening, the nocturnal flight resumed—only to be grounded this morning during the pre-dawn hours by the west-to-east passage of a fast-moving line of strong thundershowers. The NOAA/National Weather Service images that follow show the thunderstorms as well as returns created by thousands of migrating birds as they pass through the Doppler Radar coverage areas that surround the lower Susquehanna valley.

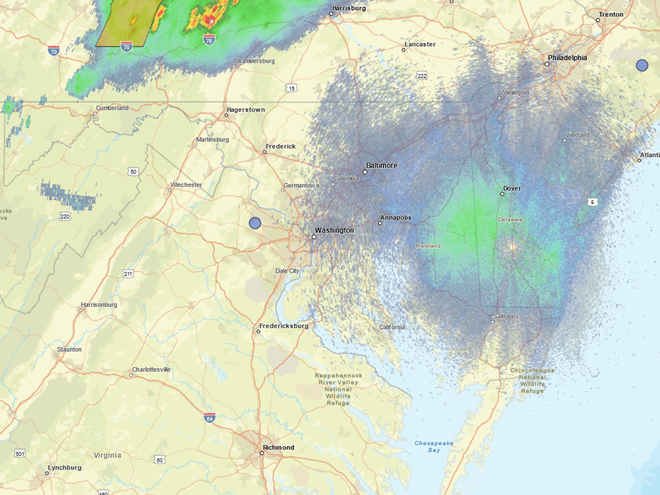
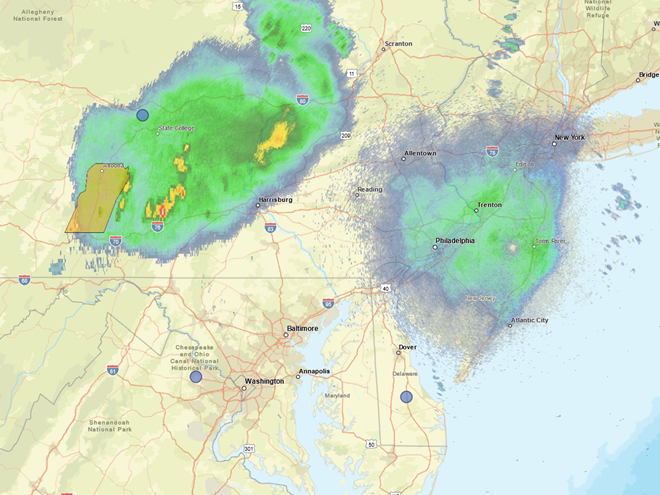
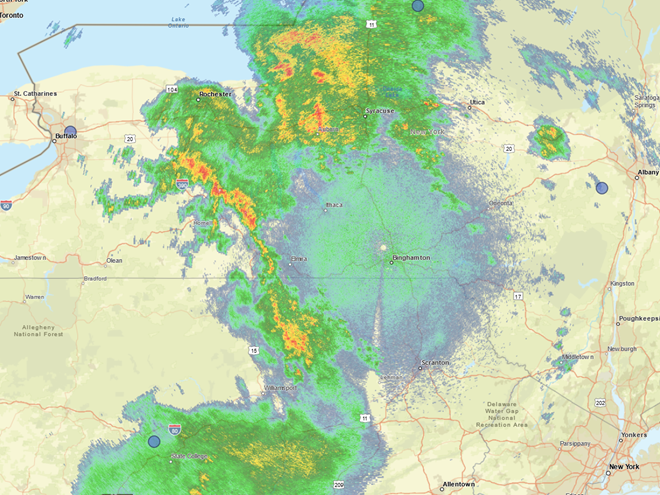
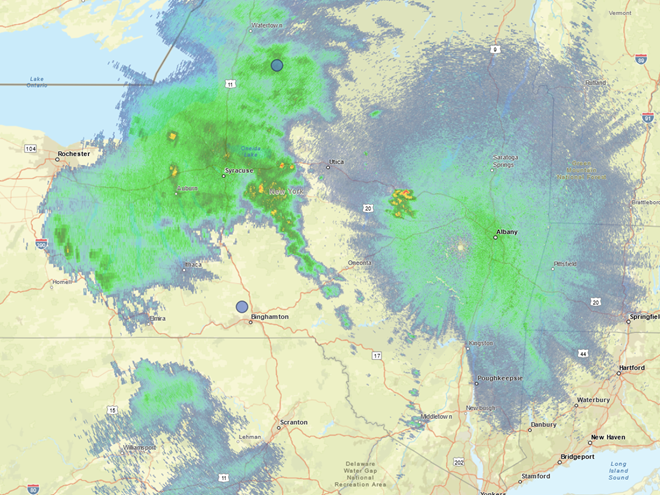
Just after 4 A.M., flashes of lightning in rapid succession repeatedly illuminated the sky over susquehannawildlife.net headquarters. Despite the rumbles of thunder and the din of noises typical for our urban setting, the call notes of nocturnal migrants could be heard as these birds descended in search of a suitable place to make landfall and seek shelter from the storm. At least one Wood Thrush and a Swainson’s Thrush (Catharus ustulatus) were in the mix of species passing overhead. A short time later at daybreak, a Great Crested Flycatcher was heard calling from a stand of nearby trees and a White-crowned Sparrow was seen in the garden searching for food. None of these aforementioned birds is regular here at our little oasis, so it appears that a significant and abrupt fallout has occurred.
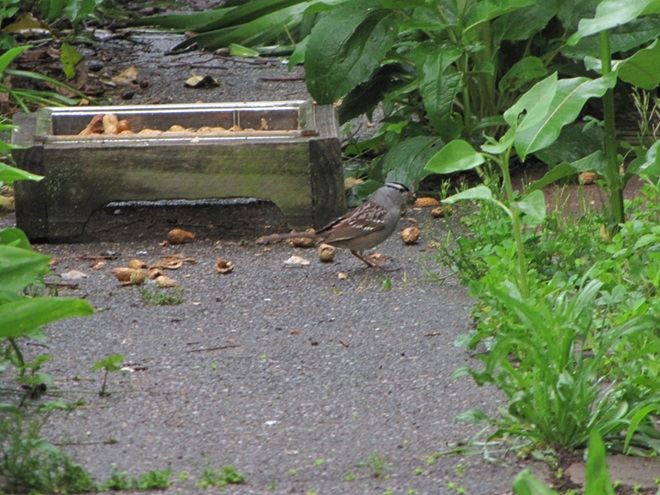

Looks like a good day to take the camera for a walk. Away we go!
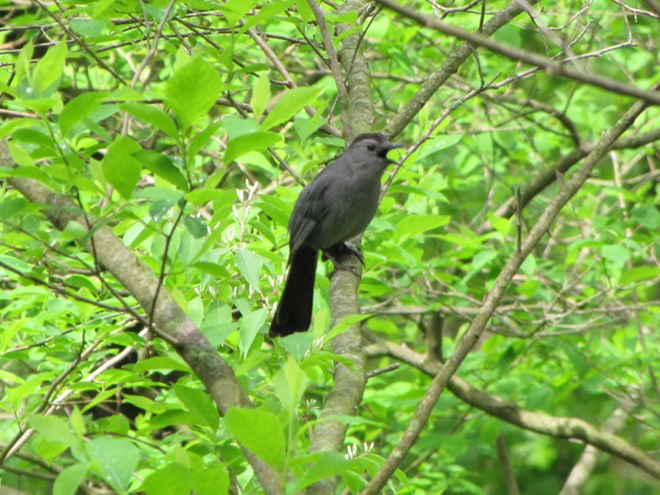
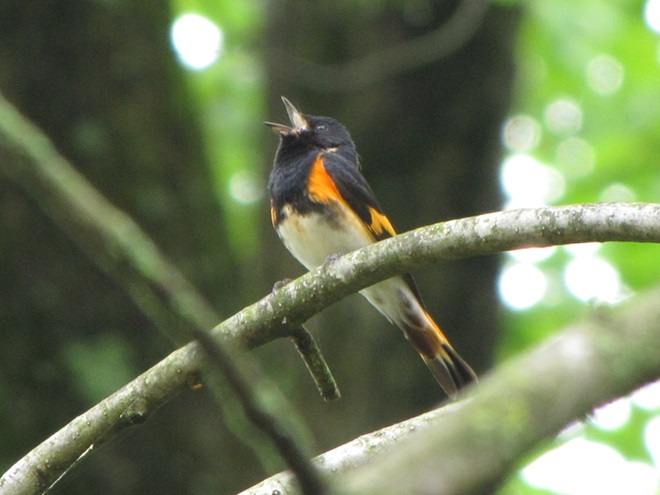
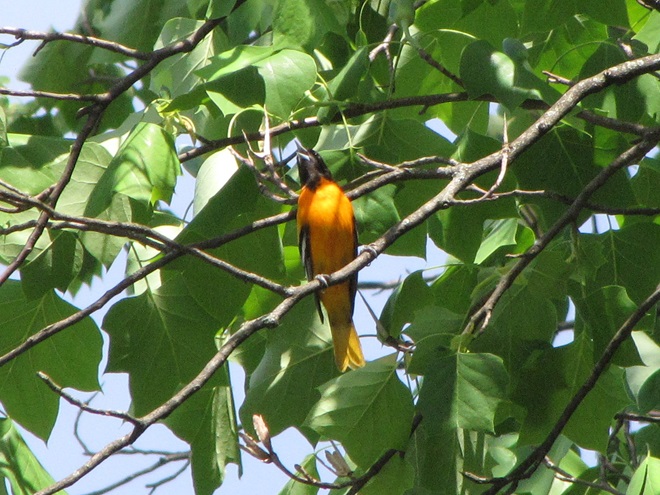
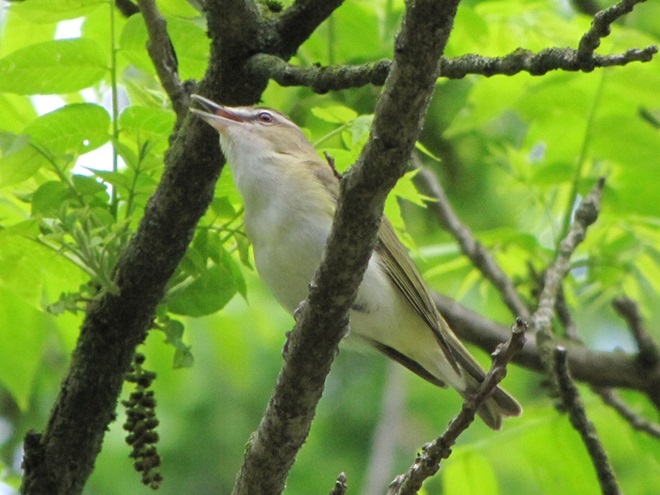
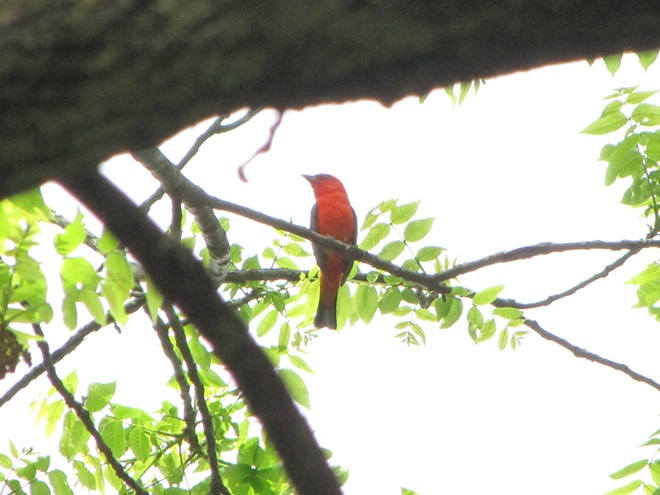
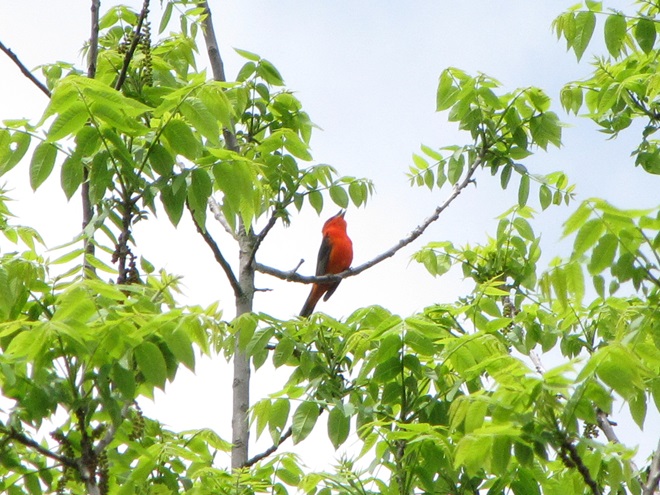
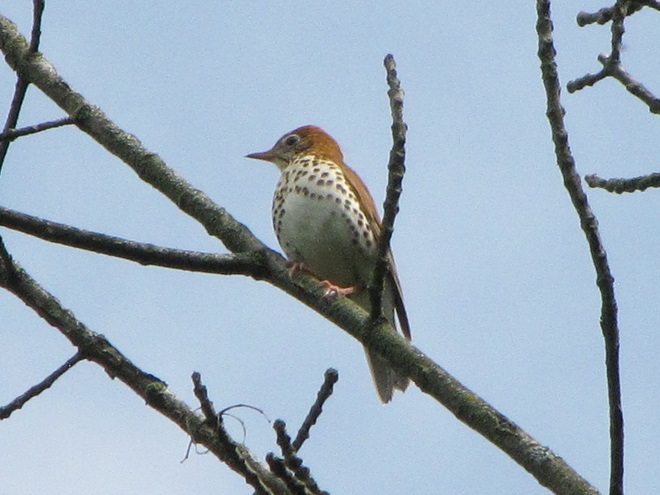
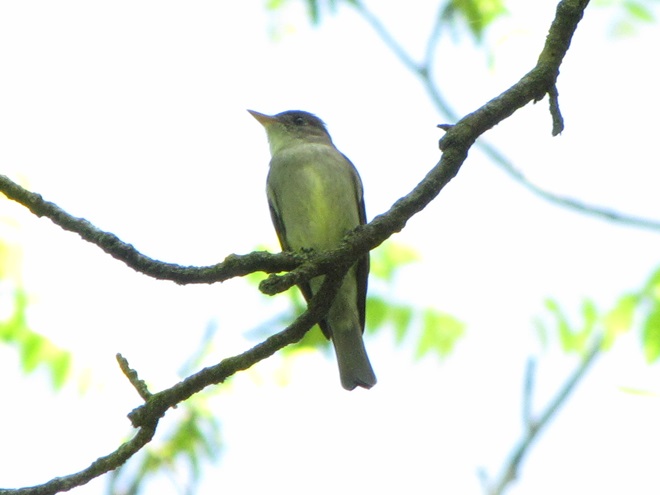
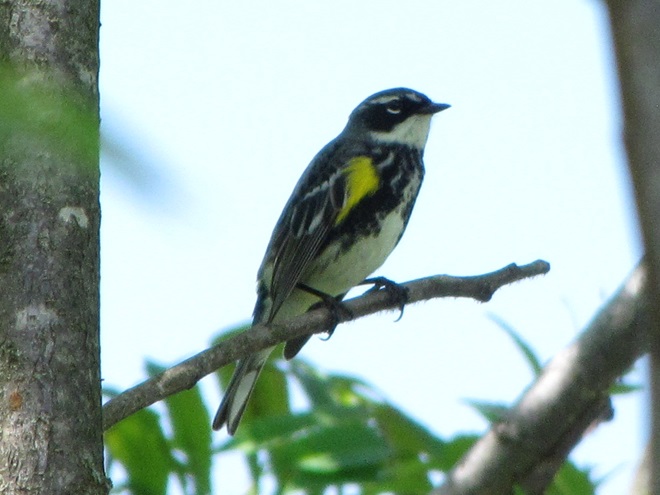
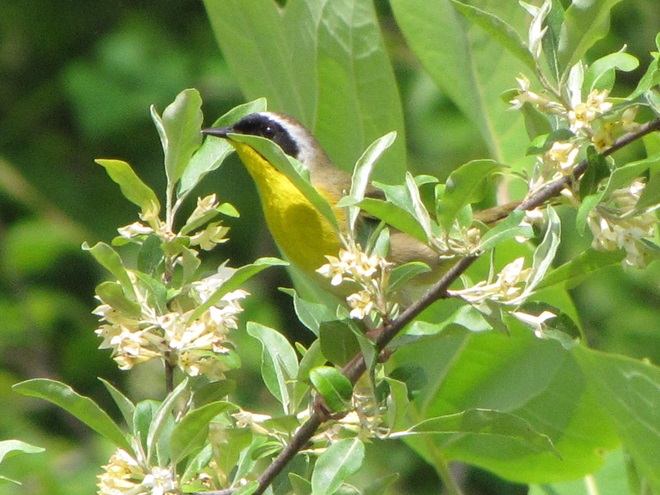
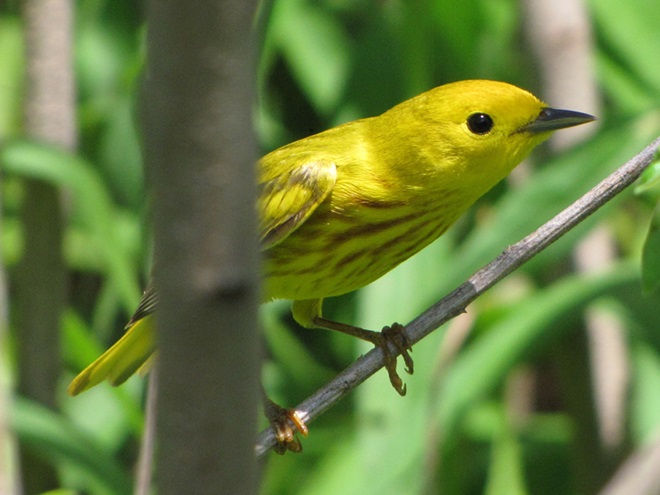
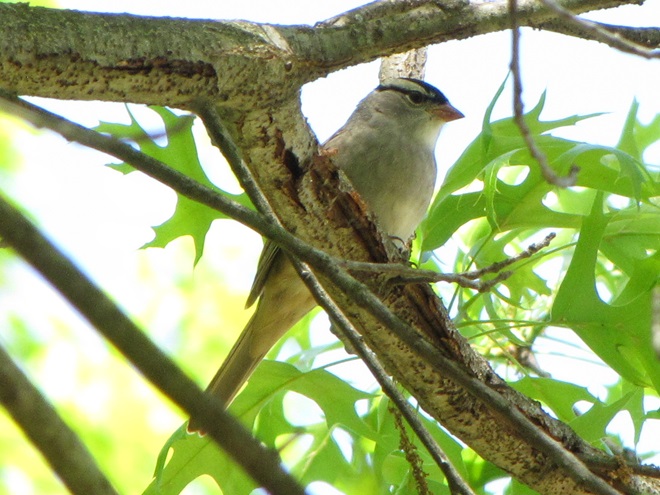
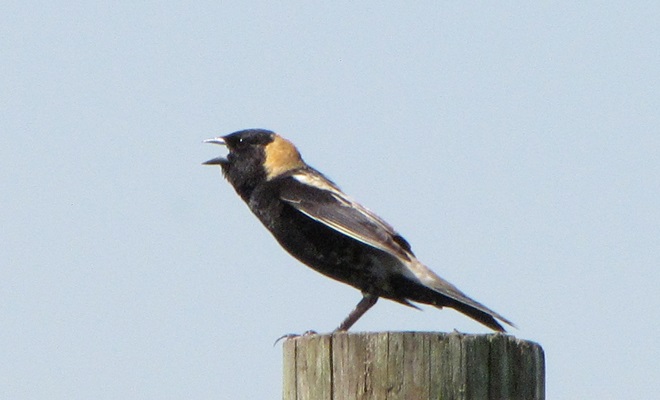
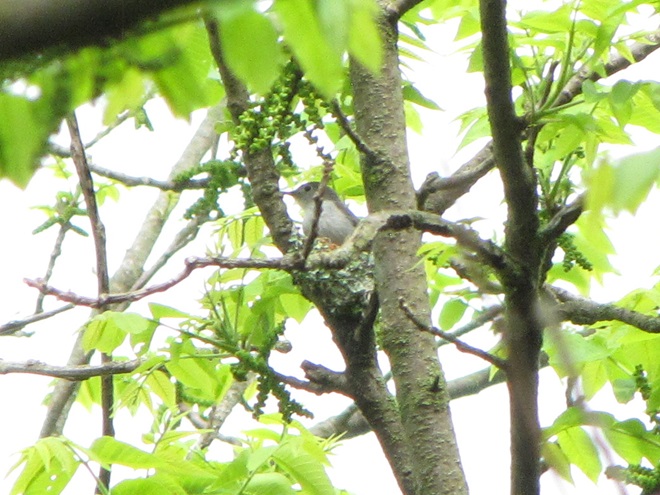
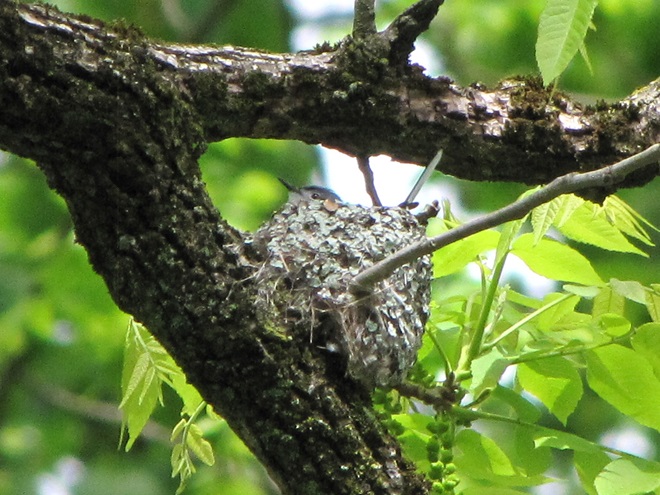















There’s obviously more spring migration to come, so do make an effort to visit an array of habitats during the coming weeks to see and hear the wide variety of birds, including the spectacular Neotropical species, that visit the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed each May. You won’t regret it!


Homo sapiens owes much of its success as a species to an acquired knowledge of how to make, control, and utilize fire. Using fire to convert the energy stored in combustible materials into light and heat has enabled humankind to expand its range throughout the globe. Indeed, humans in their furless incomplete mammalian state may have never been able to expand their populations outside of tropical latitudes without mastery of fire. It is fire that has enabled man to exploit more of the earth’s resources than any other species. From cooking otherwise unpalatable foods to powering the modern industrial society, fire has set man apart from the rest of the natural world.
In our modern civilizations, we generally look at the unplanned outbreak of fire as a catastrophe requiring our immediate intercession. A building fire, for example, is extinguished as quickly as possible to save lives and property. And fires detected in fields, brush, and woodlands are promptly controlled to prevent their exponential growth. But has fire gone to our heads? Do we have an anthropocentric view of fire? Aren’t there naturally occurring fires that are essential to the health of some of the world’s ecosystems? And to our own safety? Indeed there are. And many species and the ecosystems they inhabit rely on the periodic occurrence of fire to maintain their health and vigor.

Man has been availed of the direct benefits of fire for possibly 40,000 years or more. Here in the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed, the earliest humans arrived as early as 12,000 years ago—already possessing skills for using fire. Native plants and animals on the other hand, have been part of the ever-changing mix of ecosystems found here for a much longer period of time—millions to tens of millions of years. Many terrestrial native species are adapted to the periodic occurrence of fire. Some, in fact, require it. Most upland ecosystems need an occasional dose of fire, usually ignited by lightning (though volcanism and incoming cosmic projectiles are rare possibilities), to regenerate vegetation, release nutrients, and maintain certain non-climax habitat types.
But much of our region has been deprived of natural-type fires since the time of the clearcutting of the virgin forests during the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries. This absence of a natural fire cycle has contributed to degradation and/or elimination of many forest and non-forest habitats. Without fire, a dangerous stockpile of combustible debris has been collecting, season after season, in some areas for a hundred years or more. Lacking periodic fires or sufficient moisture to sustain prompt decomposition of dead material, wildlands can accumulate enough leaf litter, thatch, dry brush, tinder, and fallen wood to fuel monumentally large forest fires—fires similar to those recently engulfing some areas of the American west. So elimination of natural fire isn’t just a problem for native plants and animals, its a potential problem for humans as well.
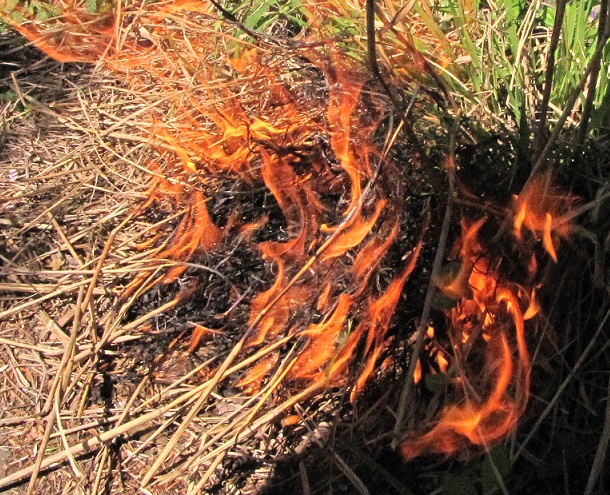

To address the habitat ailments caused by a lack of natural fires, federal, state, and local conservation agencies are adopting the practice of “prescribed fire” as a treatment to restore ecosystem health. A prescribed fire is a controlled burn specifically planned to correct one or more vegetative management problems on a given parcel of land. In the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed, prescribed fire is used to…
Let’s look at some examples of prescribed fire being implemented right here in our own neighborhood…
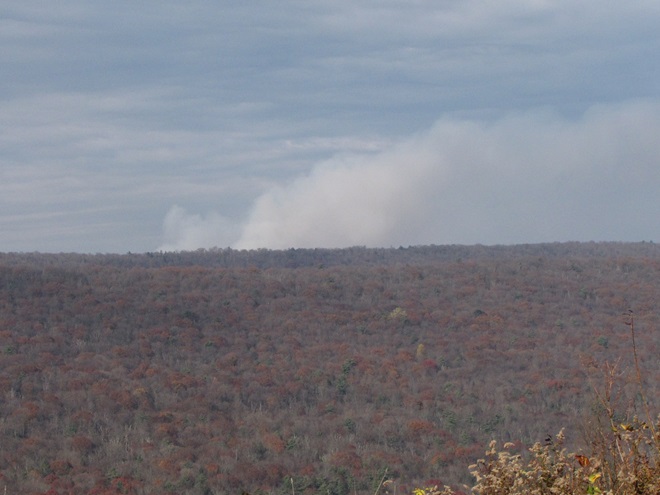
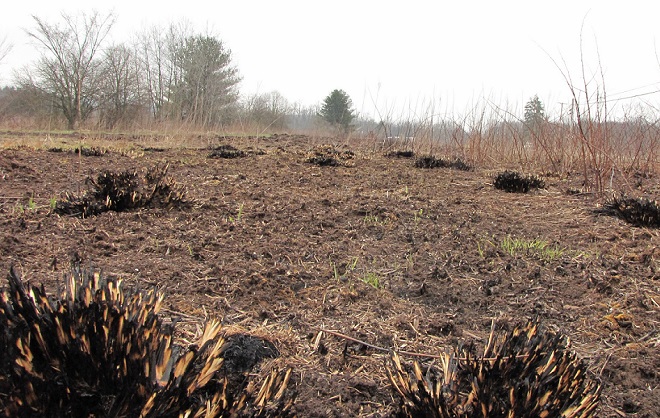
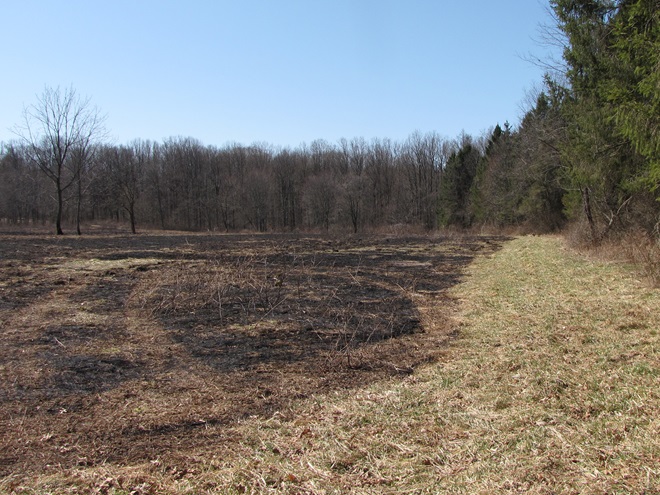
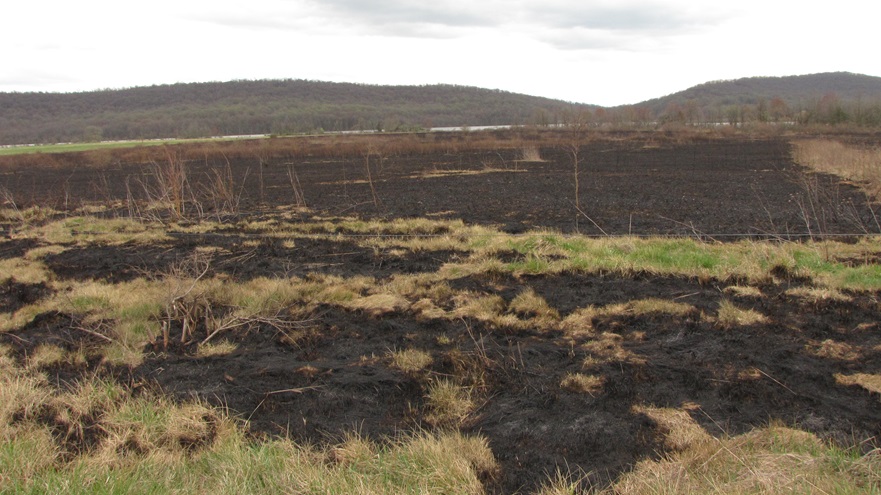

























In Pennsylvania, state law provides landowners and crews conducting prescribed fire burns with reduced legal liability when the latter meet certain educational, planning, and operational requirements. This law may help encourage more widespread application of prescribed fire in the state’s forests and other ecosystems where essential periodic fire has been absent for so very long. Currently in the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed, prescribed fire is most frequently being employed by state agencies on state lands—in particular, the Department of Conservation and Natural Resources on State Forests and the Pennsylvania Game Commission on State Game Lands. Prescribed fire is also part of the vegetation management plan at Fort Indiantown Gap Military Reservation and on the land holdings of the Hershey Trust. Visitors to the nearby Gettysburg National Military Park will also notice prescribed fire being used to maintain the grassland restorations there.
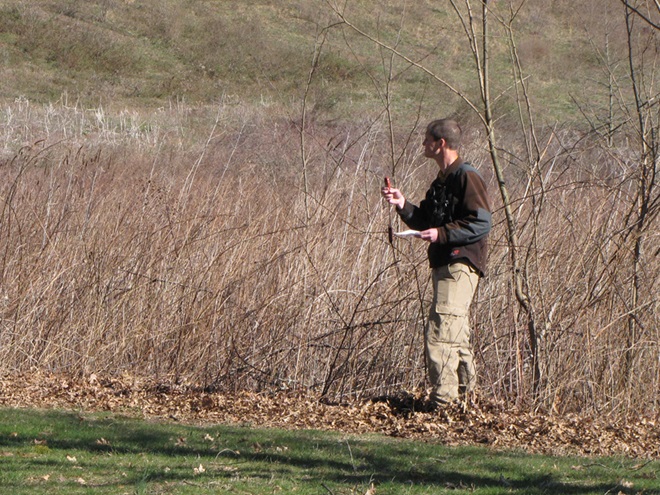
For crews administering prescribed fire burns, late March and early April are a busy time. The relative humidity is often at its lowest level of the year, so the probability of ignition of previous years’ growth is generally at its best. We visited with a crew administering a prescribed fire at Middle Creek Wildlife Management Area last week. Have a look…
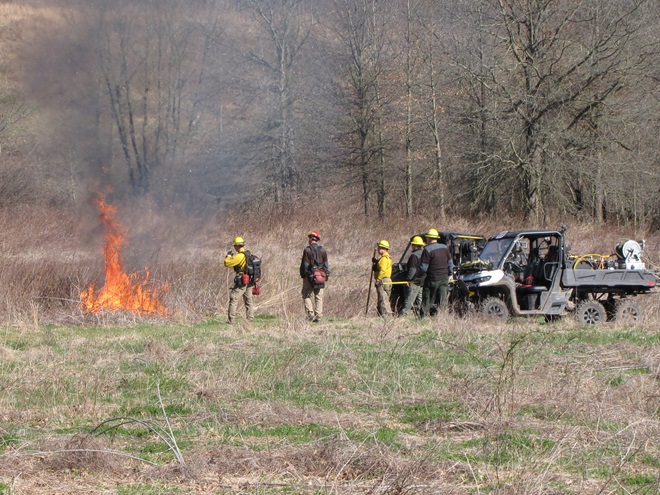
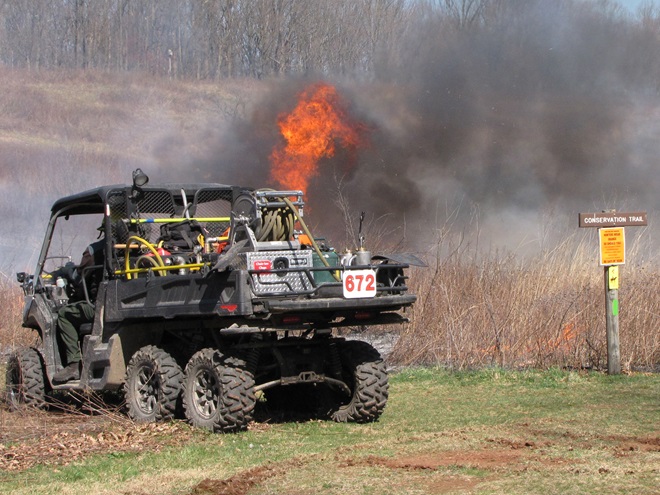
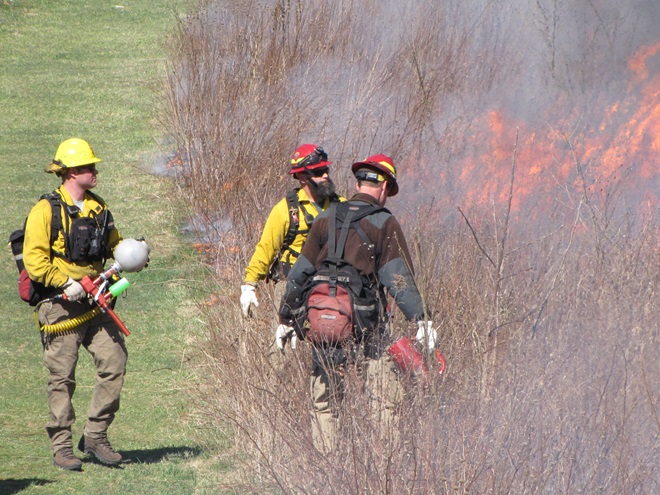
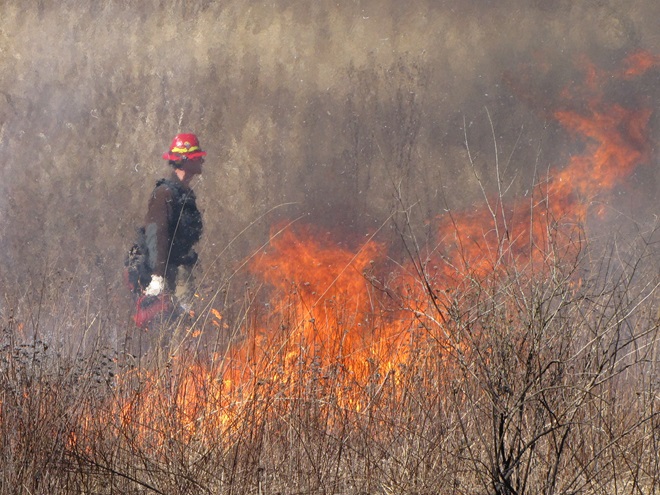

















Prescribed burns aren’t a cure-all for what ails a troubled forest or other ecosystem, but they can be an effective remedy for deficiencies caused by a lack of periodic episodes of naturally occurring fire. They are an important option for modern foresters, wildlife managers, and other conservationists.
To take advantage of this unusually mild late-winter day, observers arrived by the thousands to have a look at an even greater number of migratory birds gathered at the Pennsylvania Game Commission’s Middle Creek Wildlife Management Area. Here are some highlights…
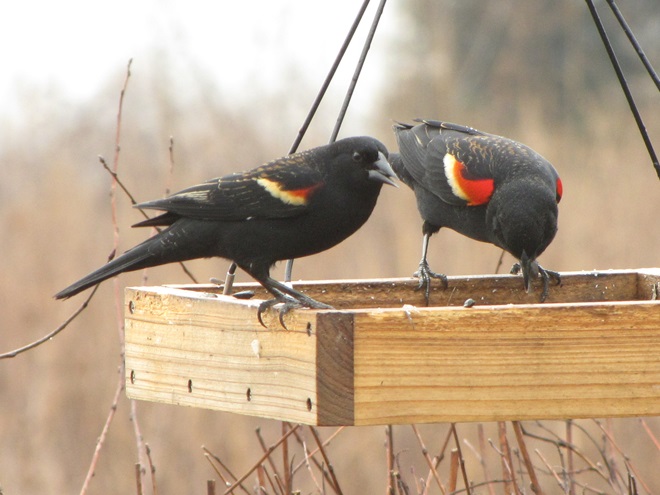
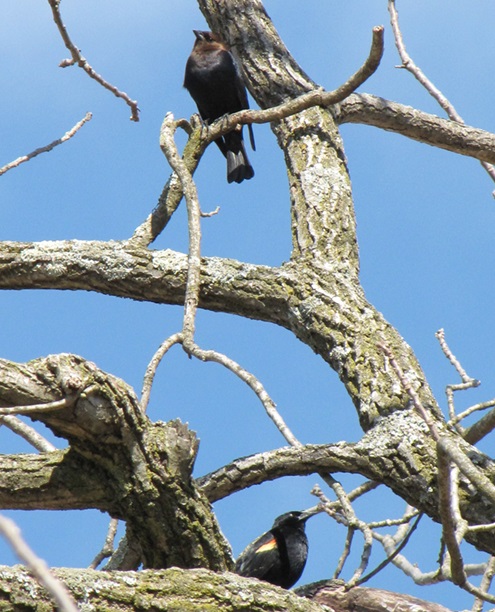
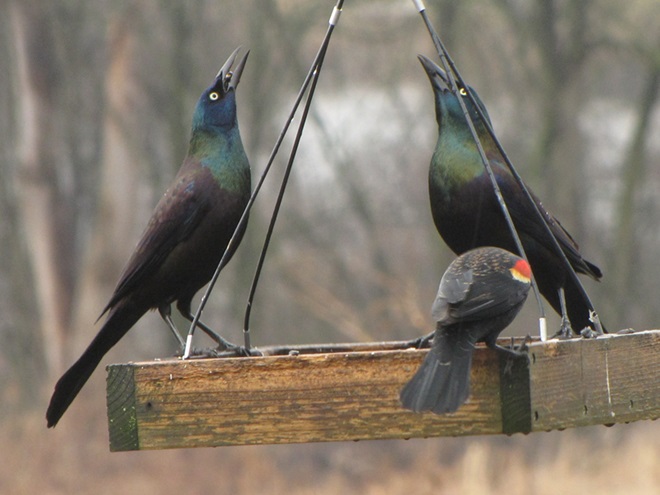
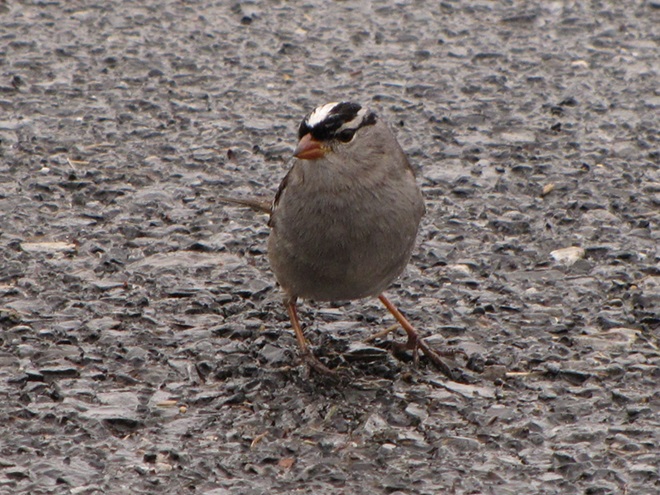
























Since Tuesday’s snow storm, the susquehannawiildlife.net headquarters garden continues to bustle with bird activity.
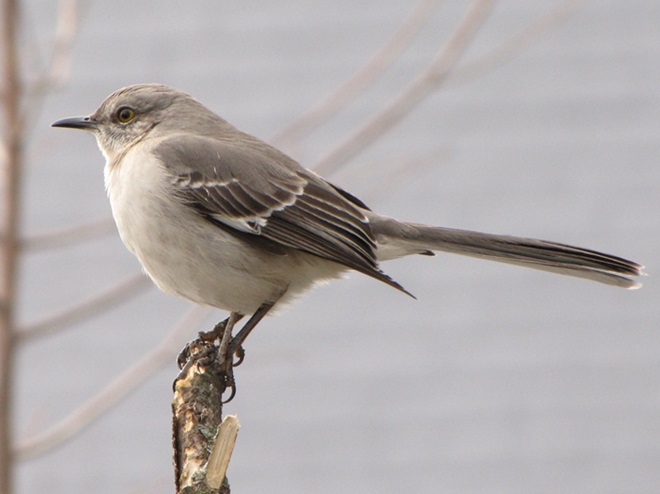




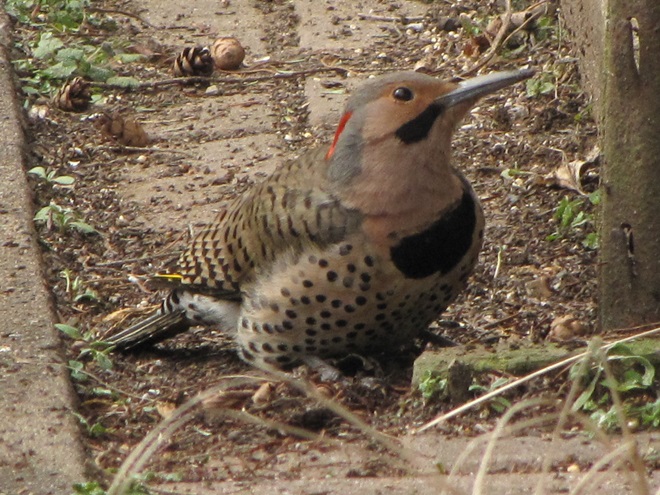
Today, there arrived three species of birds we haven’t seen here since autumn. These birds are, at the very least, beginning to wander in search of food. Then too, these may be individuals creeping slowly north to secure an advantage over later migrants by being the first to establish territories on the most favorable nesting grounds.



They say the early bird gets the worm. More importantly, it gets the most favorable nesting spot. What does the early birder get? He or she gets out of the house and enjoys the action as winter dissolves into the miracle of spring. Do make time to go afield and marvel a bit, won’t you? See you there!
As week-old snow and ice slowly disappears from the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed landscape, we ventured out to see what might be lurking in the dense clouds of fog that for more than two days now have accompanied a mid-winter warm spell.
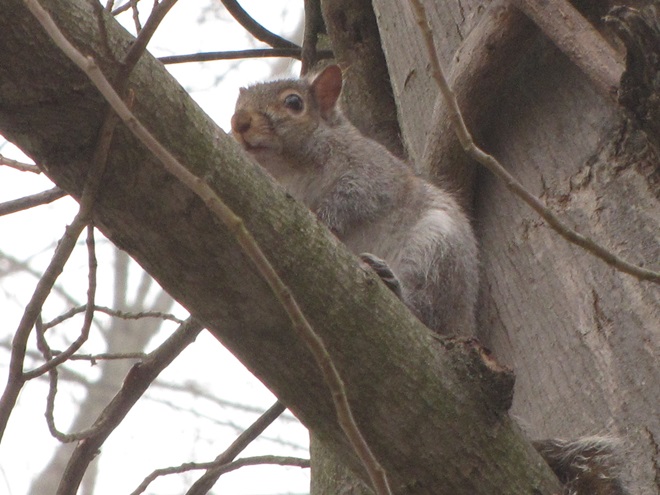
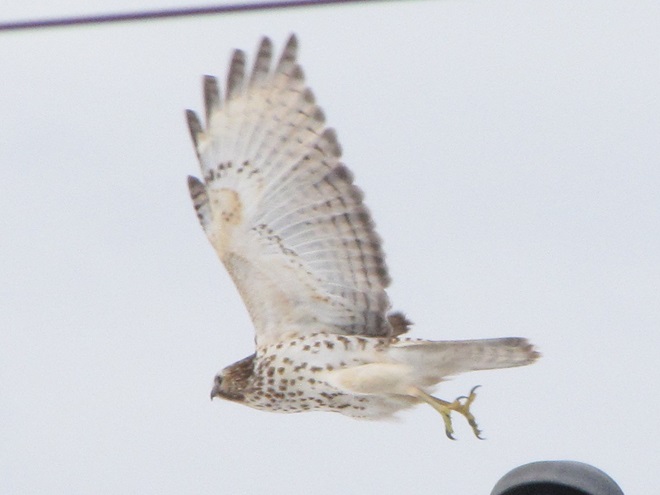
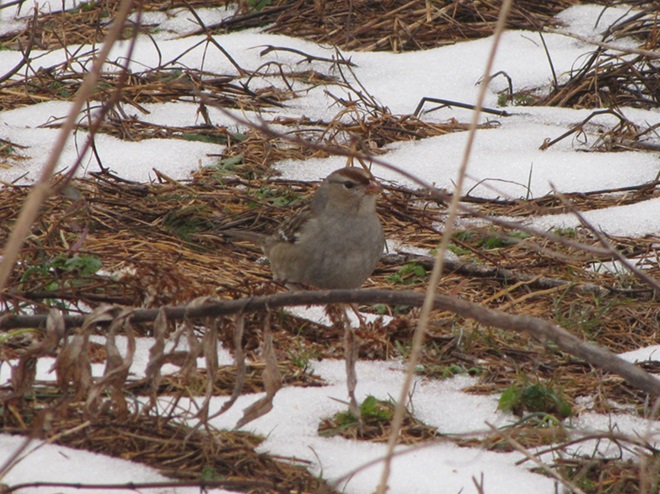
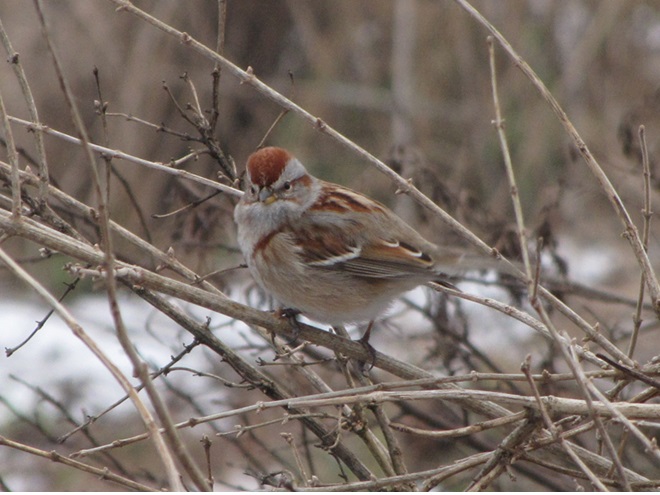















If scenes of a January thaw begin to awaken your hopes and aspirations for all things spring, then you’ll appreciate this pair of closing photographs…


Just as bare ground along a plowed road attracts birds in an otherwise snow-covered landscape, a receding river or large stream can provide the same benefit to hungry avians looking for food following a winter storm.
Here is a small sample of some of the species seen during a brief stop along the Susquehanna earlier this week.
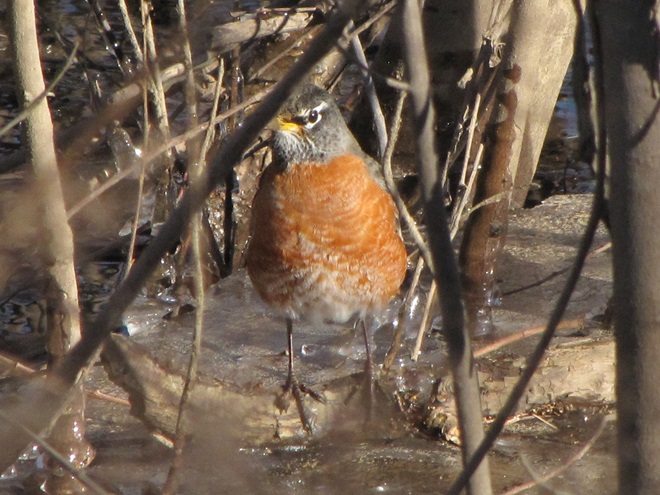
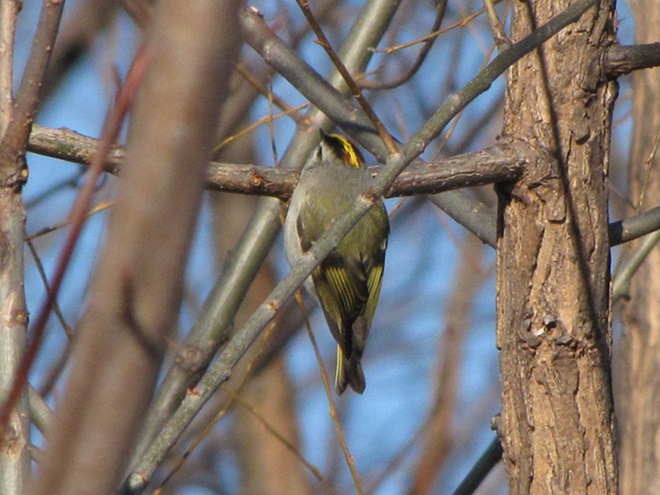
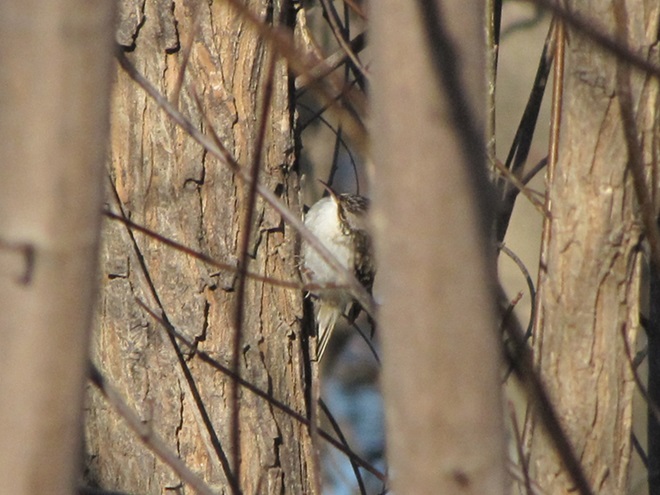
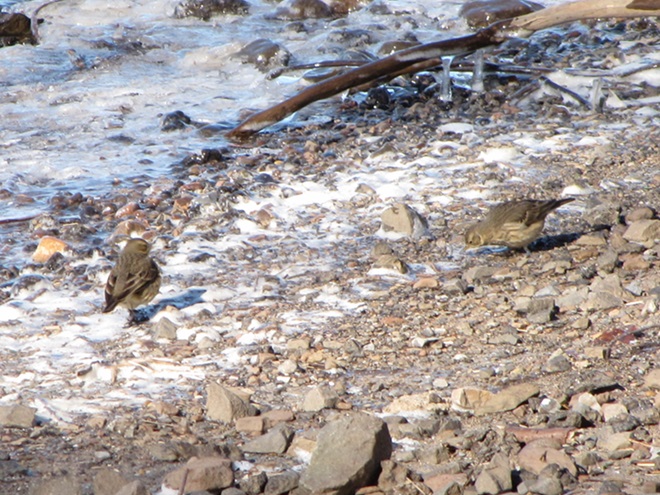






When the ground becomes snow covered, it’s hard to imagine anything lives in the vast wide-open expanses of cropland found in the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed’s fertile valleys.

Yet, there is one group of birds that can be found scrounging a living from what little exists after a season of high-intensity farming. Meet the Horned Lark.
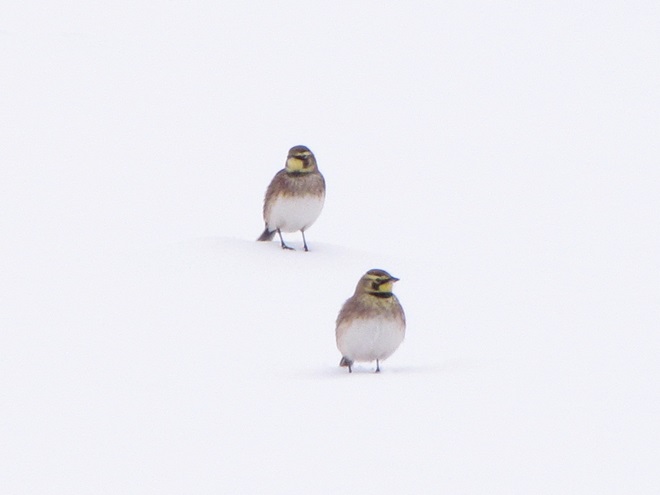
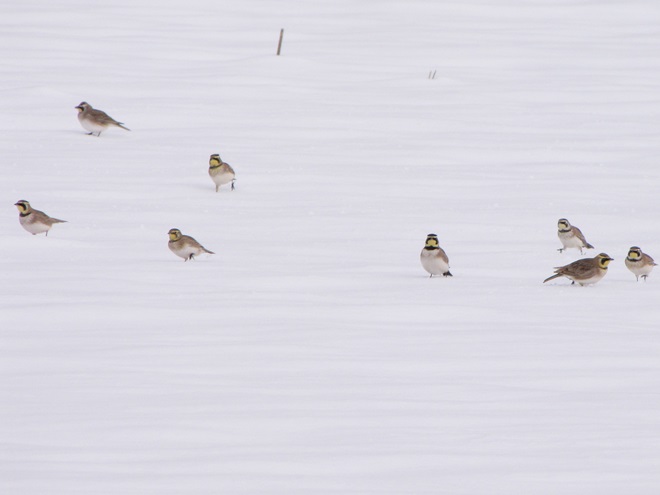
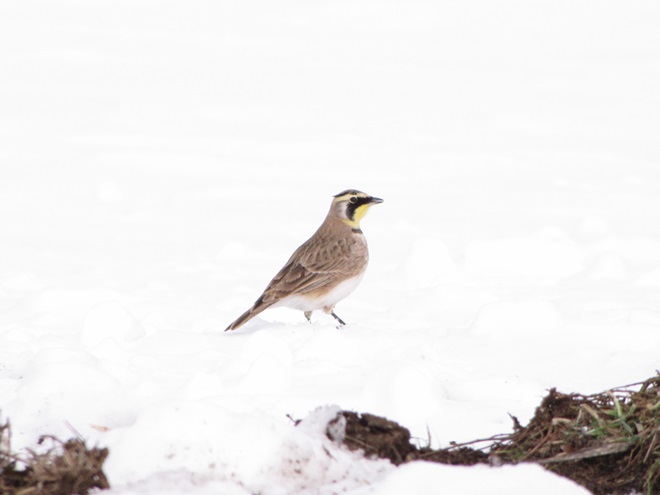
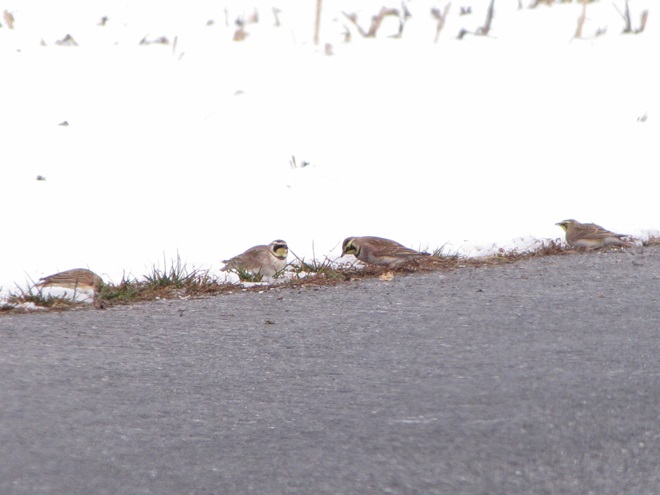
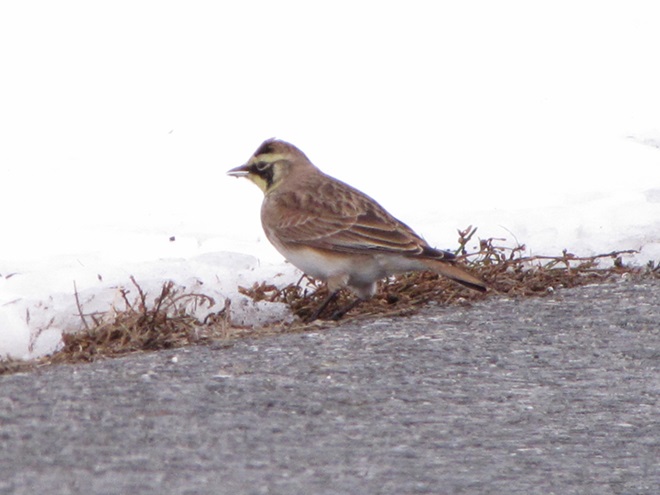
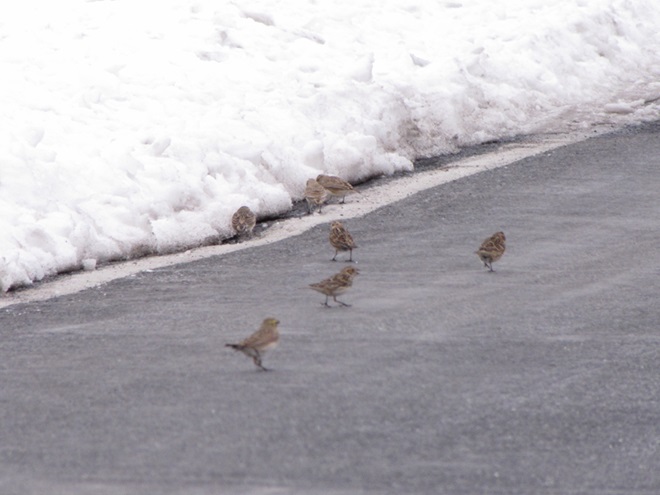
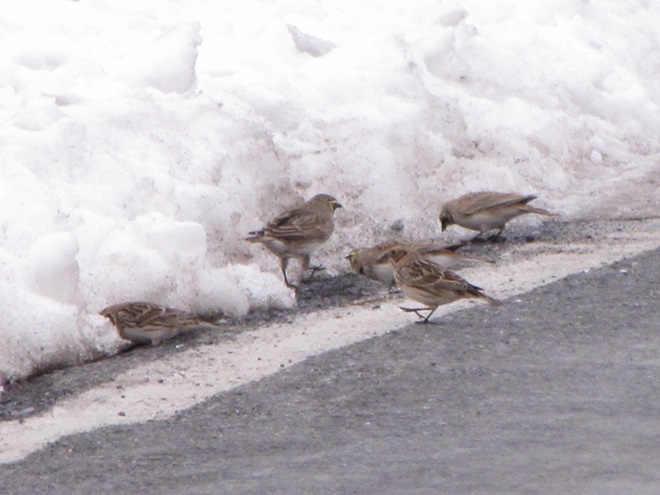
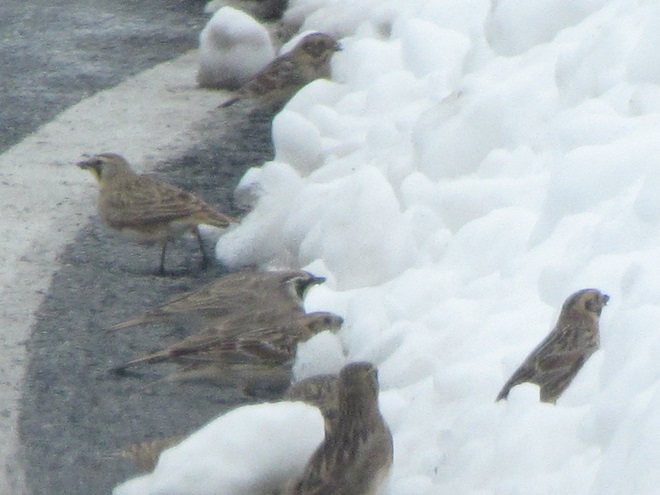










If you decide to take a little post-storm trip to look for Horned Larks and Lapland Longspurs, be sure to drive carefully. Do your searching on quiet rural roads with minimal traffic. Stop and park only where line-of-sight and other conditions allow it to be done safely. Use your flashers and check your mirrors often. Think before you stop and park—don’t get stuck or make a muddy mess. And most important of all, be aware that you’re on a roadway—get out of the way of traffic.
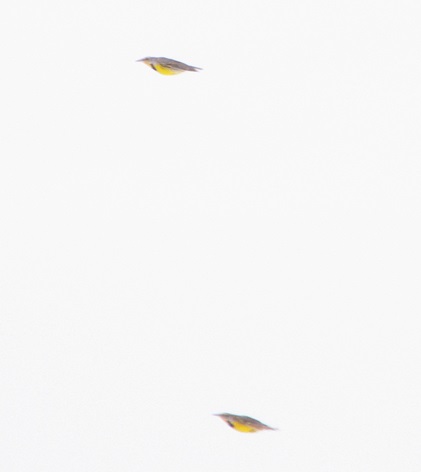

If you’re not going out to look for larks and longspurs, we do have a favor to ask of you. Please remember to slow down while you’re driving. Not only is this an accident-prone time of year for people in cars and trucks, it’s a dangerous time for birds and other wildlife too. They’re at greatest peril of getting run over while concentrated along roadsides looking for food following snow storms.
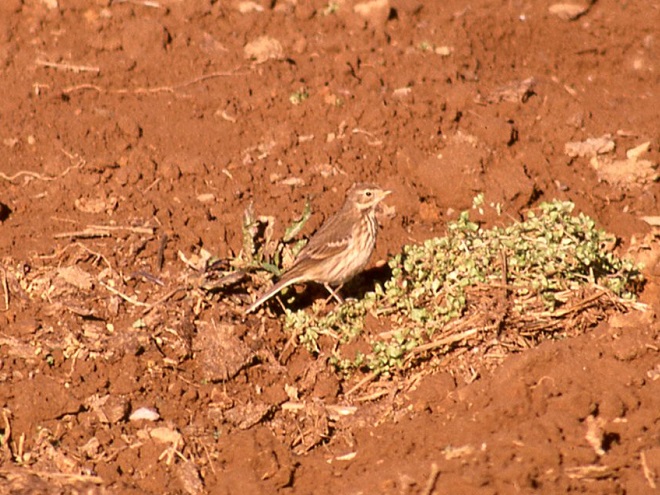
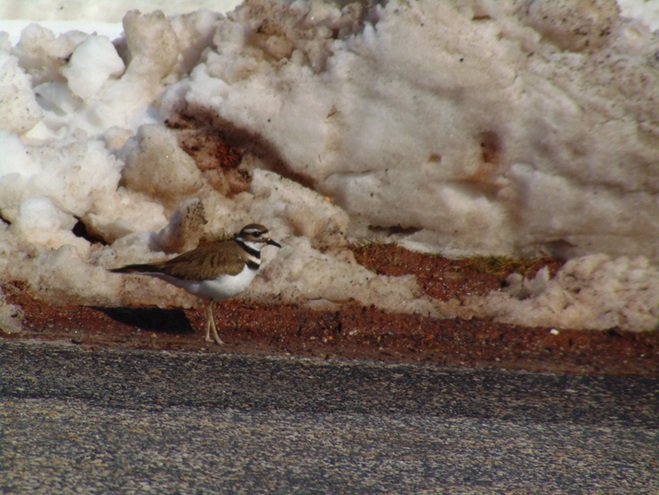



With the earth at perihelion (its closest approach to the sun) and with our home star just 27 degrees above the horizon at midday, bright low-angle light offered the perfect opportunity for doing some wildlife photography today. We visited a couple of grasslands managed by the Pennsylvania Game Commission to see what we could find…
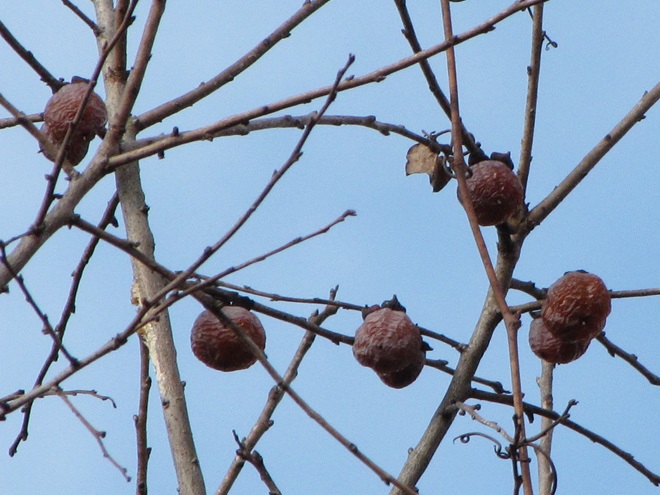
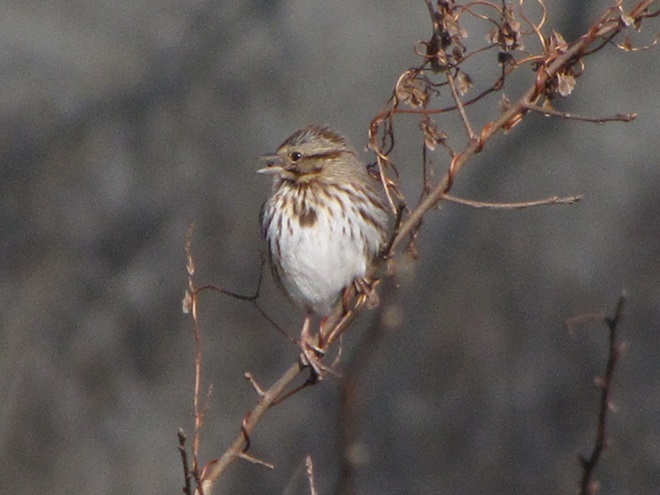
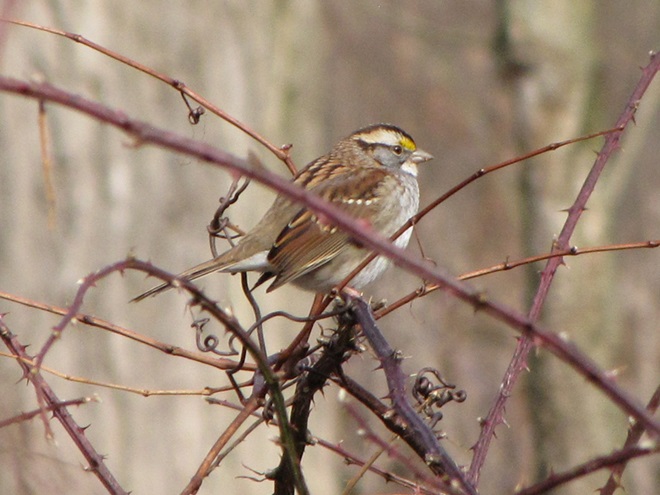
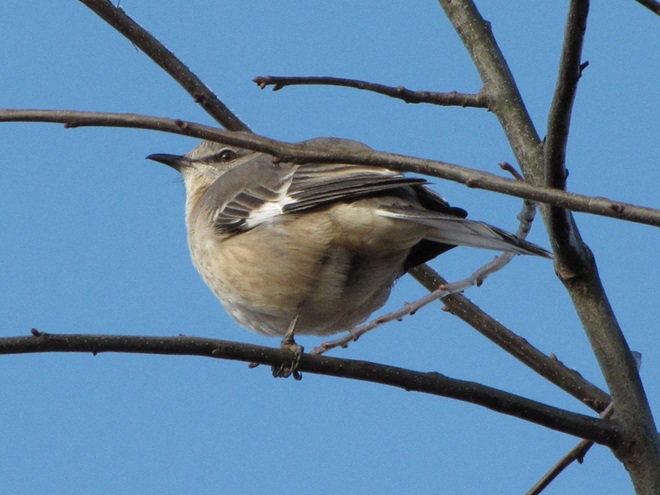
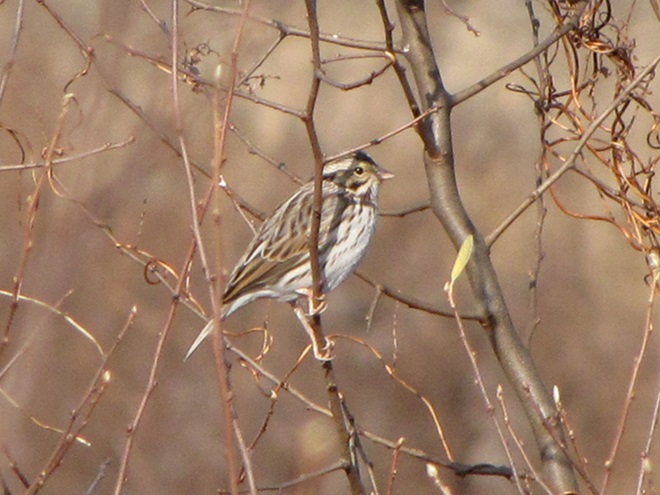
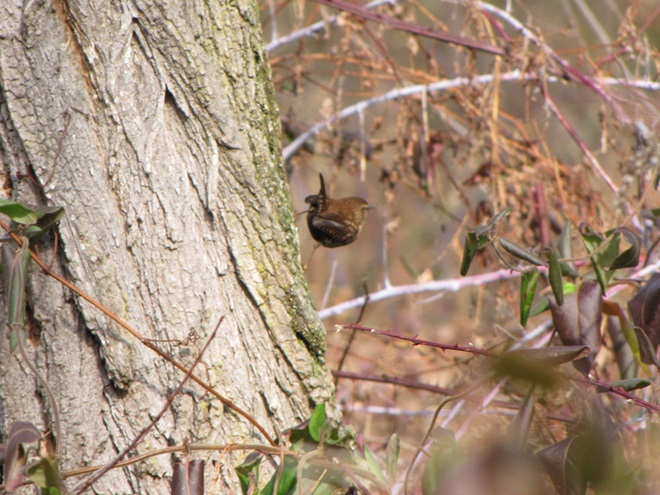
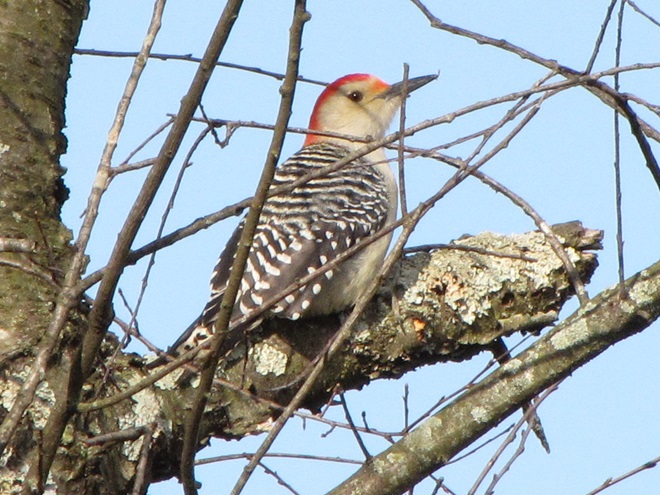
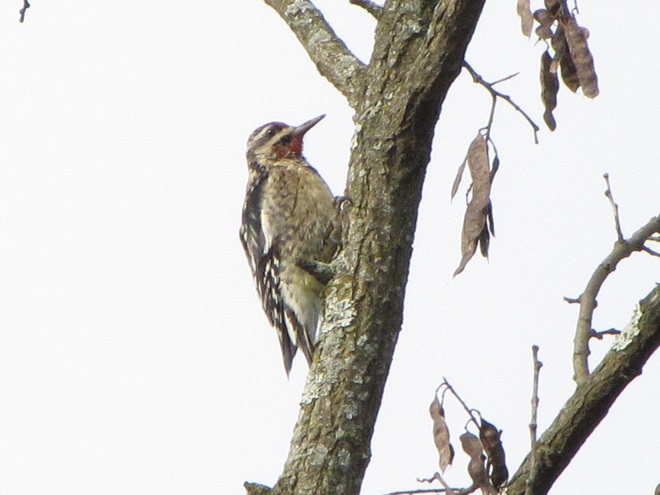
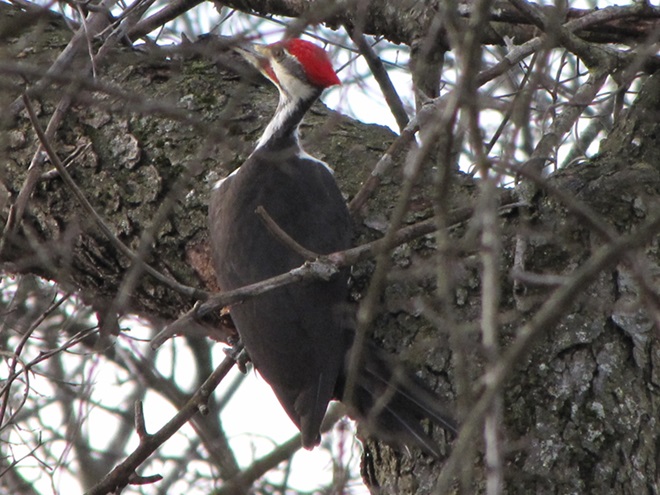
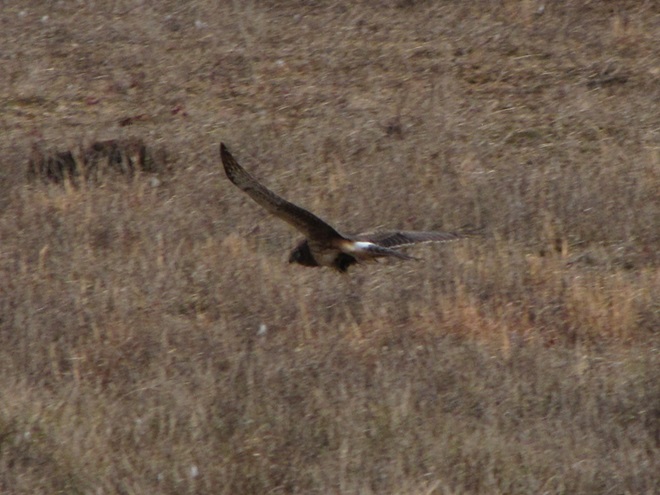



















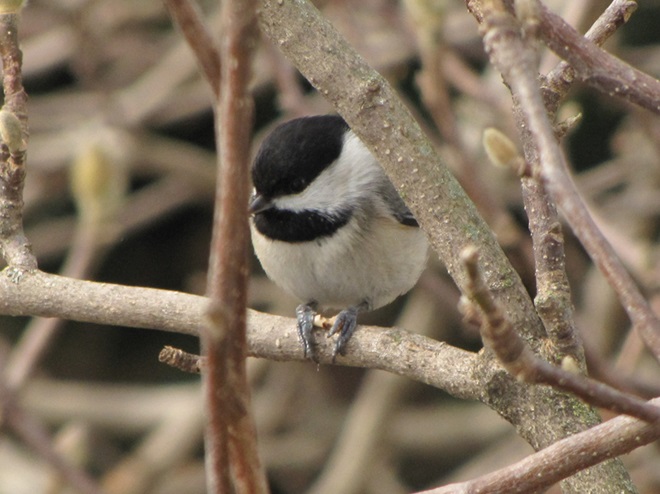
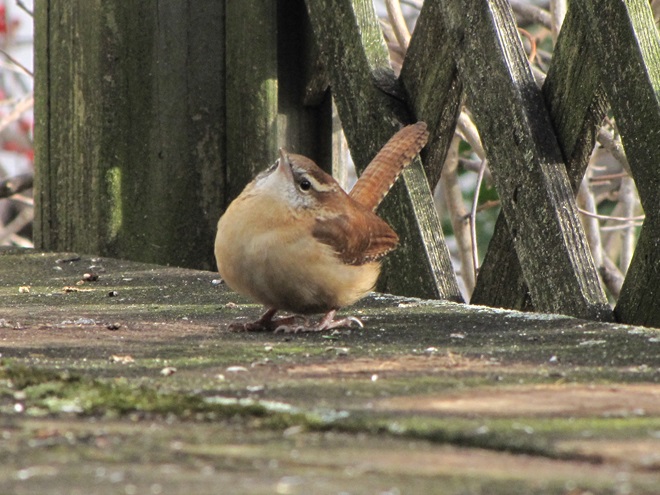
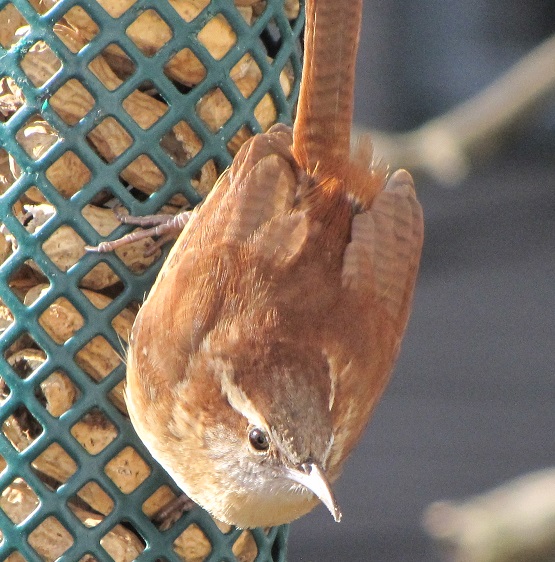
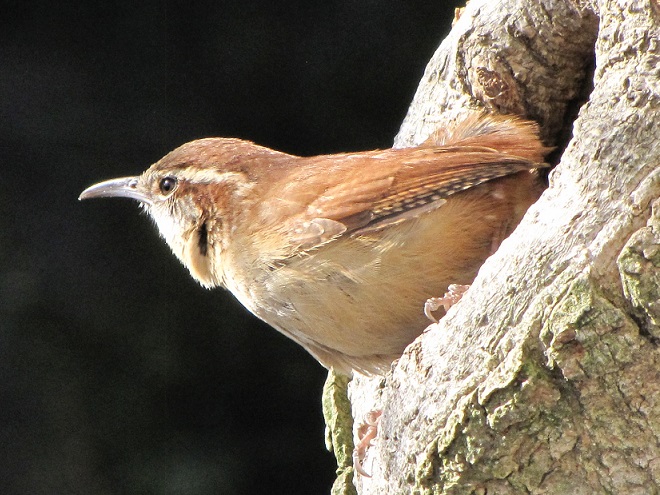
While trimming the trees and shrubs in the susquehannawildlife.net garden, it didn’t seem particularly unusual to hear the resident Carolina Chickadees and Carolina Wrens scolding our every move. But after a while, their persistence did seem a bit out of the ordinary, so we took a little break to have a look around…
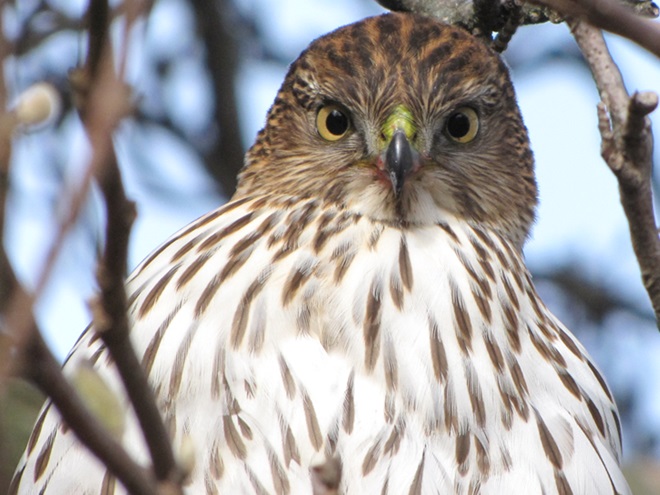
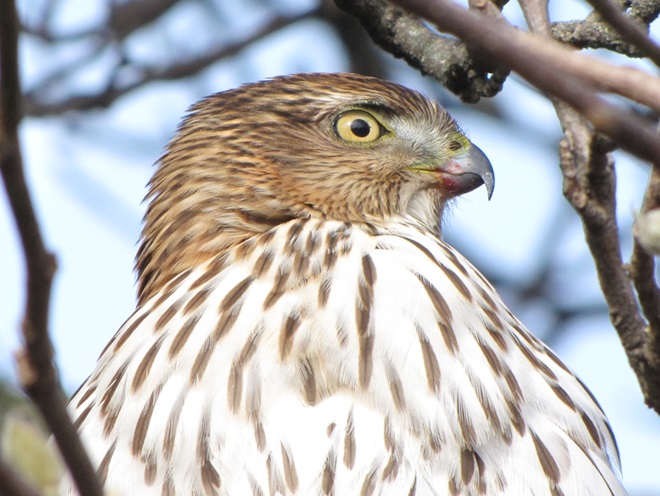
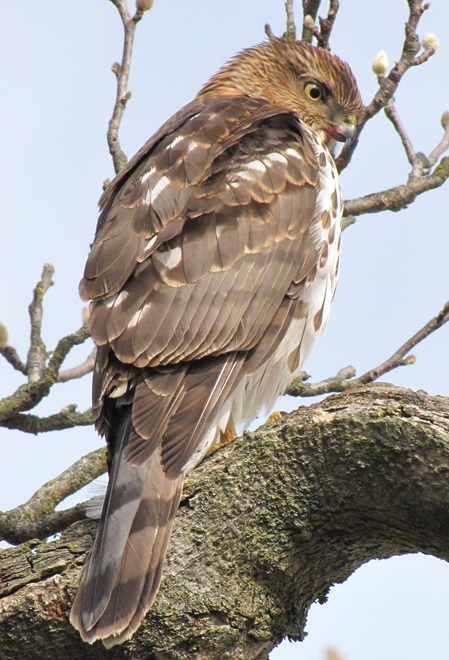






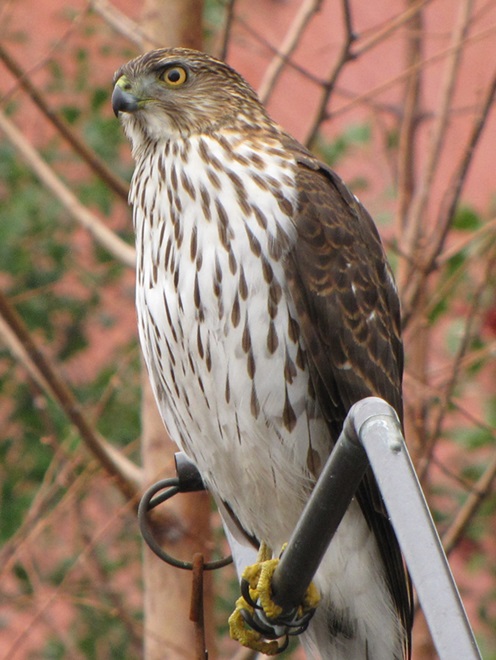
Here at susquehannawildlife.net headquarters, we are visited by Cooper’s Hawks for several days during the late fall and winter each year. The small birds that visit our feeders have plenty of trees, shrubs, vines, and other natural cover in which to hide from raptors and other native predators. We don’t create unnatural concentrations of birds by dumping food all over the place. We try to keep our small birds healthy by sparingly offering fresh seed and other provisions in clean receptacles to provide a supplement to the seeds, fruits, insects, and other foods that occur naturally in the garden. With only a few vulnerable small birds around, the Cooper’s Hawks visit just long enough to cull out our weakest individuals before moving elsewhere. While they’re in our garden, they too are our welcomed guests.
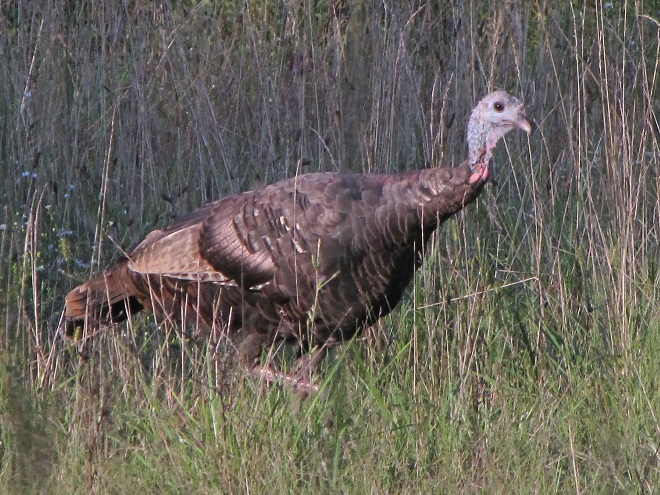
A glimpse of the rowdy guests crowding the Thanksgiving Day dinner table at susquehannawildlife.net headquarters…
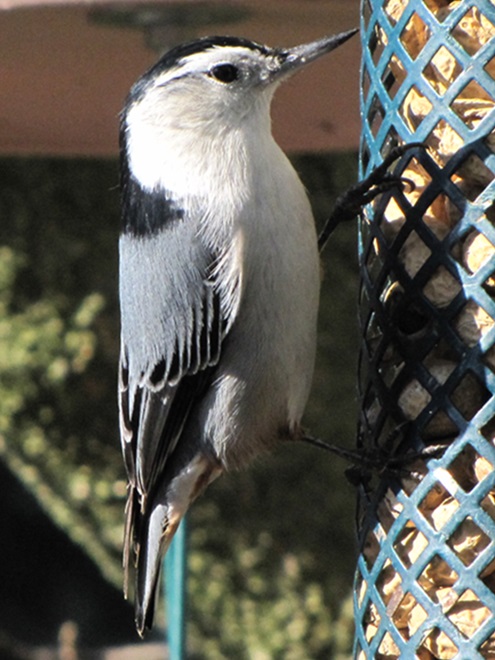
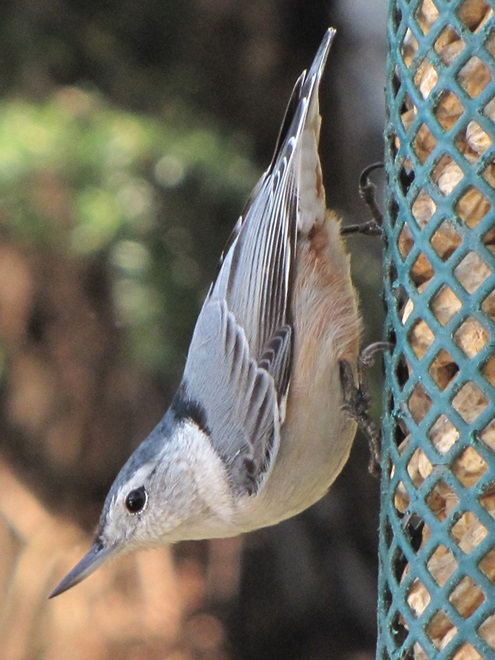
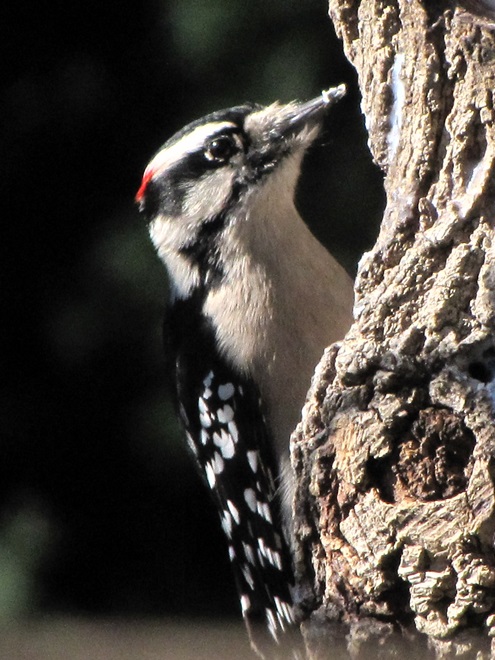
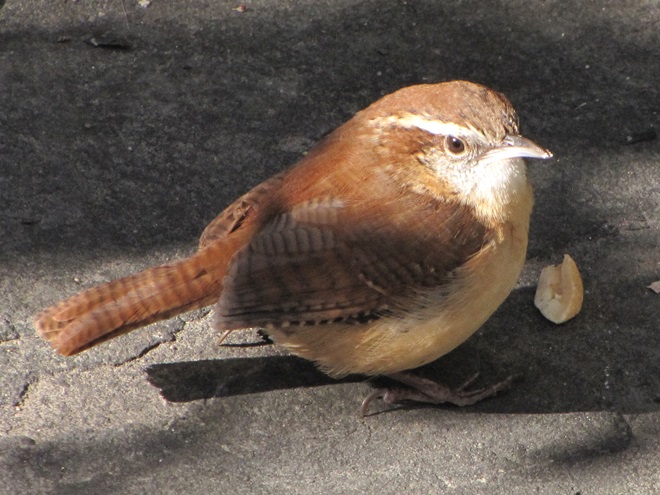
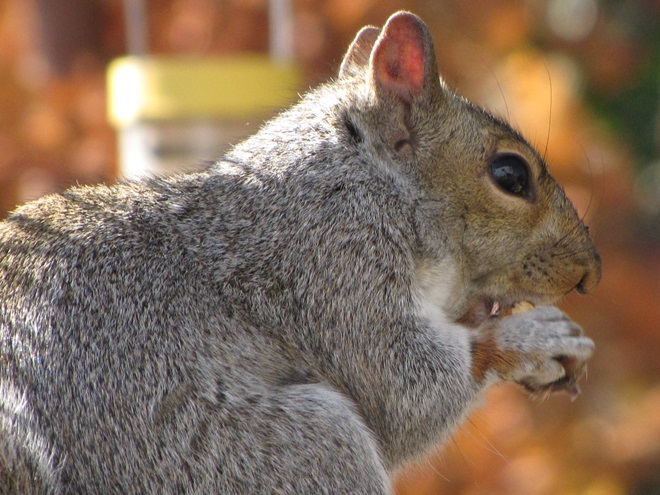
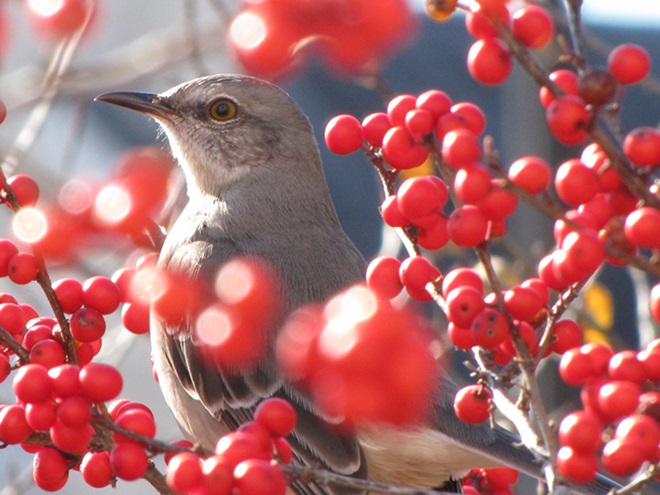
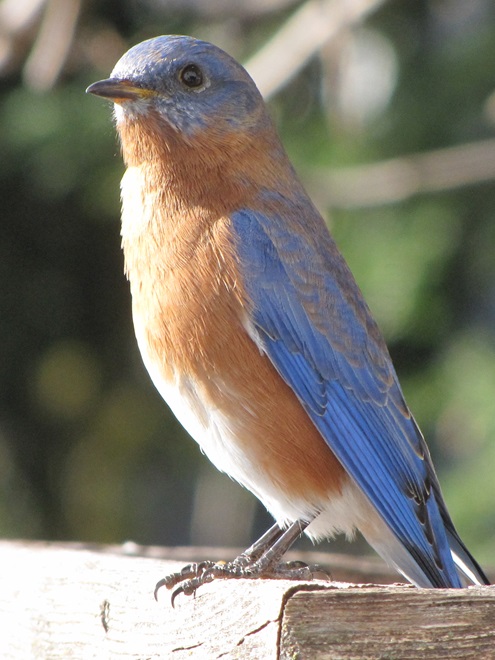
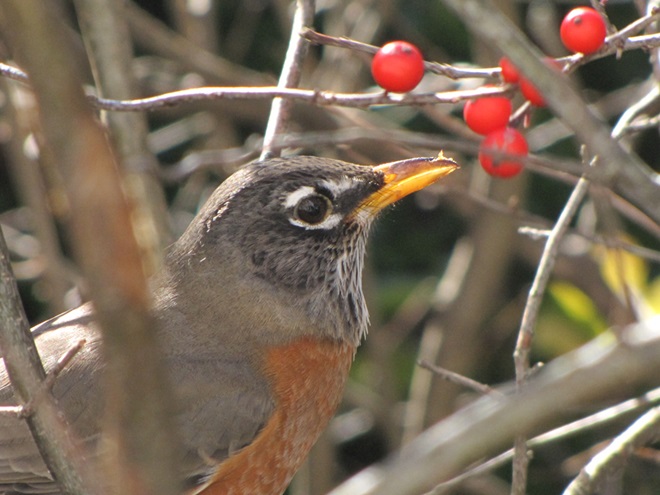
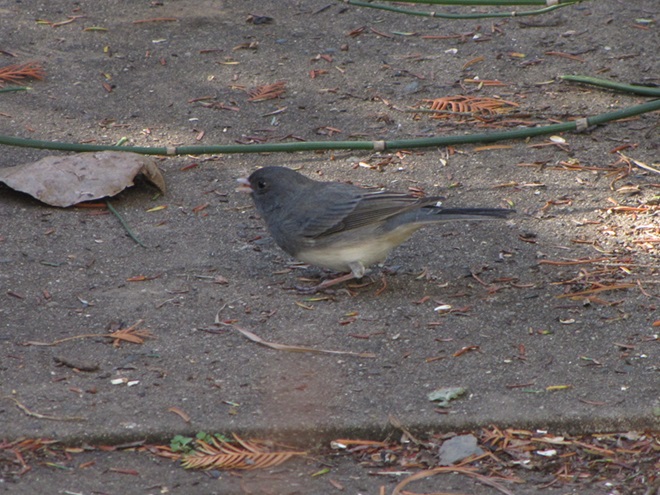









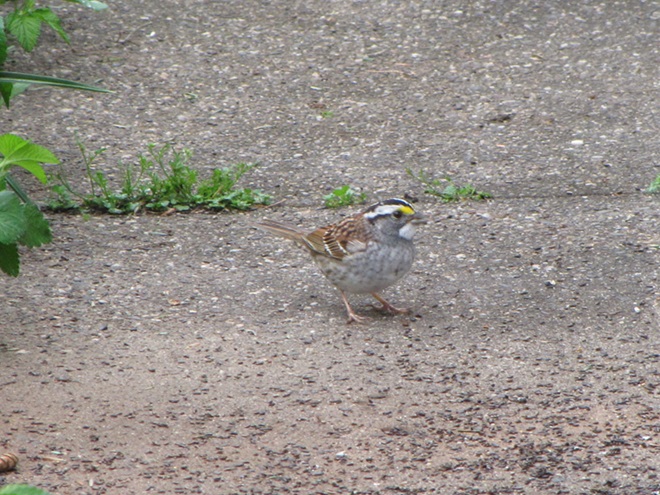
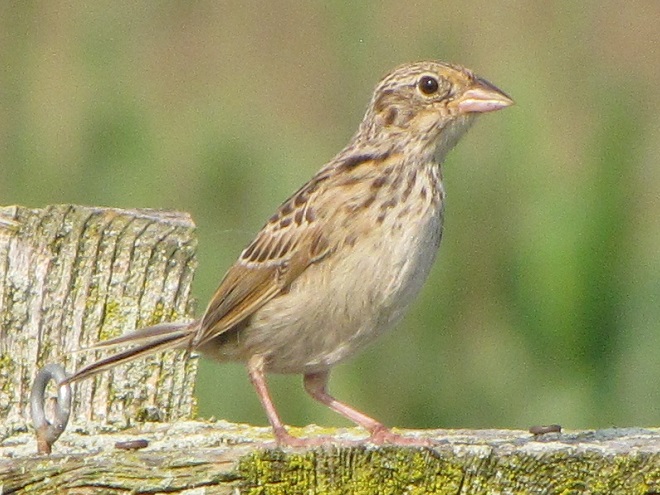
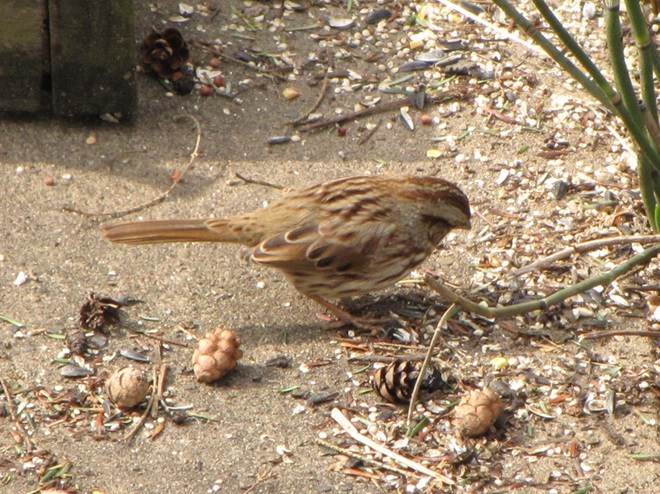
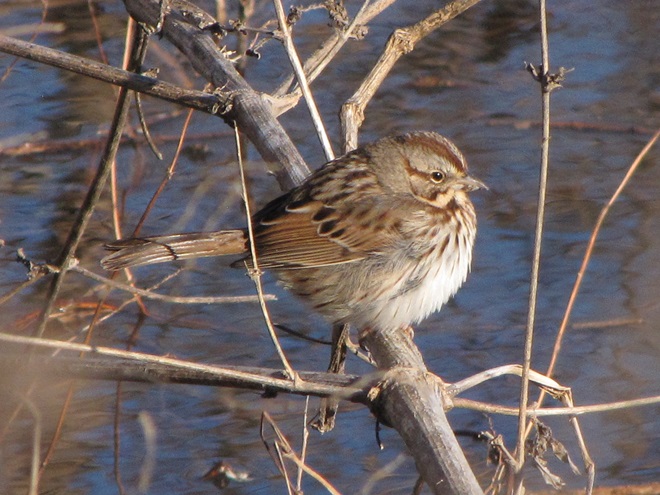
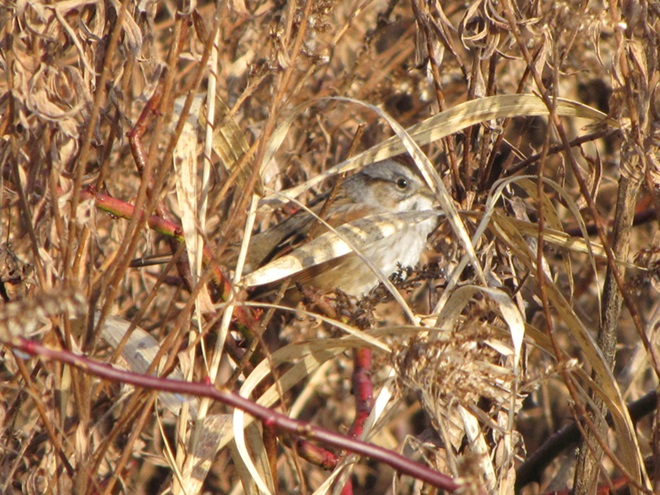
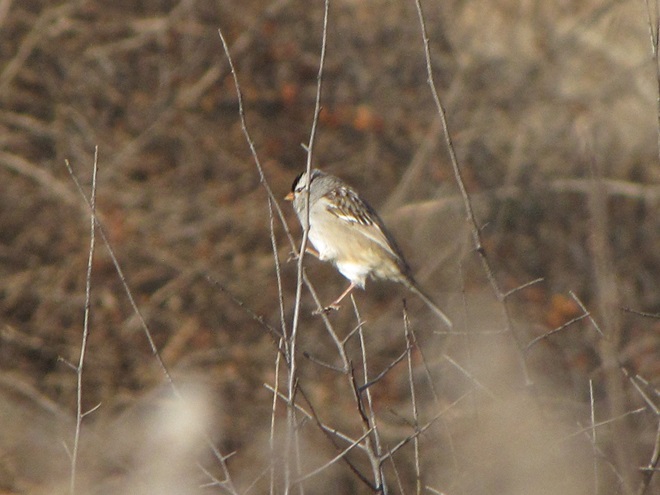
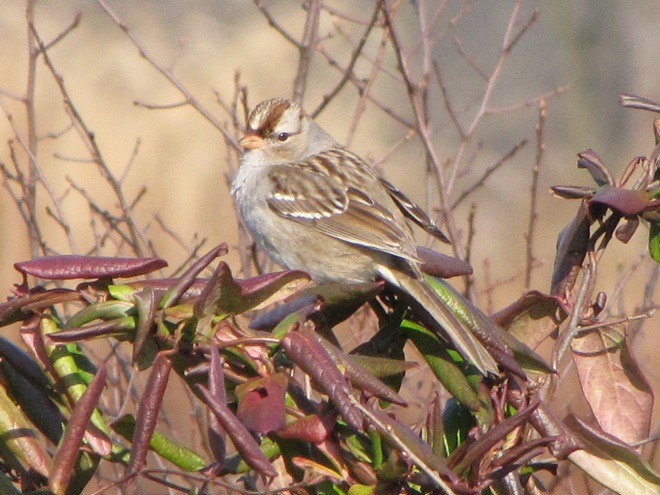
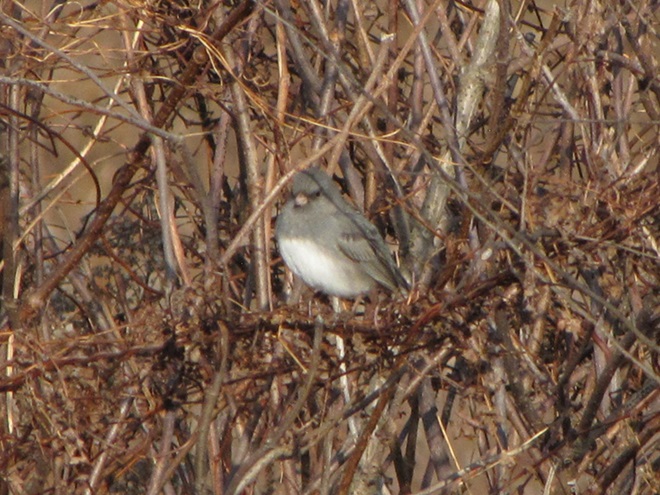
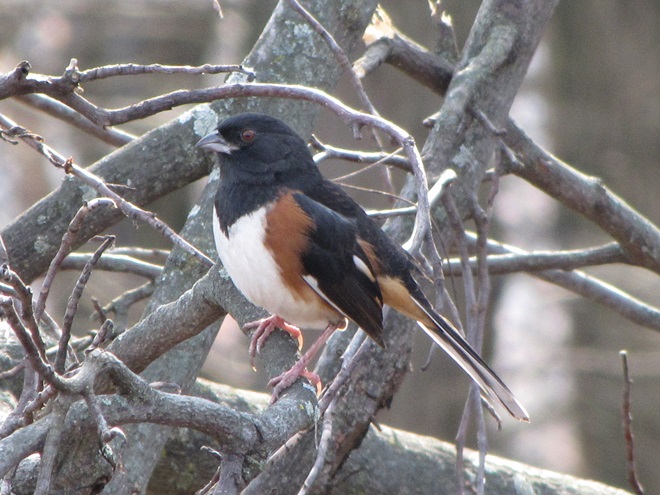
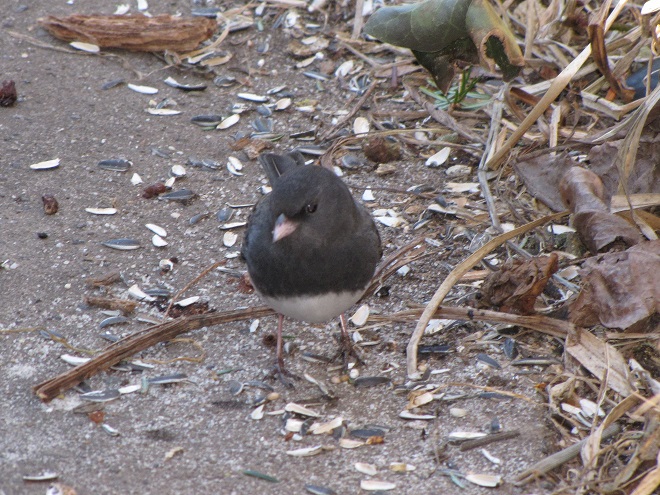
As the annual autumn songbird migration begins to reach its end, native sparrows can be found concentrating in fallow fields, early successional thickets, and brushy margins along forest edges throughout the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed.

Visit native sparrow habitat during mid-to-late November and you have a good chance of seeing these species and more…
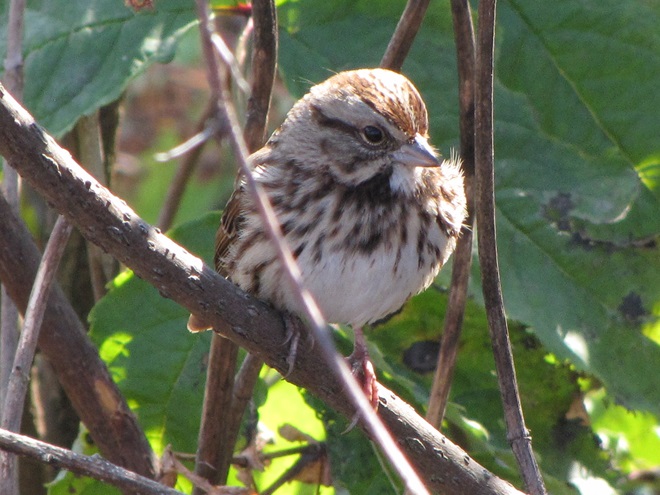
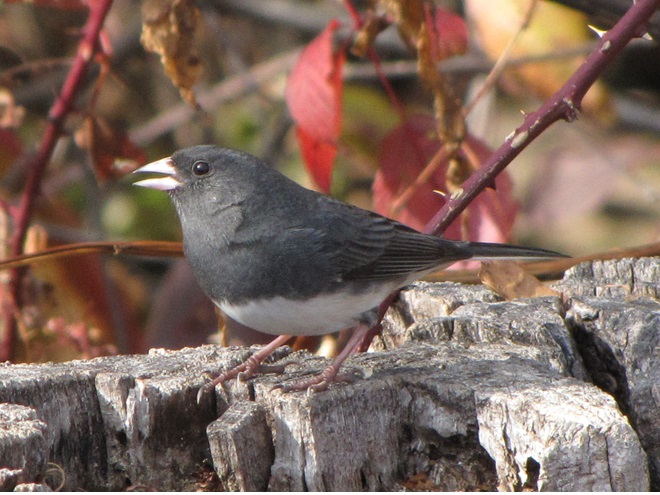
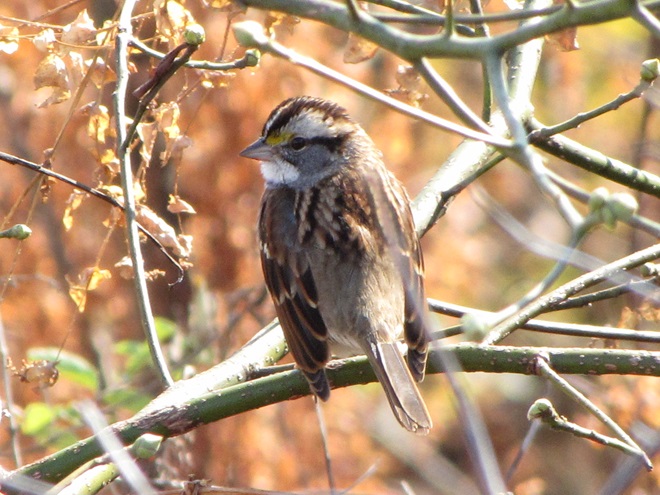
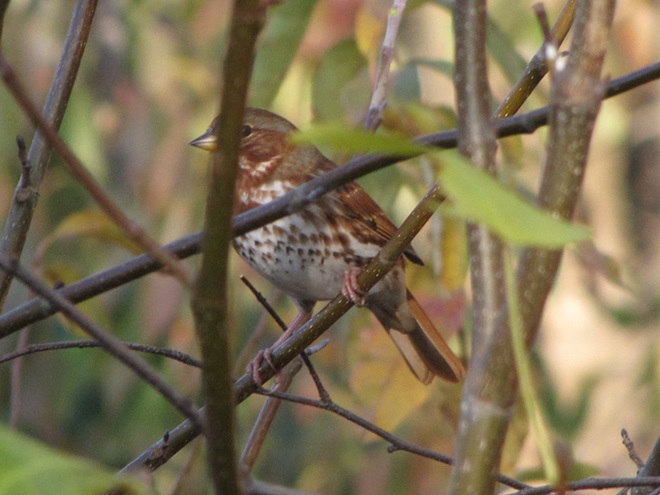





If you’re lucky enough to live where non-native House Sparrows won’t overrun your bird feeders, you can offer white millet as a supplement to the wild foods these beautiful sparrows might find in your garden sanctuary. Give it a try!
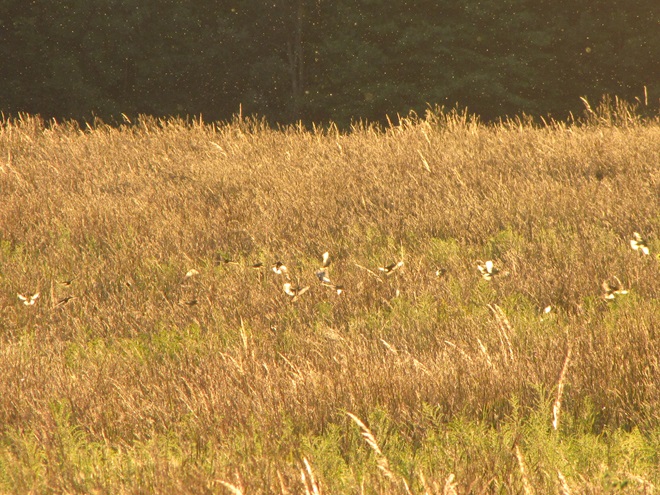
Here in a series of photographs are just a handful of the reasons why the land stewards at Middle Creek Wildlife Management Area and other properties where conservation and propagation practices are employed delay the mowing of fields composed of cool-season grasses until after August 15 each year.
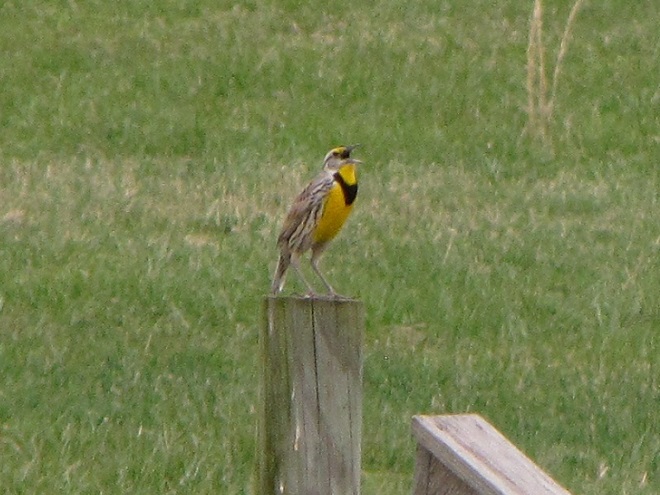
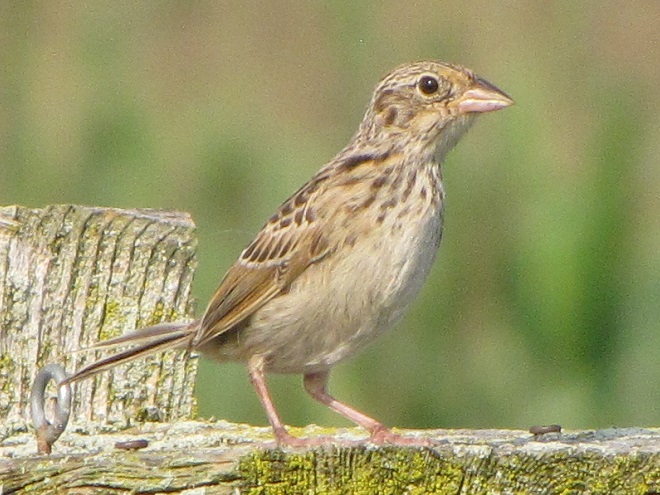
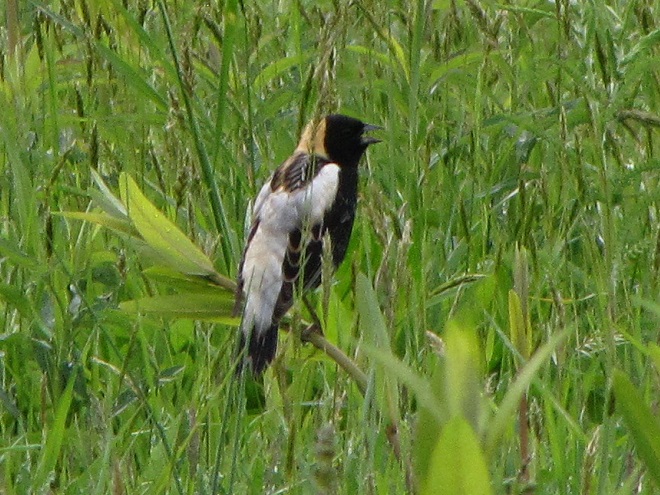
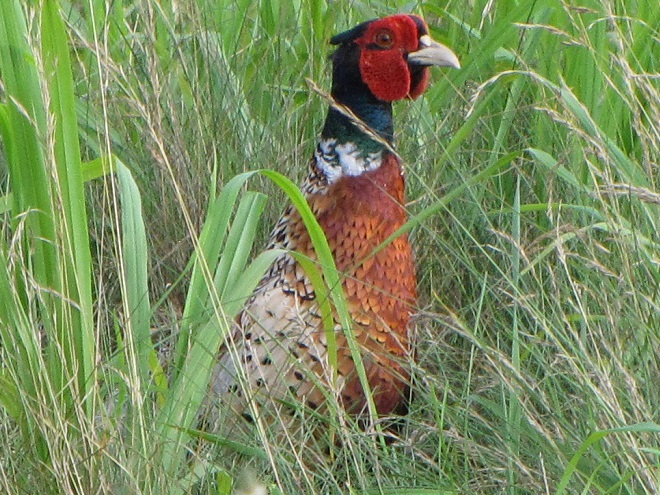
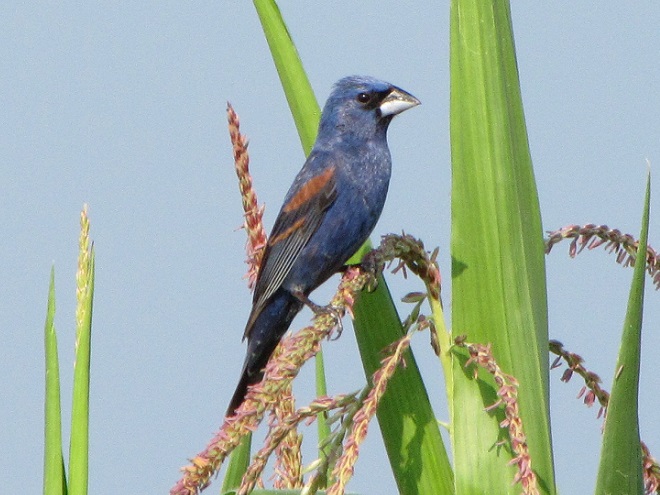





Right now is a good time to visit Middle Creek Wildlife Management Area to see the effectiveness a delayed mowing schedule can have when applied to fields of cool-season grasses. If you slowly drive, walk, or bicycle the auto tour route on the north side of the lake, you’ll pass through vast areas maintained as cool-season and warm-season grasses and early successional growth—and you’ll have a chance to see these and other grassland birds raising their young. It’s like a trip back in time to see farmlands they way they were during the middle years of the twentieth century.
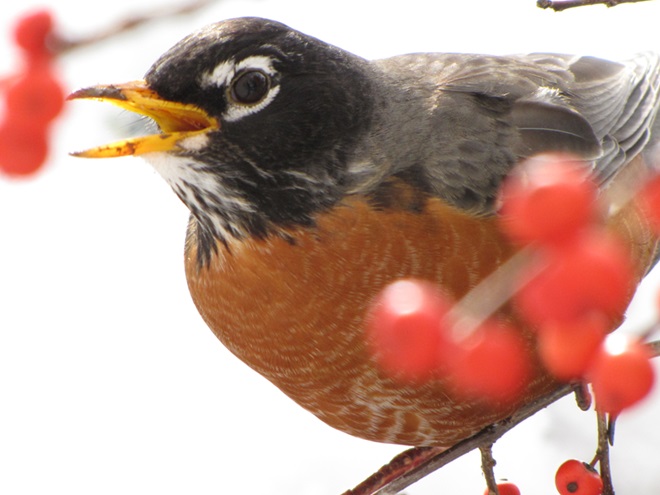
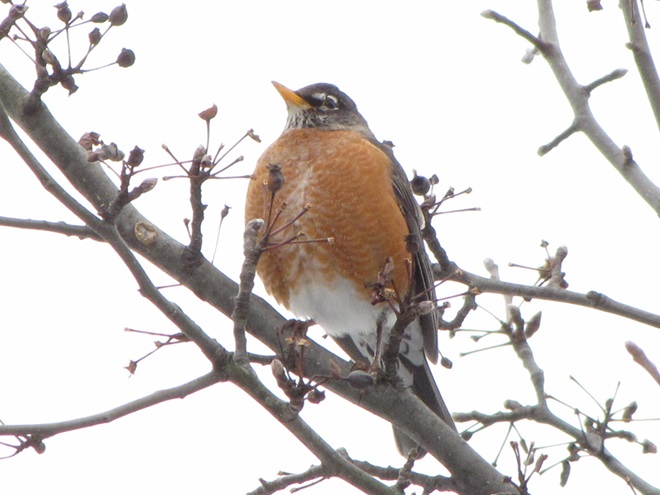
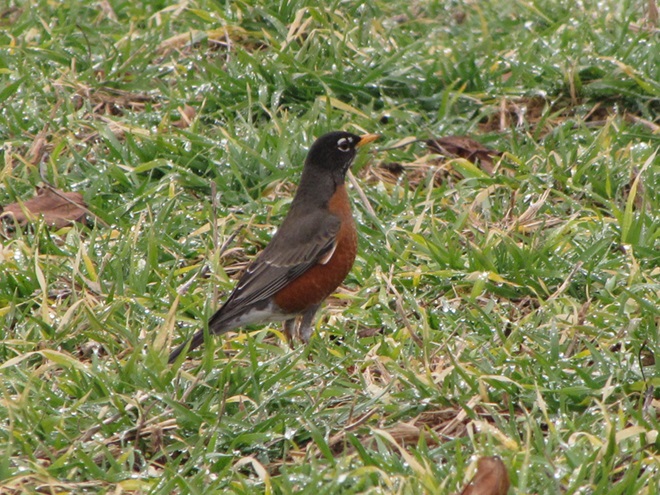
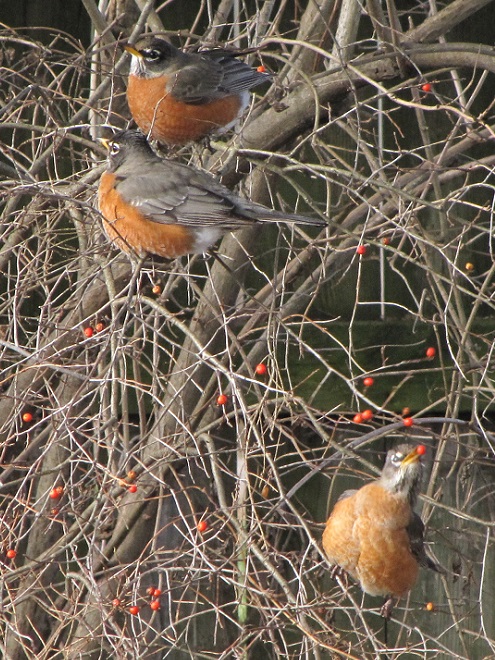
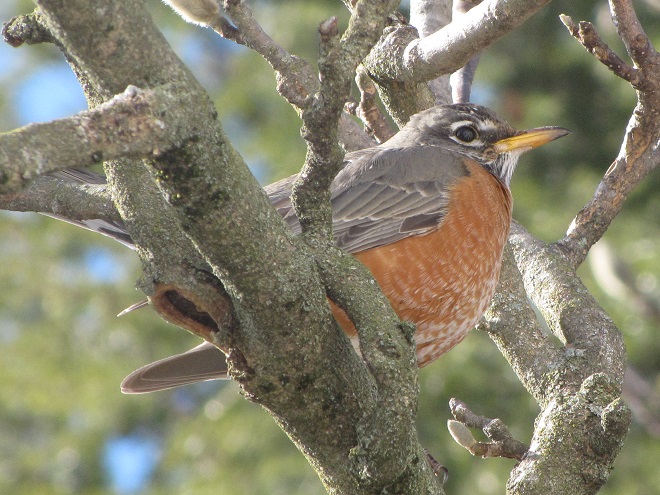
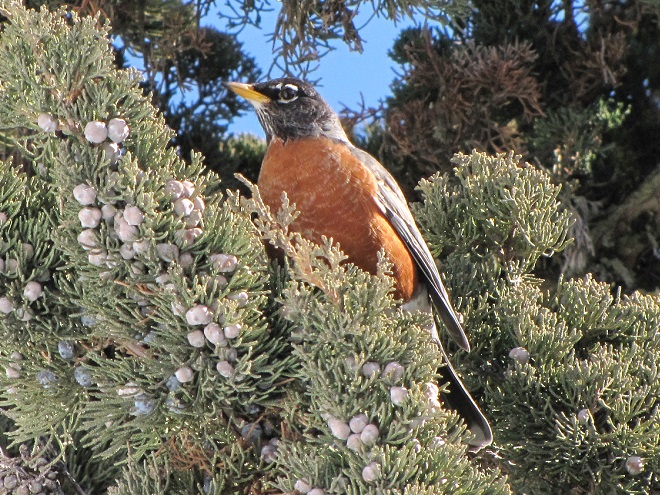
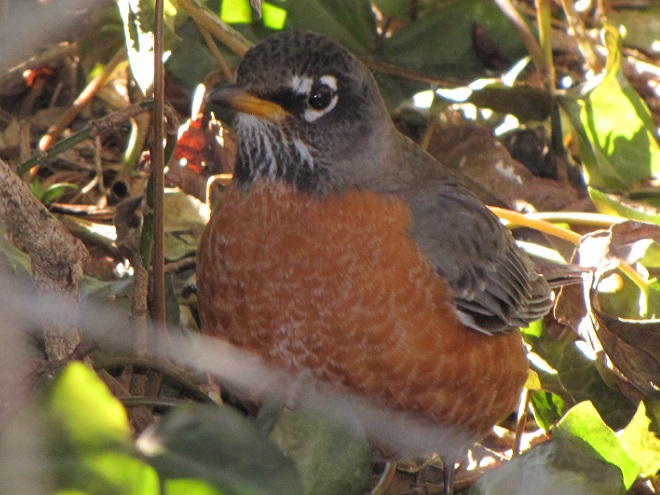
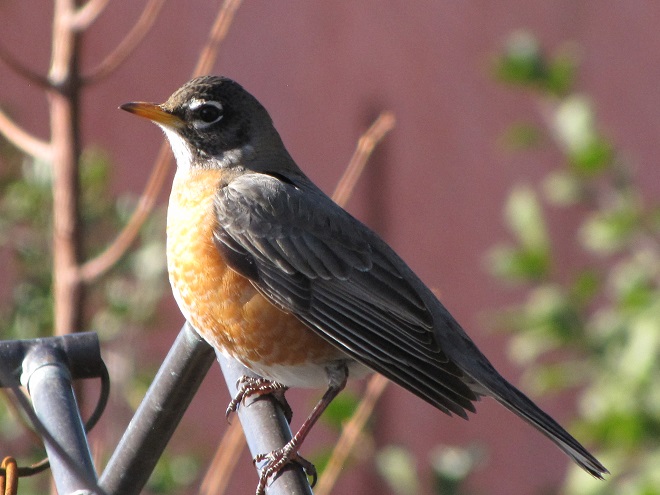
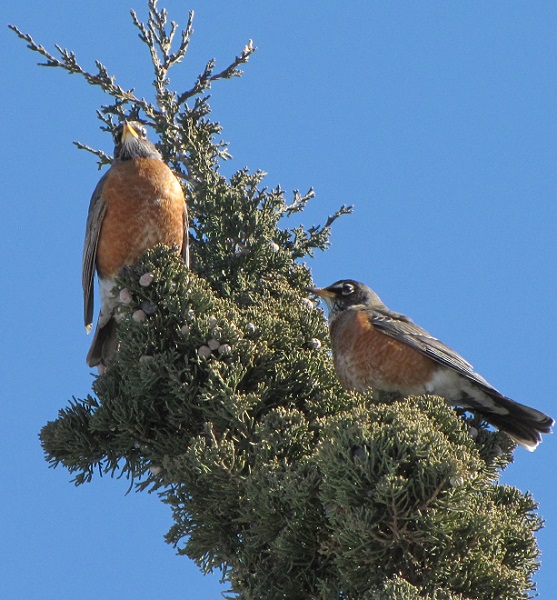
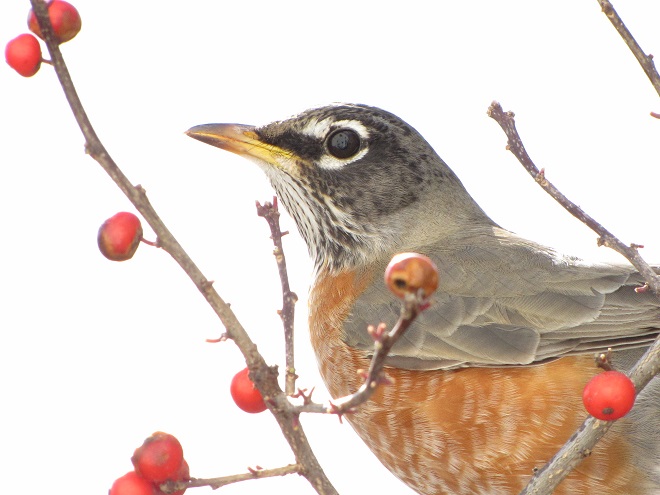
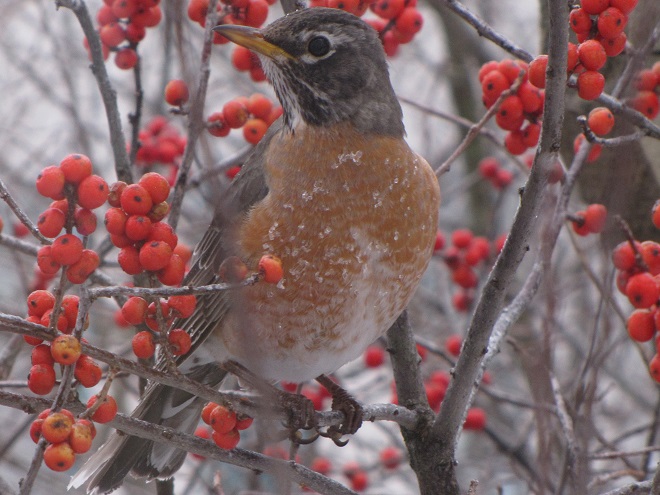
The annual arrival of hoards of American Robins to devour the fruits found on the various berry-producing shrubs and trees in the garden at susquehannawildlife.net headquarters happened to coincide with this morning’s bitter cold temperatures. Here are photos of some of those hungry robins—plus shots of the handful of other songbirds that joined them for a frosty feeding frenzy.















Happening right now, in the bright moonlight on a crisp autumn night, there is a massive movement of nocturnally migrating birds indicated on National Weather Service Radar from State College, Pennsylvania. Notice the dense wave crossing the lower Susquehanna River watershed from northeast to southwest. The coming morning may reveal plenty of new arrivals after daybreak. Look for robins, native sparrows, etc.
Despite being located in an urbanized downtown setting, blustery weather in recent days has inspired a wonderful variety of small birds to visit the garden here at the susquehannawildlife.net headquarters to feed and refresh. For those among you who may enjoy an opportunity to see an interesting variety of native birds living around your place, we’ve assembled a list of our five favorite foods for wild birds.

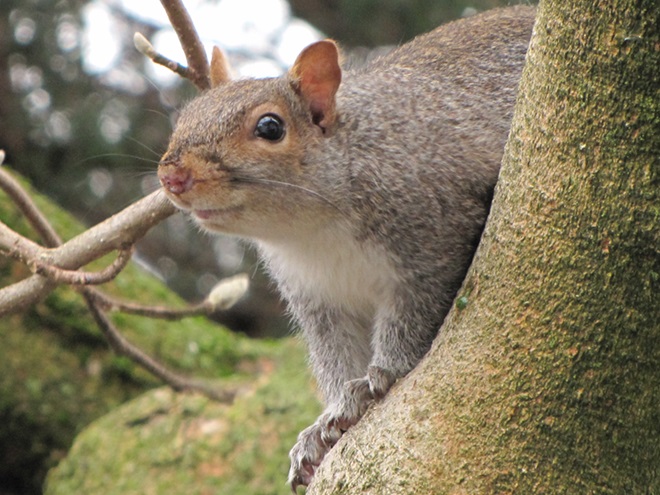
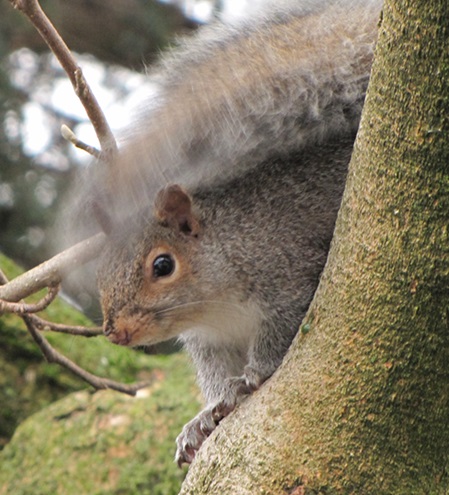
The selections on our list are foods that provide supplemental nutrition and/or energy for indigenous species, mostly songbirds, without sustaining your neighborhood’s non-native European Starlings and House Sparrows, mooching Eastern Gray Squirrels, or flock of ecologically destructive hand-fed waterfowl. We’ve included foods that aren’t necessarily the cheapest but are instead those that are the best value when offered properly.

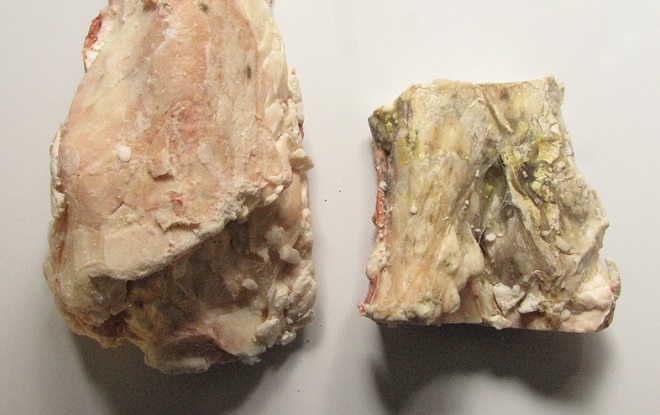
Number 5
Raw Beef Suet
In addition to rendered beef suet, manufactured suet cakes usually contain seeds, cracked corn, peanuts, and other ingredients that attract European Starlings, House Sparrows, and squirrels to the feeder, often excluding woodpeckers and other native species from the fare. Instead, we provide raw beef suet.
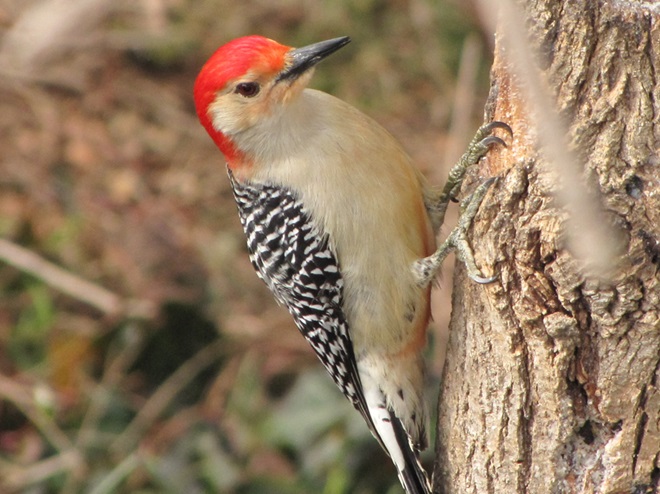
Because it is unrendered and can turn rancid, raw beef suet is strictly a food to be offered in cold weather. It is a favorite of woodpeckers, nuthatches, and many other species. Ask for it at your local meat counter, where it is generally inexpensive.
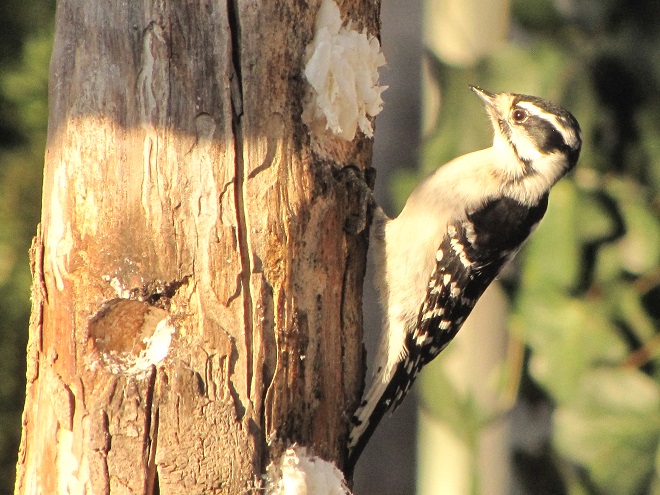
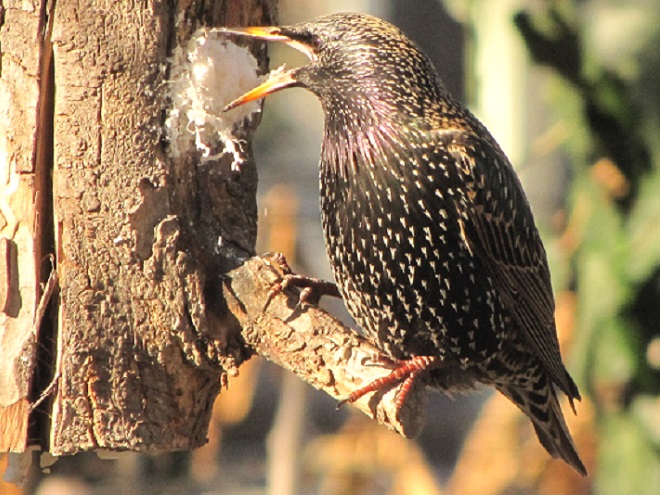
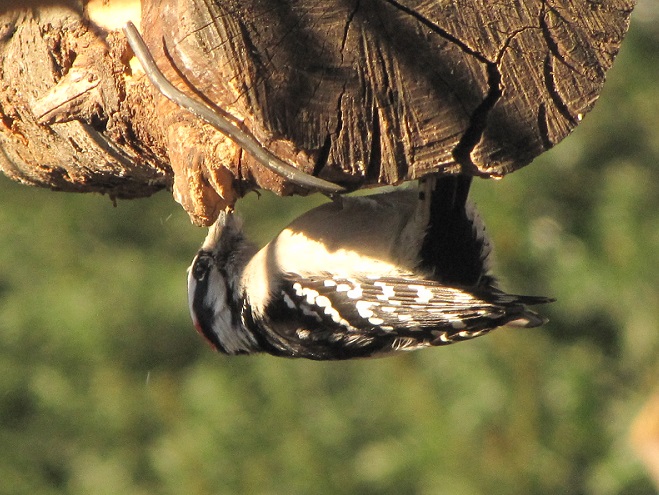
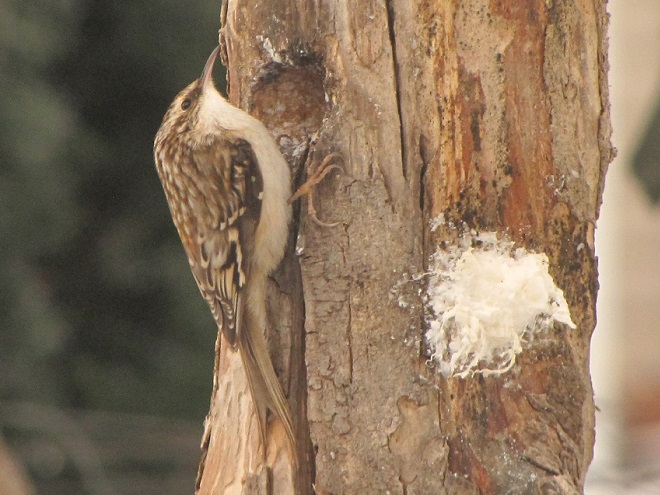
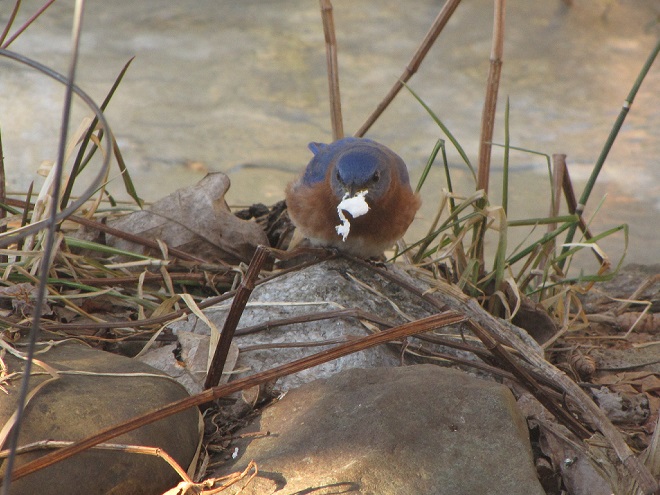






Number 4
Niger (“Thistle”) Seed
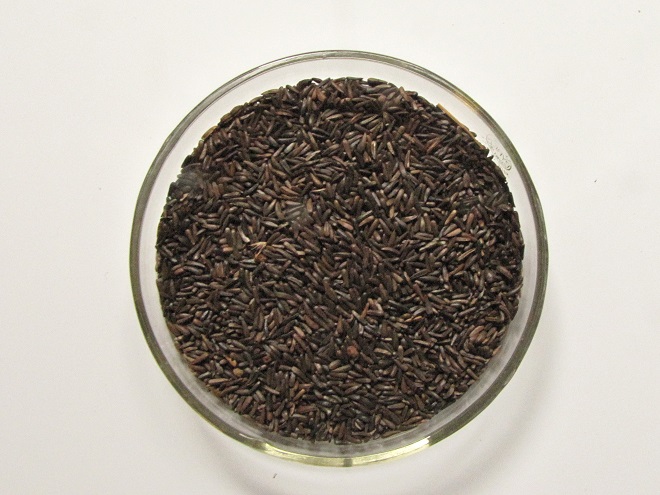
Niger seed, also known as nyjer or nyger, is derived from the sunflower-like plant Guizotia abyssinica, a native of Ethiopia. By the pound, niger seed is usually the most expensive of the bird seeds regularly sold in retail outlets. Nevertheless, it is a good value when offered in a tube or wire mesh feeder that prevents House Sparrows and other species from quickly “shoveling” it to the ground. European starlings and squirrels don’t bother with niger seed at all.
Niger seed must be kept dry. Mold will quickly make niger seed inedible if it gets wet, so avoid using “thistle socks” as feeders. A dome or other protective covering above a tube or wire mesh feeder reduces the frequency with which feeders must be cleaned and moist seed discarded. Remember, keep it fresh and keep it dry!
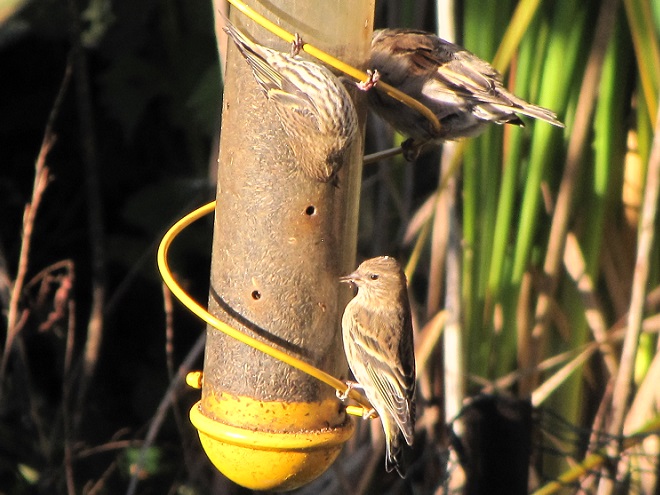
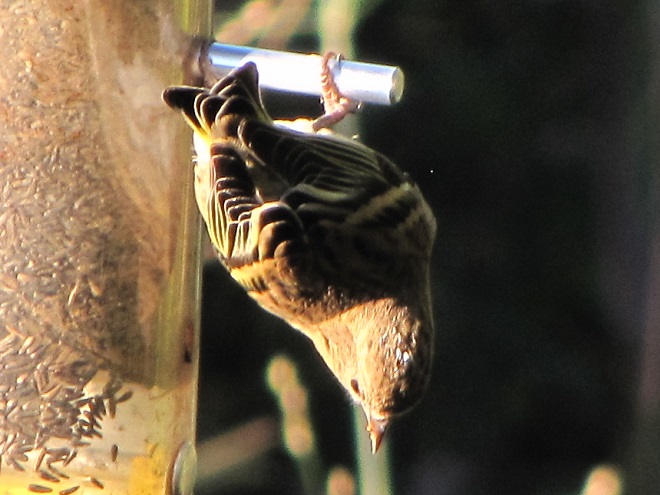





Number 3
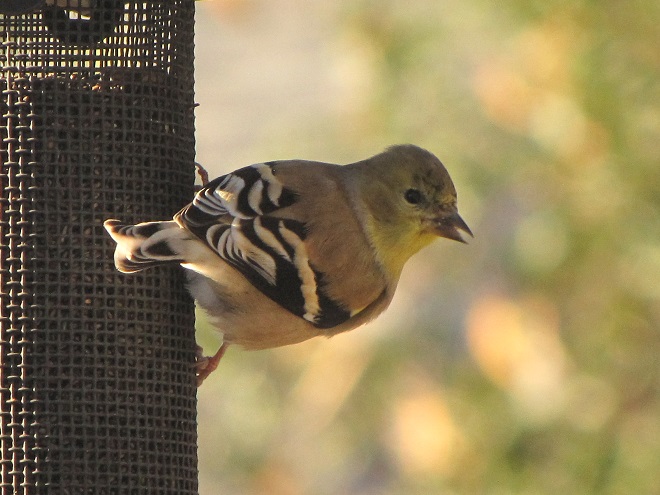
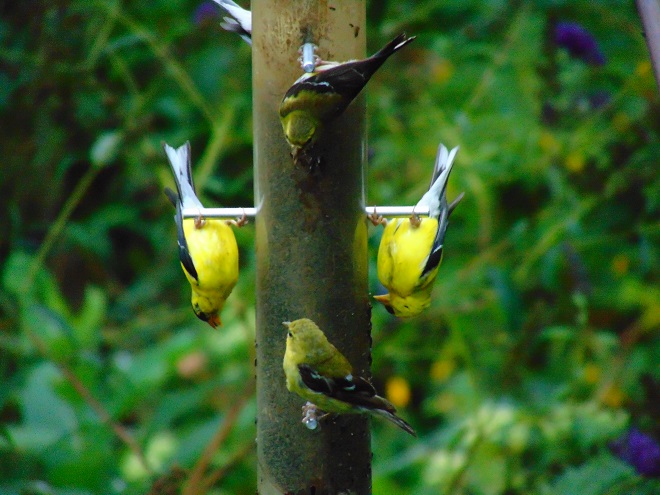
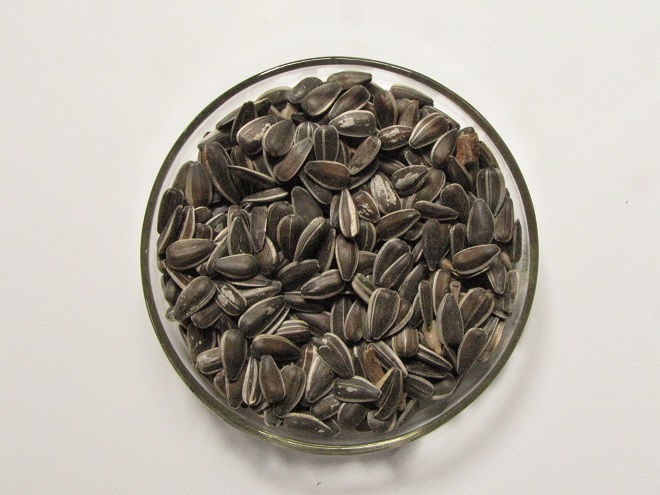
Striped Sunflower Seed
Striped sunflower seed, also known as grey-striped sunflower seed, is harvested from a cultivar of the Common Sunflower (Helianthus annuus), the same tall garden plant with a massive bloom that you grew as a kid. The Common Sunflower is indigenous to areas west of the Mississippi River and its seeds are readily eaten by many native species of birds including jays, finches, and grosbeaks. The husks are harder to crack than those of black oil sunflower seed, so House Sparrows consume less, particularly when it is offered in a feeder that prevents “shoveling”. For obvious reasons, a squirrel-proof or squirrel-resistant feeder should be used for striped sunflower seed.
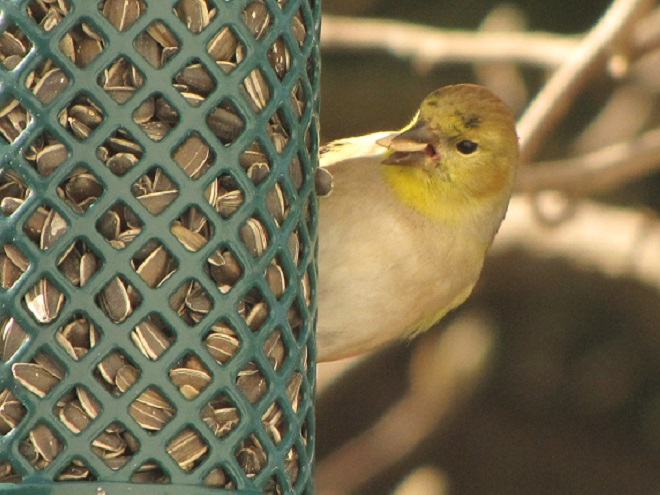
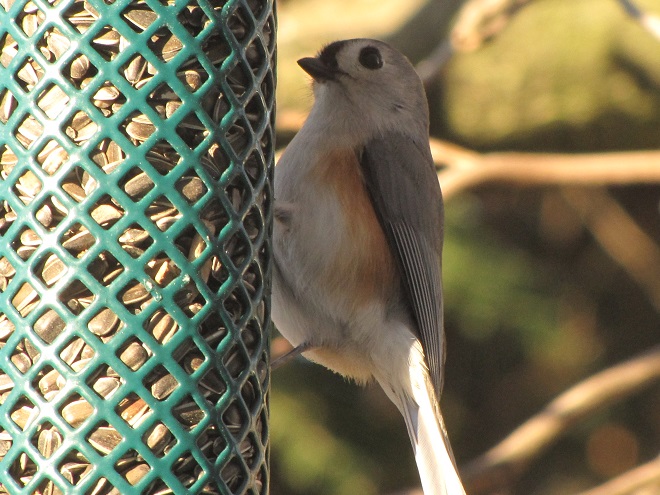
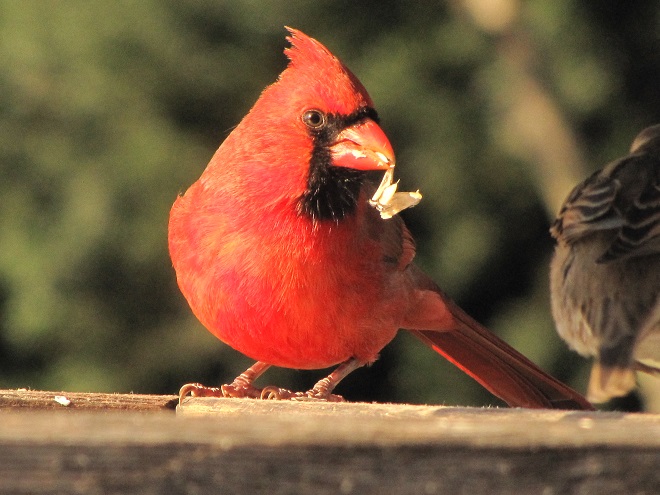
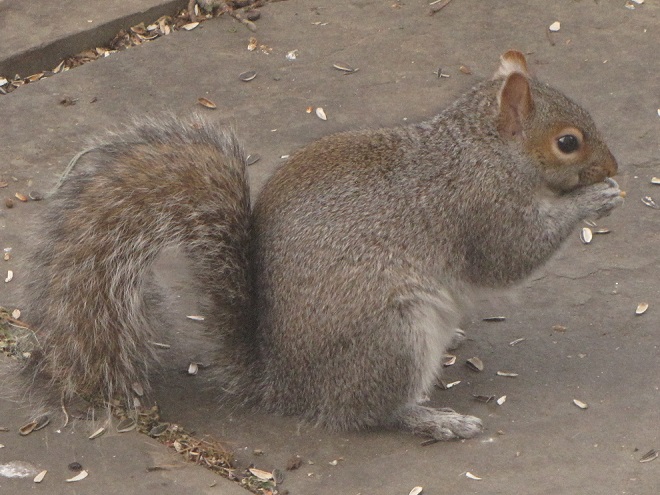






Number 2
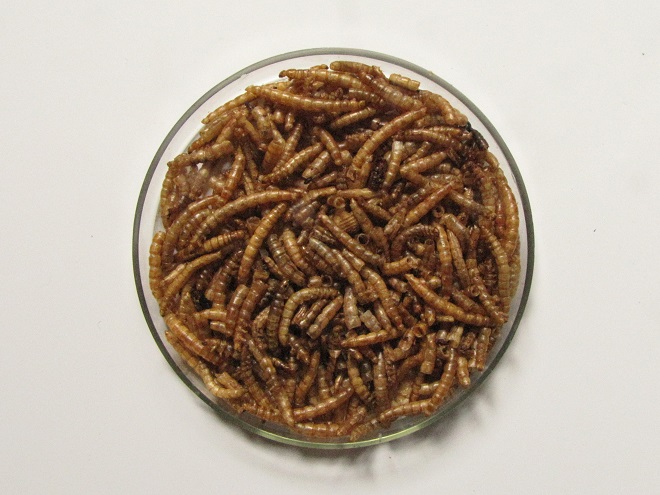
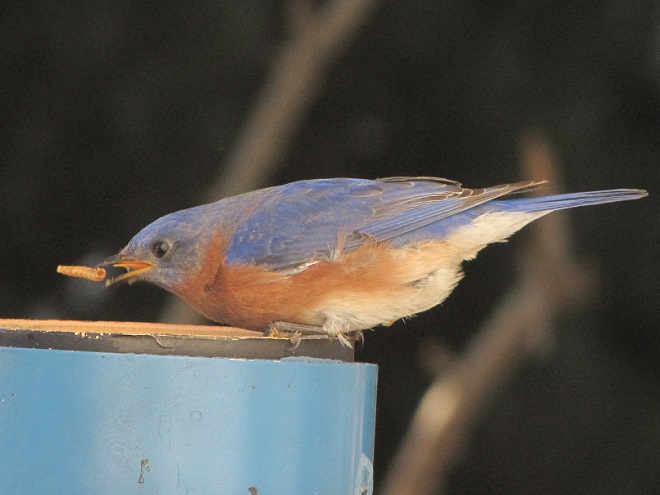
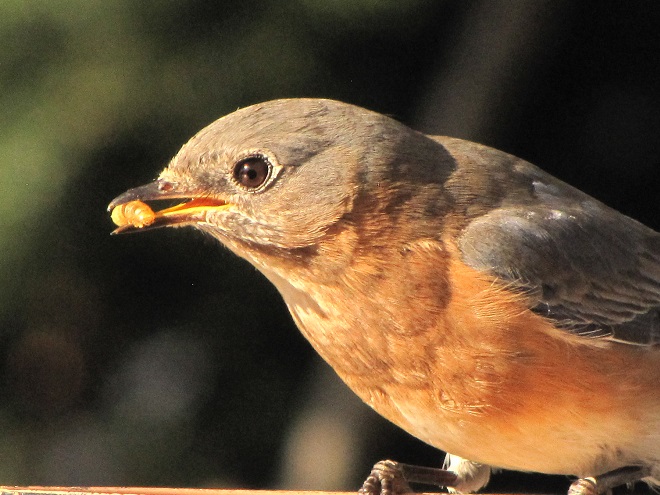
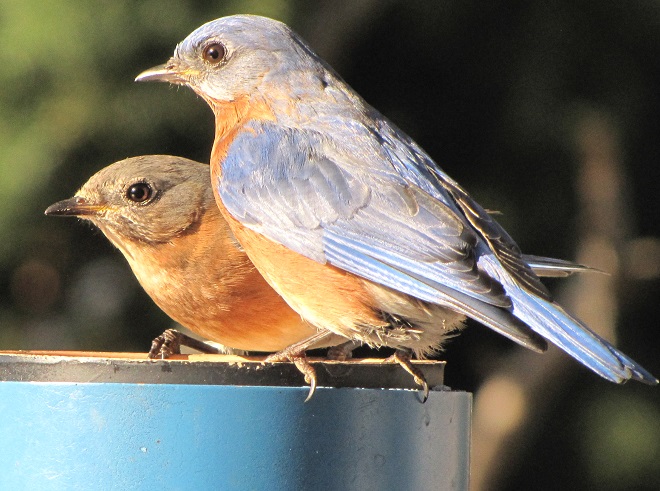
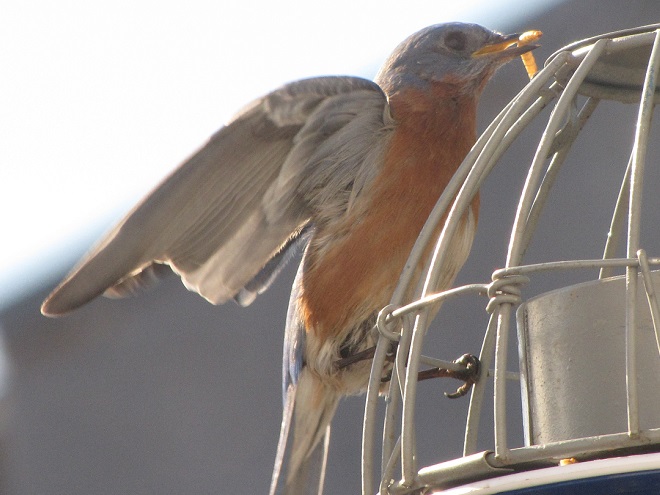
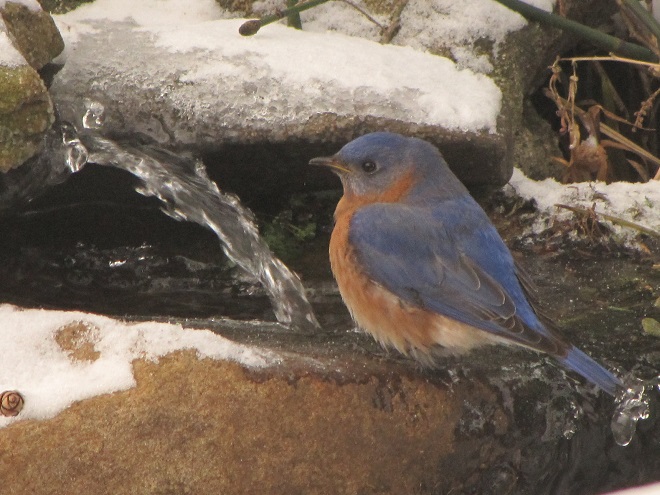
Mealworms
Mealworms are the commercially produced larvae of the beetle Tenebrio molitor. Dried or live mealworms are a marvelous supplement to the diets of numerous birds that might not otherwise visit your garden. Woodpeckers, titmice, wrens, mockingbirds, warblers, and bluebirds are among the species savoring protein-rich mealworms. The trick is to offer them without European Starlings noticing or having access to them because European Starlings you see, go crazy over a meal of mealworms.







Number 1
Food-producing Native Shrubs and Trees
The best value for feeding birds and other wildlife in your garden is to plant food-producing native plants, particularly shrubs and trees. After an initial investment, they can provide food, cover, and roosting sites year after year. In addition, you’ll have a more complete food chain on a property populated by native plants and all the associated life forms they support (insects, spiders, etc.).
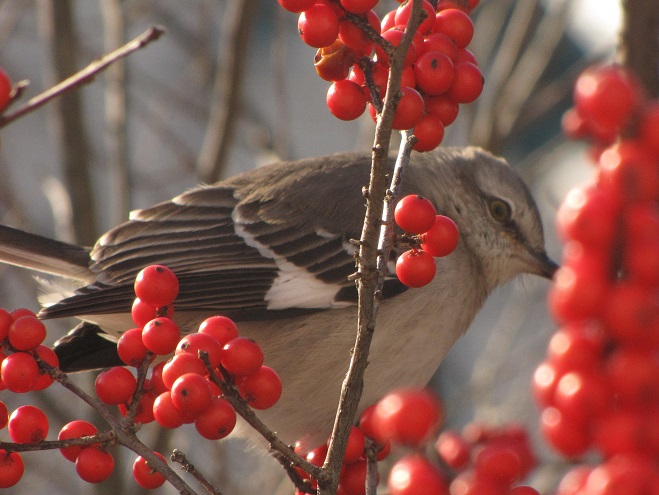





Your local County Conservation District is having its annual spring tree sale soon. They have a wide selection to choose from each year and the plants are inexpensive. They offer everything from evergreens and oaks to grasses and flowers. You can afford to scrap the lawn and revegetate your whole property at these prices—no kidding, we did it. You need to preorder for pickup in the spring. To order, check their websites now or give them a call. These food-producing native shrubs and trees are by far the best bird feeding value that you’re likely to find, so don’t let this year’s sales pass you by!