Back in late May of 1983, four members of the Lancaster County Bird Club—Russ Markert, Harold Morrrin, Steve Santner, and your editor—embarked on an energetic trip to find, observe, and photograph birds in the Lower Rio Grande Valley of Texas. What follows is a daily account of that two-week-long expedition. Notes logged by Markert some four decades ago are quoted in italics. The images are scans of 35 mm color slide photographs taken along the way by your editor.
DAY EIGHT—May 28, 1983
“Bentsen State Park, Texas”
“Alarm at 6:00 A.M. After breakfast we traveled to Falcon State Park and toured the whole camp area, stopping many places to observe birds. We ran up a good list.”
And so we left what had been our home for the last several days and headed west. In the forty years since our departure that morning, Bentsen-Rio Grande State Park has experienced a number of operational changes. Today, it is a World Birding Center site. For conducting the seasonal hawk census, a tower has been erected to provide counters and observes with an unrestricted view above the treetops. If you wanted to camp in the park now, you would need reservations and would have to hike your gear in to one of only a few primitive campsites. Trailer and motor home accommodations no longer exist. A tram service is now available for touring the park by motor vehicle.
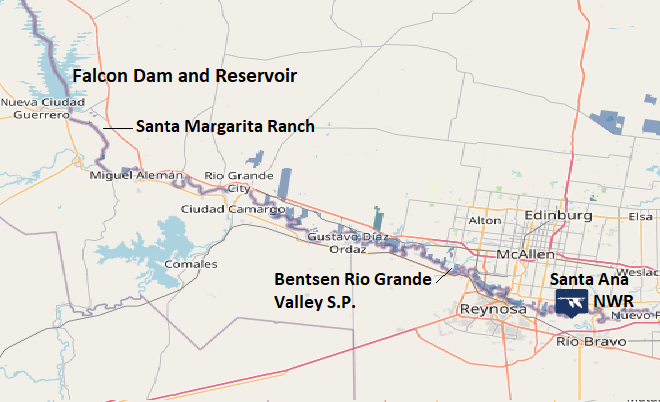
Falcon State Park is located along the east shore of Falcon Reservoir. There are no shade trees beneath which one can escape the scorching rays of the sun on a hot day. This is the easternmost section of the scrubland’s Tamaulipan Saline Thornscrub, a xeric plant community of head-high brush found only on clay soils with a particularly high salinity. Many of the plants look similar to other varieties of shrubs and small trees with which one may be familiar, except nearly all of them are covered with nasty thorns and prickles. And yes, there are cactus. You can’t make your way bushwhacking cross country without obtaining cuts, gashes, and scars to show for it. The Falcon State Recreation Area bird checklist published in 1977 has a nice description of the plants found there—mesquite, ebano, guaycan, blackbrush and catclaw acacia, granjeno, coyotillo, huisache, tasajillo, prickly pear, allthorn, cenizo, colima, and yucca. In the margins between the thornscrub growth, there is an abundance of grasses and wildflowers. On nearby ridges, Tamaulipan Calcareous Thornscrub, a similar xeric plant community, occupies soils with a higher content of calcium carbonate. Together, these communities comprise much of the Tamaulipan Mezquital ecoregion of scrublands in Starr County and western Hidalgo County in the Rio Grande valley of Texas.
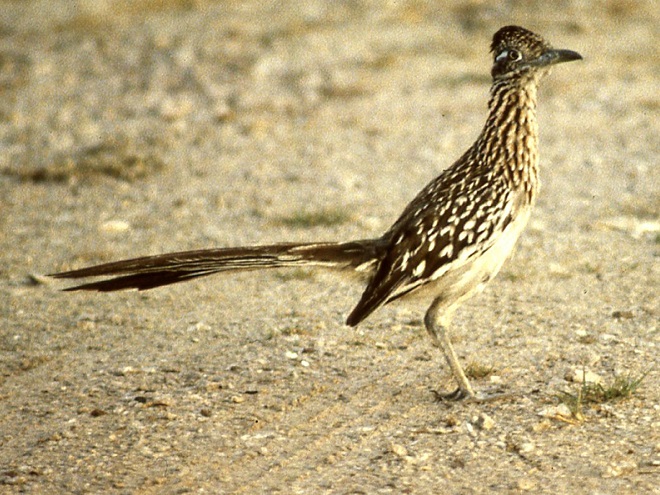
After being greeted by a Greater Roadrunner at the campsite, we took a walk to the nearby shoreline of the reservoir. We spotted Olivaceous Cormorants perched on some dead limbs in the water nearby. Known today as Neotropic Cormorant (Phalacrocorax brasilianus), it is yet another specialty of the Rio Grande Valley. Elsewhere on or near the water—Cattle Egret, Great Egret, Black-bellied Whistling Duck, Osprey, Common Gallinule, Killdeer, Laughing Gull, Forster’s Tern (Sterna forsteri), Least Tern, and Caspian Tern were seen.

In the thornscrub around the campground, which, like Bentsen-Rio Grande State Park, we had pretty much to ourselves, we saw Scissor-tailed Flycatcher, Curve-billed Thrasher, White-winged Dove, Mourning Dove, Ground Dove, Inca Dove, and White-tipped Dove. A single Chihuahuan Raven was a fly by. We saw and smelled several road-killed Nine-banded Armadillos (Dasypus novemcinctus), but never found one alive.
Then, it started to rain. Not just a shower, but a soaker that persisted through much of the day. Rainy days can make for great birding, so we kept at it. Unfortunately, such days aren’t too ideal for photography, so we did only what we could without ruining our equipment.
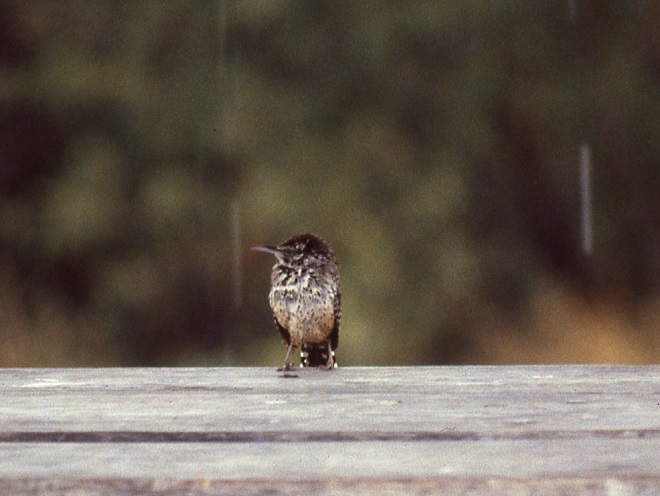
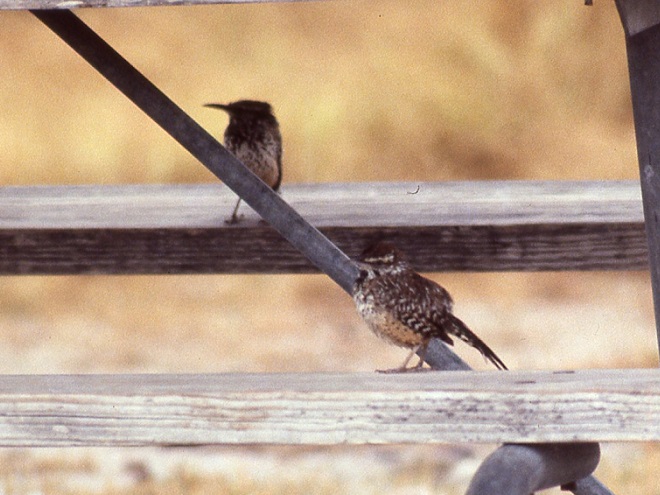


“Finally we drove to the spillway of the dam and parked.”
Falcon Dam was another of the numerous flood-control projects built on the Rio Grande during the middle of the twentieth century. Behind it, Falcon Reservoir stores water for irrigation and operation of a hydroelectric generating station located within the dam complex. Construction of the dam and power plant was a joint venture shared by Mexico and the United States. The project was dedicated by Presidents Adolfo Ruiz Cortines and Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1953.
Rainy days aside, the route precipitation takes to reach the Falcon Reservoir and the Lower Rio Grande Valley includes hundreds of miles through arid grasslands and scrublands. Along the way, much of that water is lost to natural processes including evaporation and aquifer recharge, but an increasing percentage of the volume is being removed by man for civil, industrial, and agricultural uses. Can the Rio Grande and its tributaries continue to meet demand?

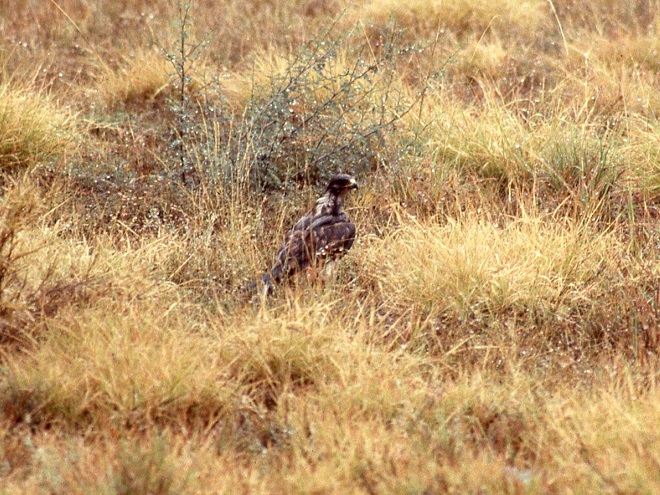
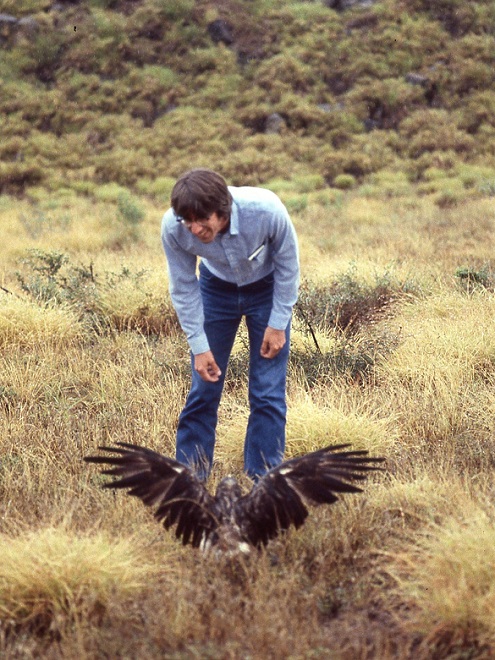
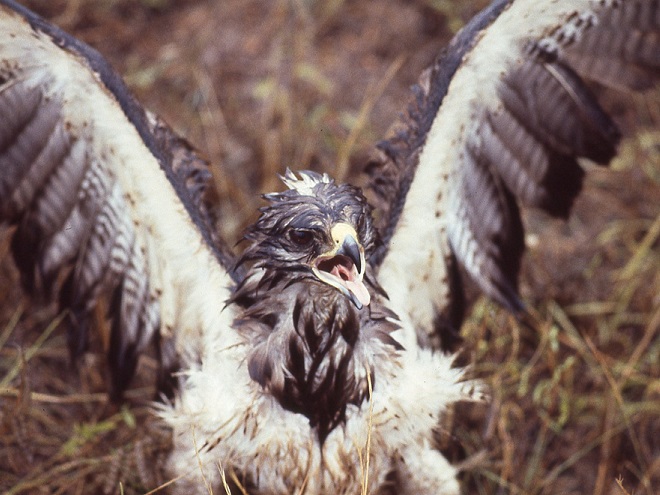
“On the way in we saw and photographed an apparent sick or injured Swainson’s Hawk. We approached it very close.”
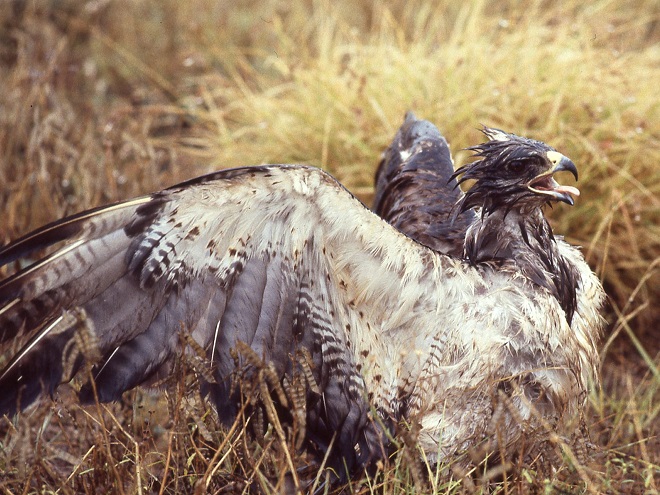
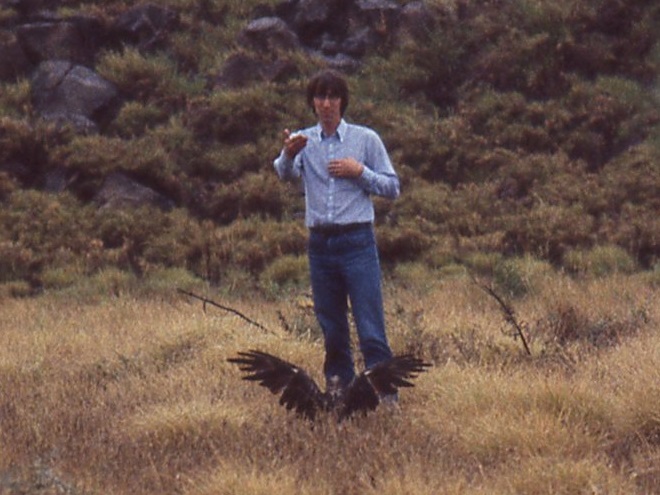





“At the spillway we sat in the camper, except when the rain slackened, then we stood out and watched in vain for the Green or Ringed Kingfisher, which we never did see.”
At the spillway House Sparrows, Rough-winged Swallows, and Cliff Swallows were nesting on the dam, the latter two species grabbing flying insects above the waters of the Rio Grande.

“I made dinner here at this spillway and we continued to watch. The rain almost stopped, so we walked down the road about 1 1/2 miles, during which time we saw a lifer for Harold — Hook-billed Kite. We followed Father Tom’s directions to a spot for the Ferruginous Owl — no luck.”

“Back at the spillway we had supper and then repeated the hike — no Ferruginous Owl, but a Barn Owl and Great Horned Owl. Back to our #201 campsite and wrote up the day’s log.”
Trees along the river provided habitat for orioles and other species. Since the rain had subsided, we decided to see what might come out and begin feeding. Soon, we not only saw an Altamira Oriole, but found Hooded Oriole (Icterus cucullatus) and the yellow and black tropical species, Audubon’s Oriole (Icterus graduacauda), formerly known as Black-headed Oriole. Three species of orioles on a backdrop of lush green subtropical foliage, it was magnificent.
Along the dirt road below the dam, the mix of scrubland and subtropical riparian forest made for excellent birding. We not only found a soaring Hook-billed Kite, one of the target birds for the trip, but we had good looks at both a Great Horned Owl, then a Barn Owl (Tyto alba) that we flushed from the bare ground in openings among the vegetation as we walked the through. Both had probably pounced on some sort of small prey species prior to our arrival. Because there are seldom crows or ravens to bother them, owls here are more active during than day than they are elsewhere. The subject of this afternoon’s intensive search, the elusive and diminutive Ferruginous Pygmy Owl (Glaucidium brasilianum), is routinely diurnal. Other sightings on our two walks included Turkey Vulture, Black Vulture, White-tailed Kite, Northern Bobwhite, Yellow-billed Cuckoo, Golden-fronted Woodpecker, Ladder-backed Woodpecker, Couch’s Kingbird, Brown-crested Flycatcher, Green Jay, Black-crested Titmouse, Mockingbird, Long-billed Thrasher, Great-tailed Grackle, Bronzed Cowbird, Northern Cardinal, and Painted Bunting.
The day finished as so many others had earlier during the trip—with insect-hunting Common Nighthawks calling from the skies around our campsite.
