
Photo of the Day


LIFE IN THE LOWER SUSQUEHANNA RIVER WATERSHED
A Natural History of Conewago Falls—The Waters of Three Mile Island

Where does all the time go? Already in 2024, half the calendar is in the trash and the gasoline and gunpowder gang’s biggest holiday of the year is upon us. Instead of bringing you the memory-making odors of quick-burning sulfur or the noise and multi-faceted irritations that revved-up combustion engines bring, we thought it best to provide our readers with a taste of history for this Fourth of July. Join us, won’t you, for a look back at one of the many events that shaped the landscape of our present-day world.
The early morning’s sun had just begun bathing the verdant gardens of the olde towne centre with a warm glowing light. Birds were singing and the local folk were beginning to stir in preparation for their day’s chores. Then, suddenly, something was stirring afoot.
The great battle had commenced. Within minutes, thousands of colonists spilled onto the pavement to join the melee and defend their homes.




The fighting was at close quarters—face to face with dominant soldiers sparing no effort to prevail in the struggle.

After about an hour had passed, the tide had turned and the fighting mass drifted to the south of the battle’s starting point. The aggressors had been repelled. The dispute was resolved—at least for a little while.



It wasn’t a struggle for independence. And it wasn’t a fight for liberty. For the sterile Pavement Ant worker, all the exertion and all the hazard of assuming the role of a soldier had but one purpose—to raise her sisters and become an aunt. Long live the queen.

With the earth at perihelion (its closest approach to the sun) and with our home star just 27 degrees above the horizon at midday, bright low-angle light offered the perfect opportunity for doing some wildlife photography today. We visited a couple of grasslands managed by the Pennsylvania Game Commission to see what we could find…
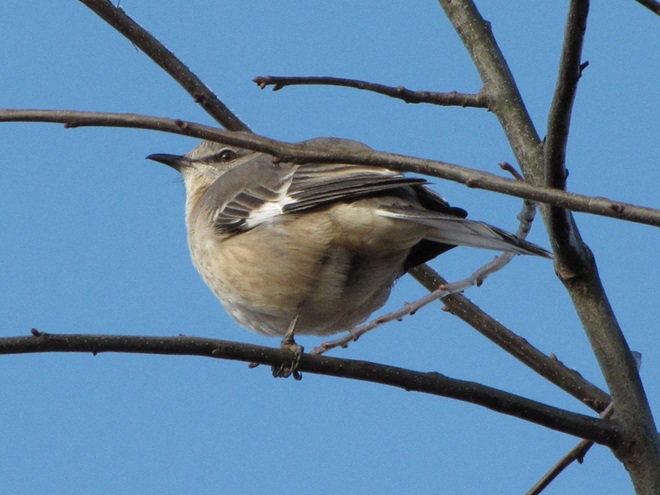
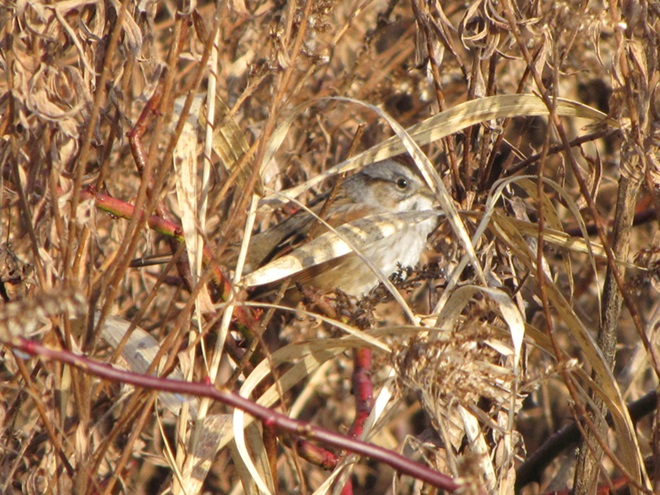
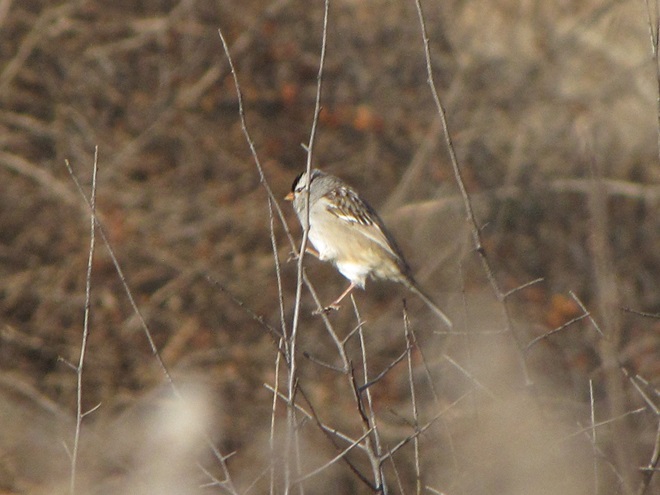
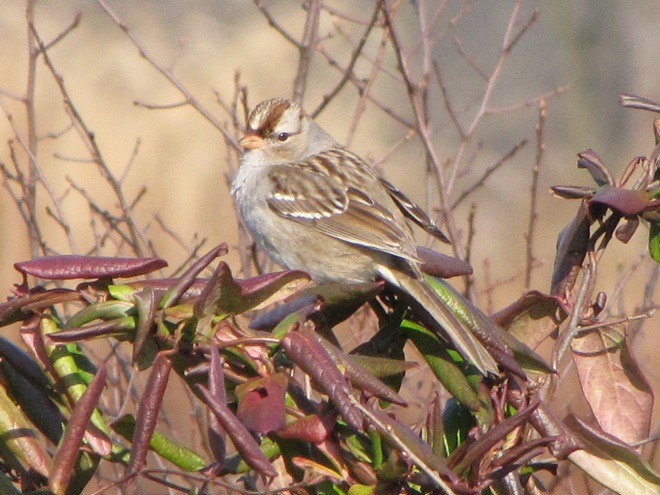
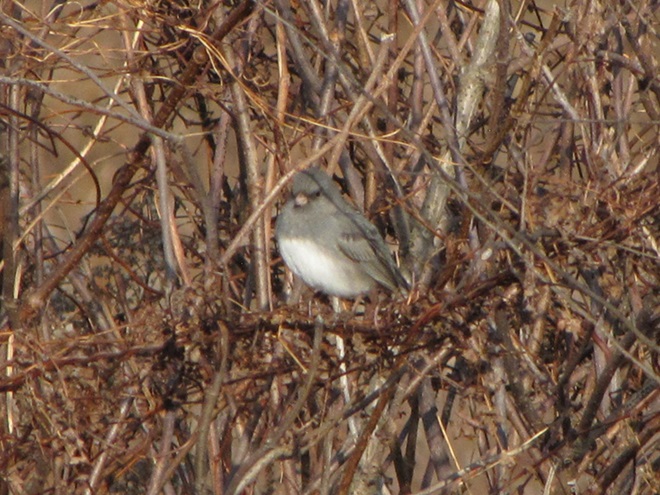
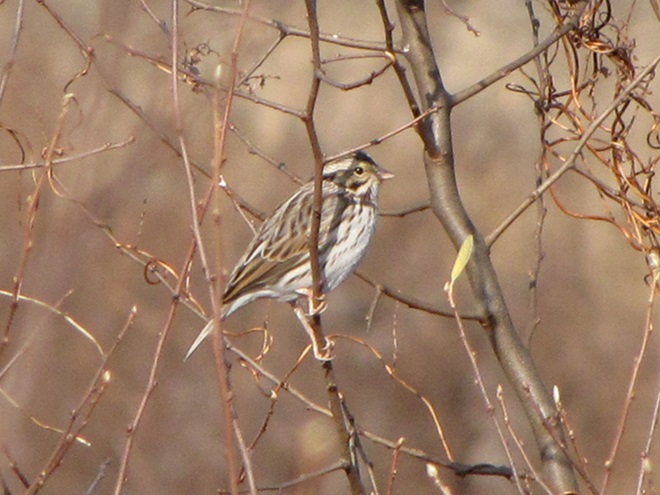
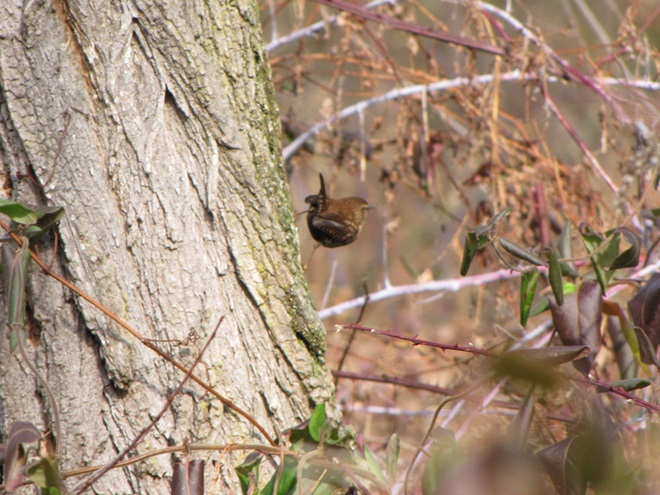
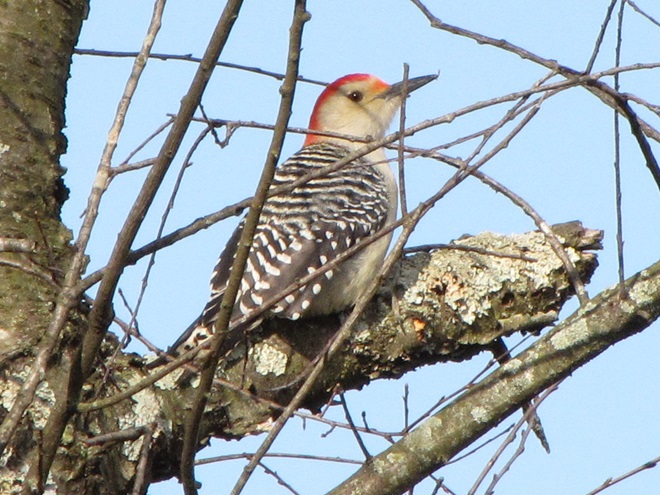
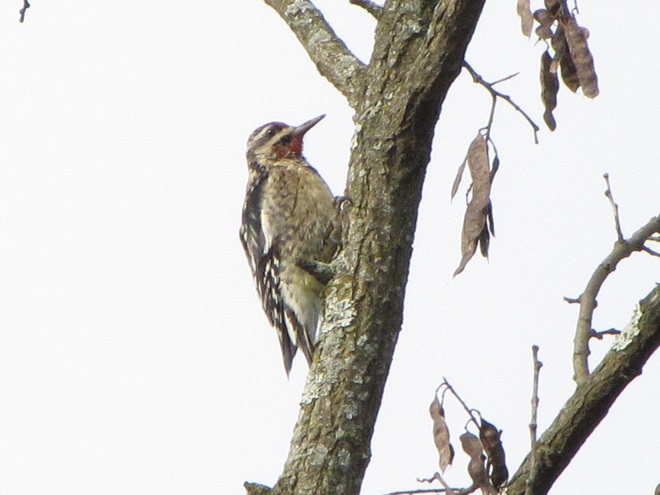
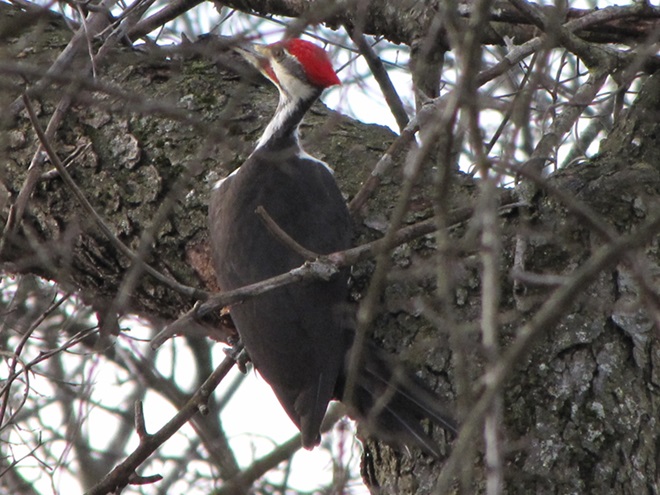
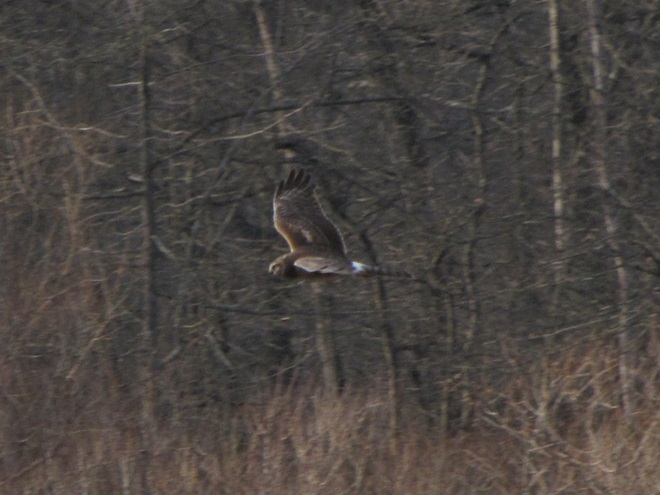
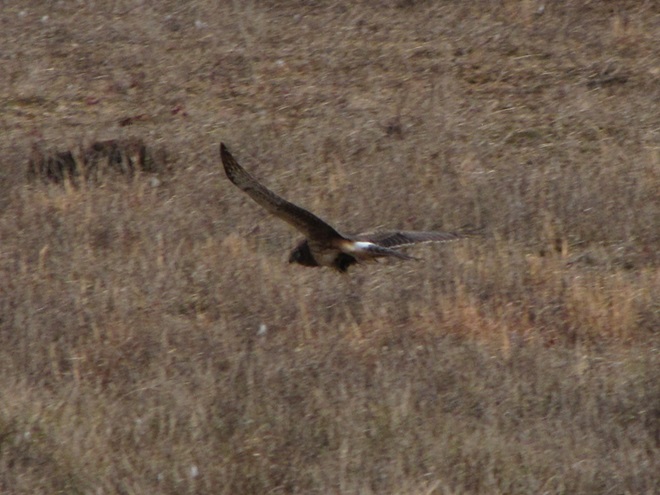



















Have you purchased your 2023-2024 Federal Duck Stamp? Nearly every penny of the 25 dollars you spend for a duck stamp goes toward habitat acquisition and improvements for waterfowl and the hundreds of other animal species that use wetlands for breeding, feeding, and as migration stopover points. Duck stamps aren’t just for hunters, purchasers get free admission to National Wildlife Refuges all over the United States. So do something good for conservation—stop by your local post office and get your Federal Duck Stamp.

Still not convinced that a Federal Duck Stamp is worth the money? Well then, follow along as we take a photo tour of Bombay Hook National Wildlife Refuge. Numbers of southbound shorebirds are on the rise in the refuge’s saltwater marshes and freshwater pools, so we timed a visit earlier this week to coincide with a late-morning high tide.
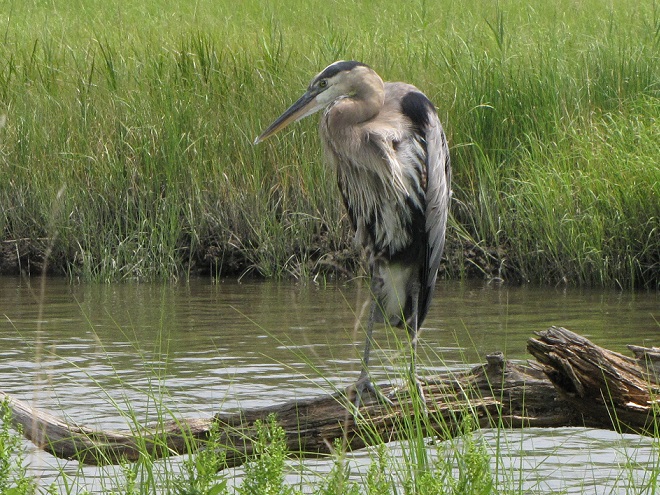
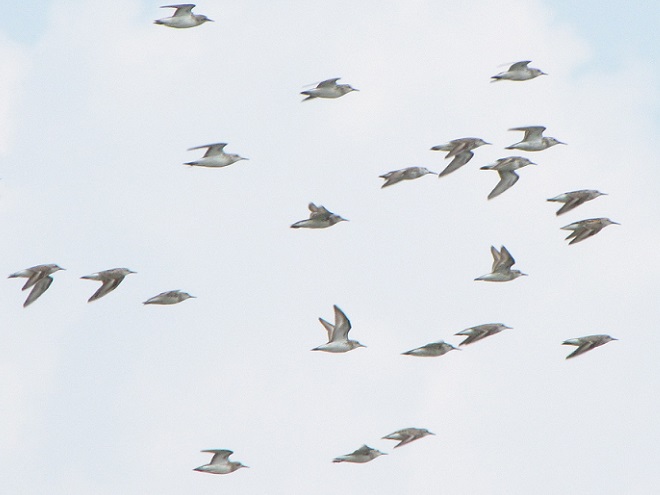
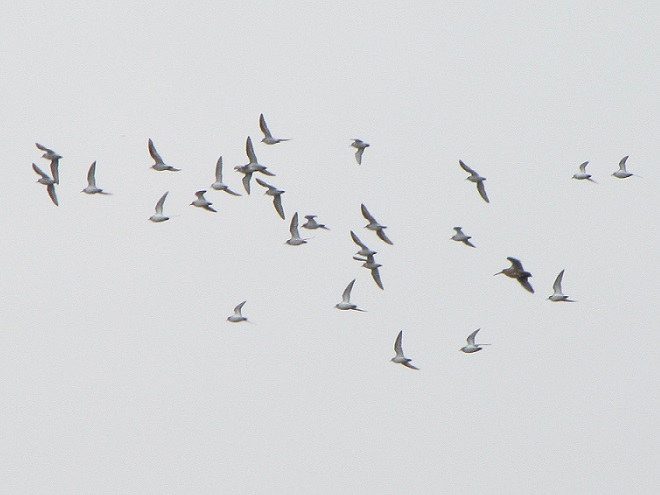
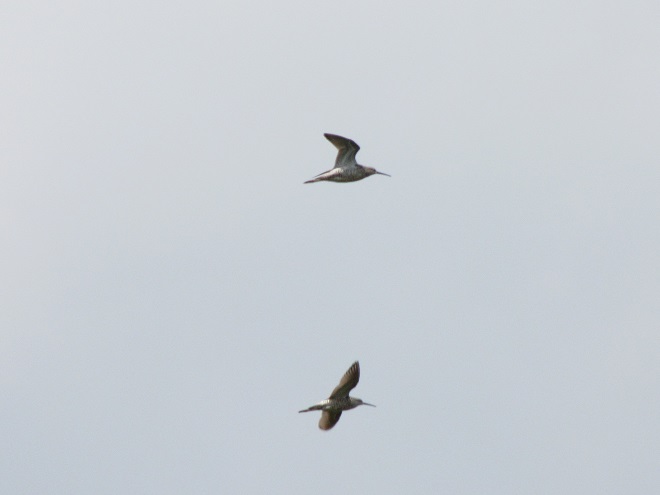
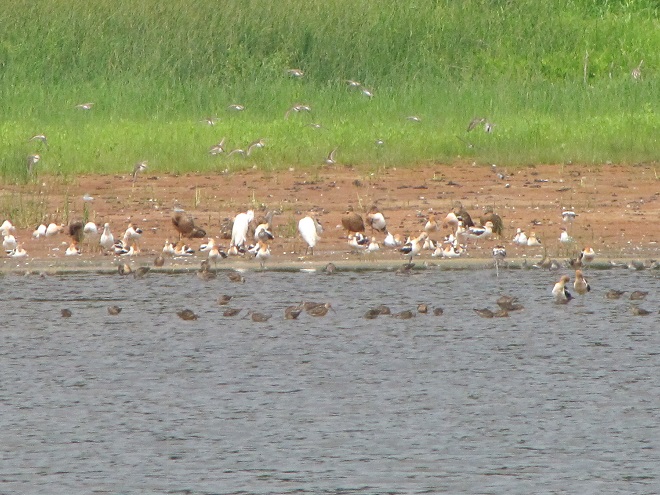
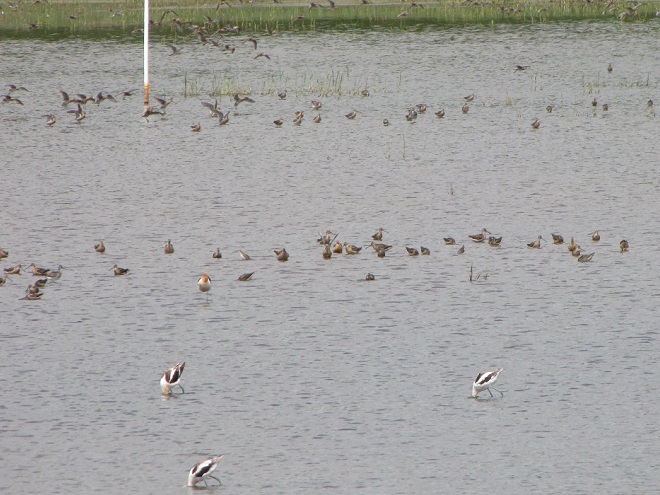
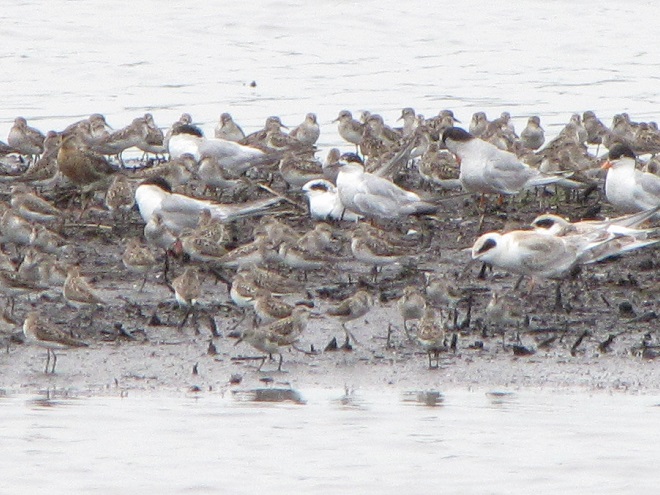
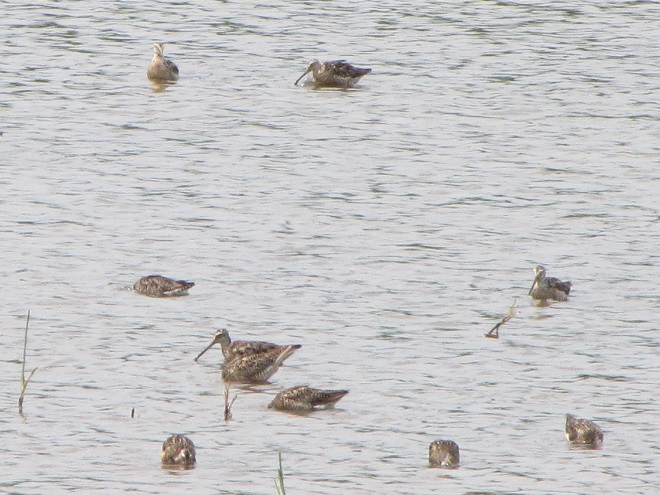
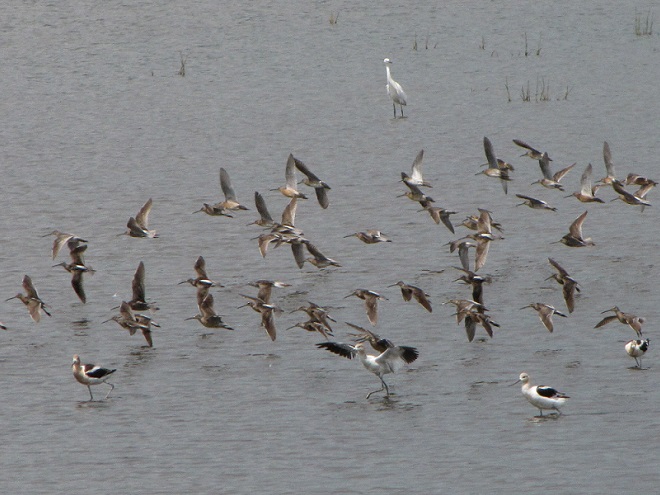
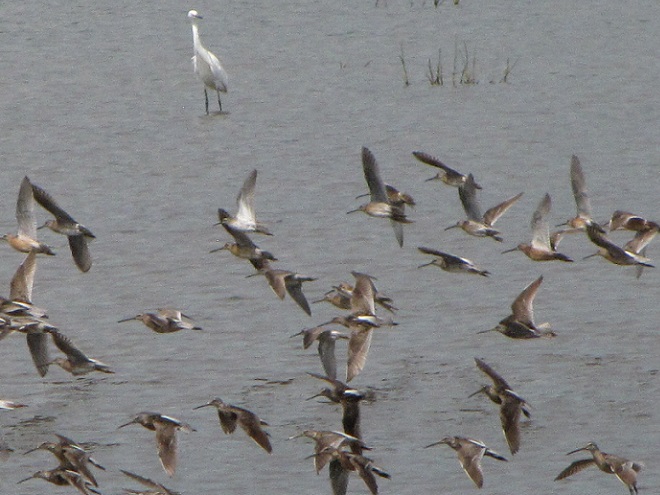
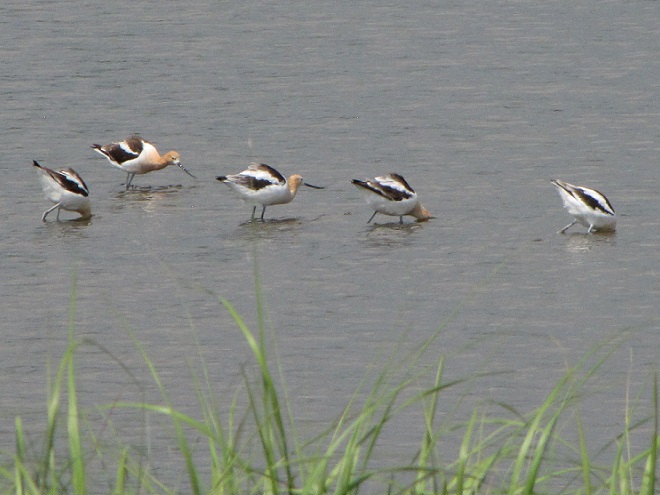
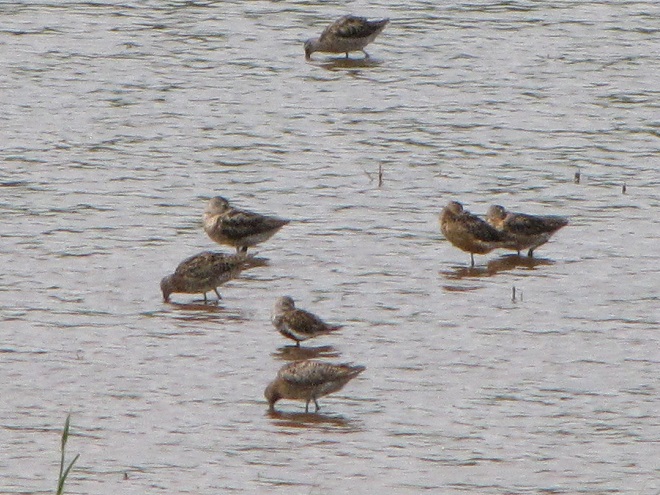
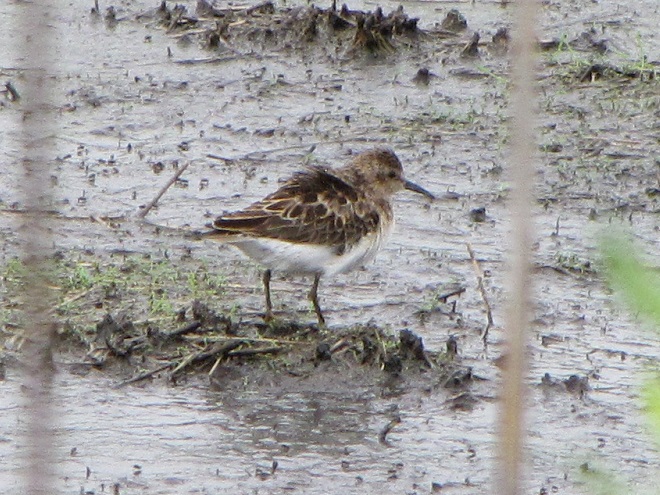
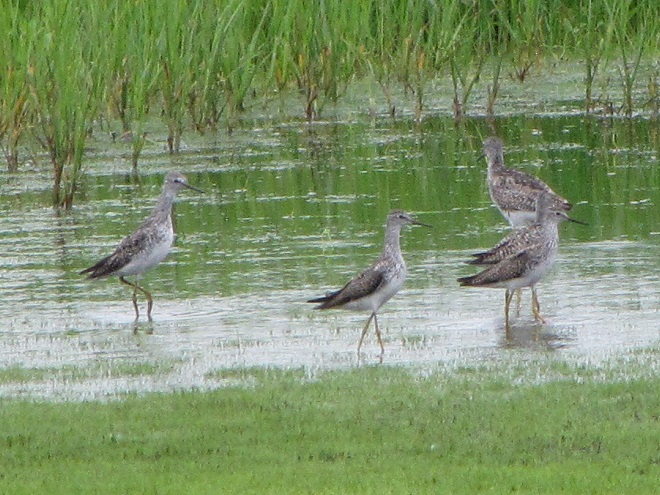
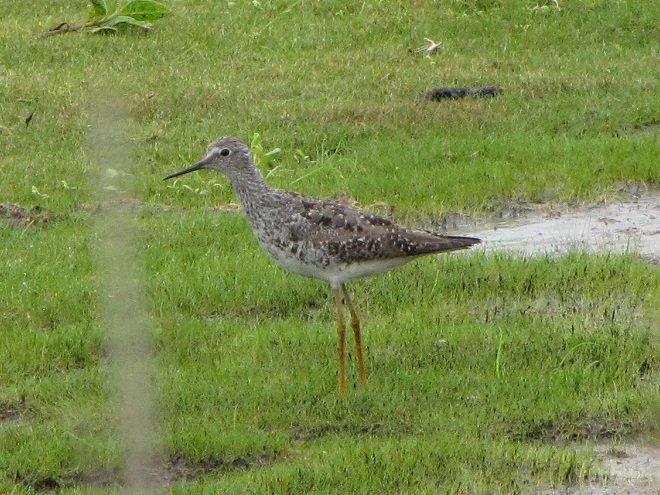
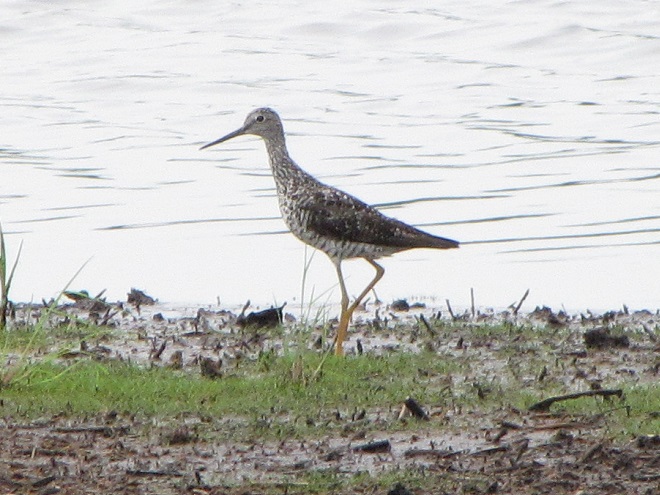
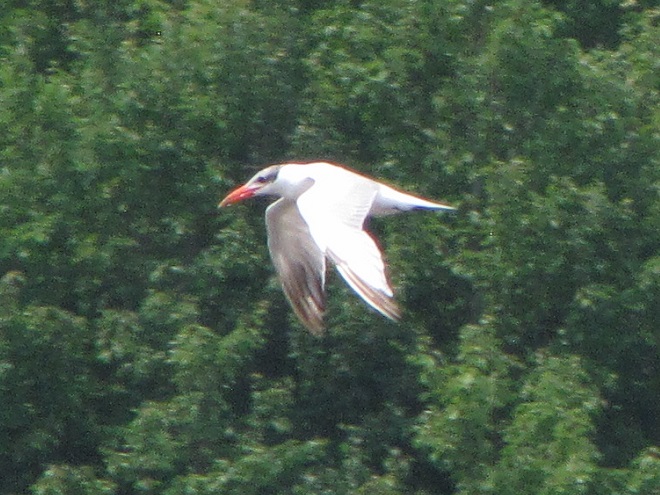
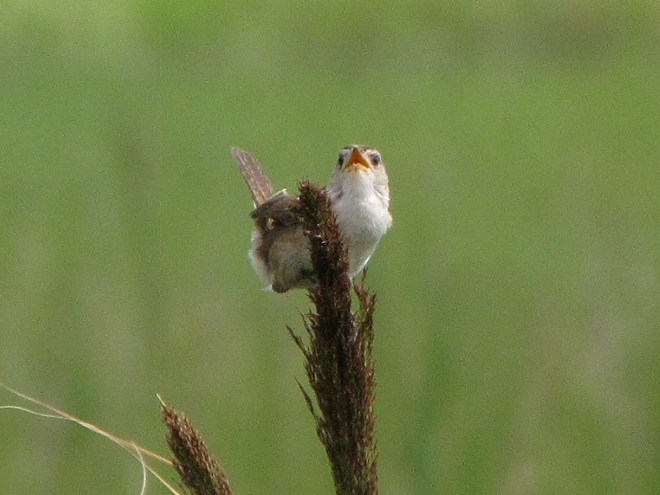
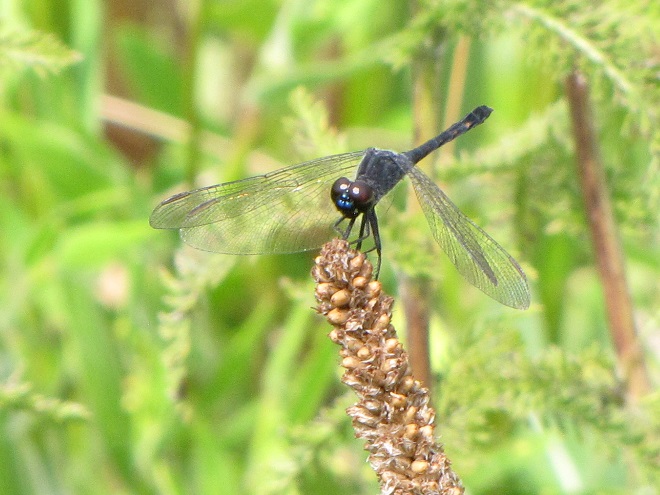
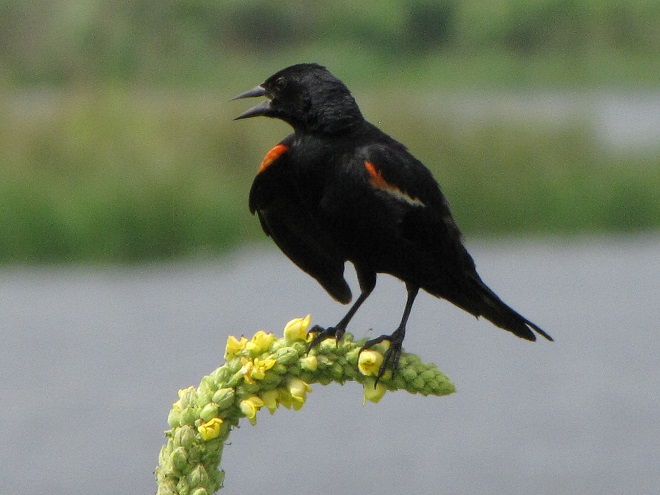
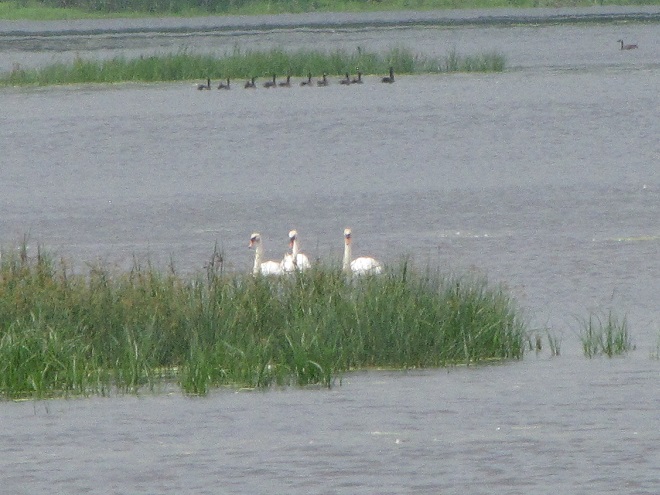
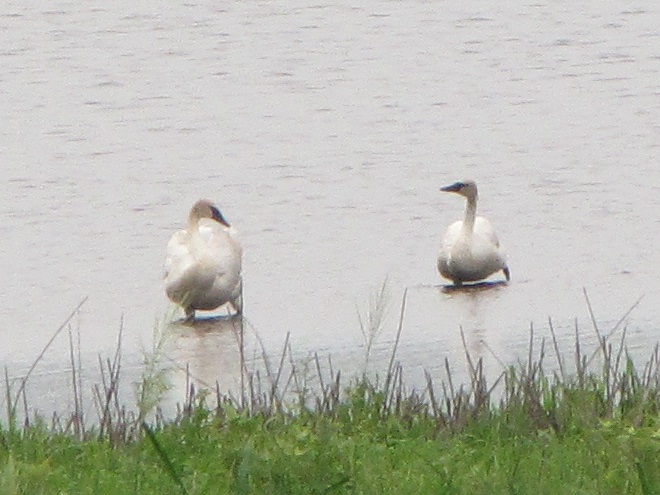
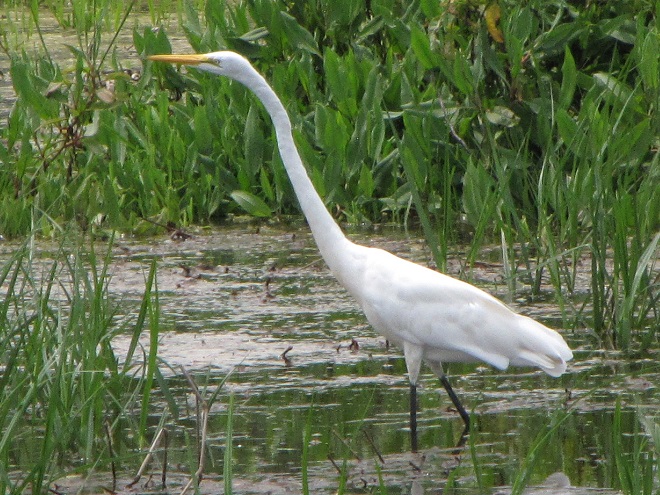
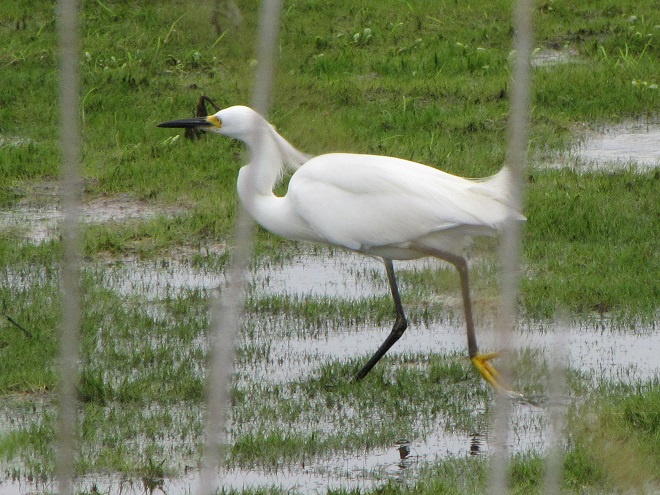
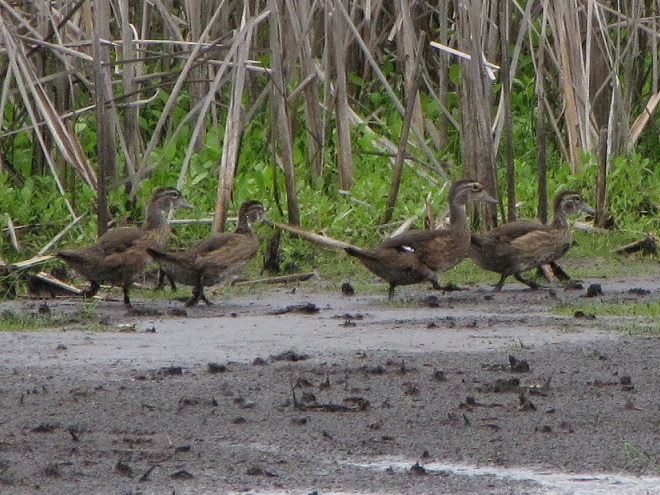
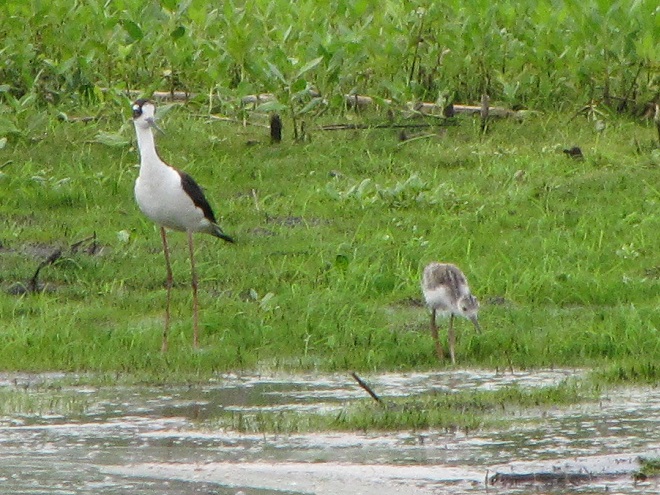
































As the tide recedes, shorebirds leave the freshwater pools to begin feeding on the vast mudflats exposed within the saltwater marshes. Most birds are far from view, but that won’t stop a dedicated observer from finding other spectacular creatures on the bay side of the tour route road.
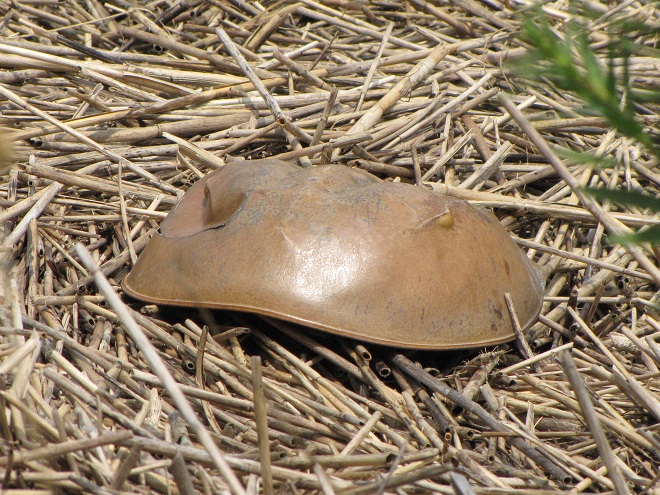
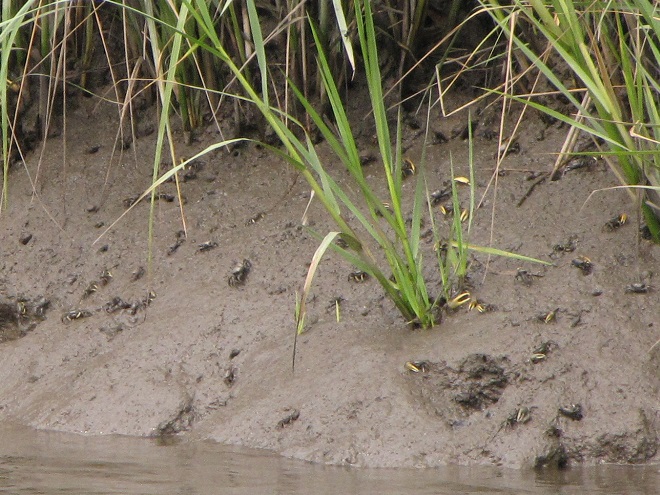
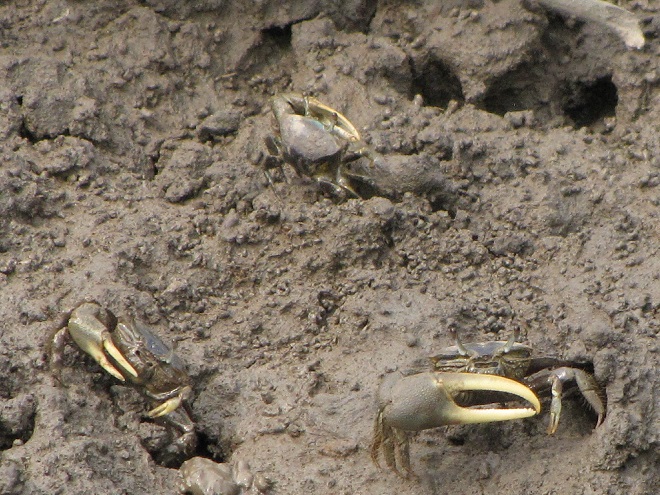
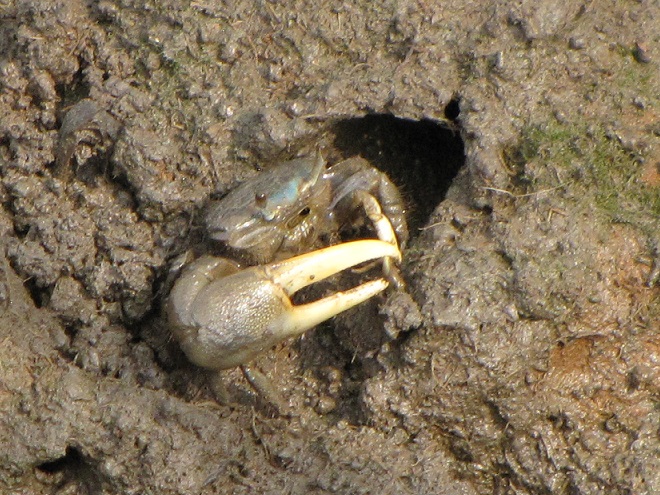
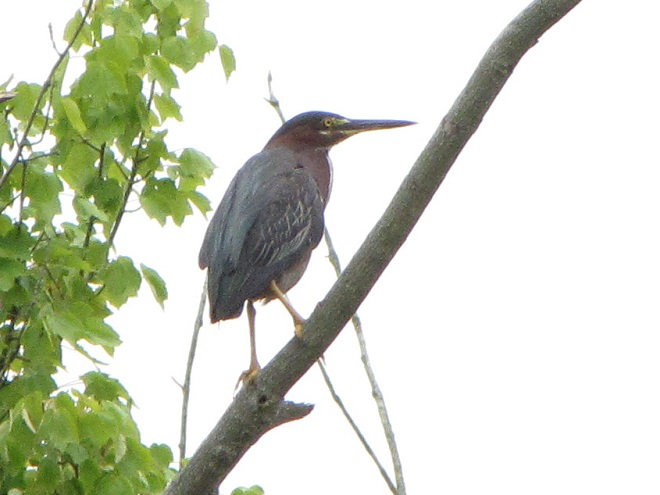
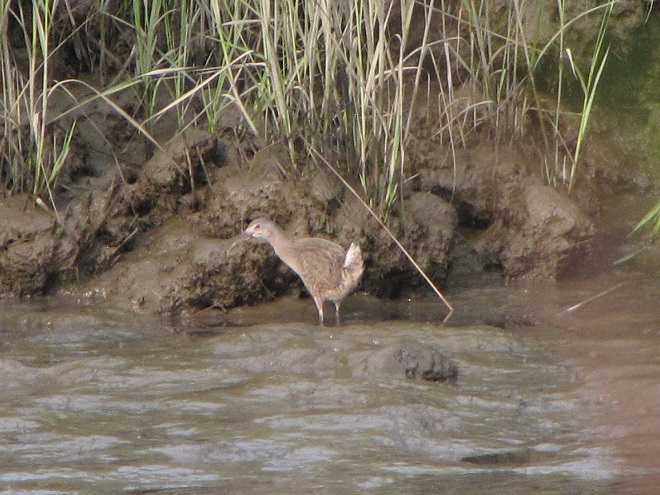











No visit to Bombay Hook is complete without at least a quick loop through the upland habitats at the far end of the tour route.
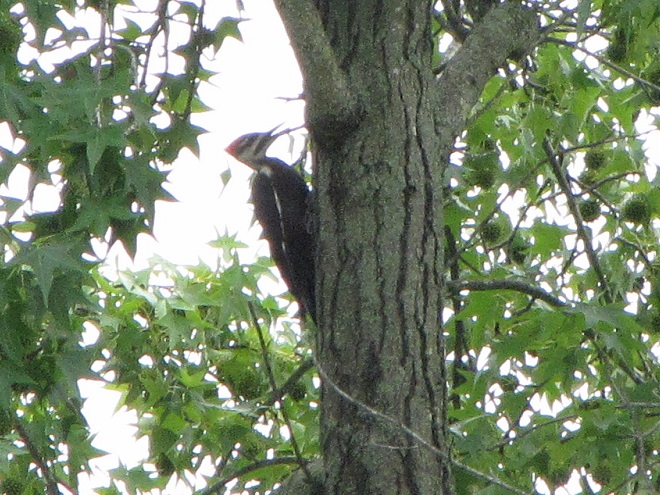
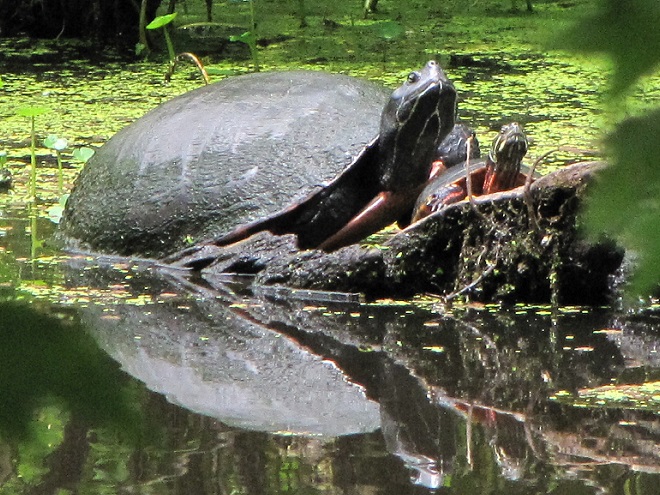
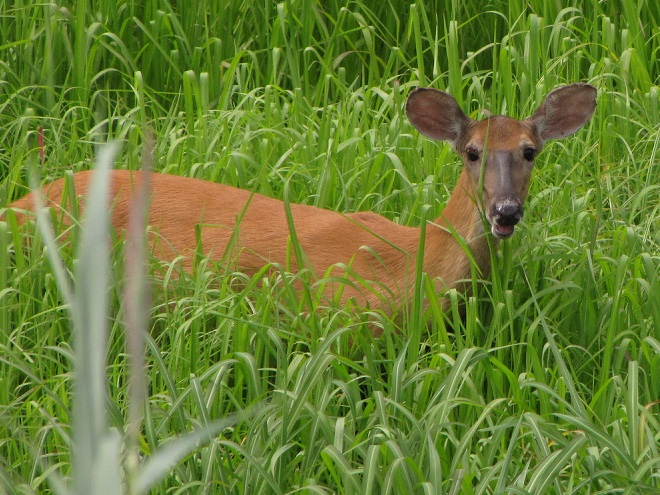
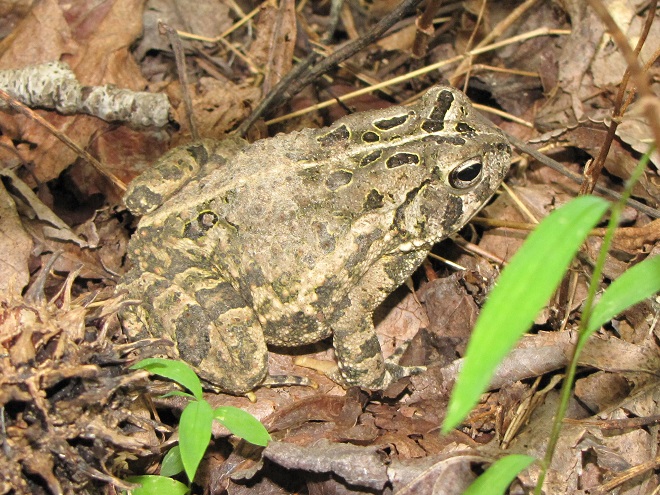









We hope you’ve been convinced to visit Bombay Hook National Wildlife Refuge sometime soon. And we hope too that you’ll help fund additional conservation acquisitions and improvements by visiting your local post office and buying a Federal Duck Stamp.

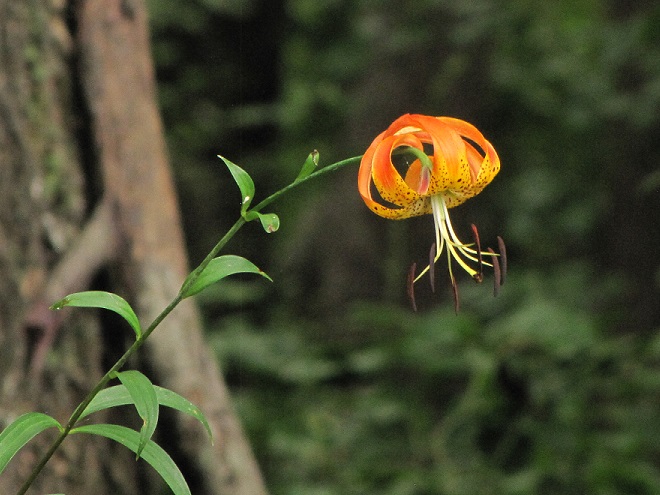
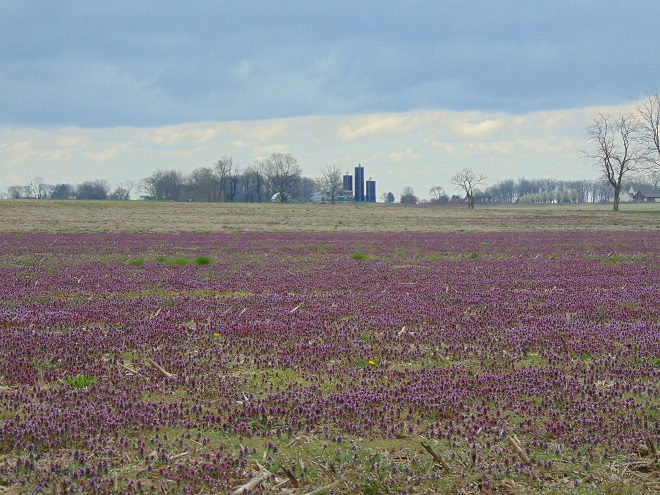
Have you noticed a purple haze across the fields right now? If so, you may have wondered, “What kind of flowers are they?”

Say hello to Purple Dead Nettle (Lamium purpureum), a non-native invasive species that has increased its prevalence in recent years by finding an improved niche in no-till cropland. Purple Dead Nettle, also known as Red Dead Nettle, is native to Asia and Europe. It has been a familiar early spring “weed” in gardens, along roadsides, and in other disturbed ground for decades.
Purple Dead Nettle owes its new-found success to the timing of its compressed growing season. Its tiny seeds germinate during the fall and winter, after crops have been harvested and herbicide application has ended for the season. The plants flower early in the spring and are thus particularly attractive to Honey Bees and other pollinators looking for a source of energy-rich nectar as they ramp up activity after winter lock down. In many cases, Purple Dead Nettle has already completed its flowering cycle and produced seeds before there is any activity in the field to prepare for planting the summer crop. The seeds spend the warmer months in dormancy, avoiding the hazards of modern cultivation that expel most other species of native and non-native plants from the agricultural landscape.
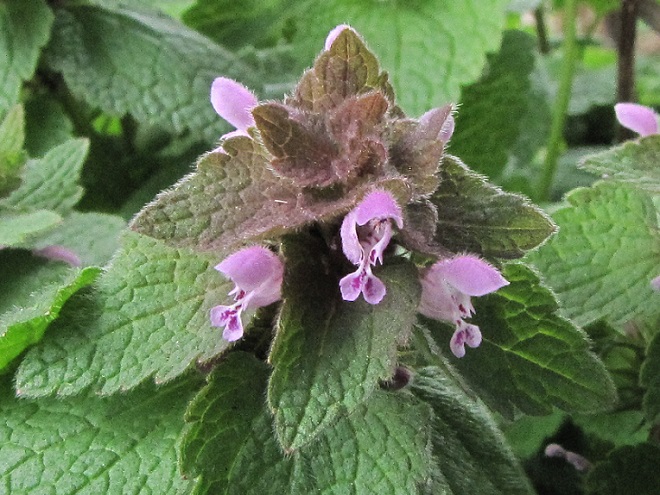
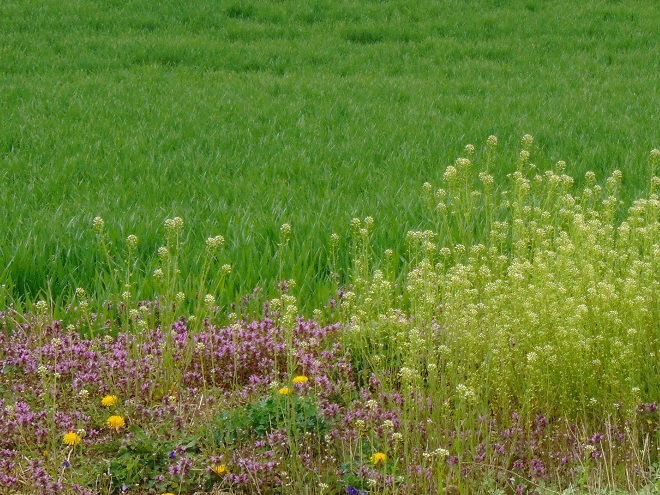




While modern farming has eliminated a majority of native plant and animal species from agricultural lands of the lower Susquehanna valley, its crop management practices have simultaneously invited vigorous invasion by a select few non-native species. High-intensity farming devotes its acreage to providing food for a growing population of people—not to providing wildlife habitat. That’s why it’s so important to minimize our impact on non-farm lands throughout the remainder of the watershed. If we continue subdividing, paving, and mowing more and more space, we’ll eventually be living in a polluted semi-arid landscape populated by little else but non-native invasive plants and animals. We can certainly do better than that.
First there was the Nautilus. Then there was the Seaview. And who can forget the Yellow Submarine? Well, now there’s the S. S. Haldeman, and today we celebrated her shakedown cruise and maiden voyage. The Haldeman is powered by spent fuel that first saw light of day near Conewago Falls at a dismantled site that presently amounts to nothing more than an electrical substation. Though antique in appearance, the vessel discharges few emissions, provided there aren’t any burps or hiccups while underway. So, climb aboard as we take a cruise up the Susquehanna at periscope depth to have a quick look around!
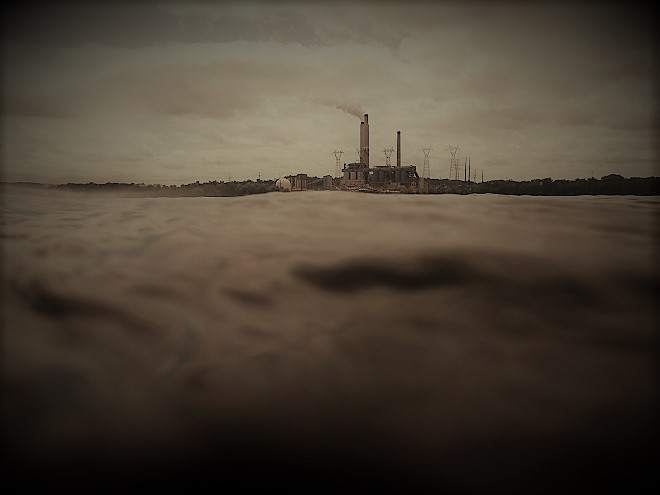




Watertight and working fine. Let’s flood the tanks and have a peek at the benthos. Dive, all dive!
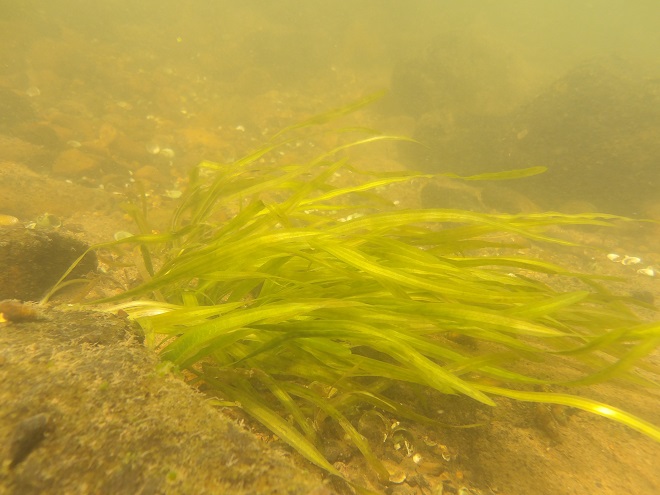
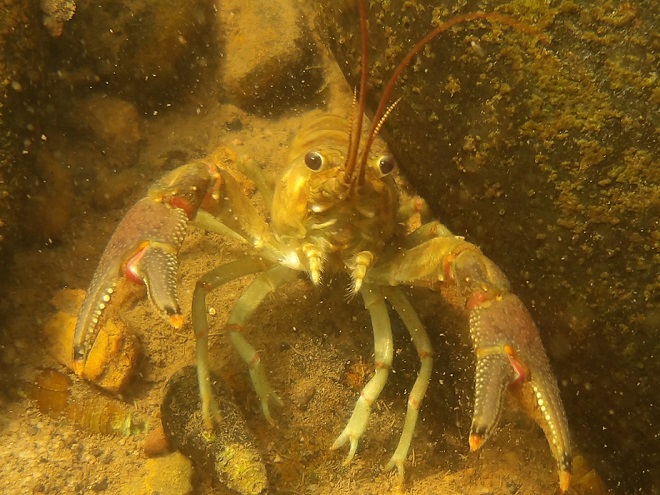
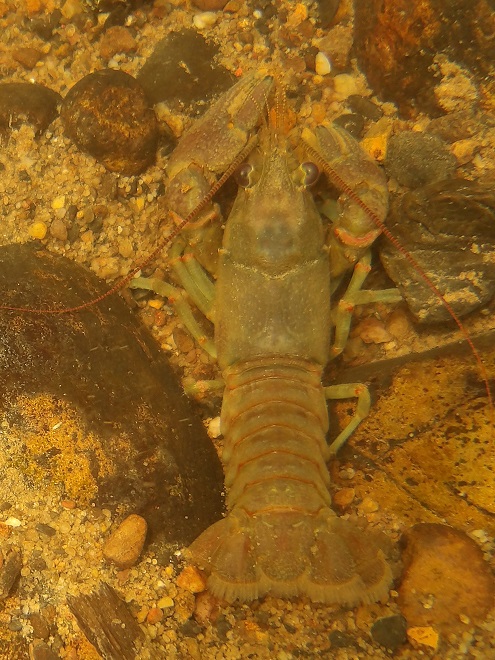
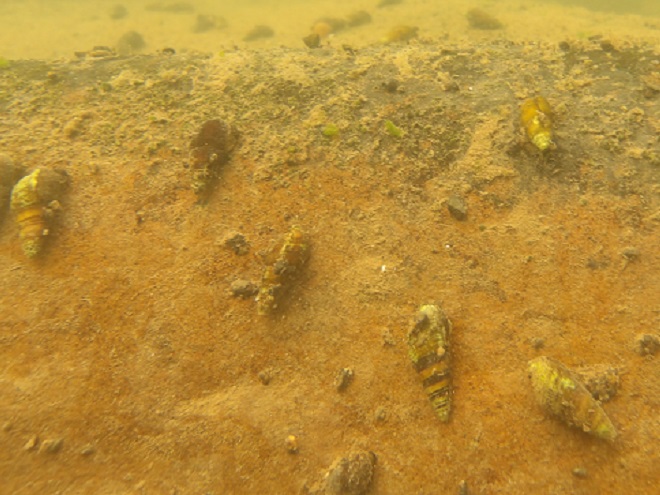
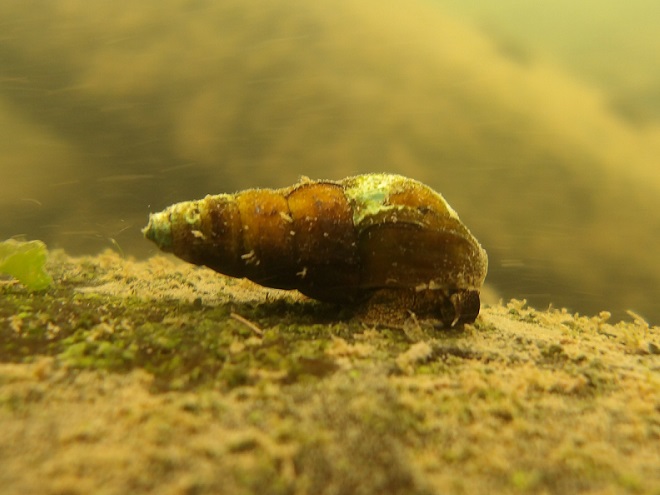
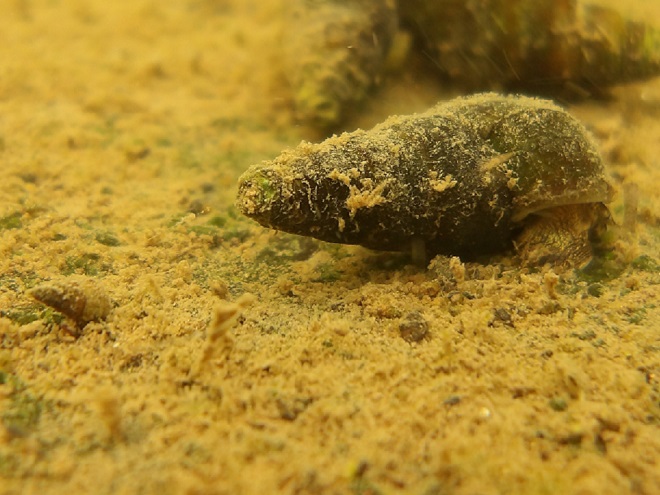
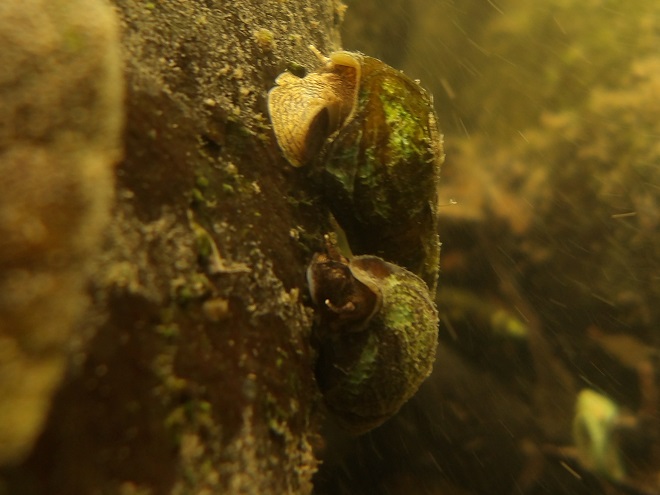
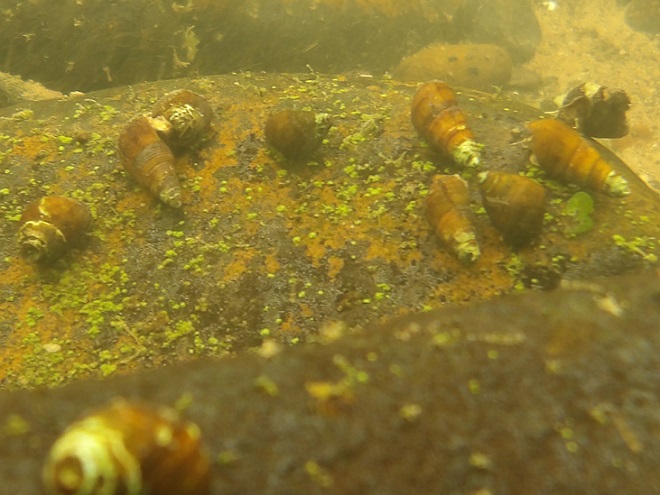
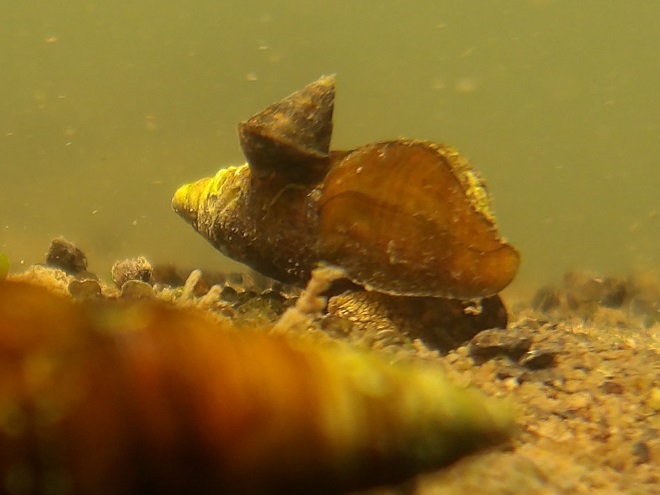
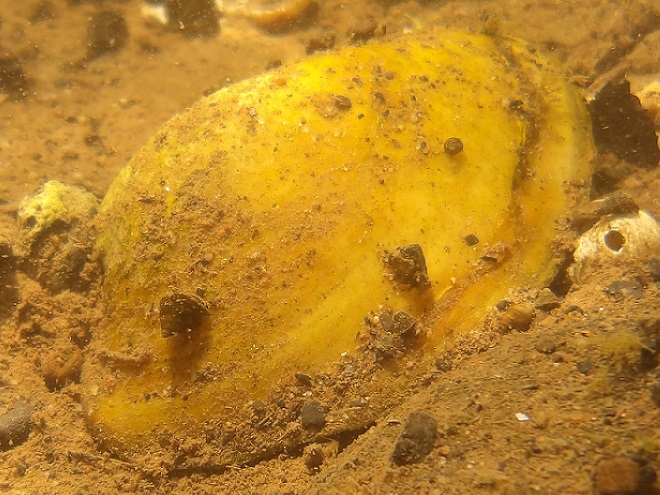
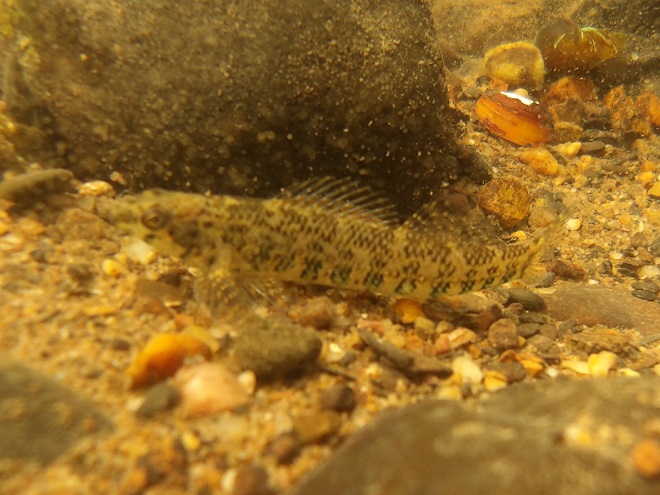
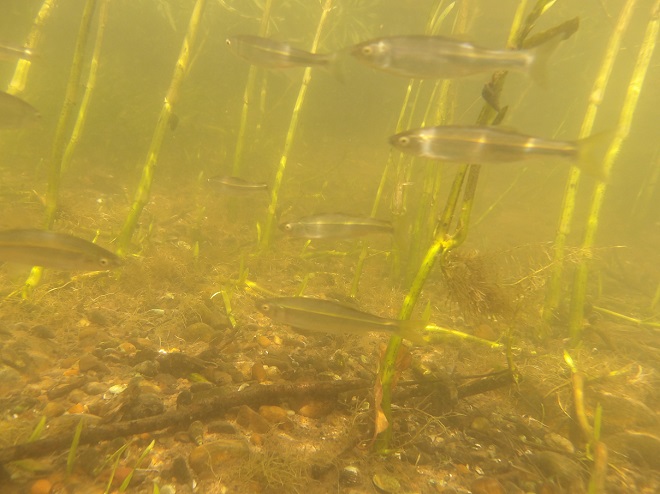
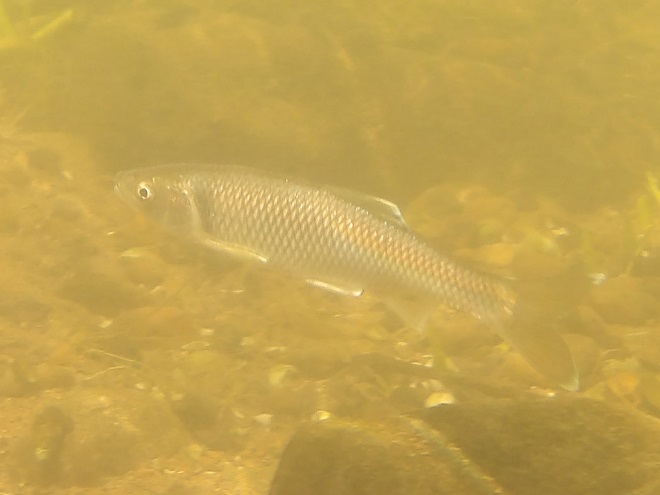
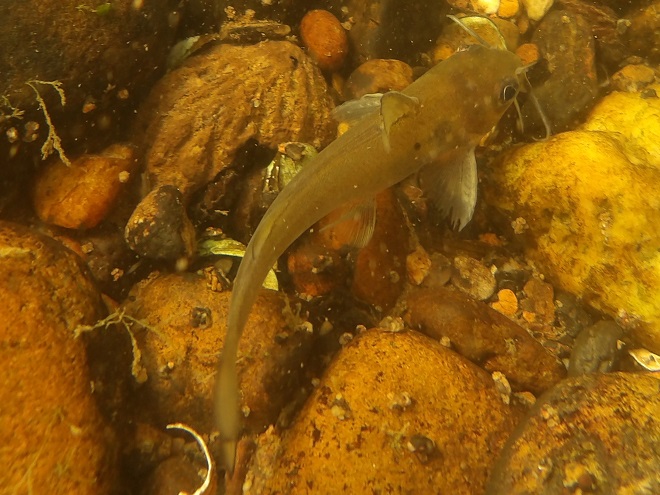


















We’re finding that a sonar “pinger” isn’t very useful while running in shallow water. Instead, we should consider bringing along a set of Pings—for the more than a dozen golf balls seen on the river bottom. It appears they’ve been here for a while, having rolled in from the links upstream during the floods. Interestingly, several aquatic species were making use of them.
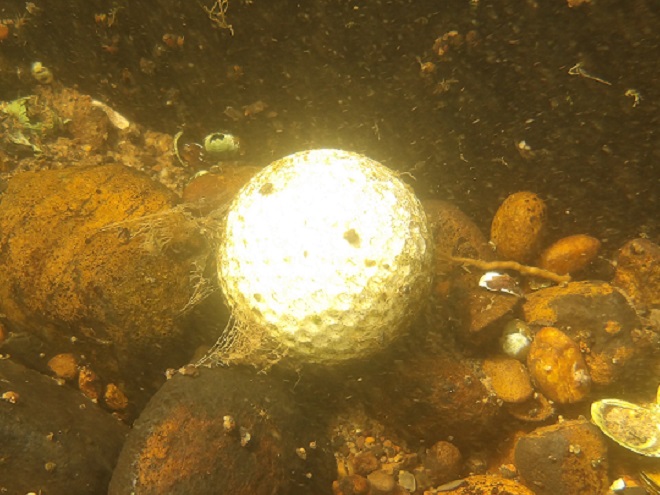
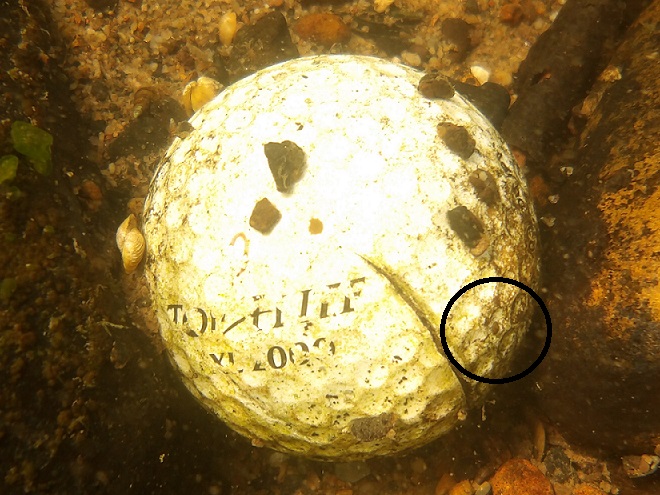
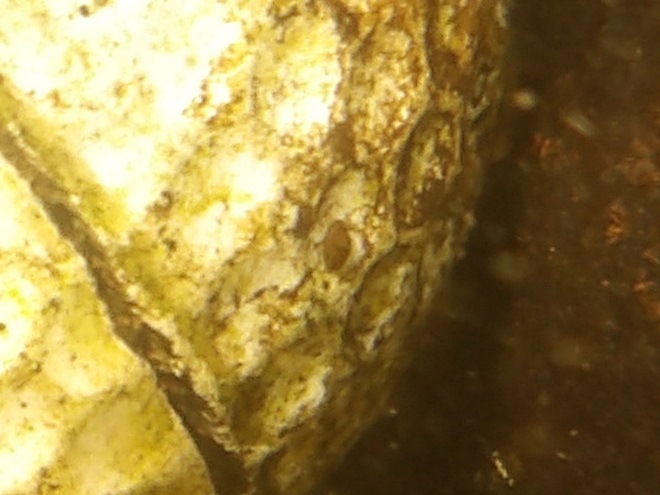





Well, it looks like the skipper’s tired and grumpy, so that’s all for now. Until next time, bon voyage!
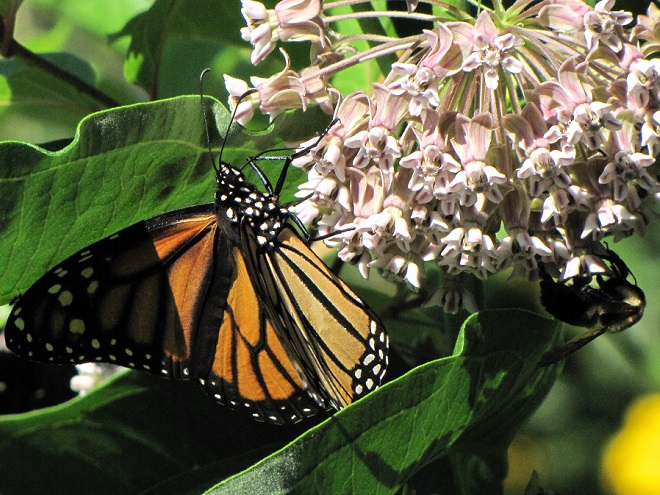
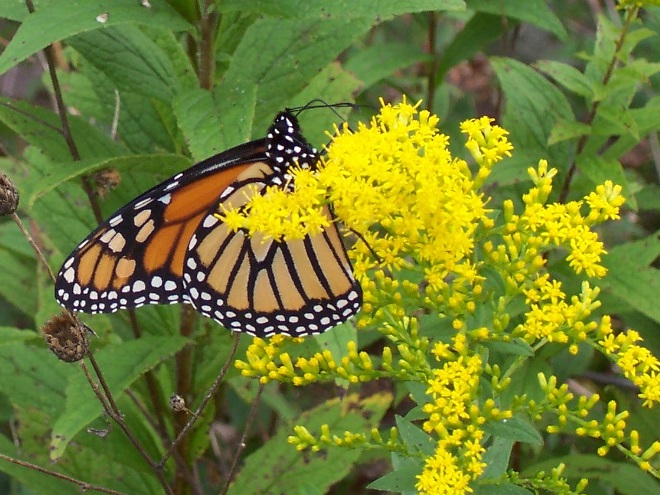
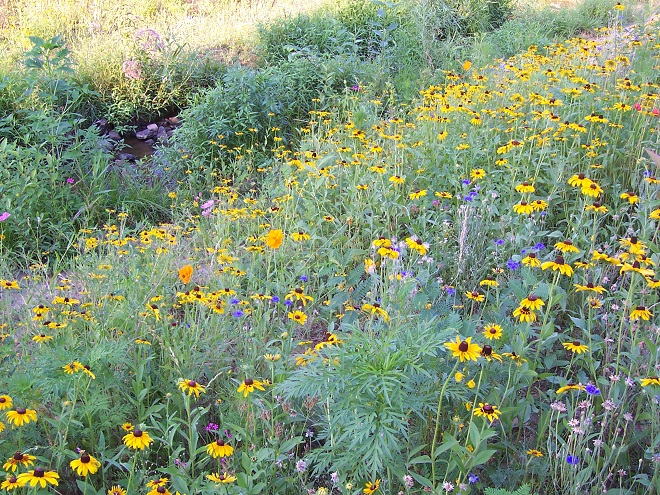
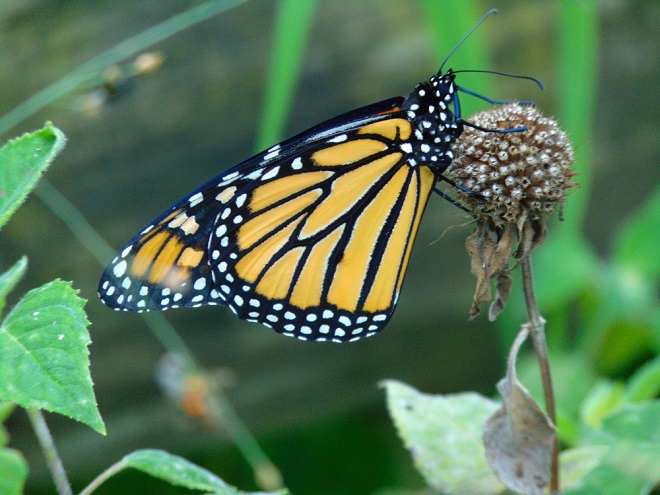
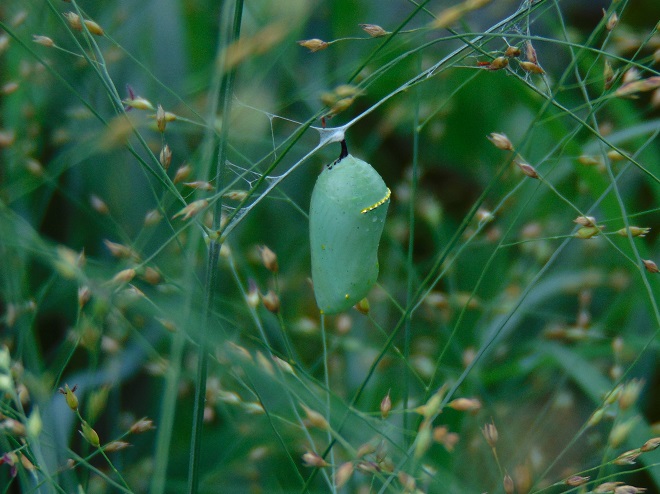
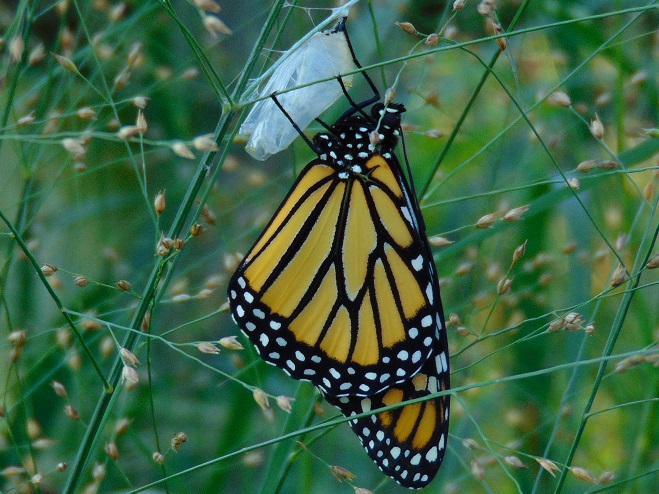
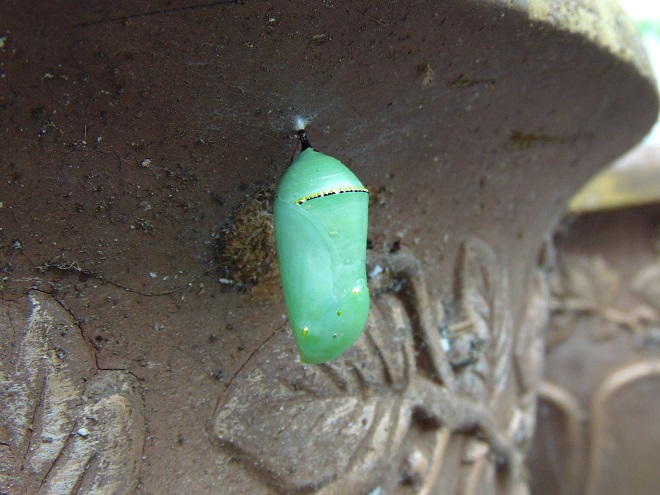
This month, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (I.U.C.N.) added the Migratory Monarch Butterfly (Danaus plexippus plexippus) to its “Red List of Threatened Species”, classifying it as endangered. Perhaps there is no better time than the present to have a look at the virtues of replacing areas of mowed and manicured grass with a wildflower garden or meadow that provides essential breeding and feeding habitat for Monarchs and hundreds of other species of animals.

If you’re not quite sure about finally breaking the ties that bind you to the cult of lawn manicuring, then compare the attributes of a parcel maintained as mowed grass with those of a space planted as a wildflower garden or meadow. In our example we’ve mixed native warm season grasses with the wildflowers and thrown in a couple of Eastern Red Cedars to create a more authentic early successional habitat.

Still not ready to take the leap. Think about this: once established, the wildflower planting can be maintained without the use of herbicides or insecticides. There’ll be no pesticide residues leaching into the soil or running off during downpours. Yes friends, it doesn’t matter whether you’re using a private well or a community system, a wildflower meadow is an asset to your water supply. Not only is it free of man-made chemicals, but it also provides stormwater retention to recharge the aquifer by holding precipitation on site and guiding it into the ground. Mowed grass on the other hand, particularly when situated on steep slopes or when the ground is frozen or dry, does little to stop or slow the sheet runoff that floods and pollutes streams during heavy rains.
What if I told you that for less than fifty bucks, you could start a wildflower garden covering 1,000 square feet of space? That’s a nice plot 25′ x 40′ or a strip 10′ wide and 100′ long along a driveway, field margin, roadside, property line, swale, or stream. All you need to do is cast seed evenly across bare soil in a sunny location and you’ll soon have a spectacular wildflower garden. Here at the susquehannawildllife.net headquarters we don’t have that much space, so we just cast the seed along the margins of the driveway and around established trees and shrubs. Look what we get for pennies a plant…

Here’s a closer look…
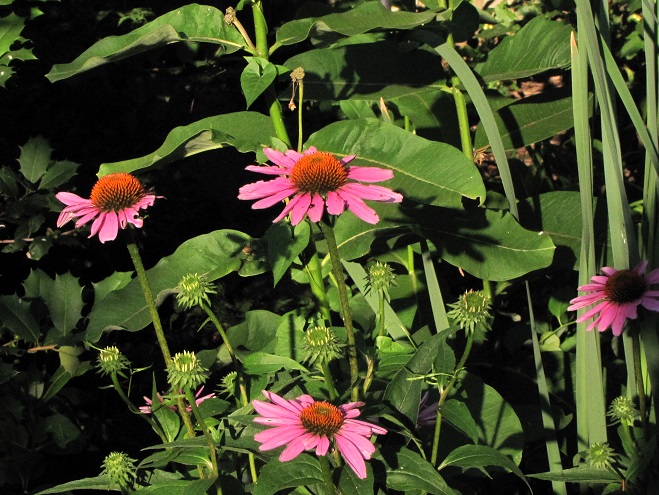
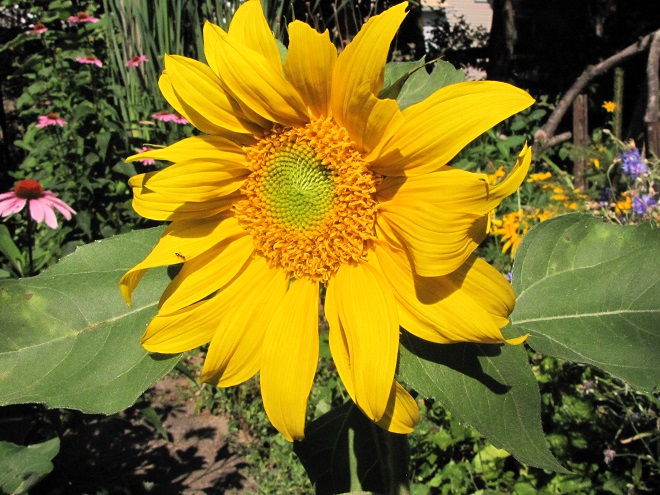
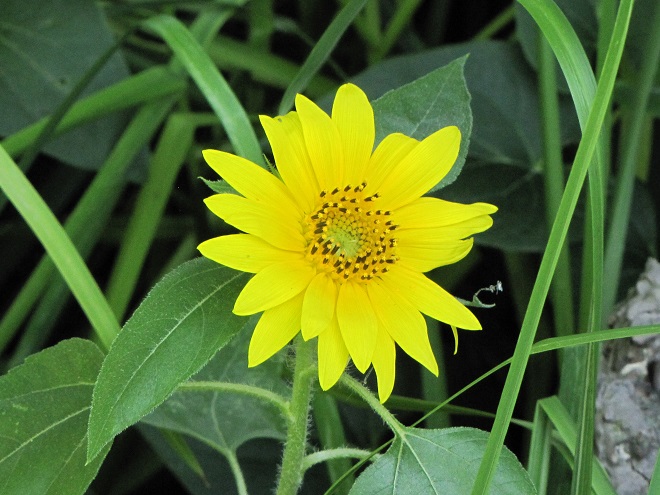






All this and best of all, we never need to mow.
Around the garden, we’ve used a northeast wildflower mix from American Meadows. It’s a blend of annuals and perennials that’s easy to grow. On their website, you’ll find seeds for individual species as well as mixes and instructions for planting and maintaining your wildflower garden. They even have a mix specifically formulated for hummingbirds and butterflies.
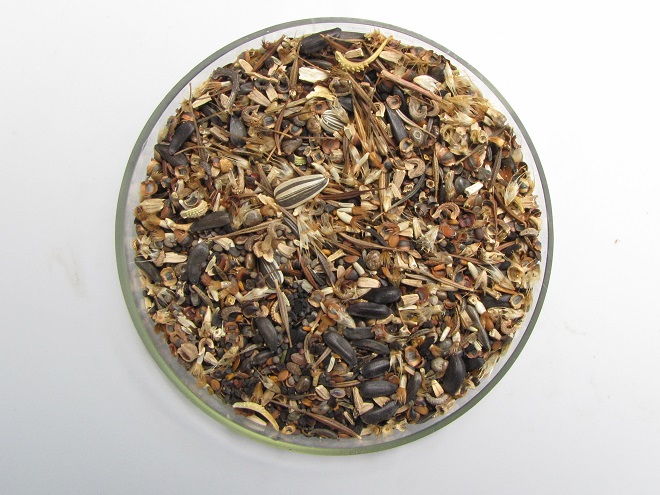


Nothing does more to promote the spread and abundance of non-native plants, including invasive species, than repetitive mowing. One of the big advantages of planting a wildflower garden or meadow is the opportunity to promote the growth of a community of diverse native plants on your property. A single mowing is done only during the dormant season to reseed annuals and to maintain the meadow in an early successional stage—preventing reversion to forest.
For wildflower mixes containing native species, including ecotypes from locations in and near the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed, nobody beats Ernst Conservation Seeds of Meadville, Pennsylvania. Their selection of grass and wildflower seed mixes could keep you planting new projects for a lifetime. They craft blends for specific regions, states, physiographic provinces, habitats, soils, and uses. Check out these examples of some of the scores of mixes offered at Ernst Conservation Seeds…
We’ve used their “Showy Northeast Native Wildflower and Grass Mix” on streambank renewal projects with great success. For Monarchs, we really recommend the “Butterfly and Hummingbird Garden Mix”. It includes many of the species pictured above plus “Fort Indiantown Gap” Little Bluestem, a warm-season grass native to Lebanon County, Pennsylvania, and milkweeds (Asclepias), which are not included in their northeast native wildflower blends. More than a dozen of the flowers and grasses currently included in this mix are derived from Pennsylvania ecotypes, so you can expect them to thrive in the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed.
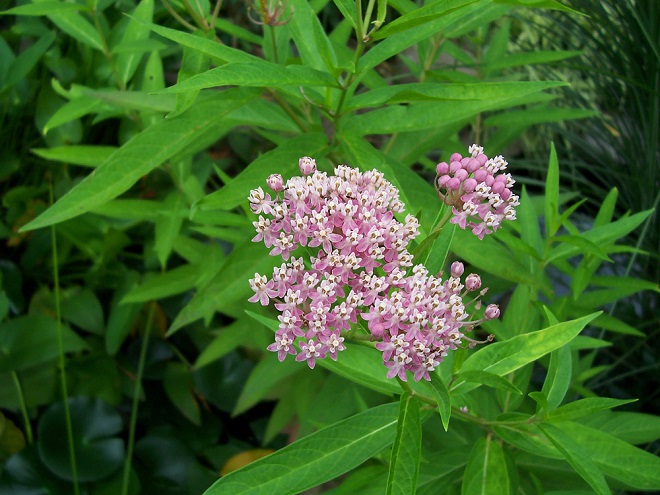
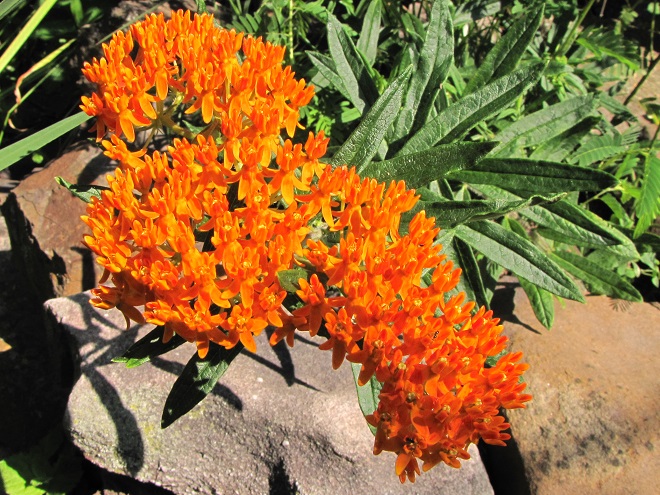




In addition to the milkweeds, you’ll find these attractive plants included in Ernst Conservation Seed’s “Butterfly and Hummingbird Garden Mix”, as well as in some of their other blends.
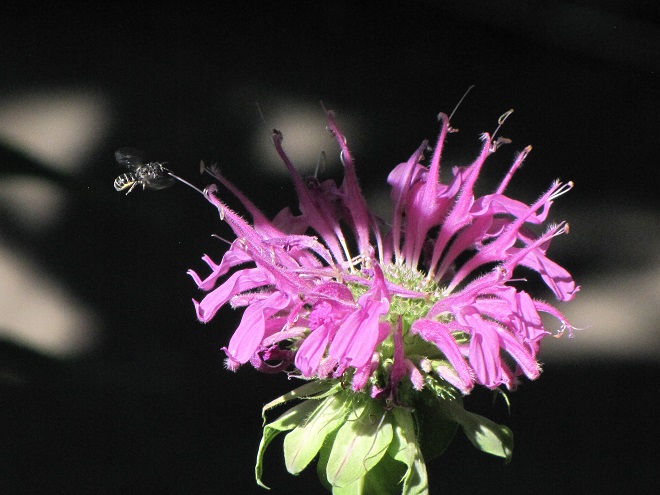
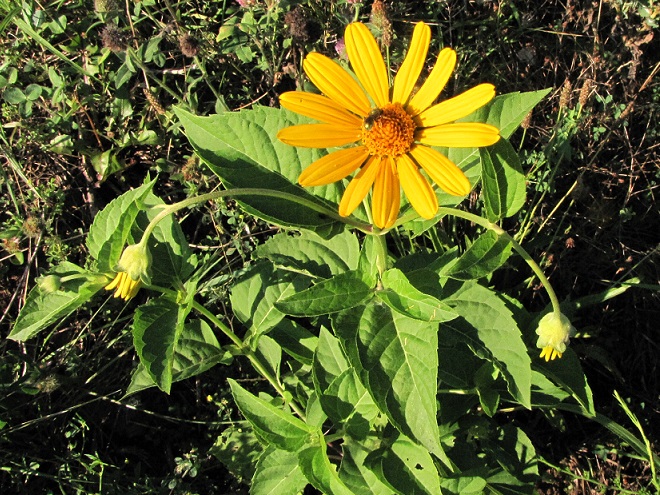
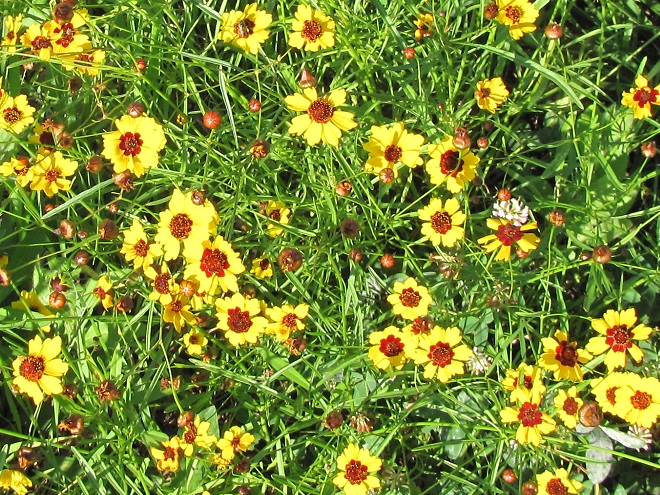
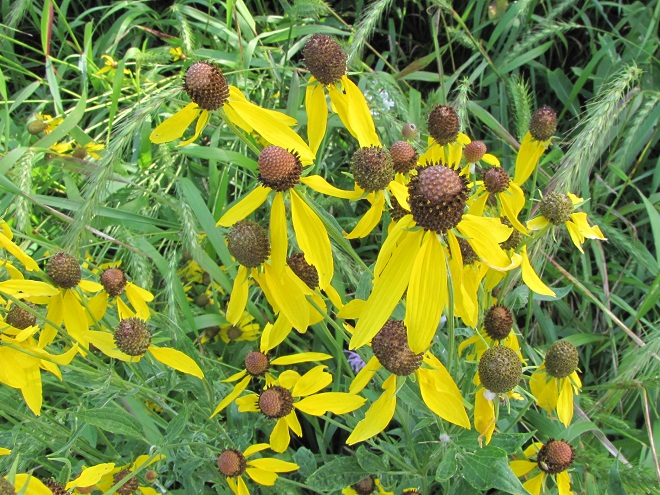







Why not give the Monarchs and other wildlife living around you a little help? Plant a wildflower garden or meadow. It’s so easy, a child can do it.




Rising prices, an exhausted workforce, political polarization, and pandemic fatigue—times are tough. Product shortages have the consumer culture in a near panic. Some say the future just isn’t what it used to be.
Well, Uncle Tyler Dyer reminds us that things could be worse. He shares with us this observation, “Man, as long as people are spending money poisoning the weeds on their lawns instead of eating them, things aren’t that bad.”
Uncle Ty is particularly fond of the Common Dandelion (Taraxacum officinale), “Check it out. Roasted dandelion roots can make a coffee substitute, the blossoms a wine, and the leaves used to create my favorites, nutrient-dense salads or green vegetable dishes.”
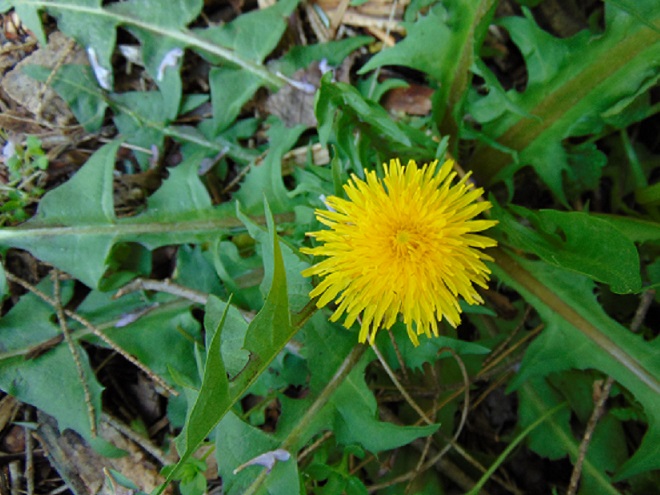


So have a homegrown salad and remember, maybe things aren’t that bad after all.
Meet the Double-crested Cormorant, a strangely handsome bird with a special talent for catching fish. You see, cormorants are superb swimmers when under water—using their webbed feet to propel and maneuver themselves with exceptional speed in pursuit of prey.
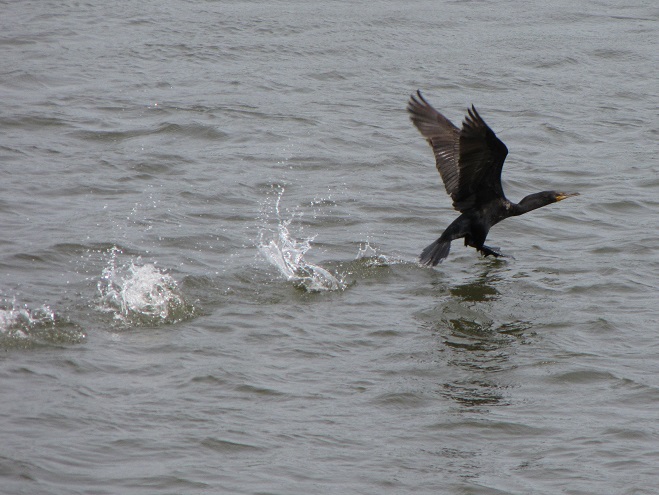

Double-crested Cormorants, hundreds of them, are presently gathered along with several other species of piscivorous (fish-eating) birds on the lower Susquehanna River below Conowingo Dam near Rising Sun, Maryland. Fish are coming up the river and these birds are taking advantage of their concentrations on the downstream side of the impoundment to provide food to fuel their migration or, in some cases, to feed their young.





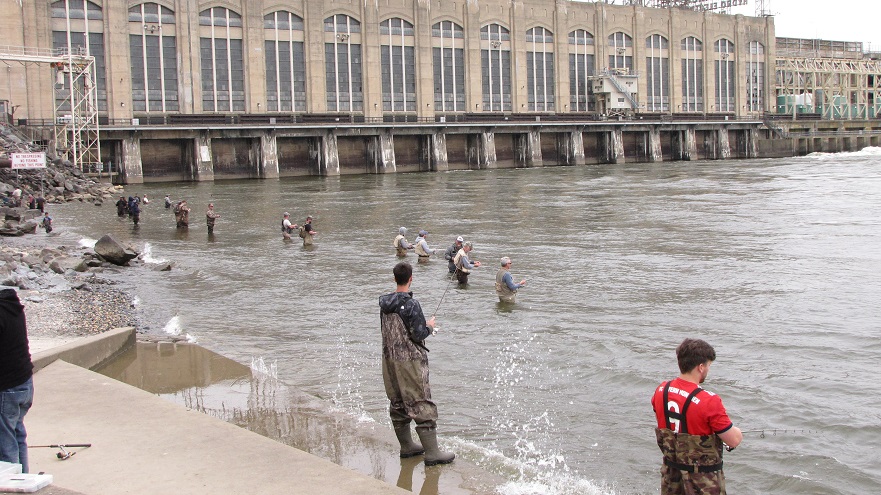
In addition to the birds, the movements of fish attract larger fish, and even larger fishermen.


The excitement starts when the sirens start to wail and the red lights begin flashing. Yes friends, it’s showtime.




Within minutes of the renewed flow, birds are catching fish.
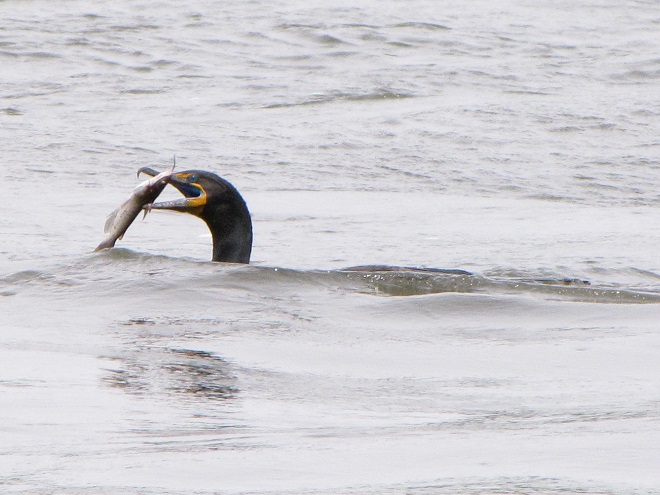
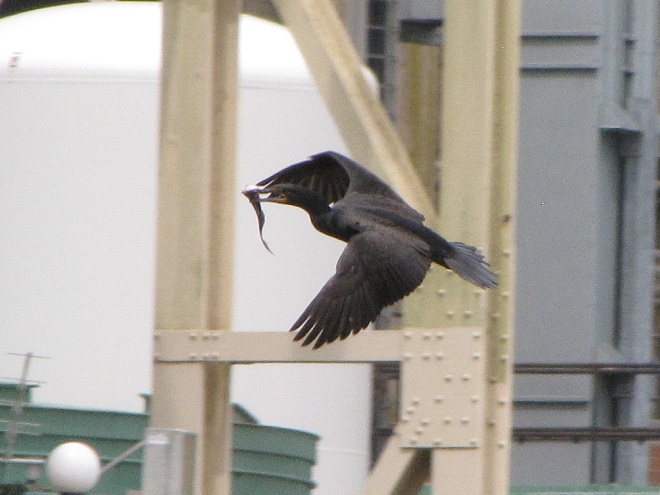
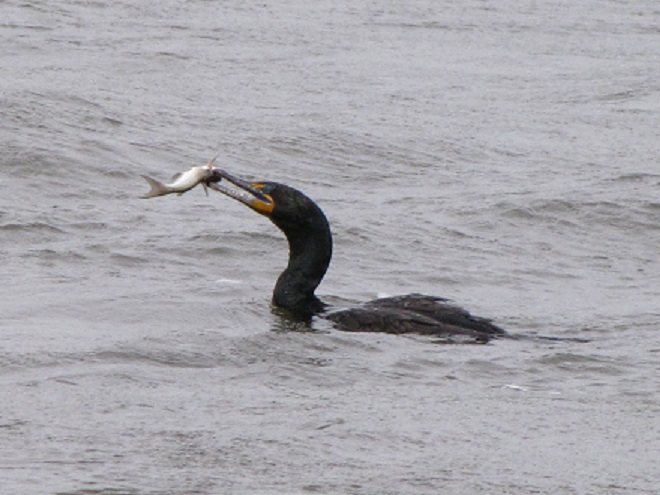





Then the anglers along the wave-washed shoreline began catching fish too.
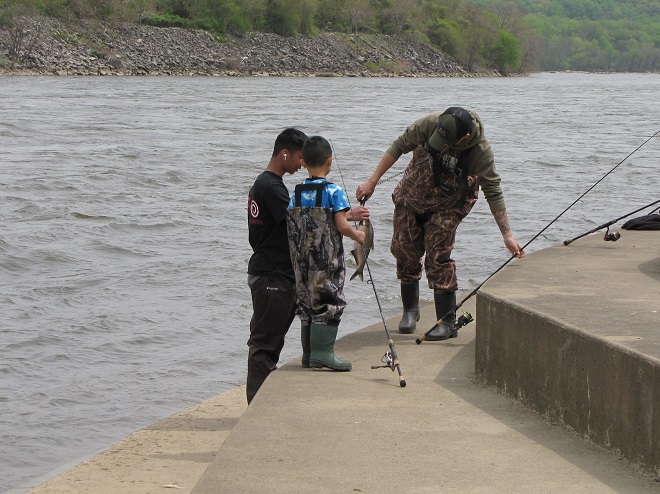
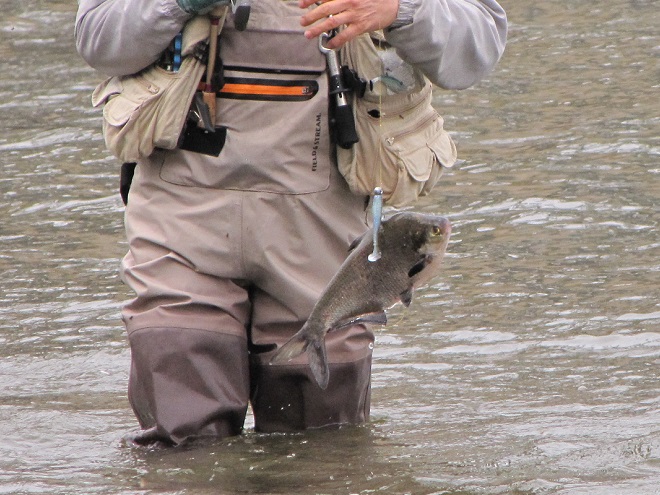
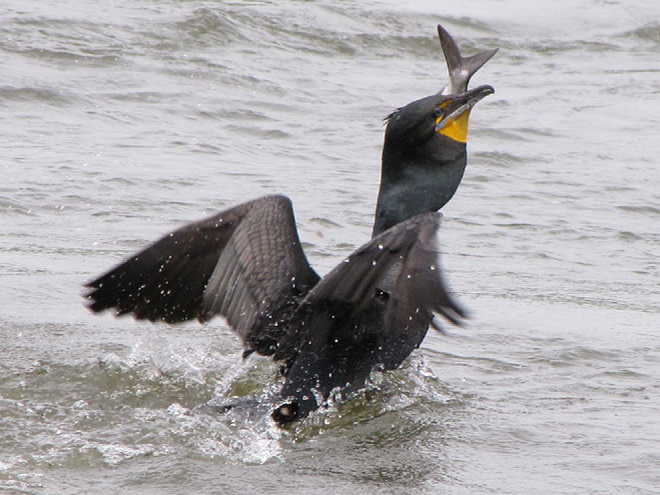
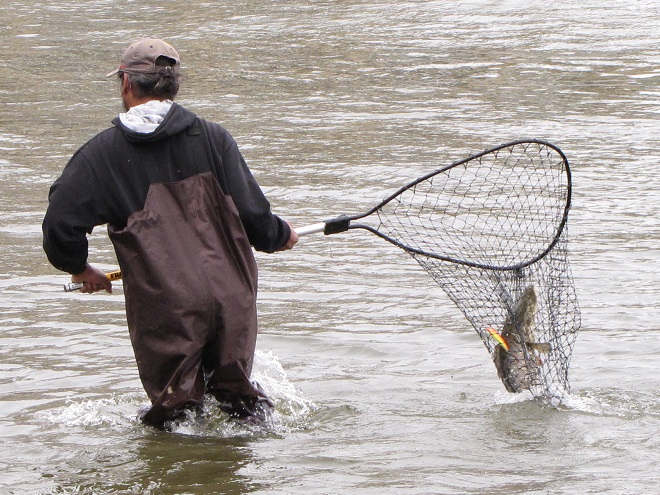
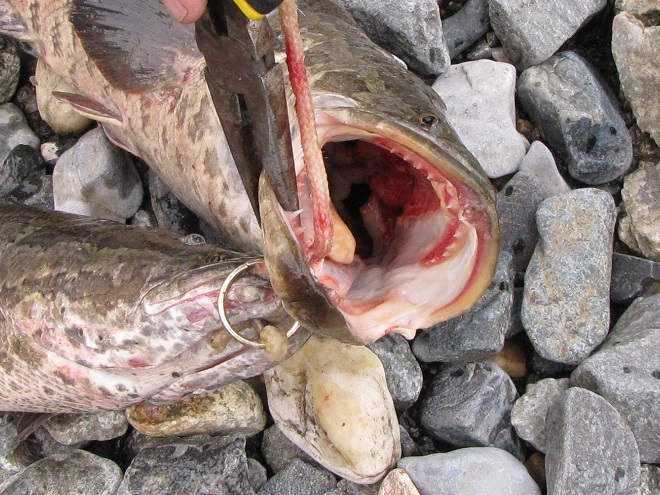
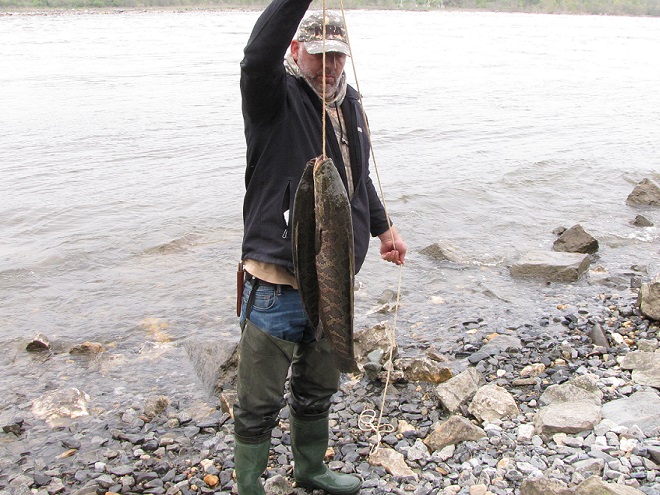
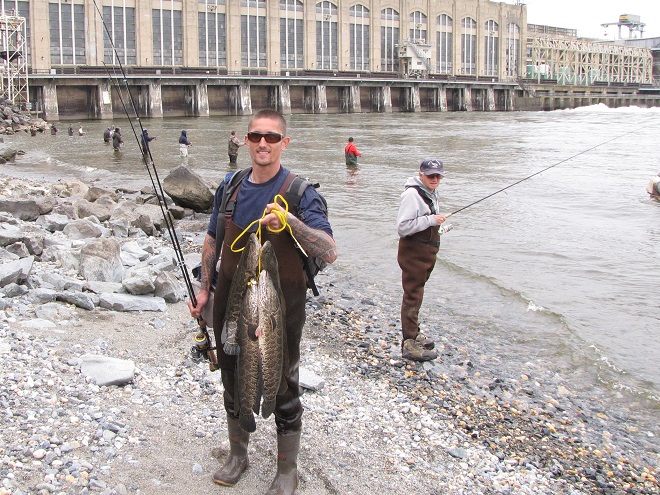
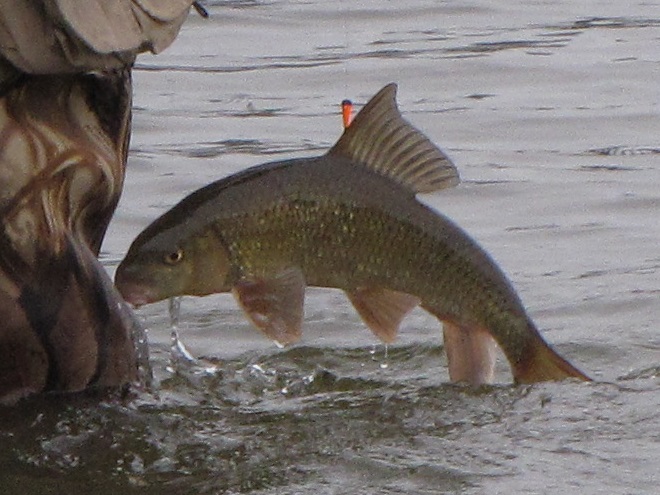
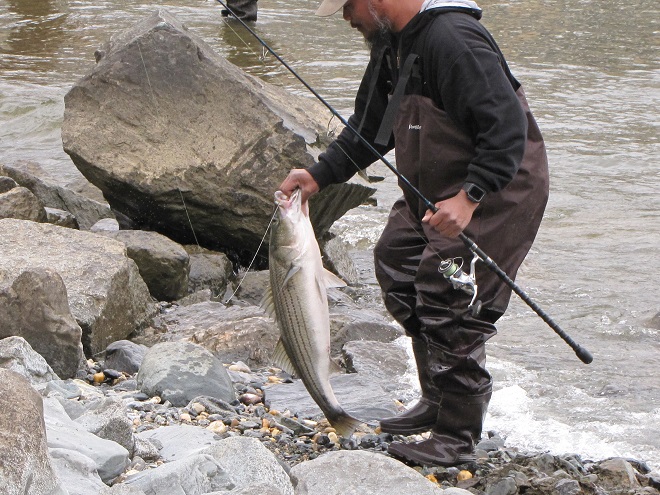
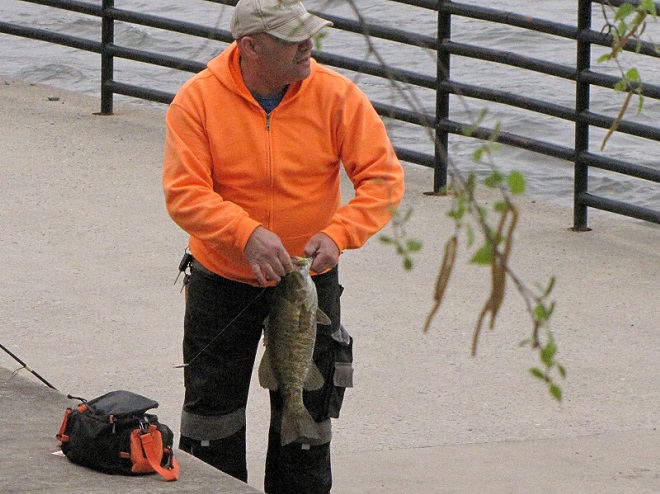
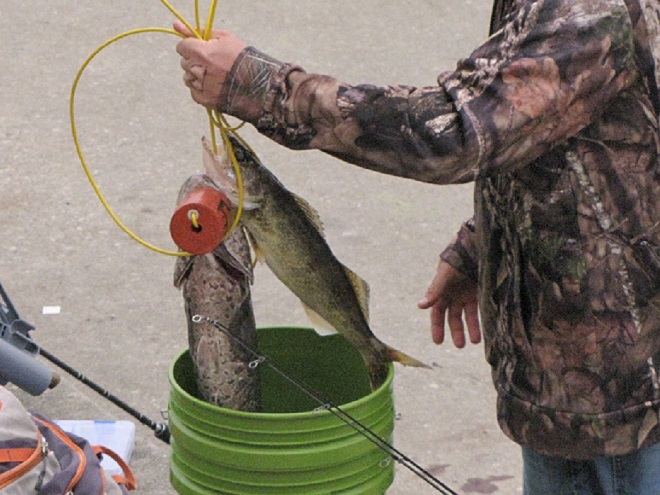
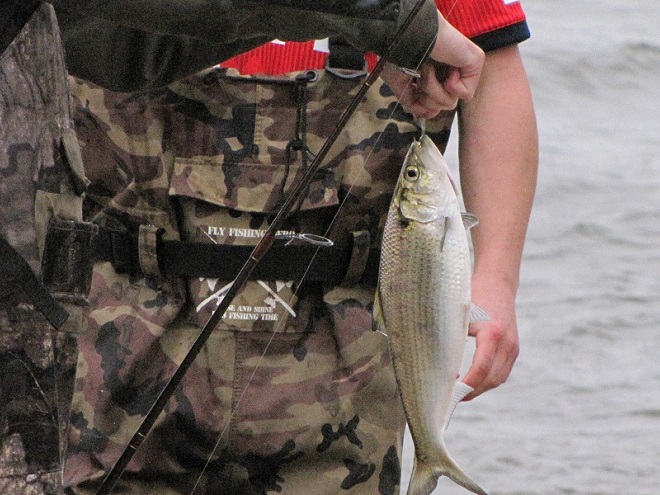
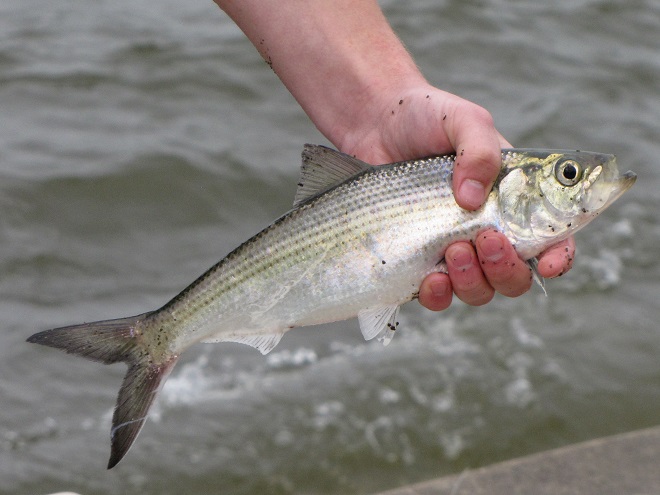
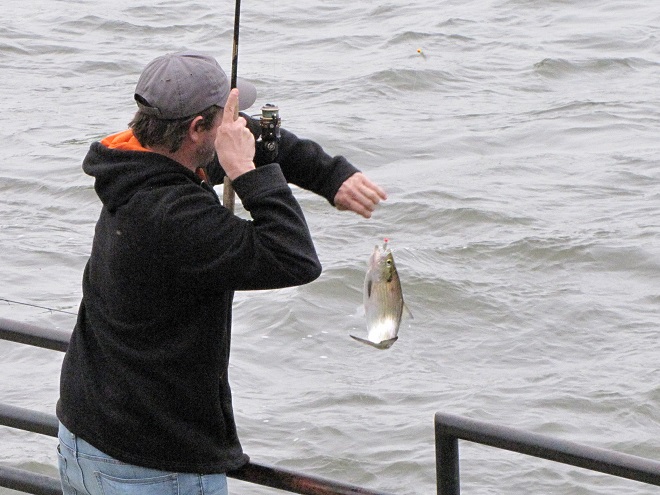
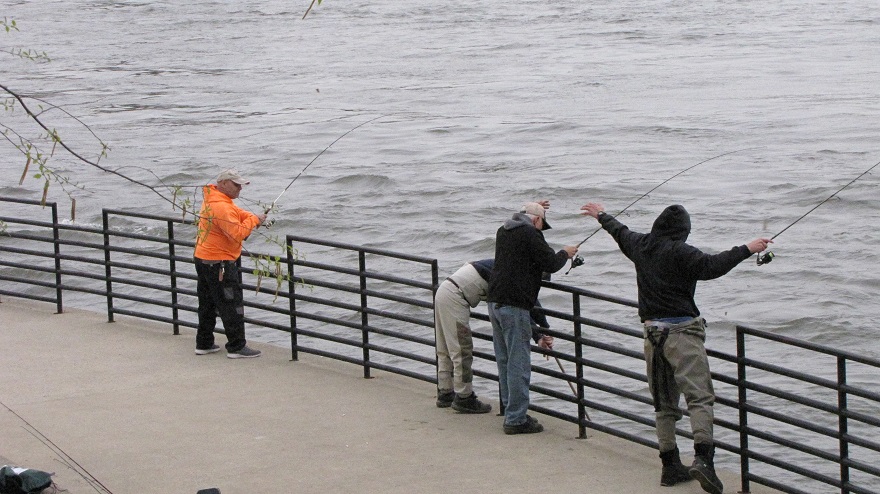
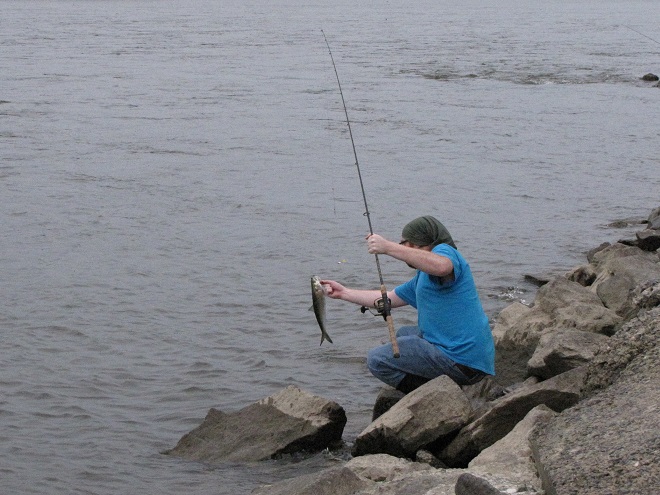






















The arrival of migrating Hickory Shad heralds the start of a movement that will soon include White Perch, anadromous American Shad, and dozens of other fish species that swim upstream during the springtime. Do visit Fisherman’s Park at Conowingo Dam to see this spectacle before it’s gone. The fish and birds have no time to waste, they’ll soon be moving on.
To reach Exelon’s Conowingo Fisherman’s Park from Rising Sun, Maryland, follow U.S. Route 1 south across the Conowingo Dam, then turn left onto Shuresville Road, then make a sharp left onto Shureslanding Road. Drive down the hill to the parking area along the river. The park’s address is 2569 Shureslanding Road, Darlington, Maryland.
A water release schedule for the Conowingo Dam can be obtained by calling Exelon Energy’s Conowingo Generation Hotline at 888-457-4076. The recording is updated daily at 5 P.M. to provide information for the following day.
And remember, the park can get crowded during the weekends, so consider a weekday visit.
Let’s take a quiet stroll through the forest to have a look around. The spring awakening is underway and it’s a marvelous thing to behold. You may think it a bit odd, but during this walk we’re not going to spend all of our time gazing up into the trees. Instead, we’re going to investigate the happenings at ground level—life on the forest floor.
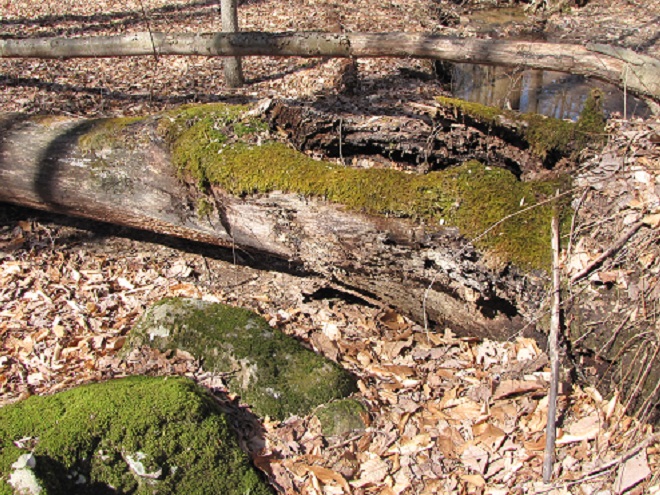
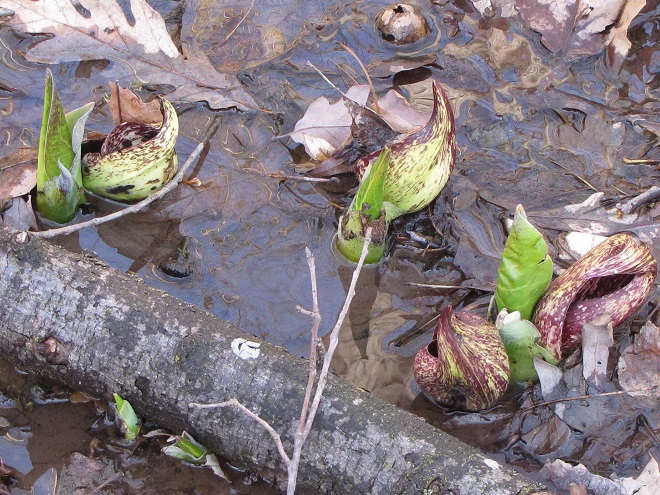
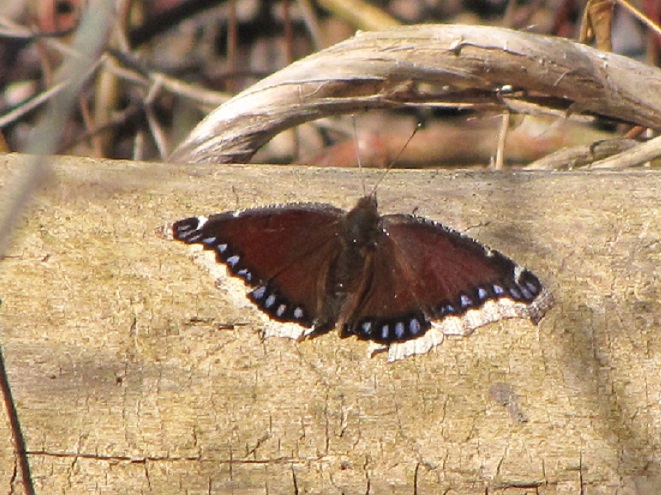
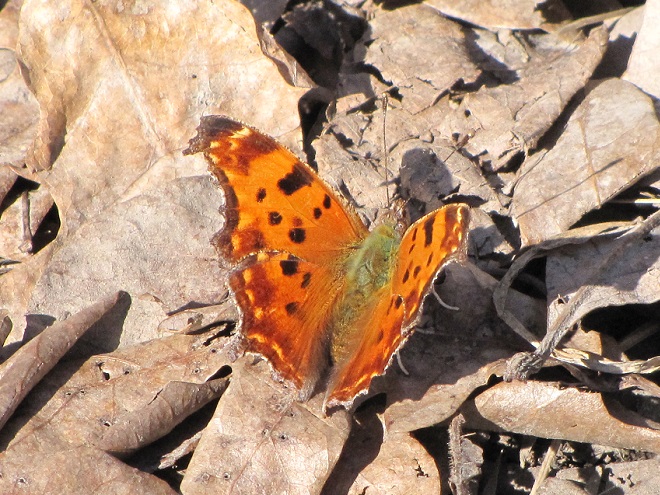
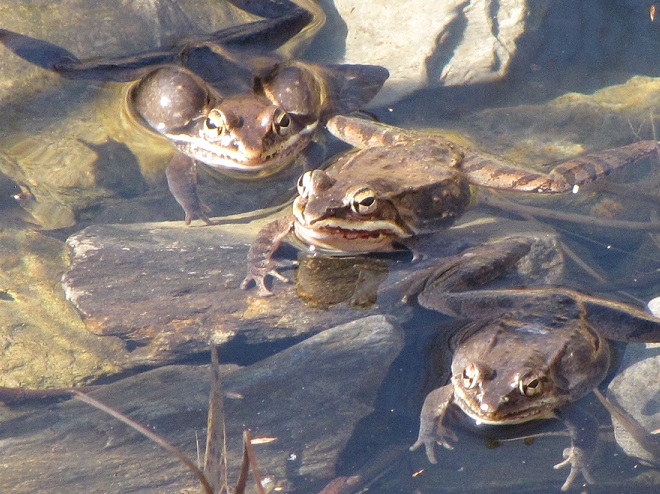
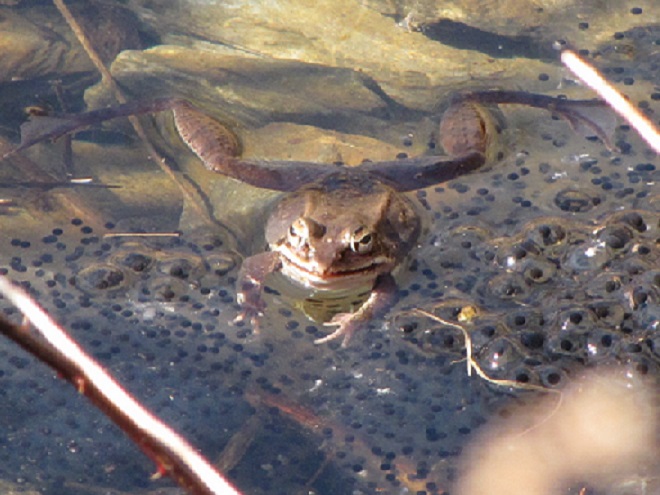
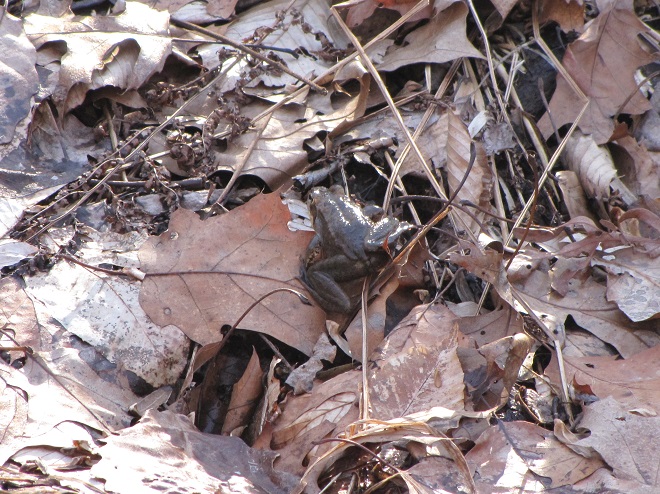
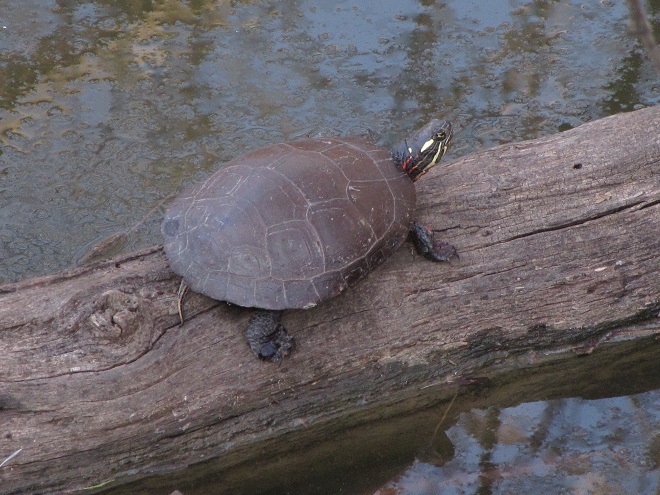












There certainly is more to a forest than the living trees. If you’re hiking through a grove of timber getting snared in a maze of prickly Multiflora Rose (Rosa multiflora) and seeing little else but maybe a wild ungulate or two, then you’re in a has-been forest. Logging, firewood collection, fragmentation, and other man-made disturbances inside and near forests take a collective toll on their composition, eventually turning them to mere woodlots. Go enjoy the forests of the lower Susquehanna valley while you still can. And remember to do it gently; we’re losing quality as well as quantity right now—so tread softly.

Second Mountain Hawk Watch is located on a ridge top along the northern edge of the Fort Indiantown Gap Military Reservation and the southern edge of State Game Lands 211 in Lebanon County, Pennsylvania. The valley on the north side of the ridge, also known as St. Anthony’s Wilderness, is drained to the Susquehanna by Stony Creek. The valley to the south is drained toward the river by Indiantown Run, a tributary of Swatara Creek.
The hawk watch is able to operate at this prime location for observing the autumn migration of birds, butterflies, dragonflies, and bats through the courtesy of the Pennsylvania Game Commission and the Garrison Commander at Fort Indiantown Gap. The Second Mountain Hawk Watch Association is a non-profit organization that staffs the count site daily throughout the season and reports data to the North American Hawk Watch Association (posted daily at hawkcount.org).
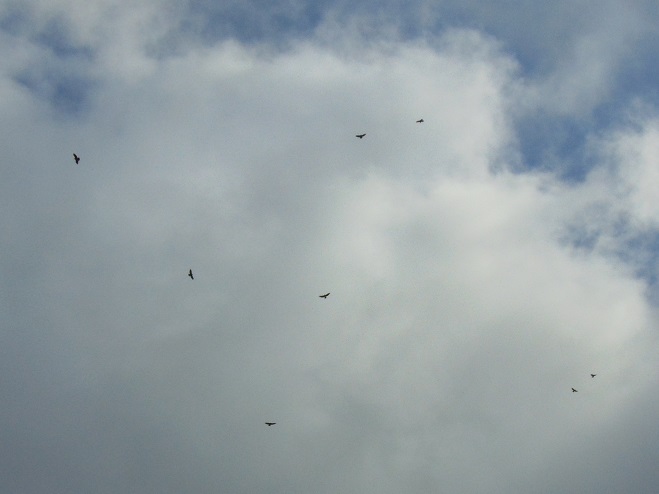
Today, Second Mountain Hawk Watch was populated by observers who enjoyed today’s break in the rainy weather with a visit to the lookout to see what birds might be on the move. All were anxiously awaiting a big flight of Broad-winged Hawks, a forest-dwelling Neotropical species that often travels back to its wintering grounds in groups exceeding one hundred birds. Each autumn, many inland hawk watches in the northeast experience at least one day in mid-September with a Broad-winged Hawk count exceeding 1,000 birds. They are an early-season migrant and today’s southeast winds ahead of the remnants of Hurricane Florence (currently in the Carolinas) could push southwest-heading “Broad-wings” out of the Piedmont Province and into the Ridge and Valley Province for a pass by the Second Mountain lookout.
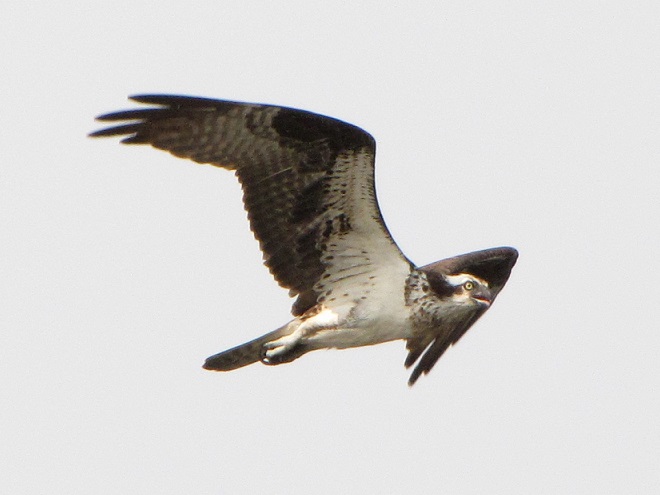
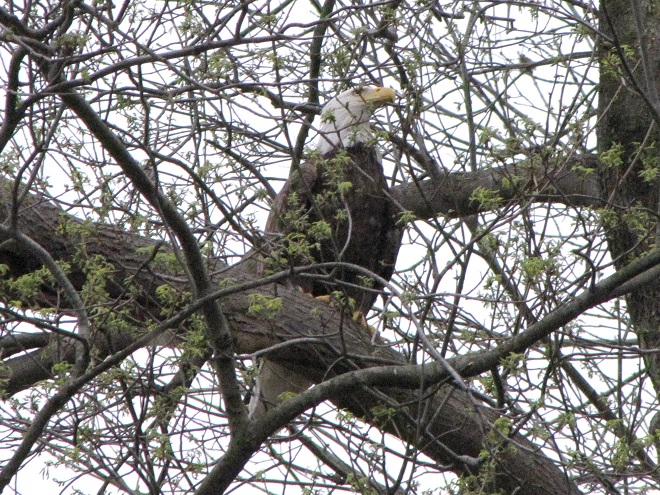
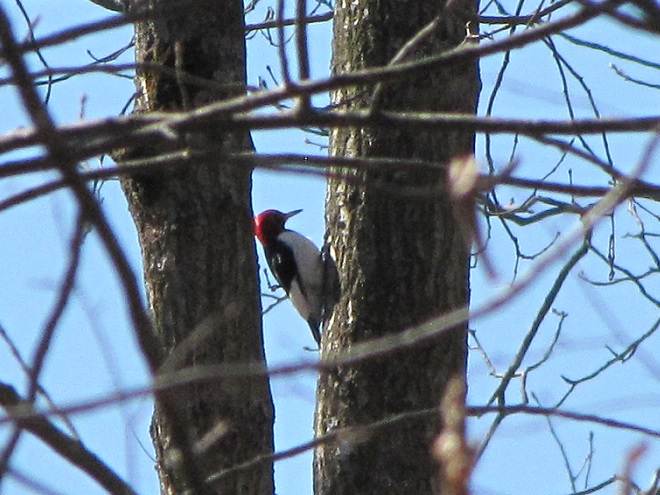
The flight turned out to be steady through the day with over three hundred Broad-winged Hawks sighted. The largest group consisted of several dozen birds. We would hope there are probably many more yet to come after the Florence rains pass through the northeast and out to sea by mid-week. Also seen today were Bald Eagles, Ospreys, American Kestrels, and a migrating Red-headed Woodpecker.

Migrating insects included Monarch butterflies, and the three commonest species of migratory dragonflies: Wandering Glider, Black Saddlebags, and Common Green Darner. The Common Green Darners swarmed the lookout by the dozens late in the afternoon and attracted a couple of American Kestrels, which had apparently set down from a day of migration. American Kestrels and Broad-winged Hawks feed upon dragonflies and often migrate in tandem with them for at least a portion of their journey.
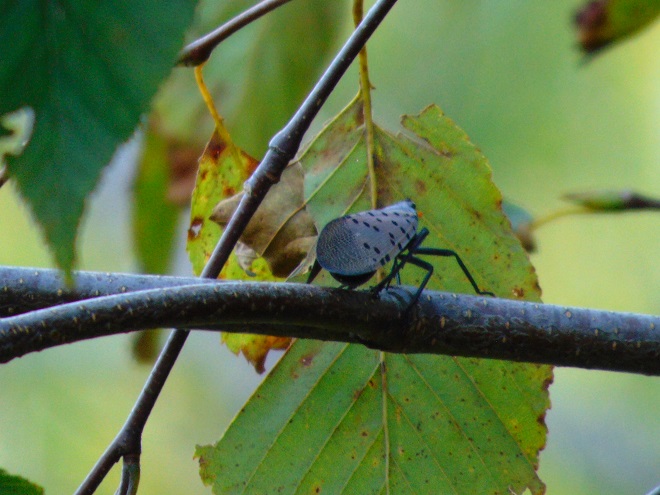
Still later, as the last of the Broad-winged Hawks descended from great heights and began passing by just above the trees looking for a place to settle down, a most unwelcome visitor arrived at the lookout. It glided in from the St. Anthony’s Wilderness side of the ridge on showy crimson-red wings, then became nearly indiscernible from gray tree bark when it landed on a limb. It was the dreaded and potentially invasive Spotted Lanternfly (Lycorma delicatula). This large leafhopper is native to Asia and was first discovered in North America in the Oley Valley of eastern Berks County, Pennsylvania in 2014. The larval stage is exceptionally damaging to cultivated grape and orchard crops. It poses a threat to forest trees as well. Despite efforts to contain the species through quarantine and other methods, it’s obviously spreading quickly. Here on the Second Mountain lookout, we know that wind has a huge influence on the movement of birds and insects. The east and southeast winds we’ve experienced for nearly a week may be carrying Spotted Lanternflies well out of their most recent range and into the forests of the Ridge and Valley Province. We do know for certain that the Spotted Lanternfly has found its way into the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed.

It’s sprayed with herbicides. It’s mowed and mangled. It’s ground to shreds with noisy weed-trimmers. It’s scorned and maligned. It’s been targeted for elimination by some governments because it’s undesirable and “noxious”. And it has that four letter word in its name which dooms the fate of any plant that possesses it. It’s the Common Milkweed, and it’s the center of activity in our garden at this time of year. Yep, we said milk-WEED.
Now, you need to understand that our garden is small—less than 2,500 square feet. There is no lawn, and there will be no lawn. We’ll have nothing to do with the lawn nonsense. Those of you who know us, know that the lawn, or anything that looks like lawn, are through.
Anyway, most of the plants in the garden are native species. There are trees, numerous shrubs, some water features with aquatic plants, and filling the sunny margins is a mix of native grassland plants including Common Milkweed. The unusually wet growing season in 2018 has been very kind to these plants. They are still very green and lush. And the animals that rely on them are having a banner year. Have a look…
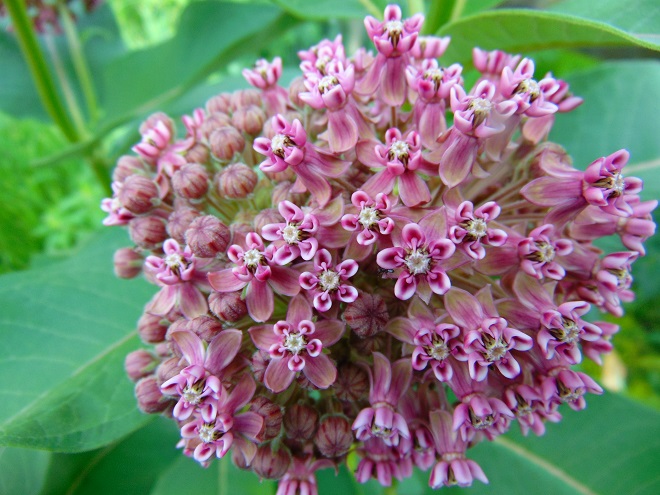
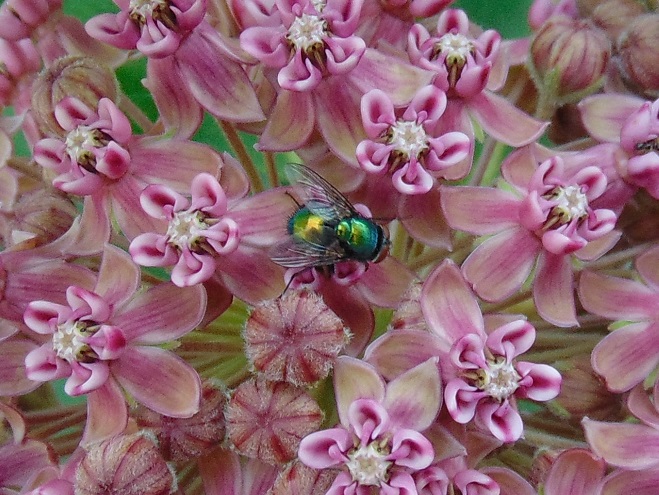





We’ve planted a variety of native grassland species to help support the milkweed structurally and to provide a more complete habitat for Monarch butterflies and other native insects. This year, these plants are exceptionally colorful for late-August due to the abundance of rain. The warm season grasses shown below are the four primary species found in the American tall-grass prairies and elsewhere.
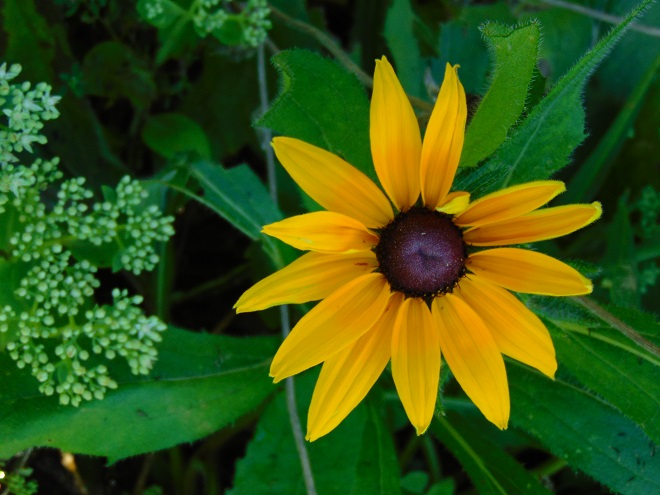






There was Monarch activity in the garden today like we’ve never seen before—and it revolved around milkweed and the companion plants.











SOURCES
Eaton, Eric R., and Kenn Kaufman. 2007. Kaufman Field Guide to Insects of North America. Houghton Mifflin Company. New York.
Temperatures plummeted to well below freezing during the past two nights, but there was little sign of it in Conewago Falls this morning. The fast current in the rapids and swirling waters in flooded Pothole Rocks did not freeze. Ice coated the standing water in potholes only in those rocks lacking a favorable orientation to the sun for collecting solar heat during the day to conduct into the water during the cold nights.
On the shoreline, the cold snap has left its mark. Ice covers the still waters of the wetlands. Frost on exposed vegetation lasted until nearly noontime in shady areas. Insect activity is now grounded and out of sight. The leaves of the trees tumble and fall to cover the evidence of a lively summer.
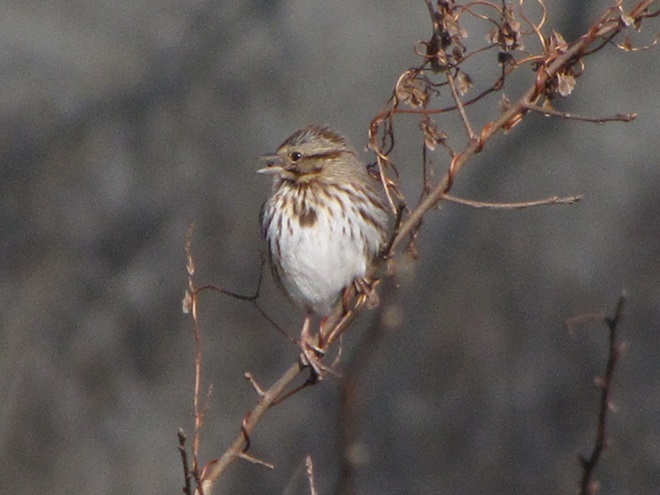
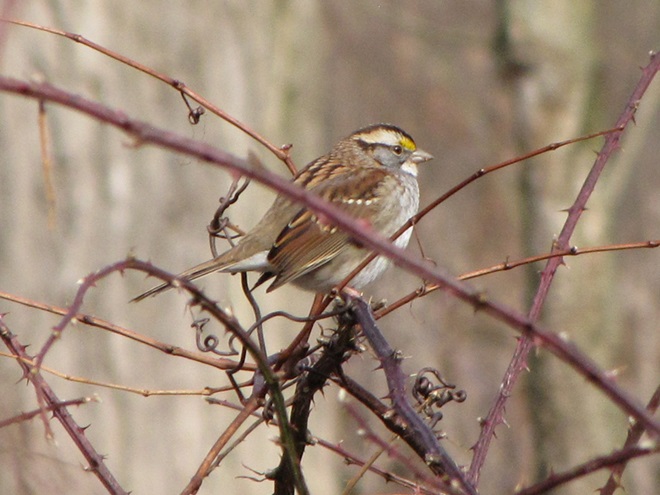
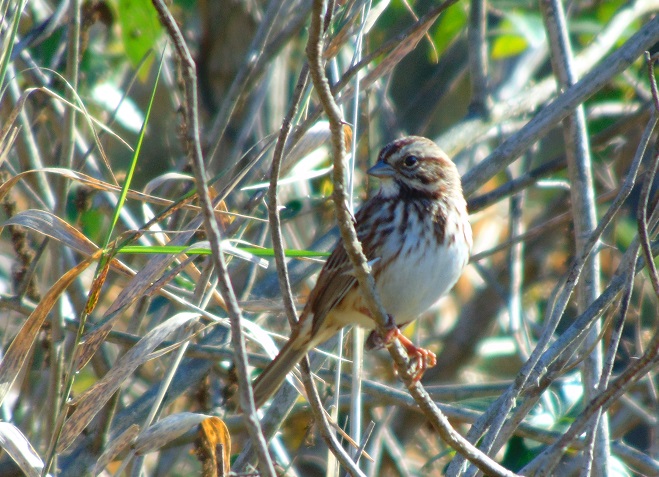
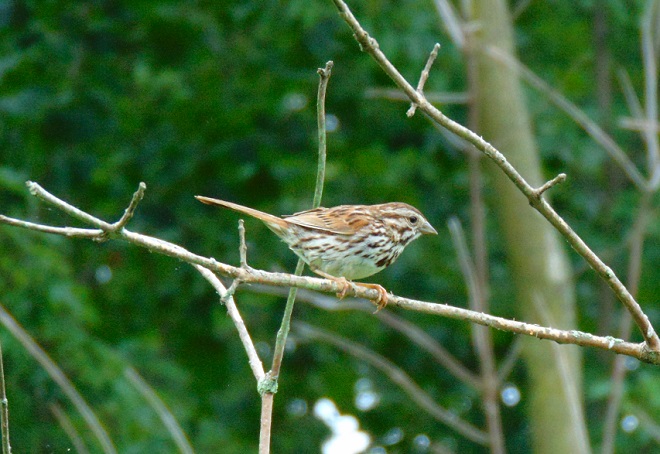
The nocturnal bird flight is narrowing down to just a few species. White-throated Sparrows, a Swamp Sparrow (Melospiza georgiana), and Song Sparrows are still on the move. Though their numbers are not included in the migration count, hundreds of the latter are along the shoreline and in edge habitat around the falls right now. Song Sparrows are present year-round, migrate at night, and are not seen far from cover in daylight, so migratory movements are difficult to detect. It is certain that many, if not all of the Song Sparrows here today have migrated and arrived here recently. The breeding population from spring and summer has probably moved further south. And many of the birds here now may remain for the winter. Defining the moment of this dynamic, yet discrete, population change and logging it in a count would certainly require different methods.

Diurnal migration was foiled today by winds from southerly directions and moderating temperatures. The only highlight was an American Robin flight that extended into the morning for a couple of hours after daybreak and totaled over 800 birds. This flight was peppered with an occasional flock of blackbirds. Then too, there were the villains.

They’re dastardly, devious, selfish, opportunistic, and abundant. Today, they were the most numerous diurnal migrant. Their numbers made this one of the biggest migration days of the season, but they are not recorded on the count sheet. It’s no landmark day. They excite no one. For the most part, they are not recognized as migrants because of their nearly complete occupation of North America south of the taiga. If people build on it or alter it, these birds will be there. They’re everywhere people are. If the rotten attributes of man were wrapped up into one bird, an “anthropoavian”, this would be it.
Meet the European Starling (Sturnus vulgaris). Introduced into North America in 1890, the species has spread across the entire continent. It nests in cavities in buildings and in trees. Starlings are aggressive, particularly when nesting, and have had detrimental impacts on the populations of native cavity nesting birds, particularly Red-headed Woodpeckers, Purple Martins (Progne subis), and Eastern Bluebirds. They commonly terrorize these and other native species to evict them from their nest sites. European Starlings are one of the earlier of the scores of introduced plants and animals we have come to call invasive species.
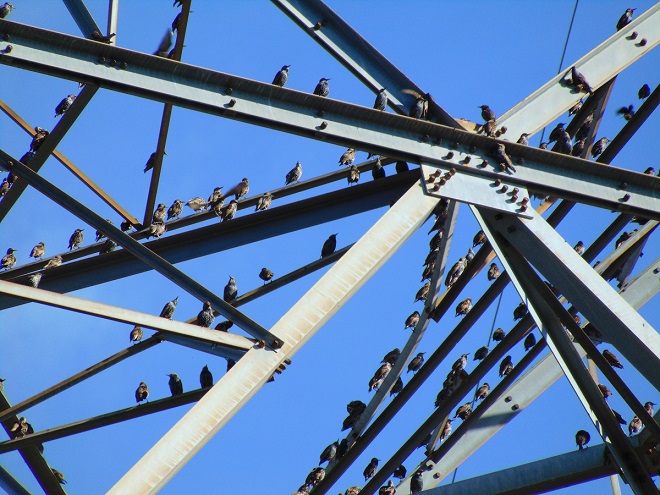

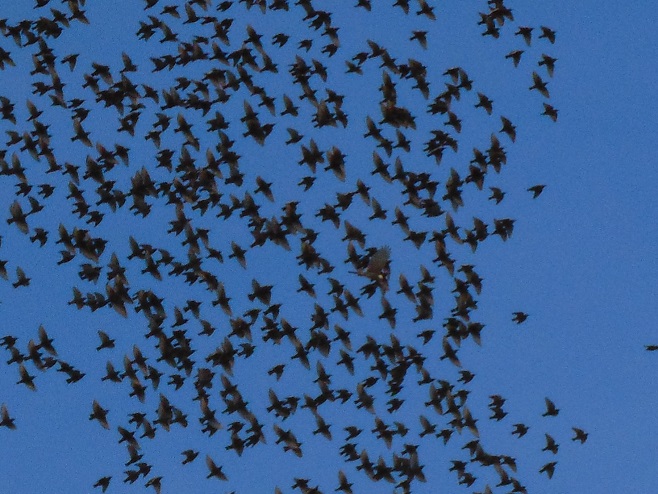
Today, thousands of European Starlings were on the move, working their way down the river shoreline and raiding berries from the vines and trees of the Riparian Woodlands. My estimate is between three and five thousand migrated through during the morning. But don’t worry, thousands more will be around for the winter.


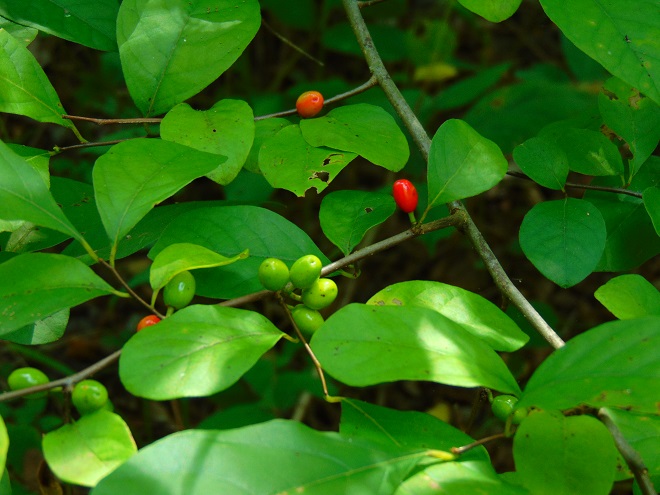
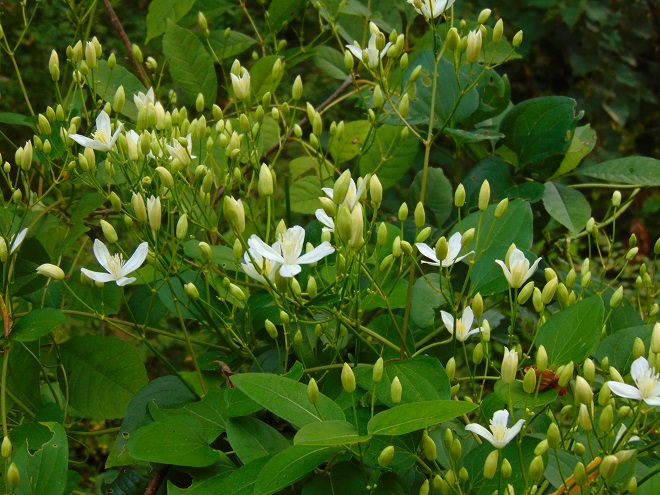
They get a touch of it here, and a sparkle or two there. Maybe, for a couple of hours each day, the glorious life-giving glow of the sun finds an opening in the canopy to warm and nourish their leaves, then the rays of light creep away across the forest floor, and it’s shade for the remainder of the day.
The flowering plants which thrive in the understory of the Riparian Woodlands often escape much notice. They gather only a fraction of the daylight collected by species growing in full exposure to the sun. Yet, by season’s end, many produce showy flowers or nourishing fruits of great import to wildlife. While light may be sparingly rationed through the leaves of the tall trees overhead, moisture is nearly always assured in the damp soils of the riverside forest. For these plants, growth is slow, but continuous. And now, it’s show time.
So let’s take a late-summer stroll through the Riparian Woodlands of Conewago Falls, minus the face full of cobwebs, and have a look at some of the strikingly beautiful plants found living in the shadows.
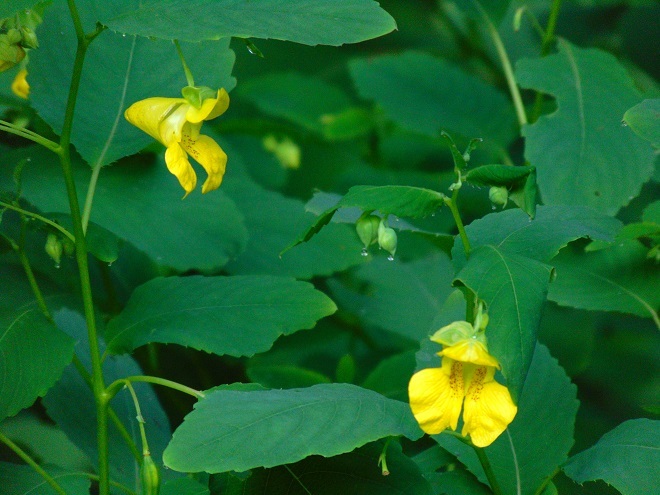
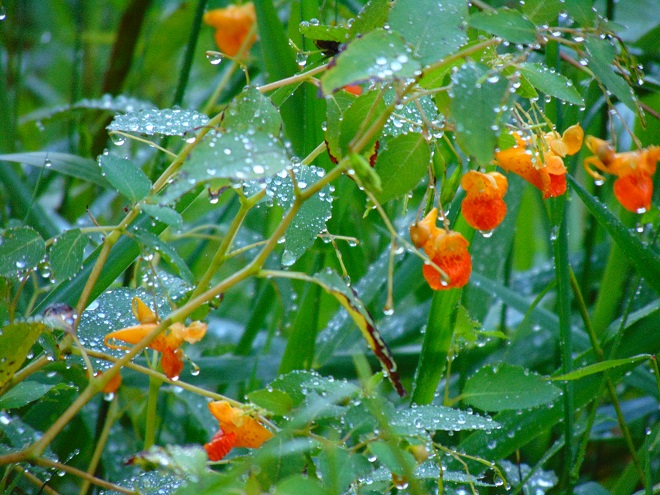
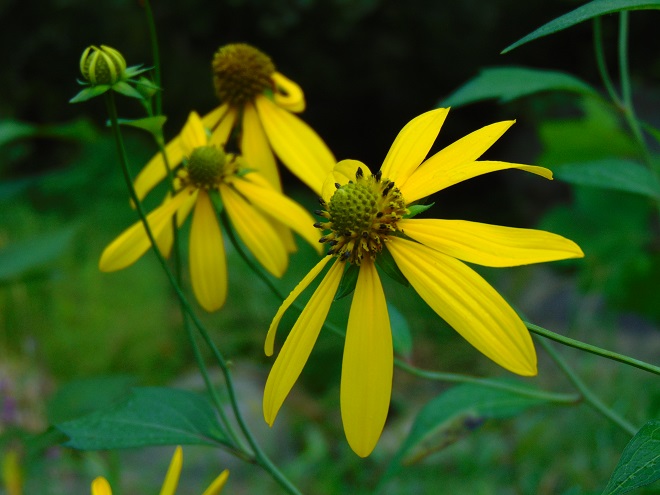
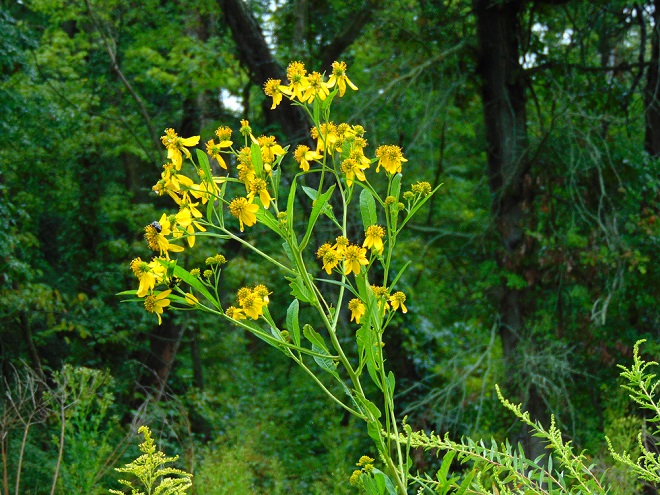
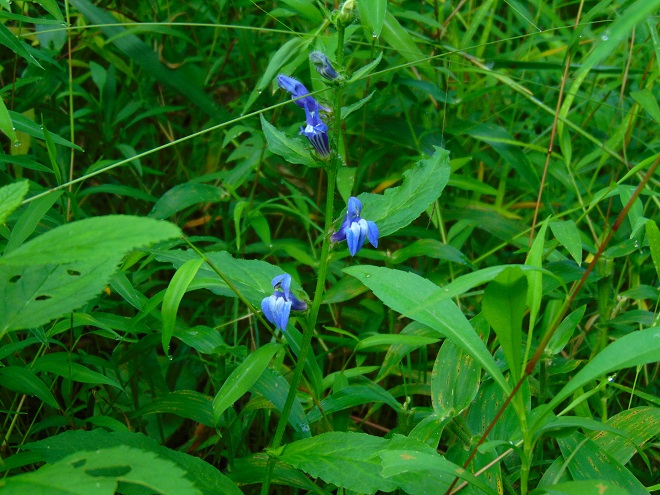
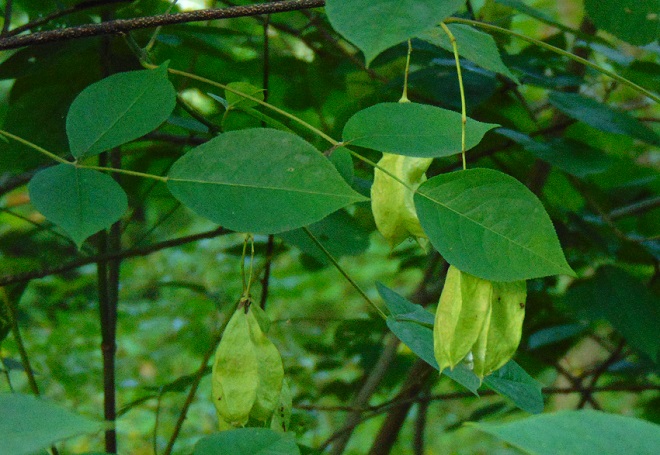
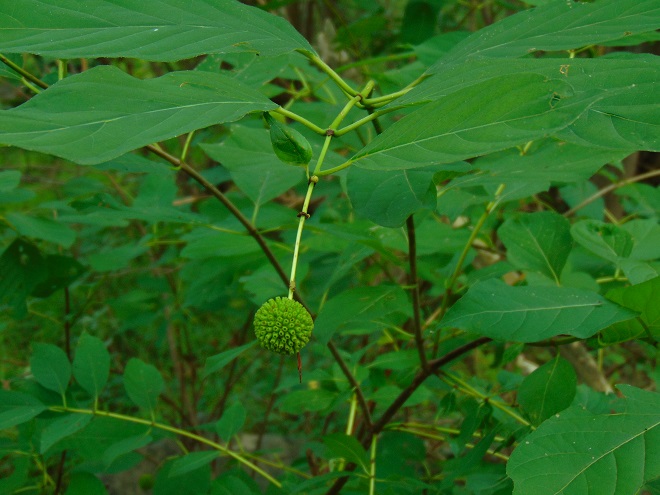
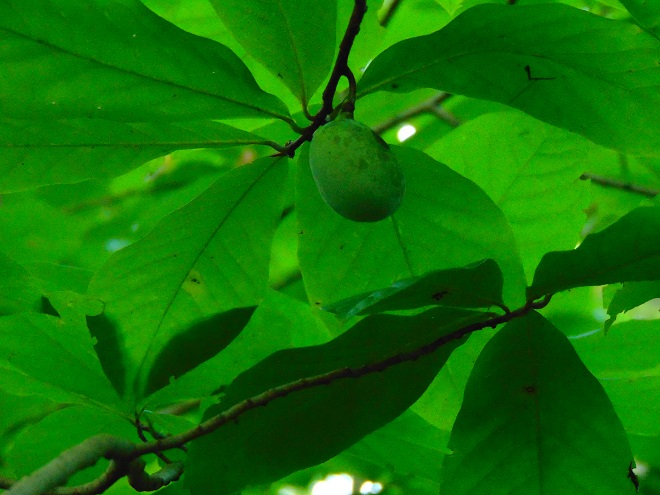











SOURCES
Long, David; Ballentine, Noel H.; and Marks, James G., Jr. 1997. Treatment of Poison Ivy/Oak Allergic Contact Dermatitis With an Extract of Jewelweed. American Journal of Contact Dermatitis. 8(3): pp. 150-153.
Newcomb, Lawrence. 1977. Newcomb’s Wildflower Guide. Little, Brown and Company. Boston, Massachusetts.
There’s something frightening going on down there. In the sand, beneath the plants on the shoreline, there’s a pile of soil next to a hole it’s been digging. Now, it’s dragging something toward the tunnel it made. What does it have? Is that alive?
We know how the system works, the food chain that is. The small stuff is eaten by the progressively bigger things, and there are fewer of the latter than there are of the former, thus the whole network keeps operating long-term. Some things chew plants, others devour animals whole or in part, and then there are those, like us, that do both. In the natural ecosystem, predators keep the numerous little critters from getting out of control and decimating certain other plant or animal populations and wrecking the whole business. When man brings an invasive and potentially destructive species to a new area, occasionally we’re fortunate enough to have a native species adapt and begin to keep the invader under control by eating it. It maintains the balance. It’s easy enough to understand.
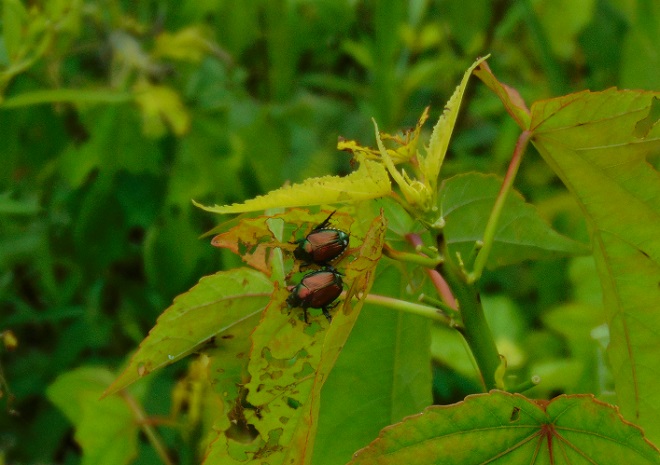


Late summer days are marked by a change in the sounds coming from the forests surrounding the falls. For birds, breeding season is ending, so the males cease their chorus of songs and insects take over the musical duties. The buzzing calls of male “Annual Cicadas” (Neotibicen species) are the most familiar. The female “Annual Cicada” lays her eggs in the twigs of trees. After hatching, the nymphs drop to the ground and burrow into the soil to live and feed along tree roots for the next two to five years. A dry exoskeleton clinging to a tree trunk is evidence that a nymph has emerged from its subterranean haunts and flown away as an adult to breed and soon thereafter die. Flights of adult “Annual Cicadas” occur every year, but never come anywhere close to reaching the enormous numbers of “Periodical Cicadas” (Magicicada species). The three species of “Periodical Cicadas” synchronize their life cycles throughout their combined regional populations to create broods that emerge as spectacular flights once every 13 or 17 years.
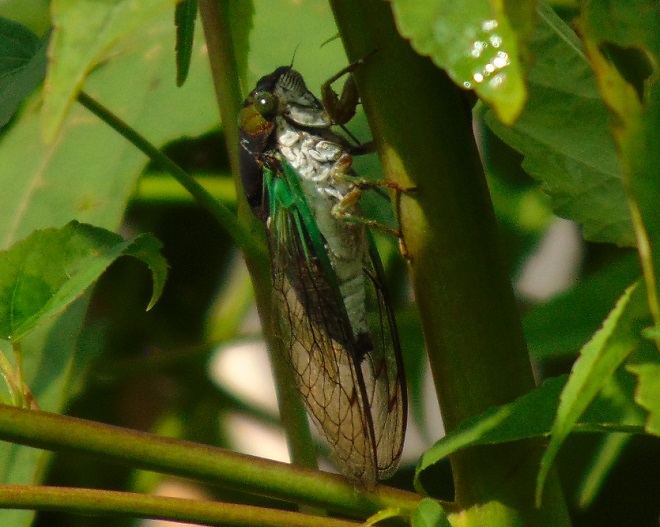

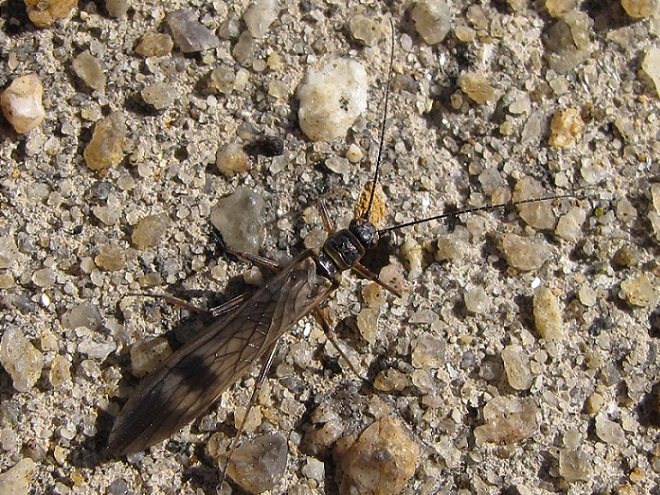
For the adult cicada, there is danger, and that danger resembles an enormous bee. It’s an Eastern Cicada Killer (Specius speciosus) wasp, and it will latch onto a cicada and begin stinging while both are in flight. The stings soon paralyze the screeching, panicked cicada. The Cicada Killer then begins the task of airlifting and/or dragging its victim to the lair it has prepared. The cicada is placed in one of more than a dozen cells in the tunnel complex where it will serve as food for the wasp’s larvae. The wasp lays an egg on the cicada, then leaves and pushes the hole closed. The egg hatches in a several days and the larval grub is on its own to feast upon the hapless cicada.
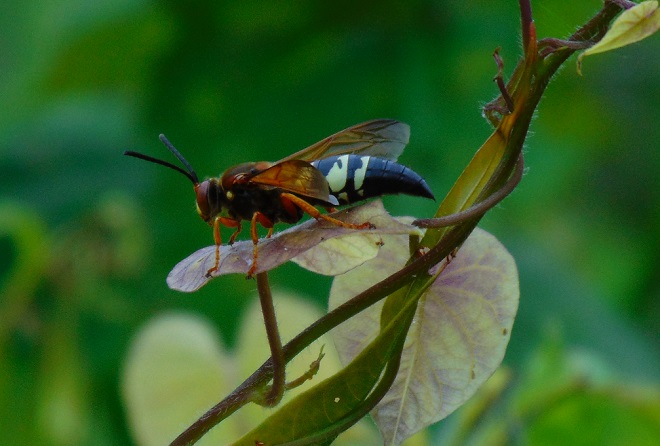

Other species in the Solitary Wasp family (Sphecidae) have similar life cycles using specific prey which they incapacitate to serve as sustenance for their larvae.
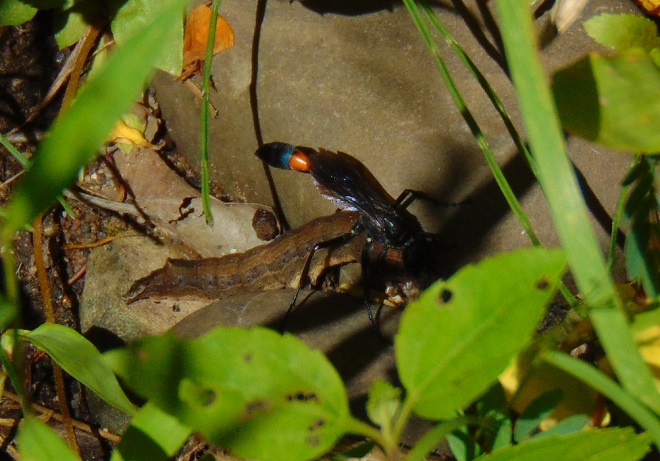

The Solitary Wasps are an important control on the populations of their respective prey. Additionally, the wasp’s bizarre life cycle ensures a greater survival rate for its own offspring by providing sufficient food for each of its progeny before the egg beginning its life is ever put in place. It’s complete family planning.
The cicadas reproduce quickly and, as a species, seem to endure the assault by Cicada Killers, birds, and other predators. The Periodical Cicadas (Magicicada), with adult flights occurring as a massive swarm of an entire population every thirteen or seventeen years, survive as species by providing predators with so ample a supply of food that most of the adults go unmolested to complete reproduction. Stay tuned, 2021 is due to be the next Periodical Cicada year in the vicinity of Conewago Falls.
SOURCES
Eaton, Eric R., and Kenn Kaufman. 2007. Kaufman Field Guide to Insects of North America. Houghton Mifflin Company. New York.
She ate only toaster pastries…that’s it…nothing else. Every now and then, on special occasions, when a big dinner was served, she’d have a small helping of mashed potatoes, no gravy, just plain, thank you. She received all her nutrition from several meals a week of macaroni and cheese assembled from processed ingredients found in a cardboard box. It contains eight essential vitamins and minerals, don’t you know? You remember her, don’t you?
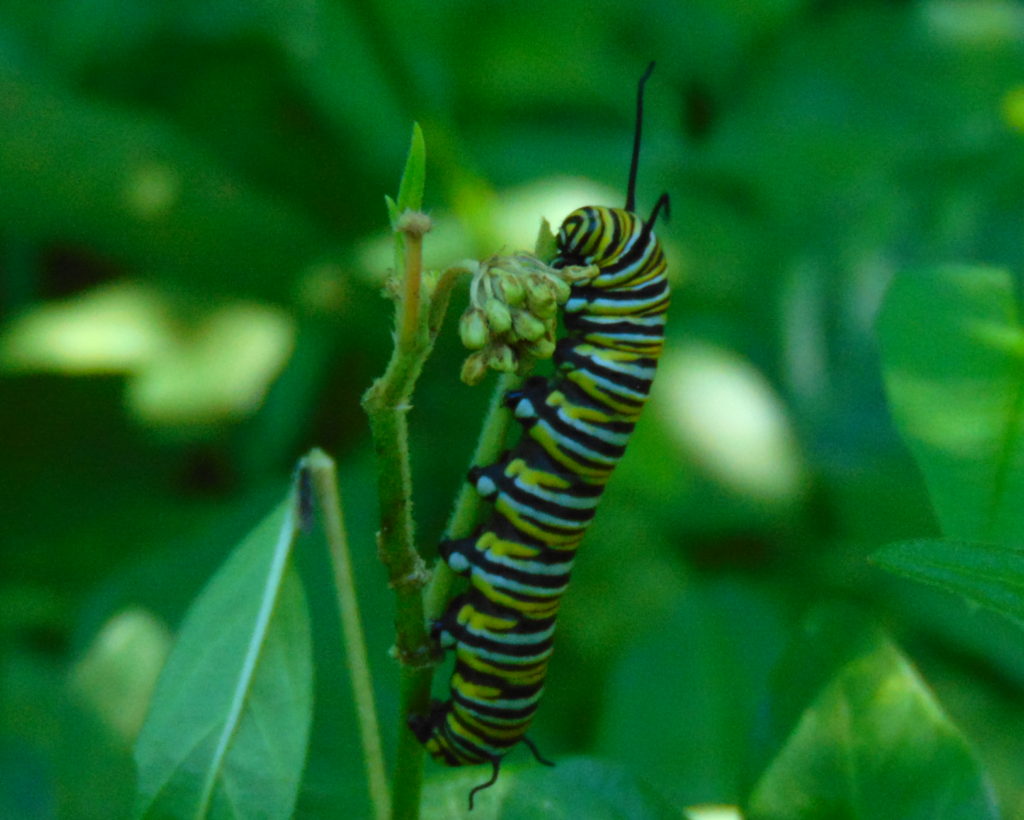
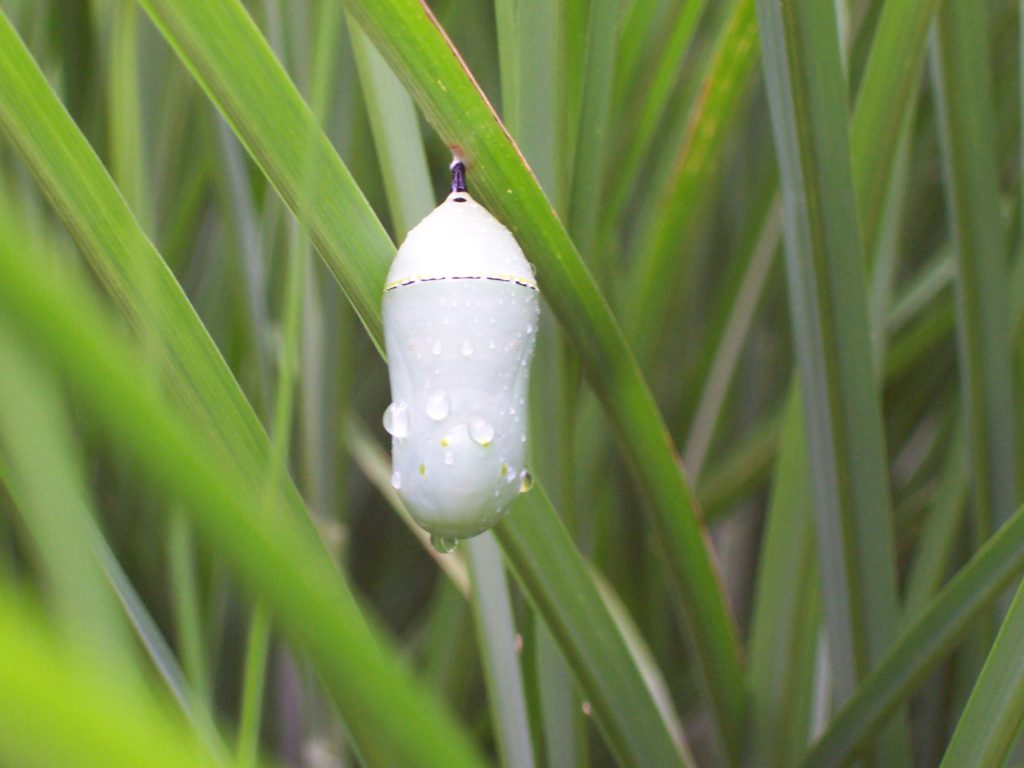
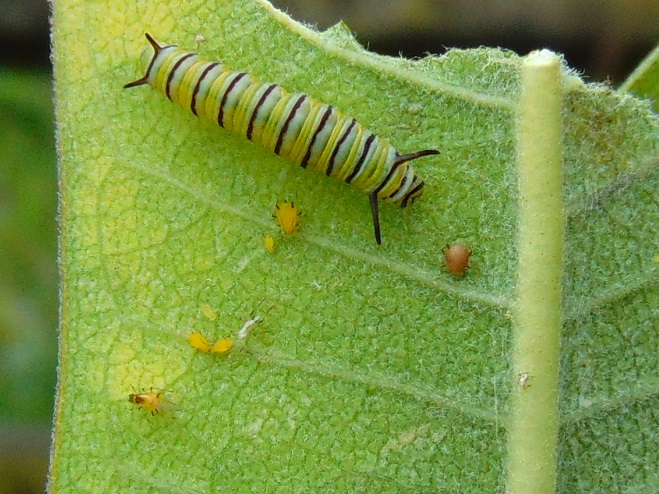
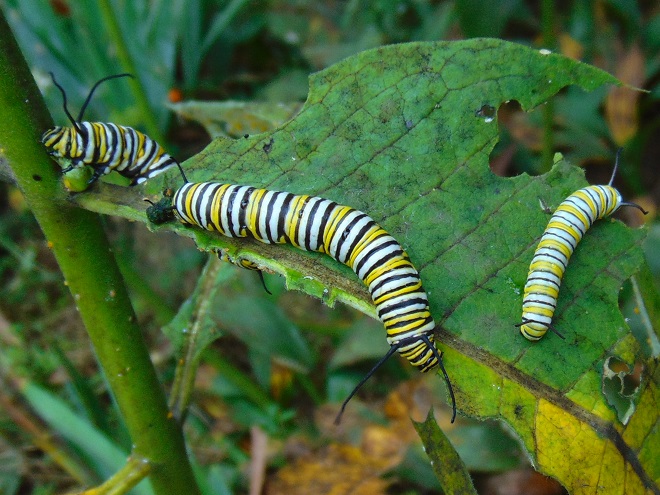
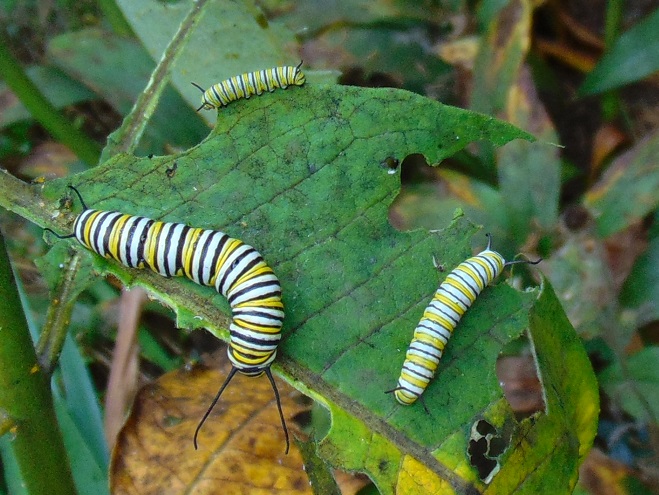
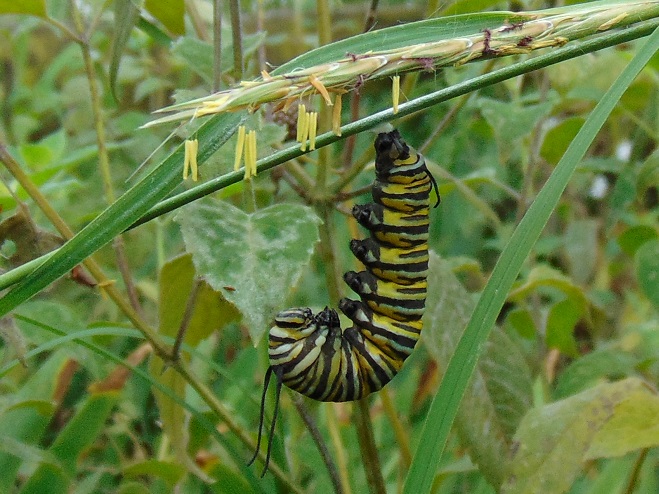
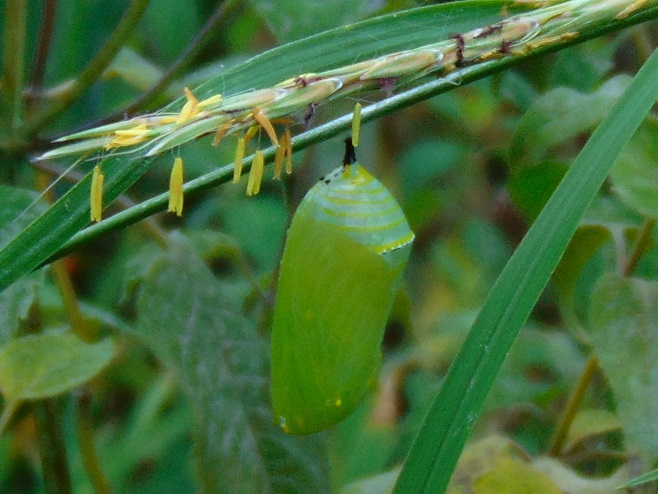
Adult female butterflies must lay their eggs where the hatched larvae will promptly find the precise food needed to fuel their growth. These caterpillars are fussy eaters, with some able to feed upon only one particular species or genus of plant to grow through the five stages, the instars, of larval life. The energy for their fifth molt into a pupa, known as a chrysalis, and metamorphosis into an adult butterfly requires mass consumption of the required plant matter. Their life cycle causes most butterflies to be very habitat specific. These splendid insects may visit the urban or suburban garden as adults to feed on nectar plants, however, successful reproduction relies upon environs which include suitable, thriving, pesticide-free host plants for the caterpillars. Their survival depends upon more than the vegetation surrounding the typical lawn will provide.
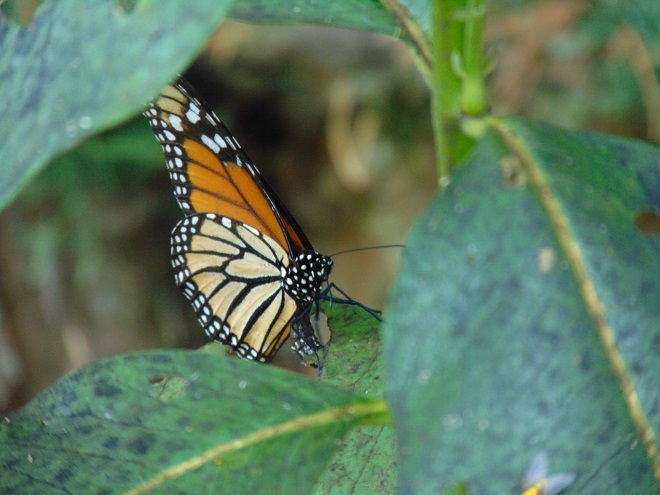
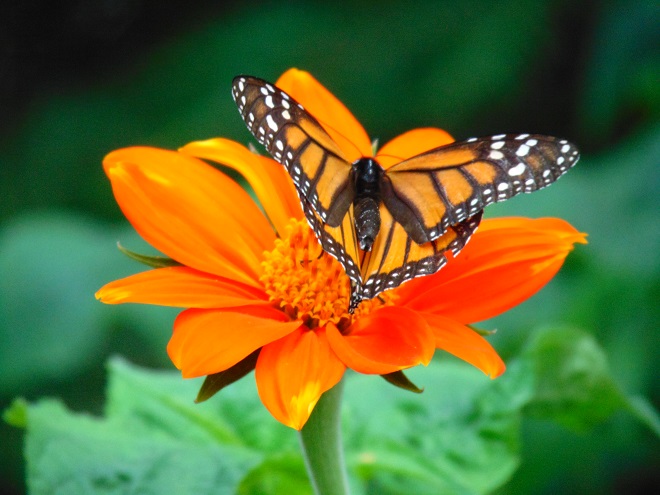
The Monarch (Danaus plexippus), a butterfly familiar in North America for its conspicuous autumn migrations to forests in Mexico, uses the milkweeds (Asclepias) almost exclusively as a host plant. Here at Conewago Falls, wetlands with Swamp Milkweed (Asclepias incarnata) and unsprayed clearings with Common Milkweed (A. syriaca) are essential to the successful reproduction of the species. Human disturbance, including liberal use of herbicides, and invasive plant species can diminish the biomass of the Monarch’s favored nourishment, thus reducing significantly the abundance of the migratory late-season generation.
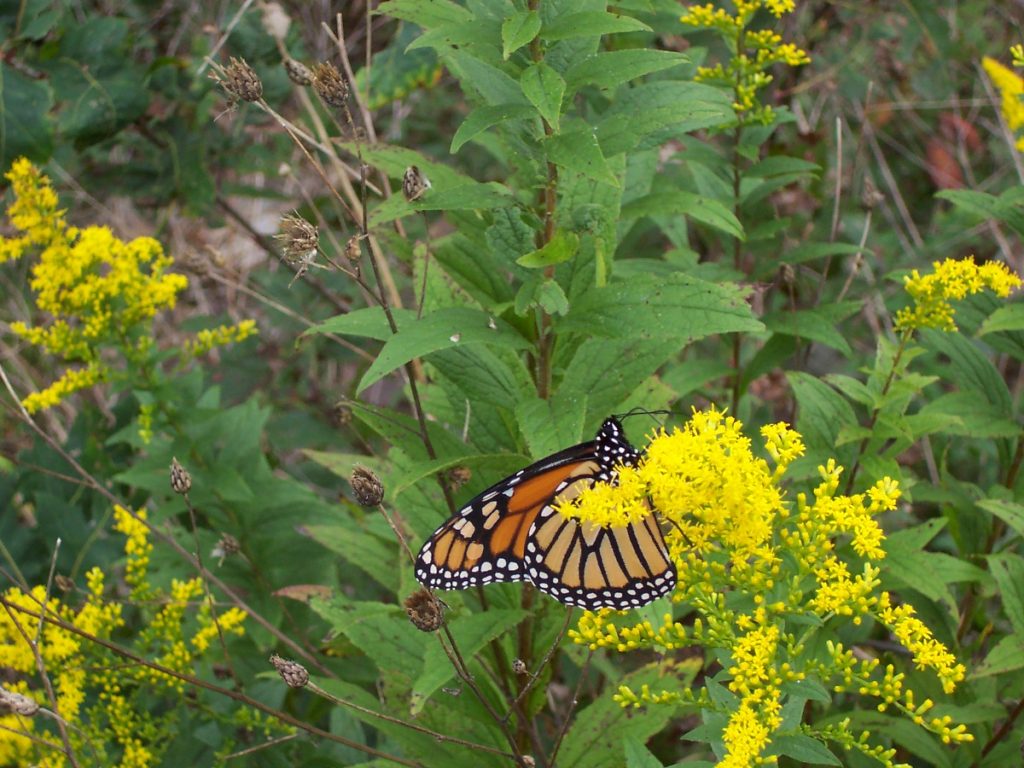



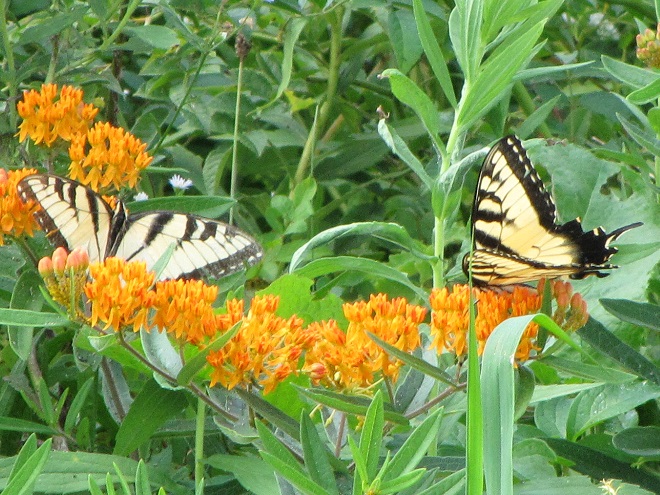
Butterflies are good indicators of the ecological health of a given environment. A diversity of butterfly species in a given area requires a wide array of mostly indigenous plants to provide food for reproduction. Let’s have a look at some of the species seen around Conewago Falls this week…
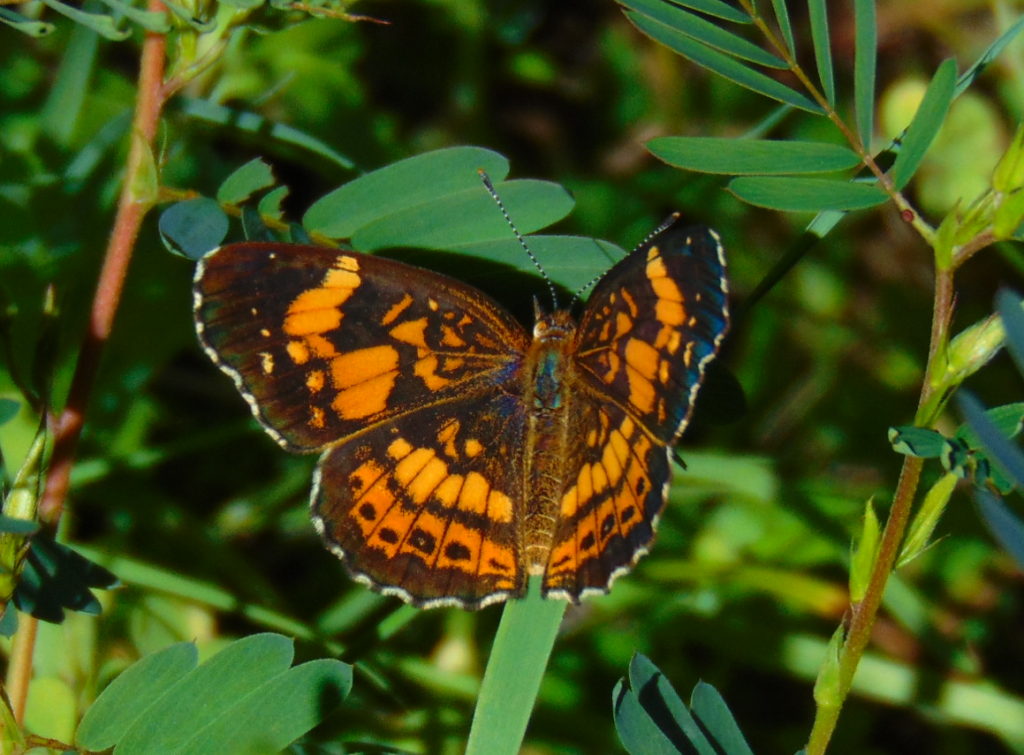
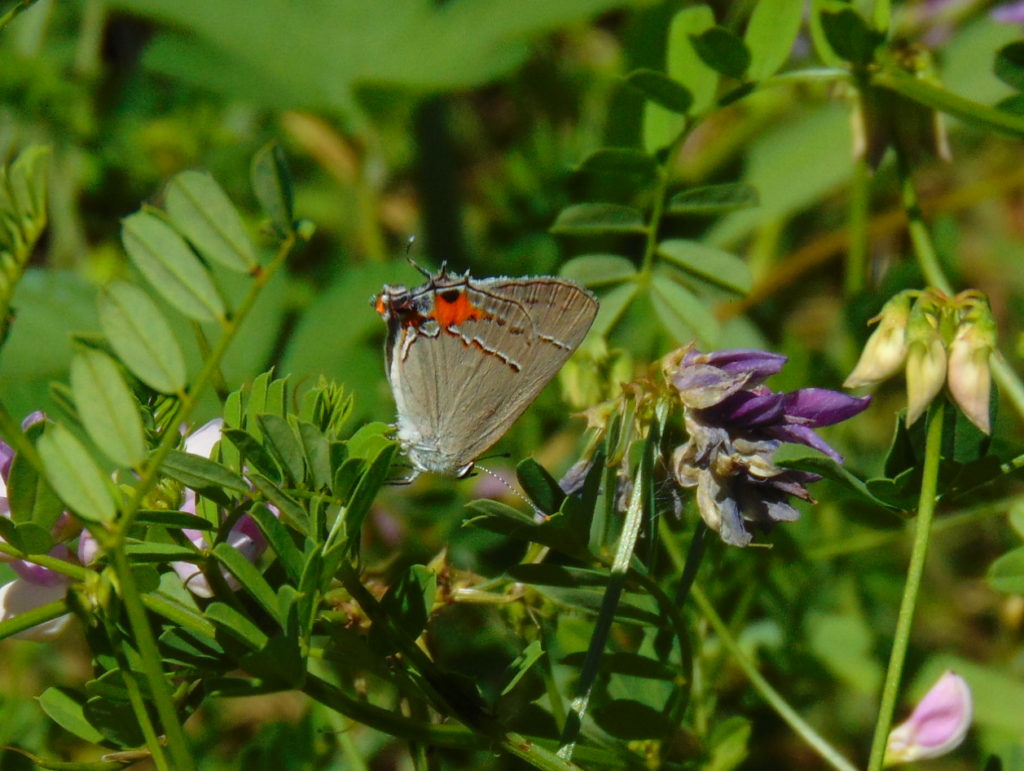
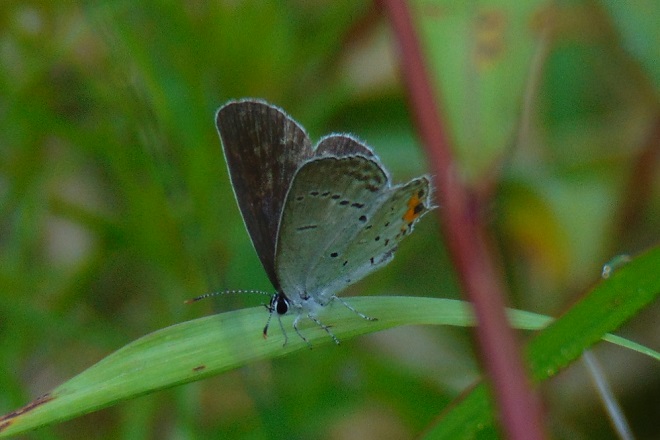
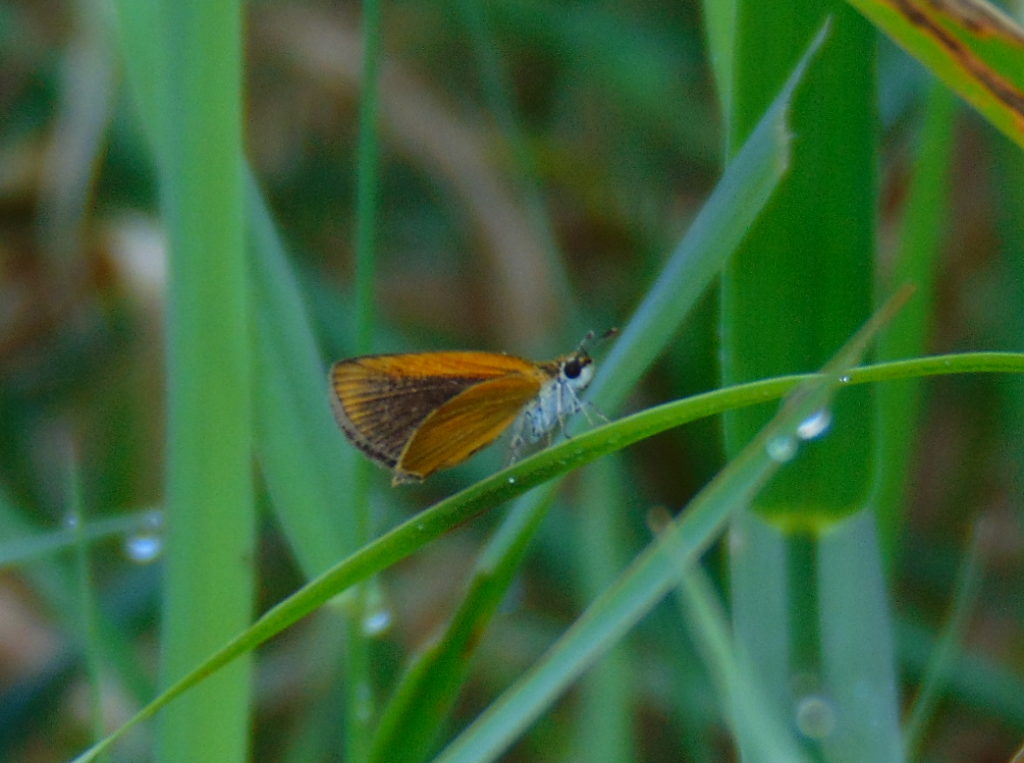
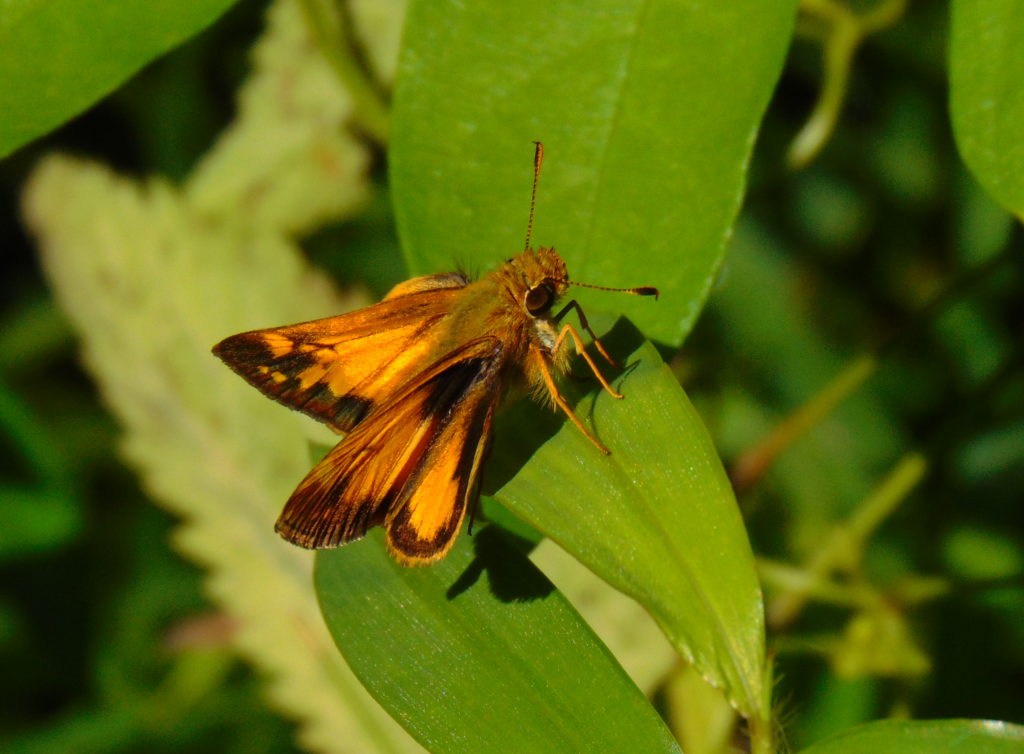
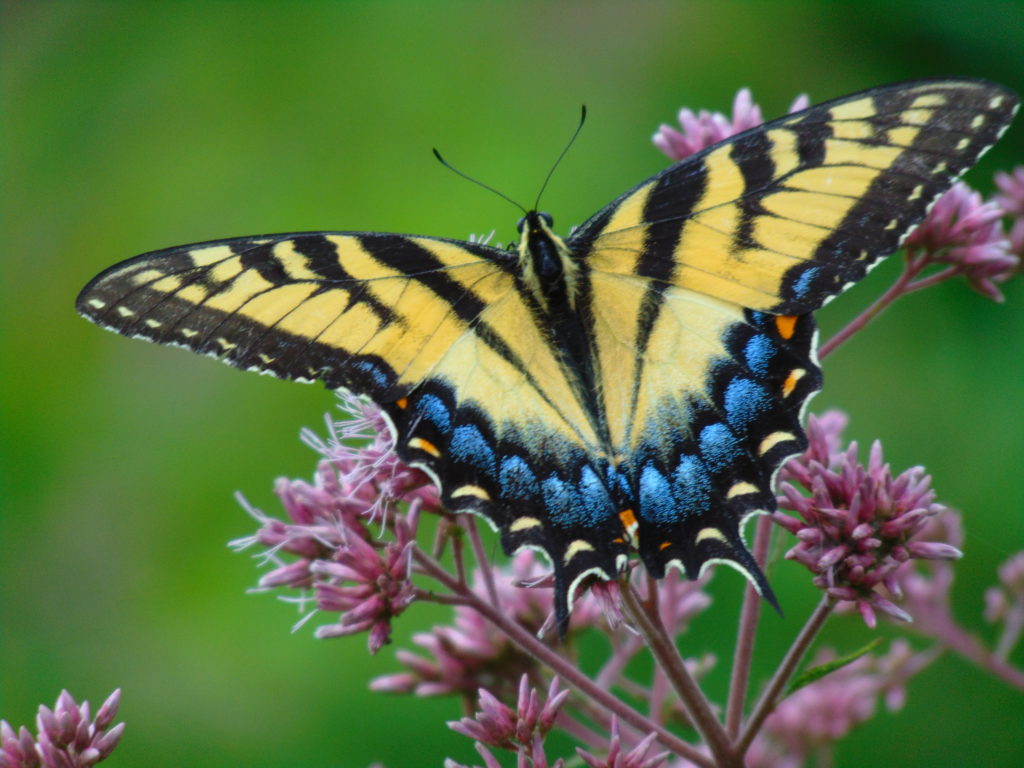
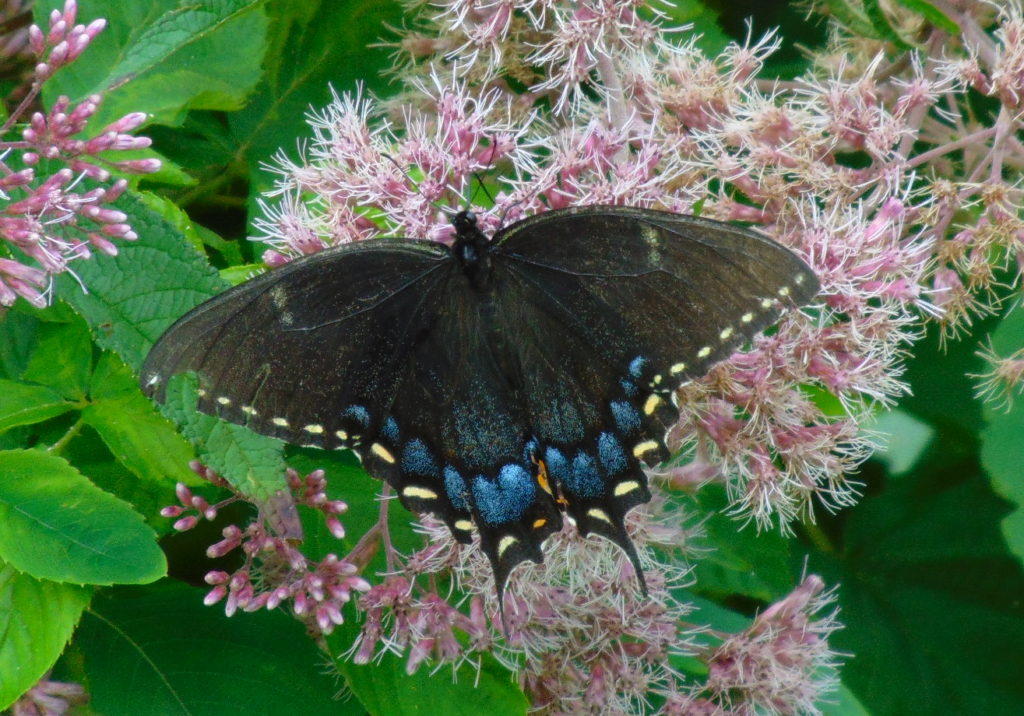
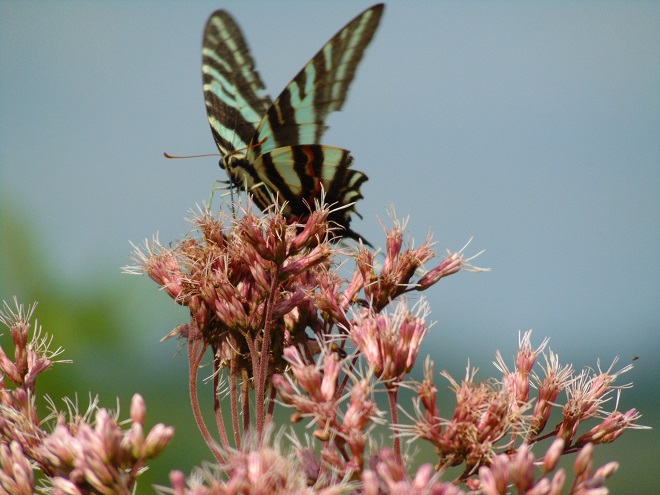








The spectacularly colorful butterflies are a real treat on a hot summer day. Their affinity for showy plants doubles the pleasure.
By the way, I’m certain by now you’ve recalled that fussy eater…and how beautiful she grew up to be.
SOURCES
Brock, Jim P., and Kaufman, Kenn. 2003. Butterflies of North America. Houghton Mifflin Company. New York, NY.