Photo of the Day


LIFE IN THE LOWER SUSQUEHANNA RIVER WATERSHED
A Natural History of Conewago Falls—The Waters of Three Mile Island

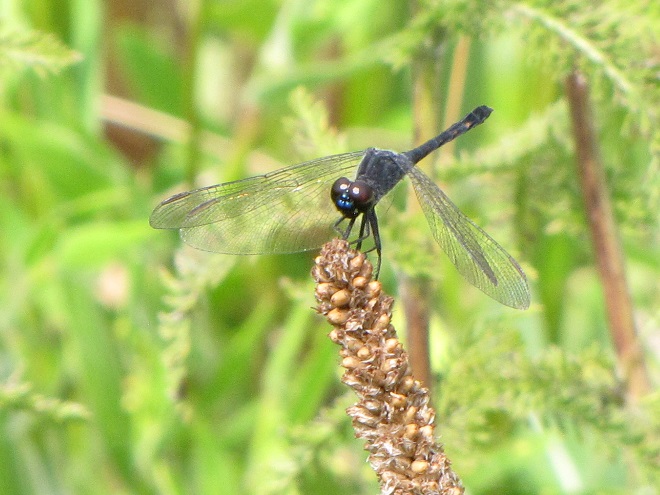
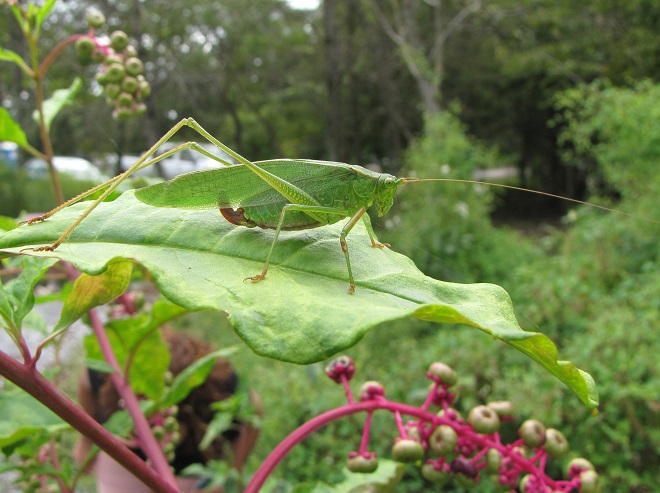
During recent weeks, as temperatures have warmed into the 70s and 80s, early season odonates—damselflies and dragonflies—have taken to the wing along our watercourses and wetlands to prey upon small flying insects.











If you’re out and about in coming days, you’ll find that flights of Common Green Darners, Black Saddlebags, and other species are underway as well. As the waters of the lower Susquehanna valley continue to warm, an even greater variety of these insects will take to the wing. To help with the identification of those you see, be certain to click the “Damselflies and Dragonflies” tab at the top of this page.
To pass the afternoon, we sat quietly along the edge of a pond created recently by North American Beavers (Castor canadensis). They first constructed their dam on this small stream about five years ago. Since then, a flourishing wetland has become established. Have a look.
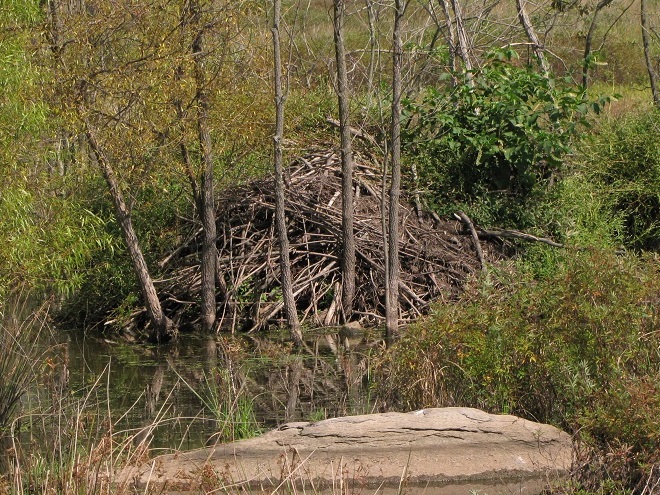
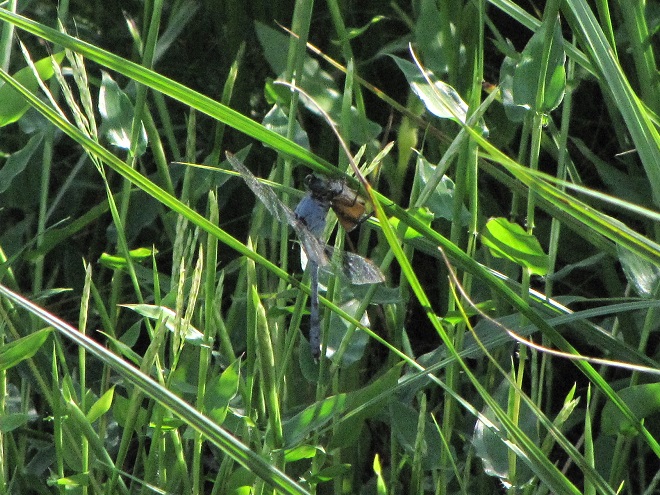
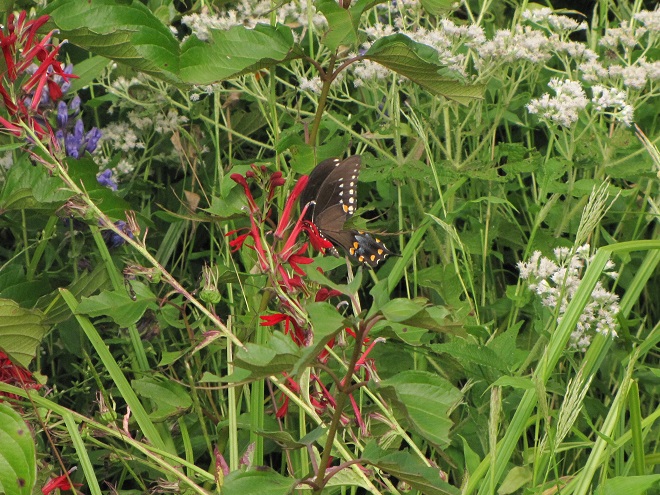
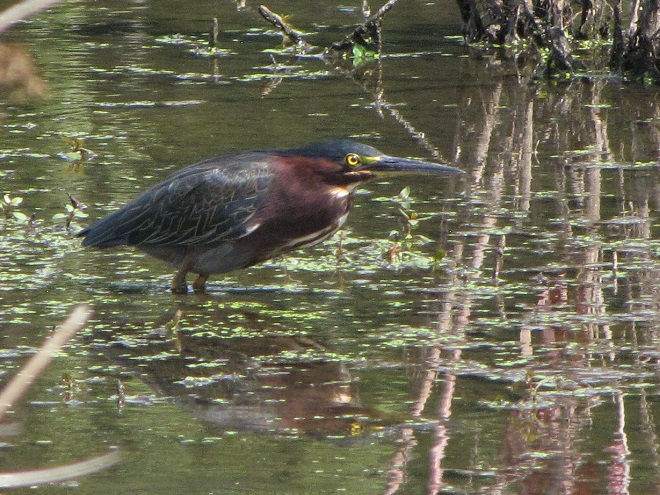
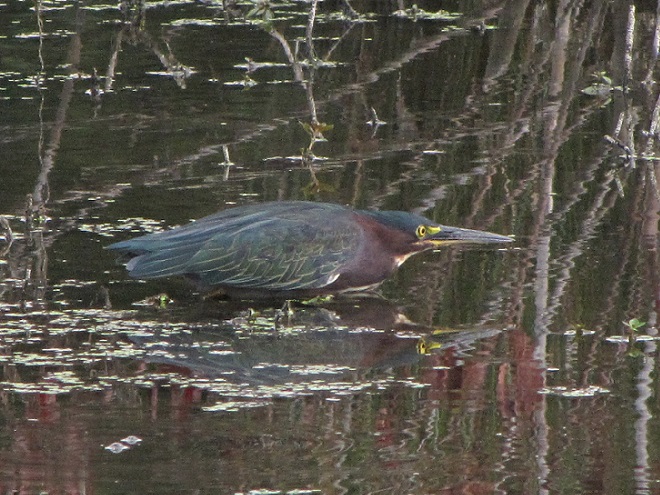
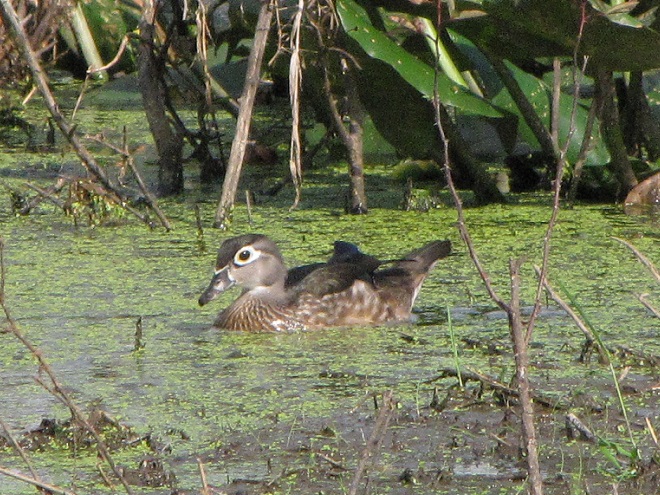















Isn’t that amazing? North American Beavers build and maintain what human engineers struggle to master—dams and ponds that reduce pollution, allow fish passage, and support self-sustaining ecosystems. Want to clean up the streams and floodplains of your local watershed? Let the beavers do the job!
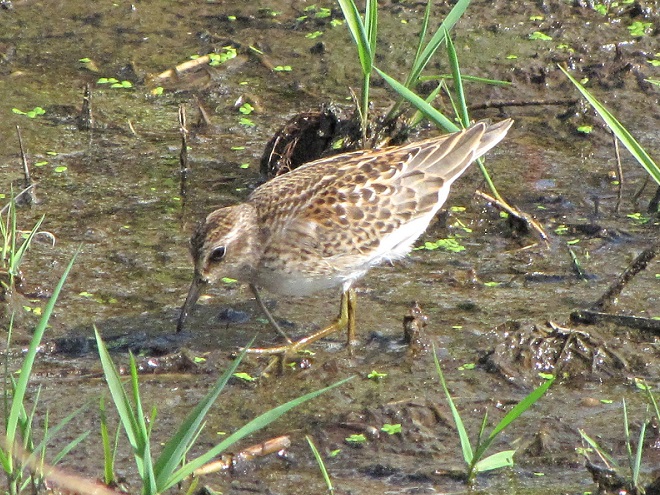
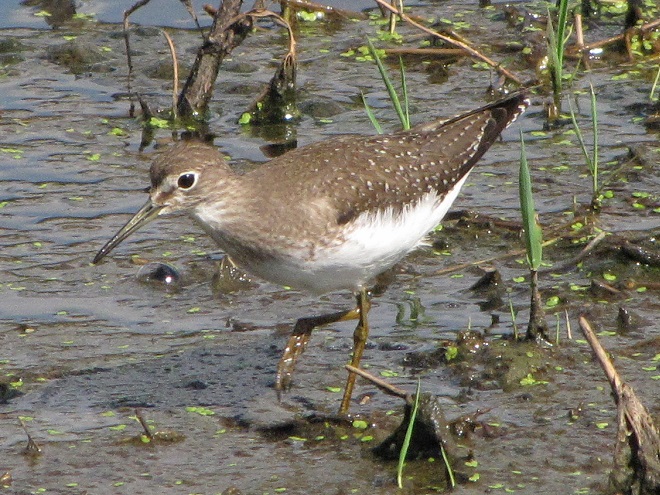
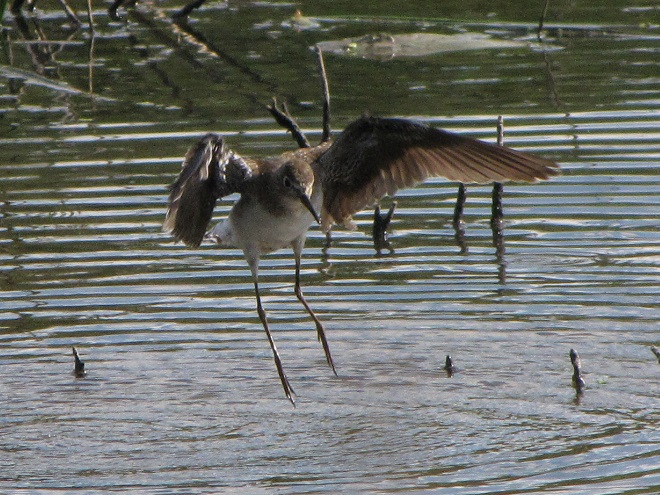
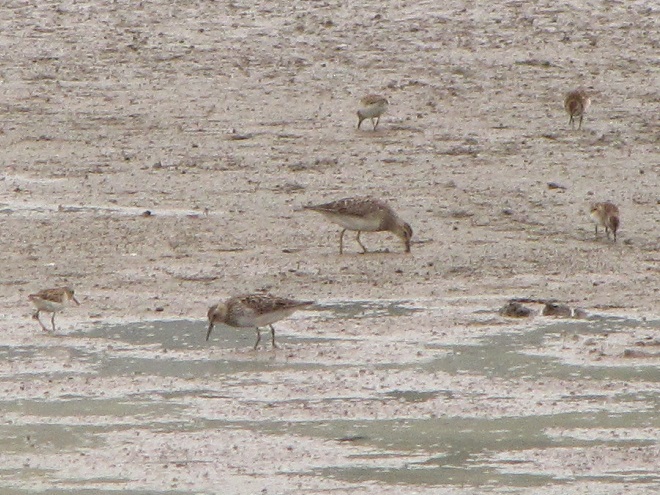
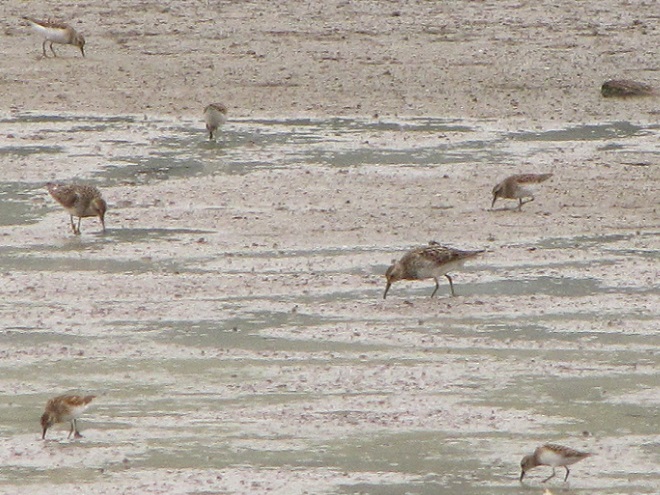
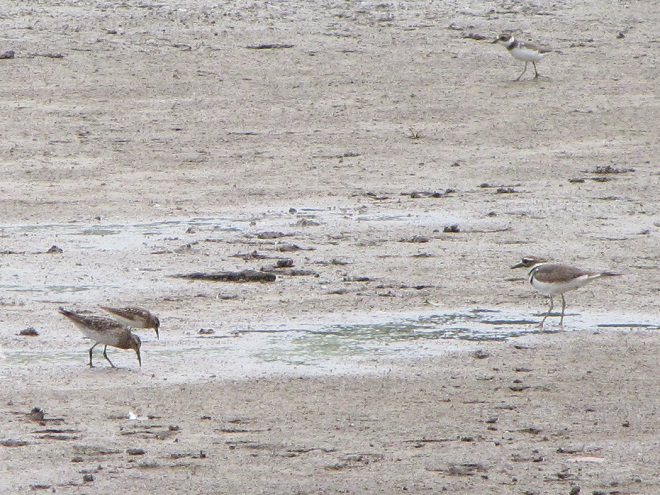
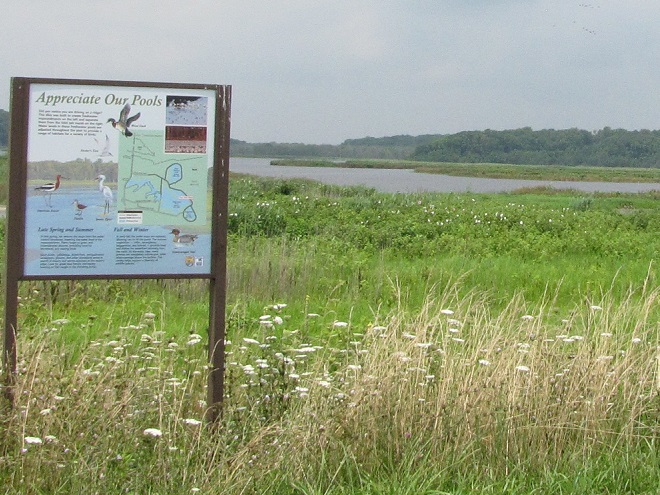
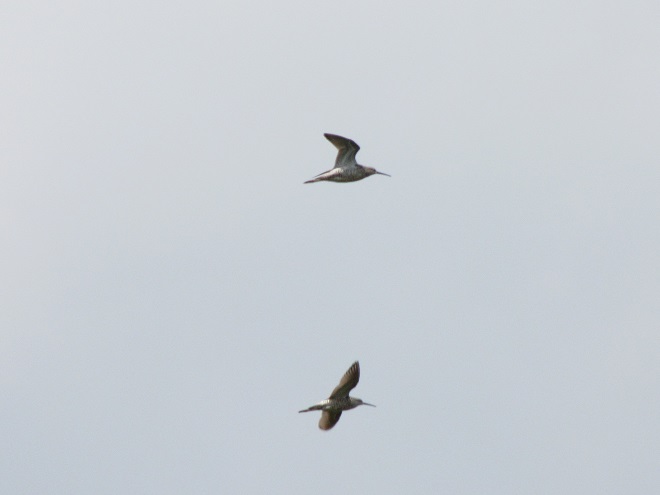
Your best bet for finding migrating shorebirds in the lower Susquehanna region is certainly a visit to a sandbar or mudflat in the river. The Conejohela Flats off Washington Boro just south of Columbia is a renowned location. Some man-made lakes including the one at Middle Creek Wildlife Management Area are purposely drawn down during the weeks of fall migration to provide exposed mud and silt for feeding and resting sandpipers and plovers. But with the Susquehanna running high due to recent rains and the cost of fuel trending high as well, maybe you want to stay closer to home to do your observing.
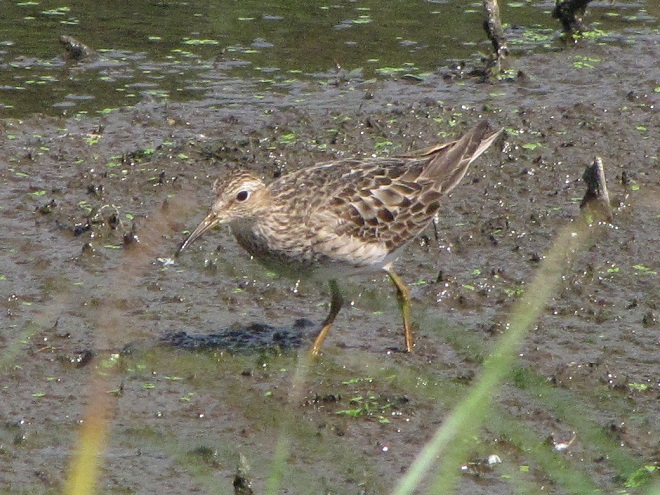
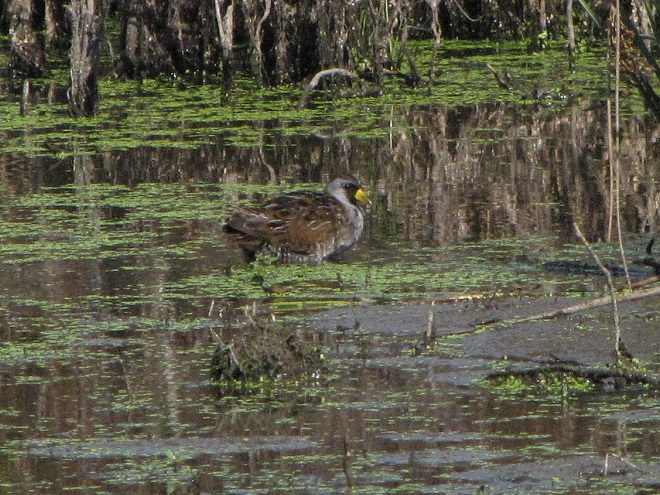
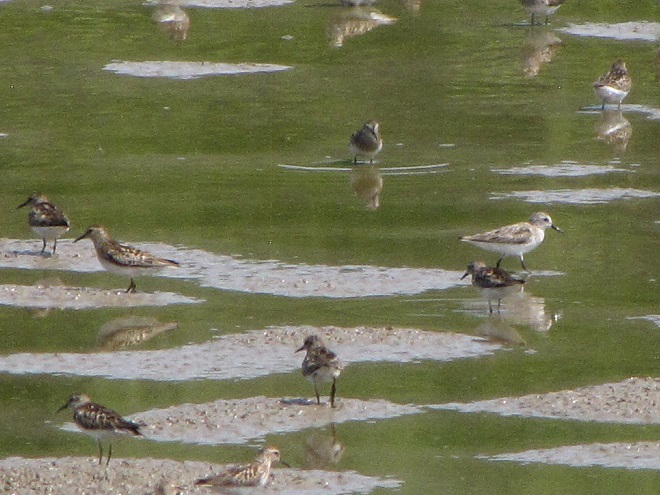
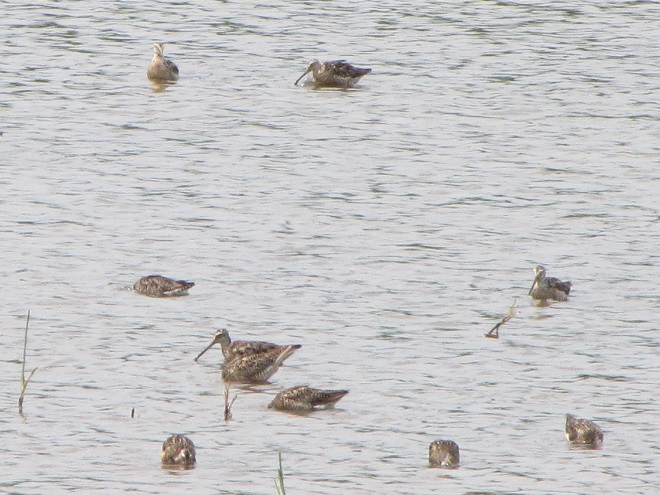
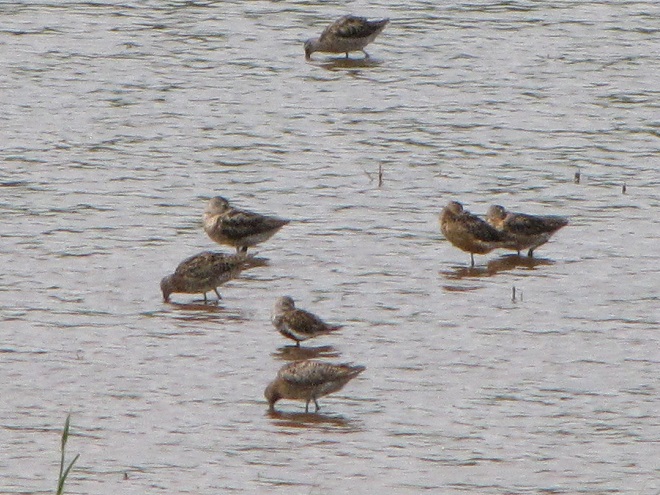
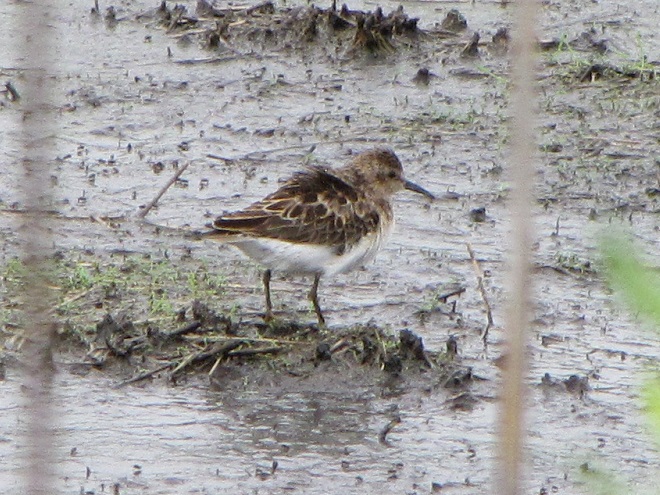
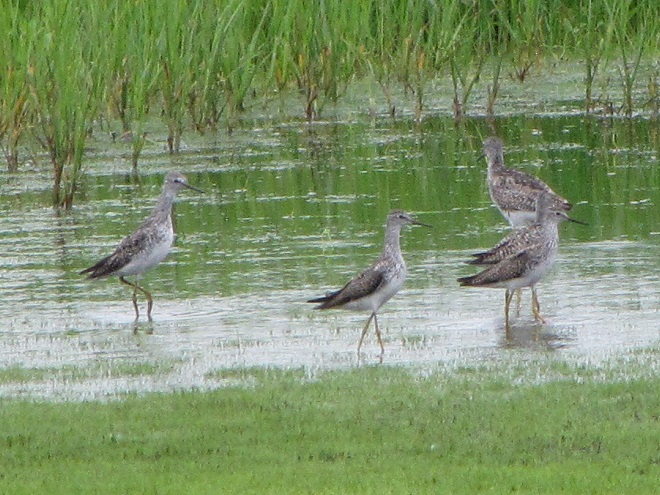
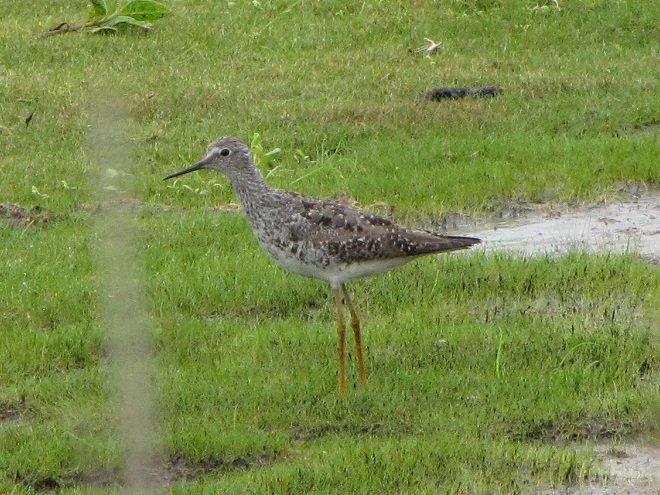
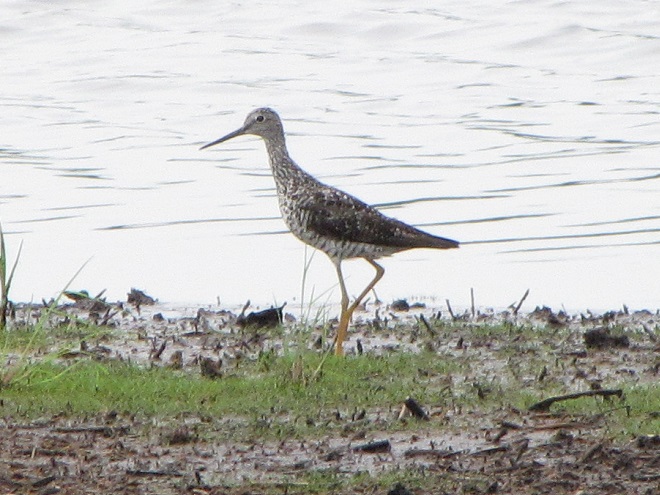
Fortunately for us, migratory shorebirds will drop in on almost any biologically active pool of shallow water and mud that they happen to find. This includes flooded portions of fields, construction sites, and especially stormwater retention basins. We stopped by a new basin just west of Hershey, Pennsylvania, and found more than two dozen shorebirds feeding and loafing there. We took each of these photographs from the sidewalk paralleling the south shore of the pool, thus never flushing or disturbing a single bird.
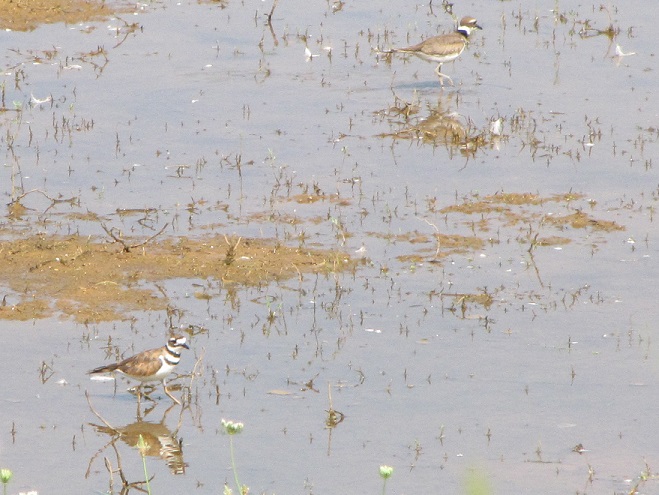
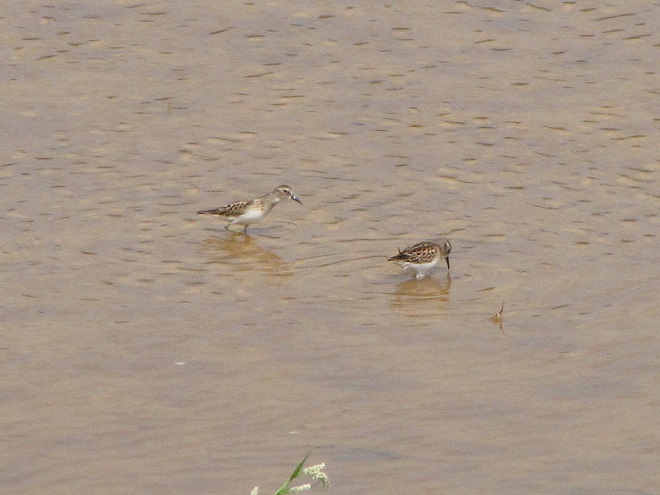
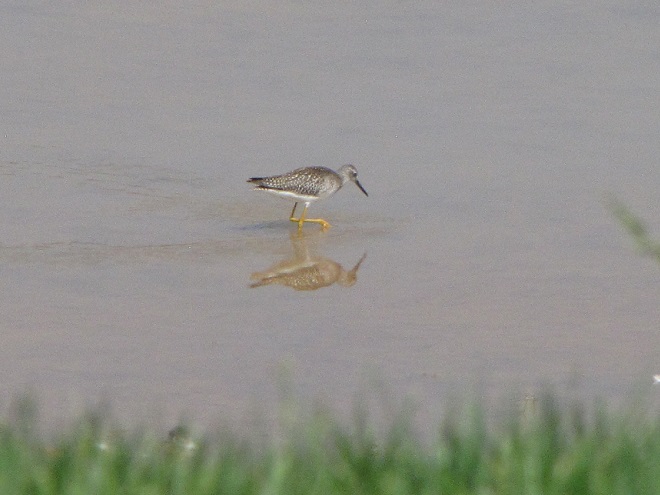
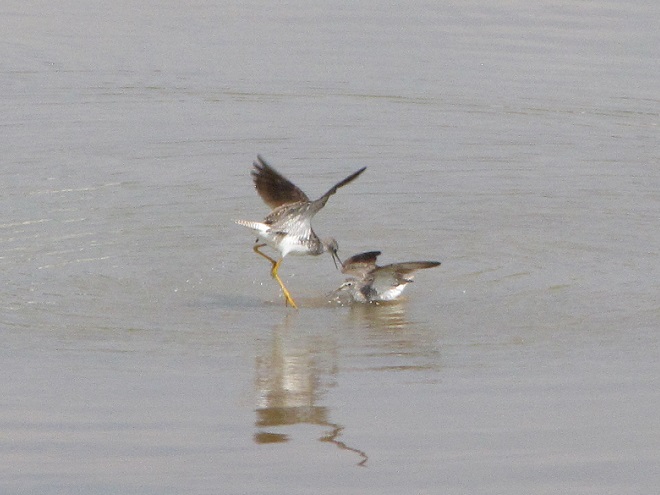
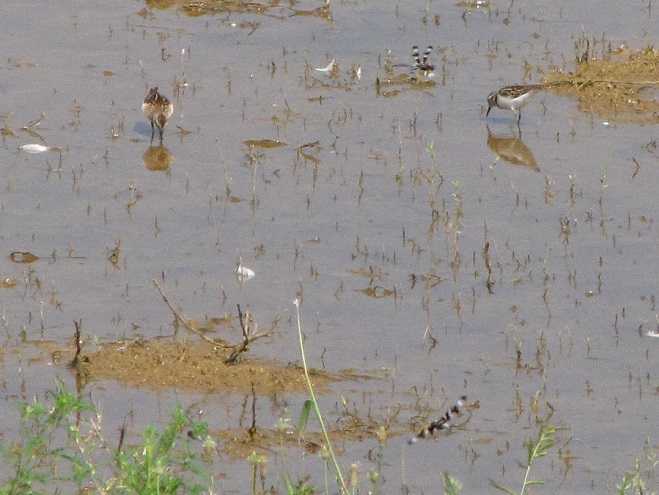






So don’t just drive by those big puddles, stop and have a look. You never know what you might find.




Have you purchased your 2023-2024 Federal Duck Stamp? Nearly every penny of the 25 dollars you spend for a duck stamp goes toward habitat acquisition and improvements for waterfowl and the hundreds of other animal species that use wetlands for breeding, feeding, and as migration stopover points. Duck stamps aren’t just for hunters, purchasers get free admission to National Wildlife Refuges all over the United States. So do something good for conservation—stop by your local post office and get your Federal Duck Stamp.

Still not convinced that a Federal Duck Stamp is worth the money? Well then, follow along as we take a photo tour of Bombay Hook National Wildlife Refuge. Numbers of southbound shorebirds are on the rise in the refuge’s saltwater marshes and freshwater pools, so we timed a visit earlier this week to coincide with a late-morning high tide.
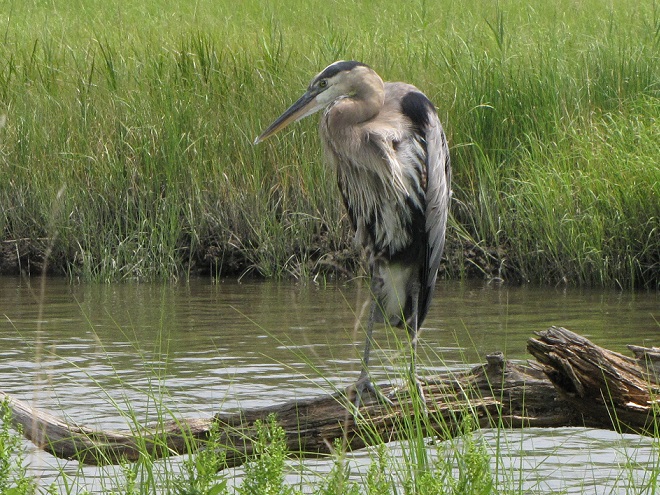
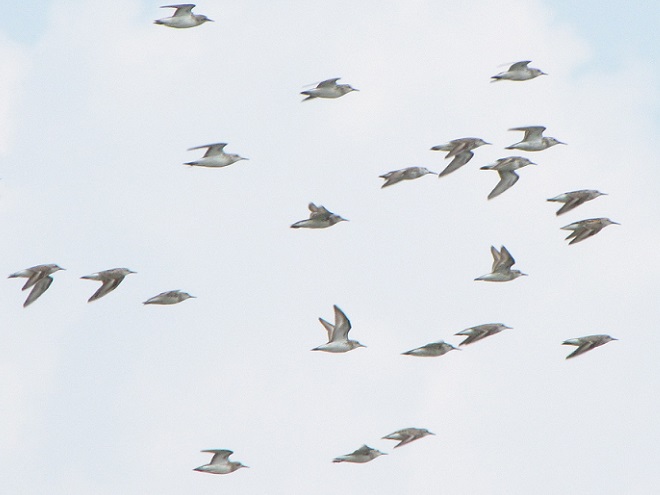
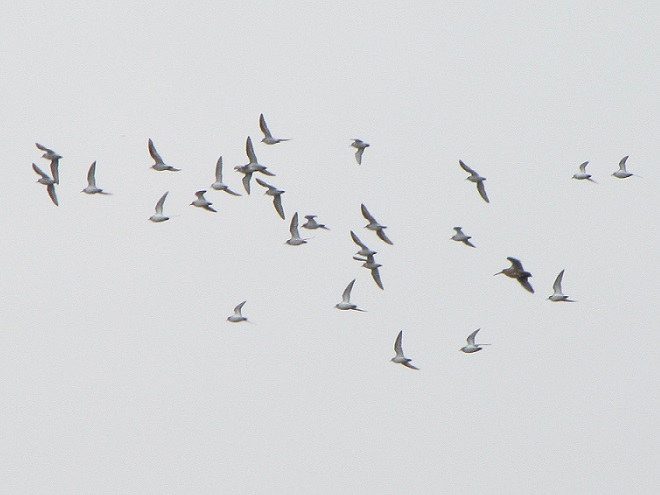
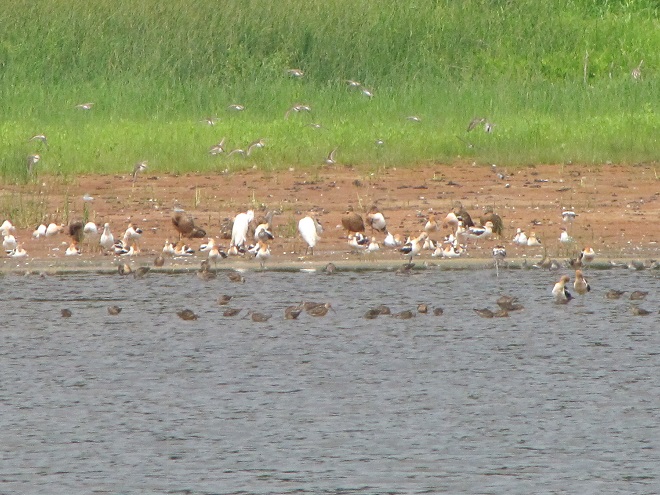
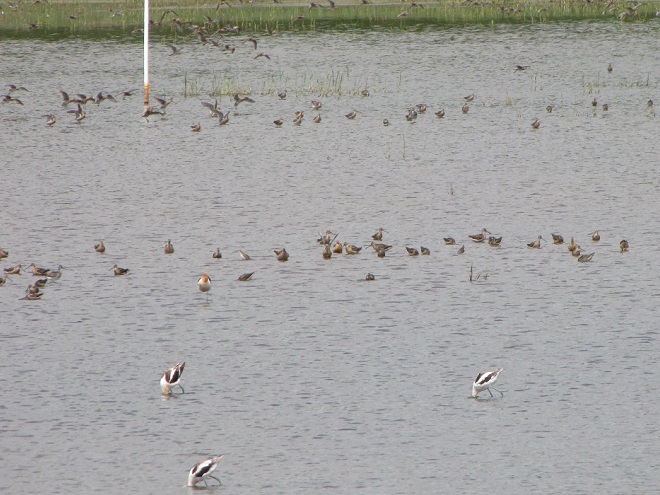
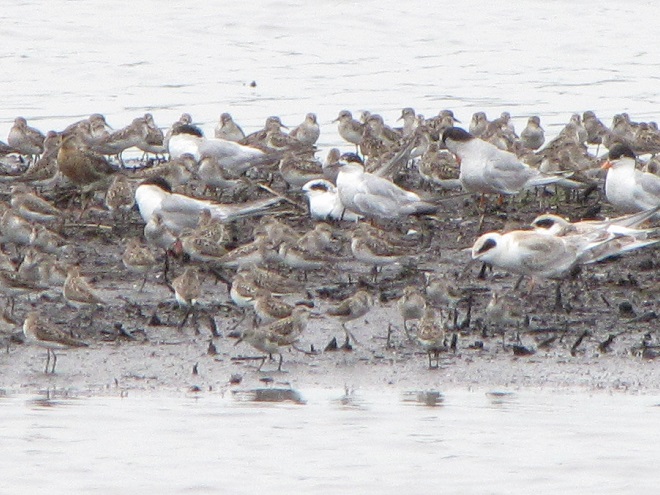
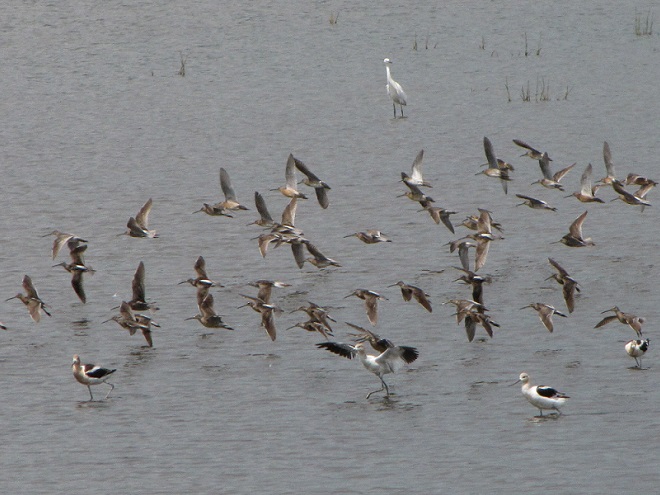
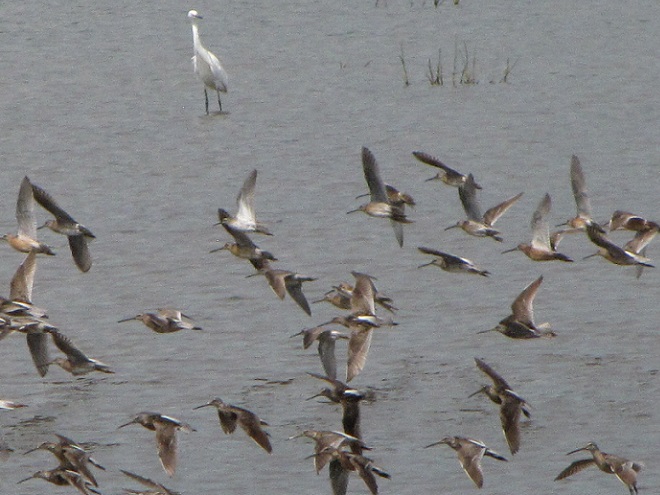
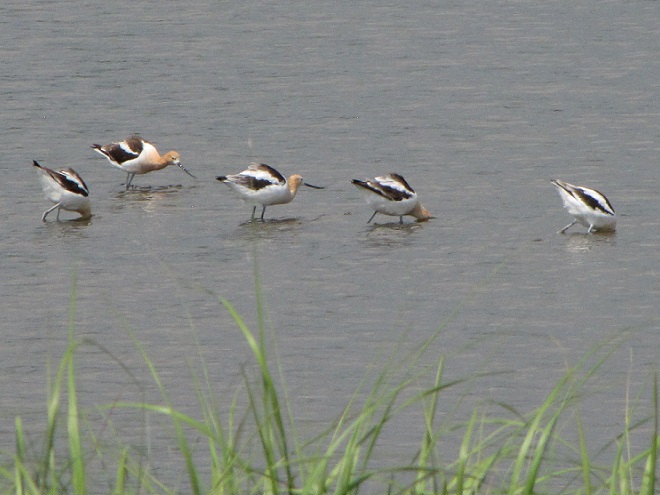
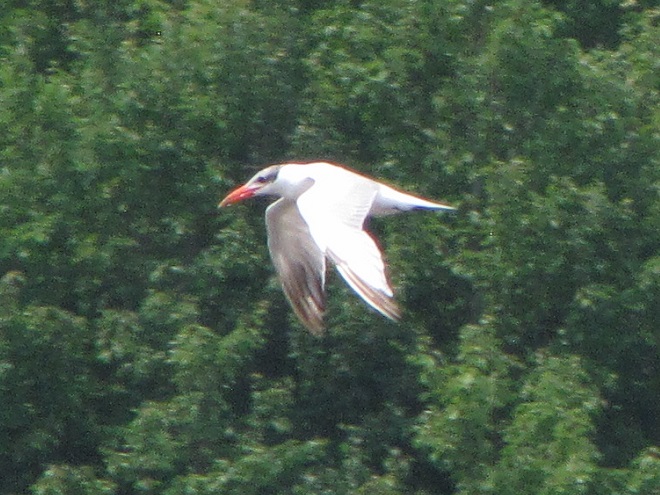
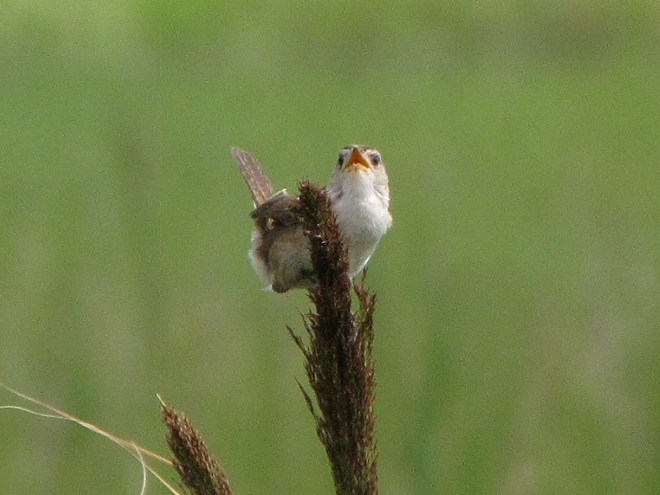
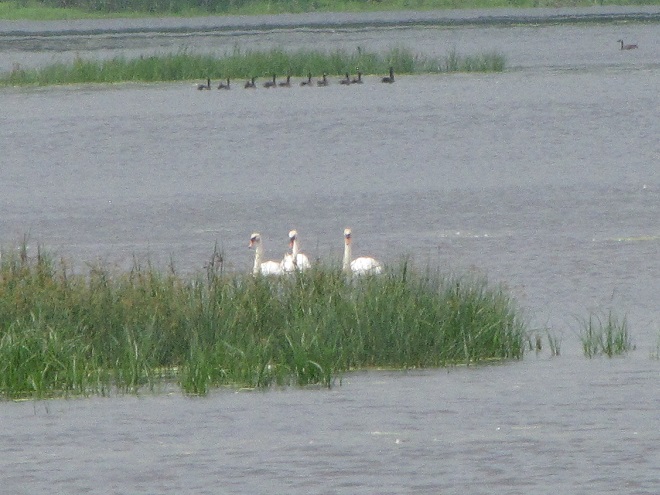
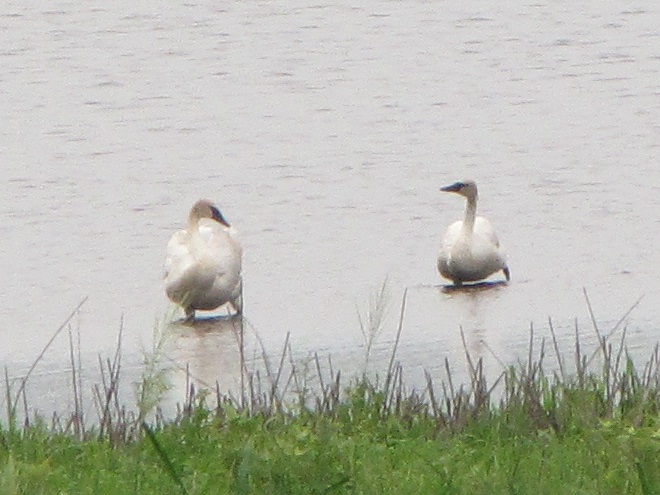
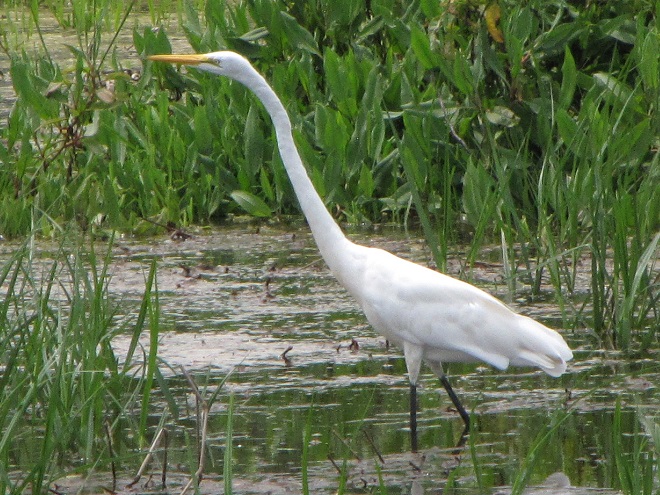
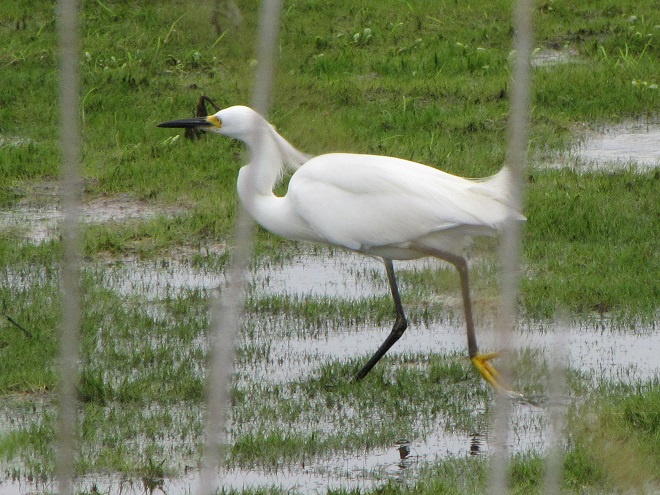
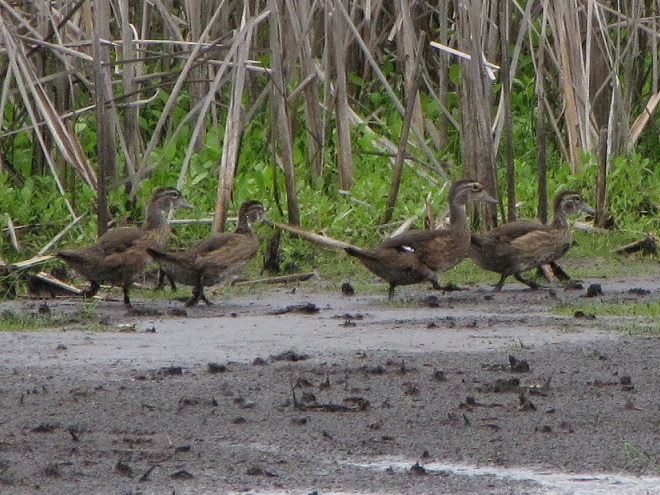
































As the tide recedes, shorebirds leave the freshwater pools to begin feeding on the vast mudflats exposed within the saltwater marshes. Most birds are far from view, but that won’t stop a dedicated observer from finding other spectacular creatures on the bay side of the tour route road.
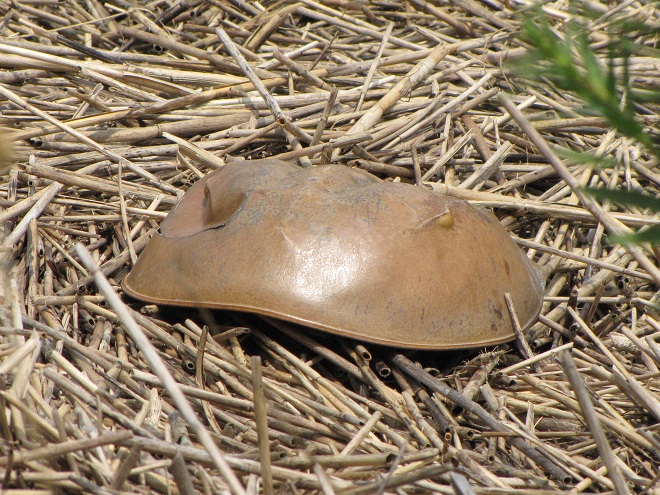
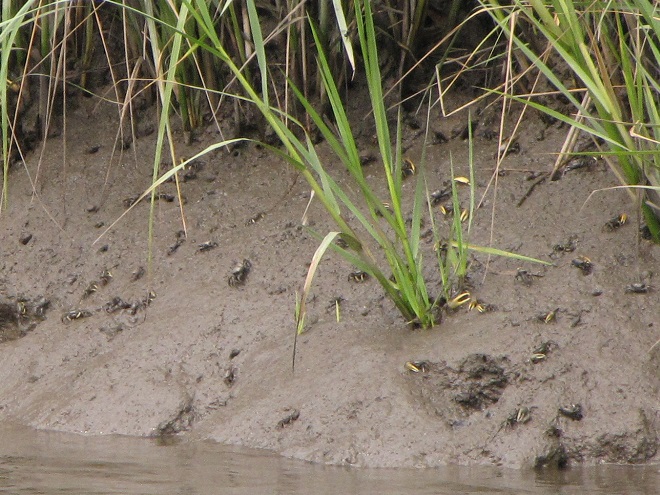
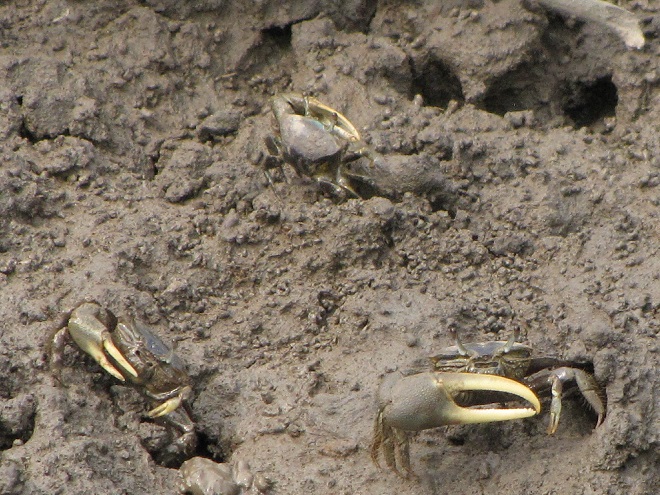
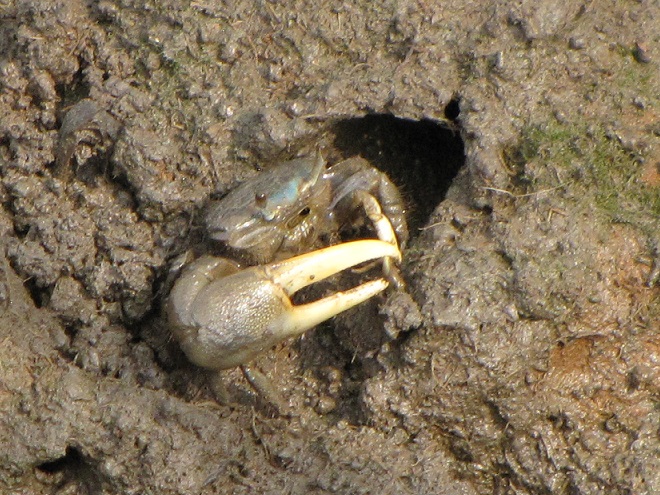
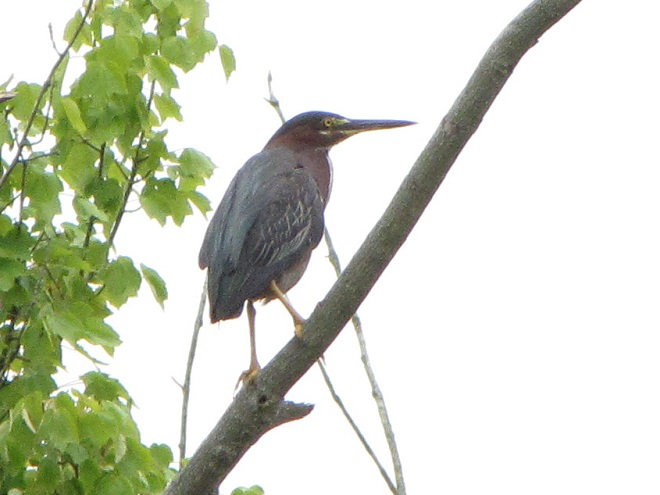
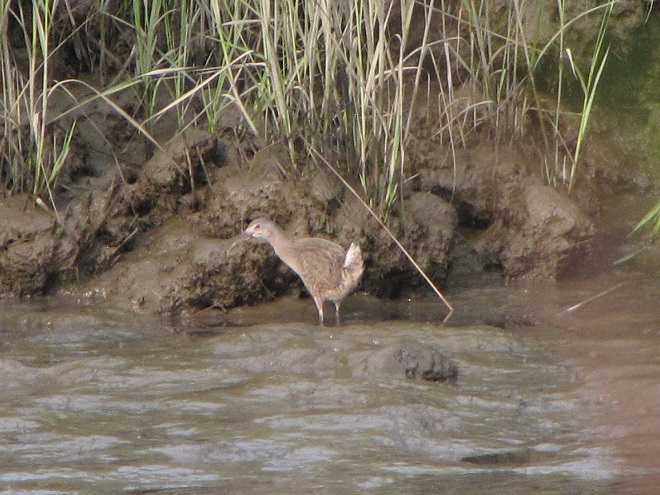
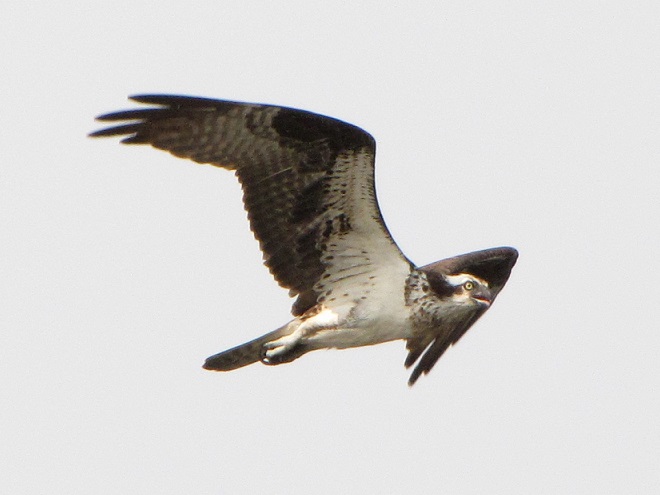











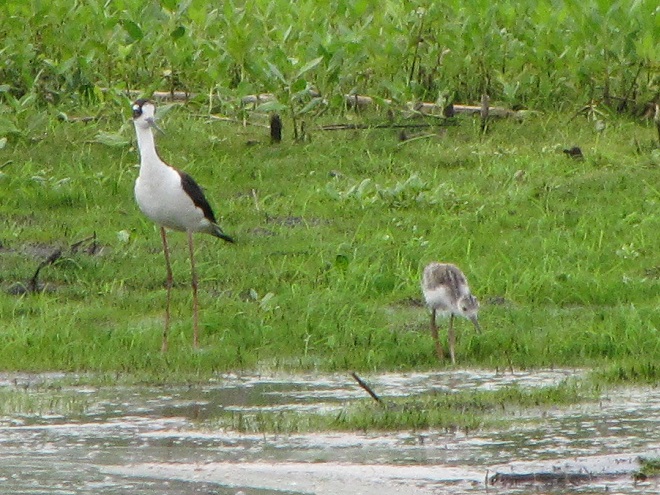
No visit to Bombay Hook is complete without at least a quick loop through the upland habitats at the far end of the tour route.
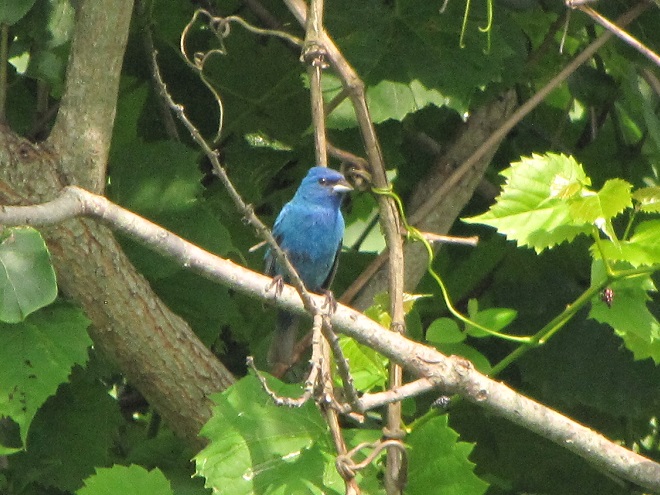
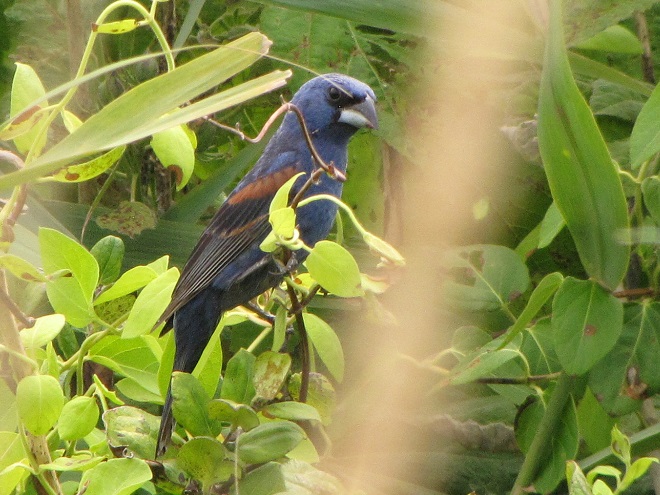
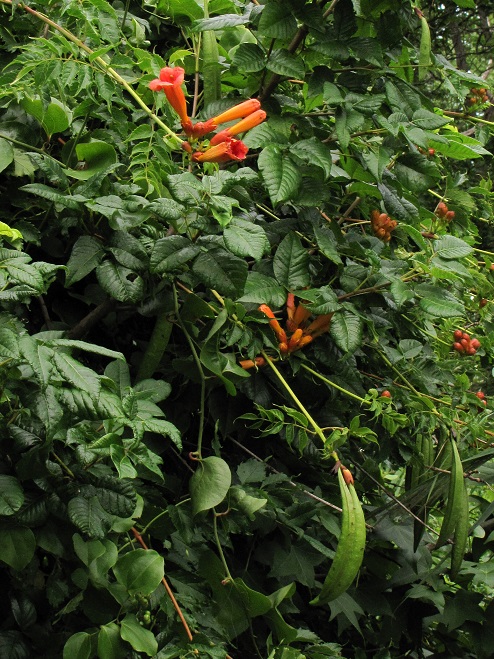
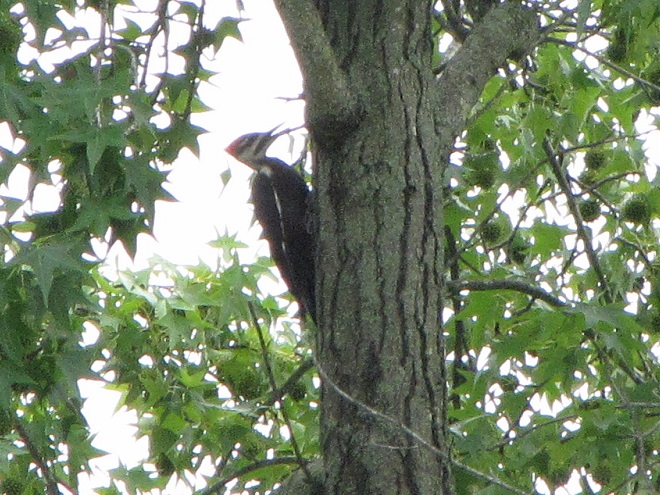
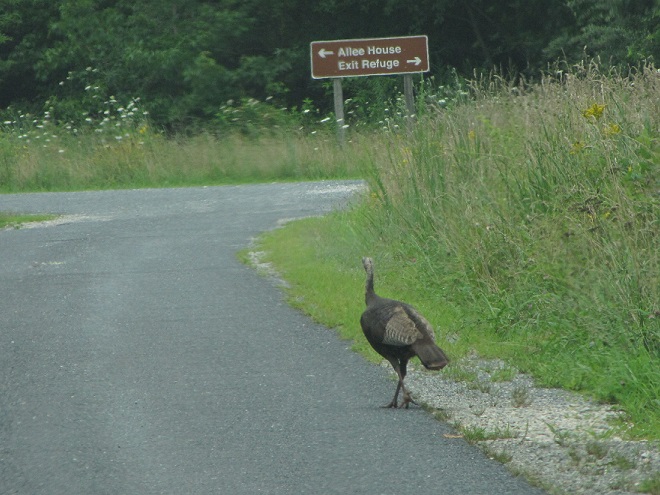









We hope you’ve been convinced to visit Bombay Hook National Wildlife Refuge sometime soon. And we hope too that you’ll help fund additional conservation acquisitions and improvements by visiting your local post office and buying a Federal Duck Stamp.
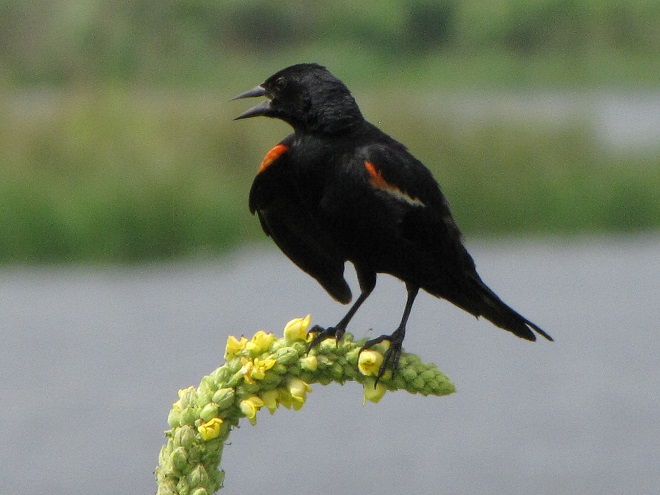
Can it be that time already? Most Neotropical birds have passed through the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed on their way south and the hardier species that will spend our winter in the more temperate climes of the eastern United States are beginning to arrive.
Here’s a gallery of sightings from recent days…
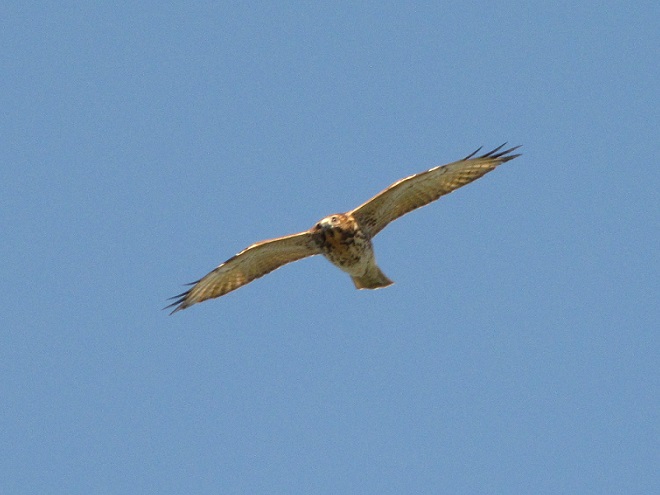
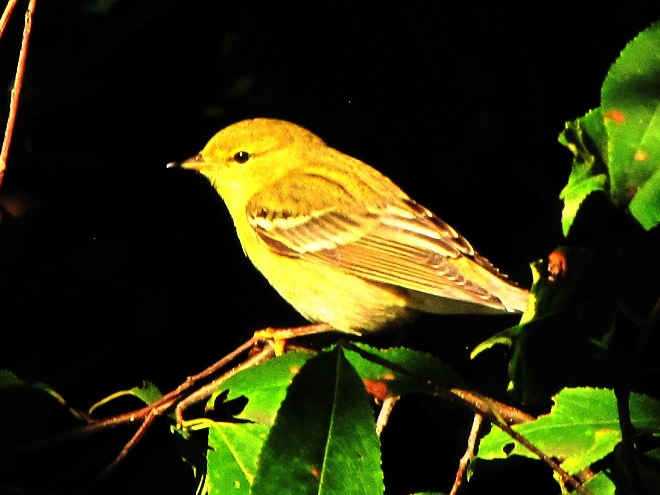
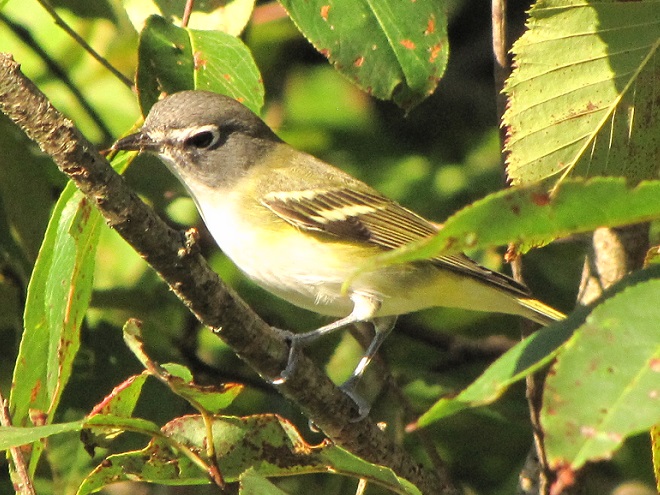
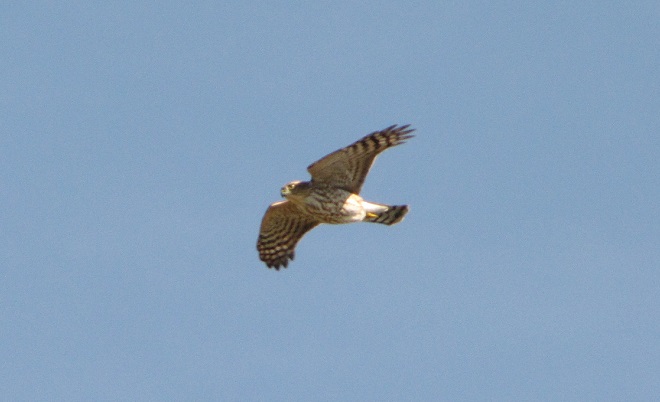
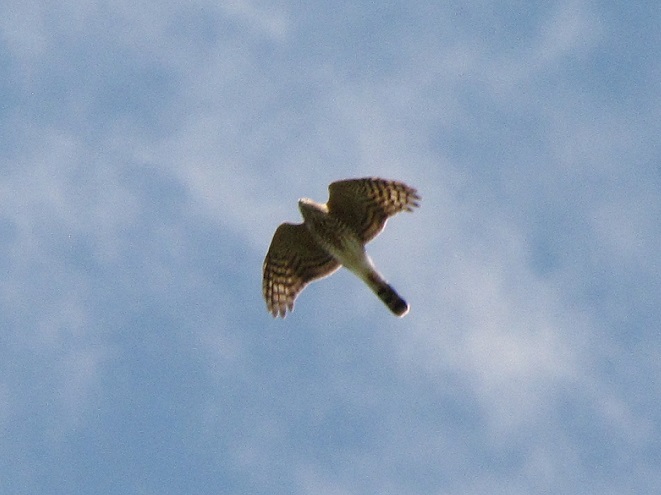
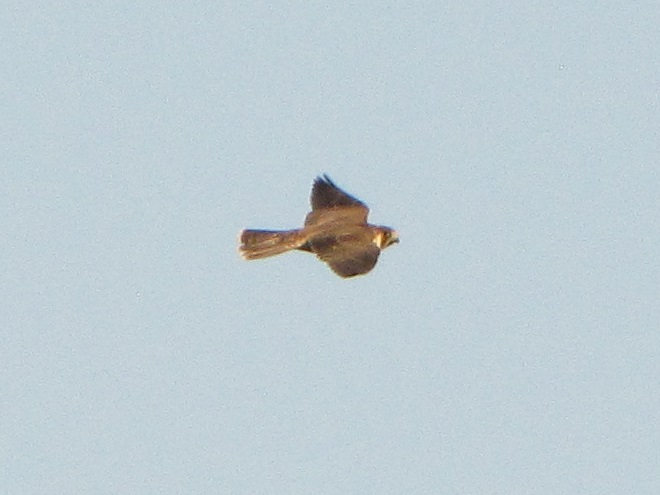
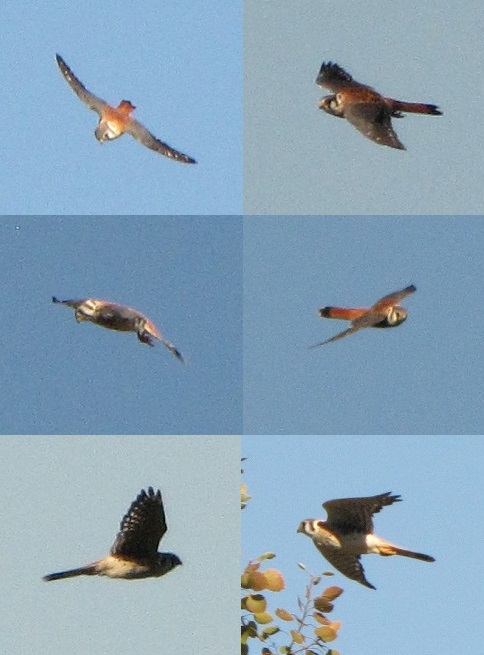
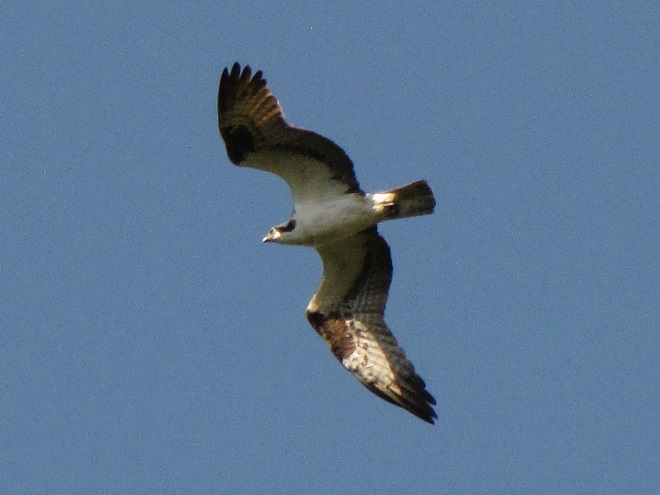
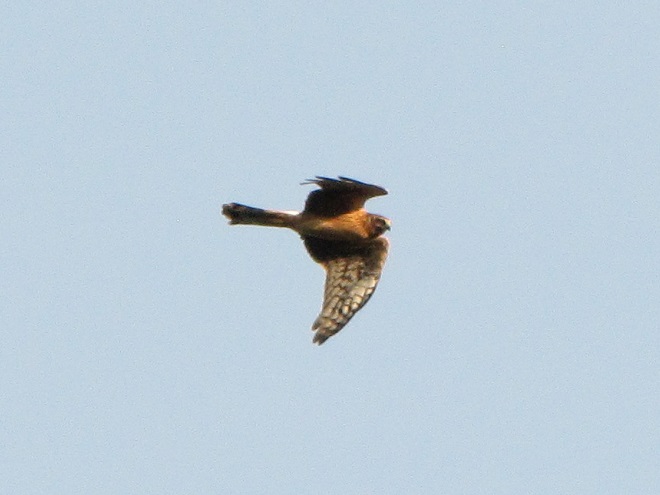
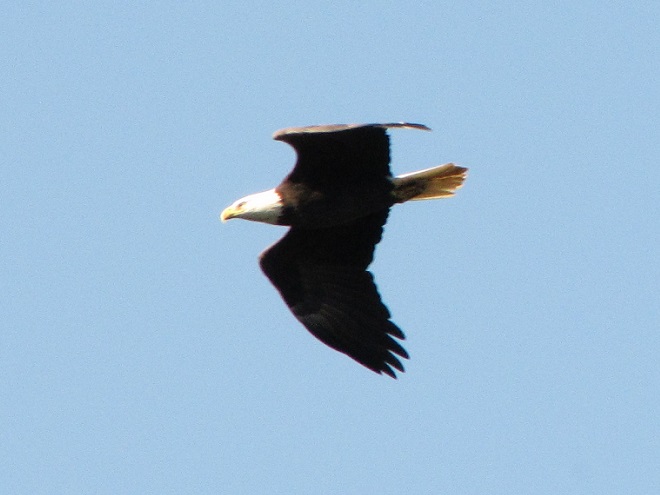
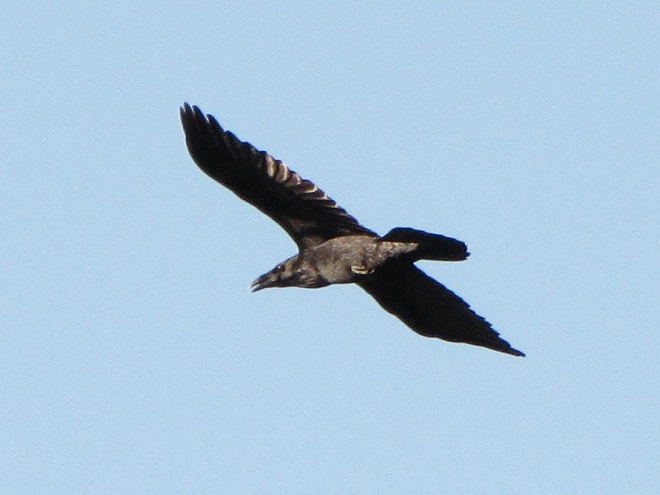
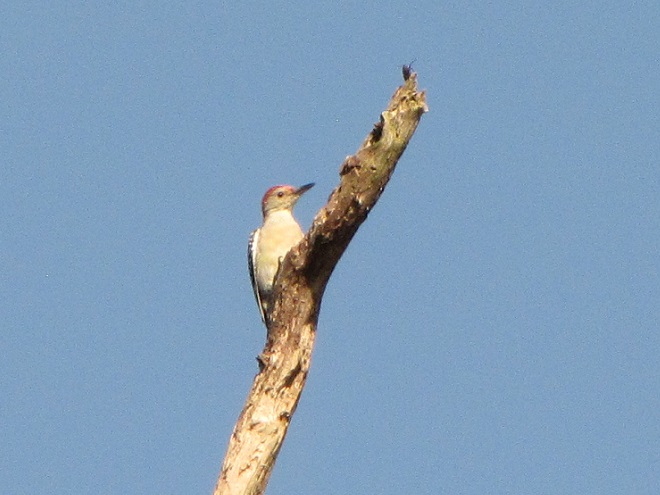
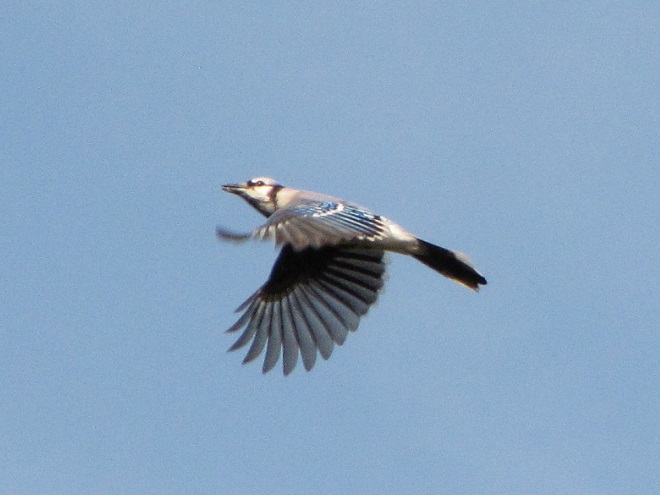



















Be sure to click on these tabs at the top of this page to find image guides to help you identify the dragonflies, birds, and raptors you see in the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed…
See you next time!
During the coming two weeks, peak numbers of migrating Neotropical birds will be passing through the northeastern United States including the lower Susquehanna valley. Hawk watches are staffed and observers are awaiting big flights of Broad-winged Hawks—hoping to see a thousand birds or more in a single day.
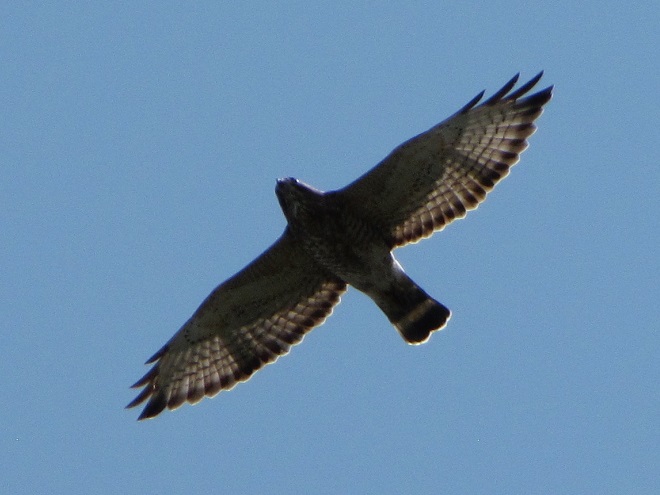
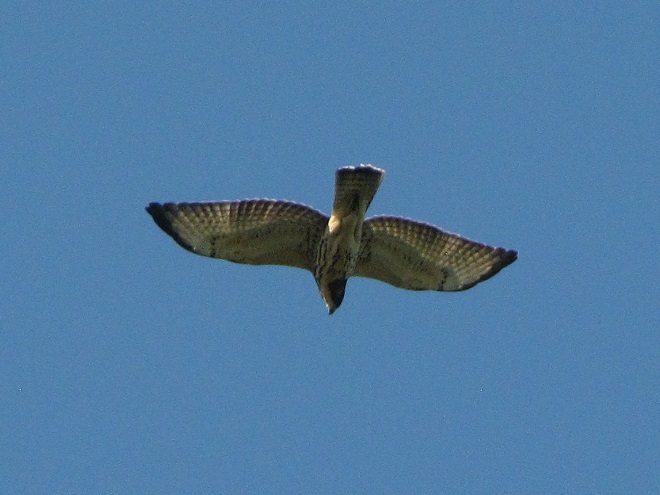


Broad-winged hawks feed on rodents, amphibians, and a variety of large insects while on their breeding grounds in the forests of the northern United States and Canada. They depart early, journeying to wintering areas in Central and South America before frost robs them of a reliable food supply.

While migrating, Broad-winged Hawks climb to great altitudes on thermal updrafts and are notoriously difficult to see from ground level. Bright sunny skies with no clouds to serve as a backdrop further complicate a hawk counter’s ability to spot passing birds. Throughout the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed, the coming week promises to be especially challenging for those trying to observe and census the passage of high-flying Broad-winged Hawks. The forecast of hot and humid weather is not so unusual, but the addition of smoke from fires in the western states promises to intensify the haze and create an especially irritating glare for those searching the skies for raptors.
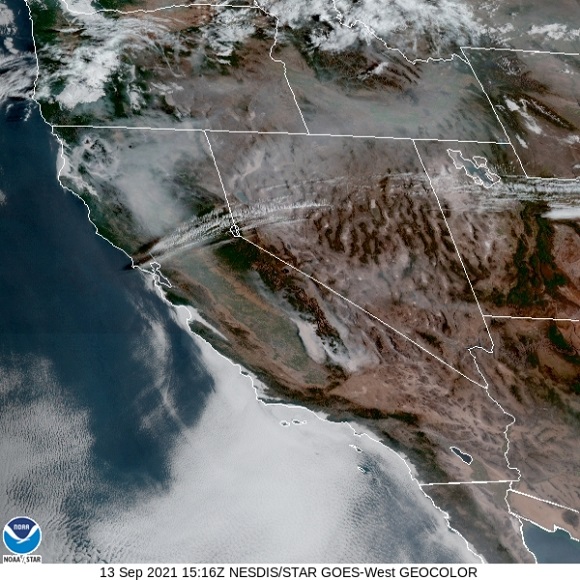

It may seem gloomy for the mid-September flights in 2021, but hawk watchers are hardy types. They know that the birds won’t wait. So if you want to see migrating “Broad-wings” and other species, you’ve got to get out there and look up while they’re passing through.



These hawk watches in the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed are currently staffed by official counters and all welcome visitors:
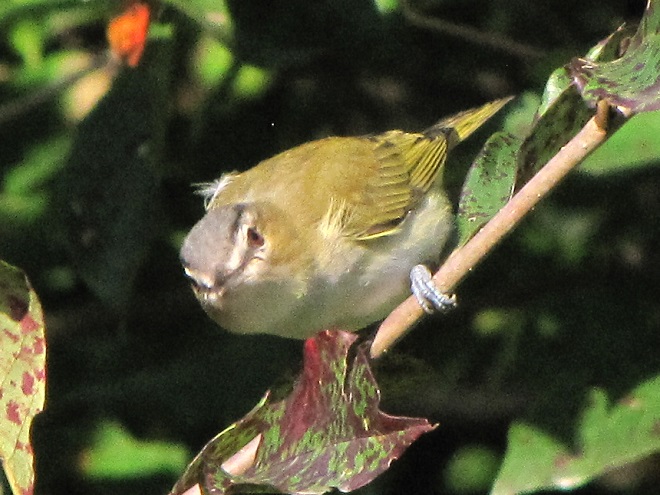
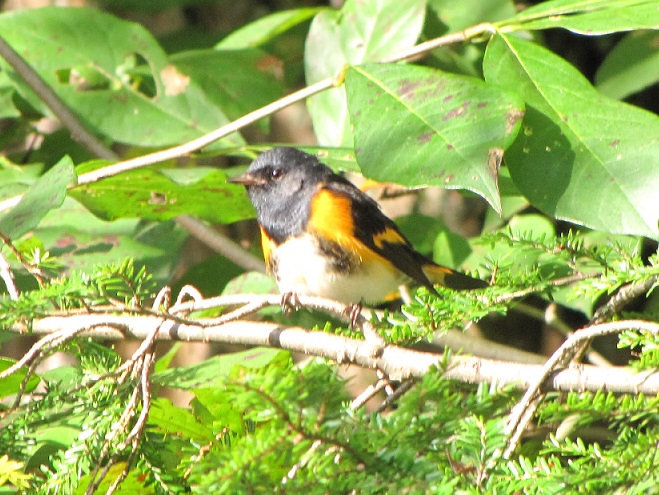
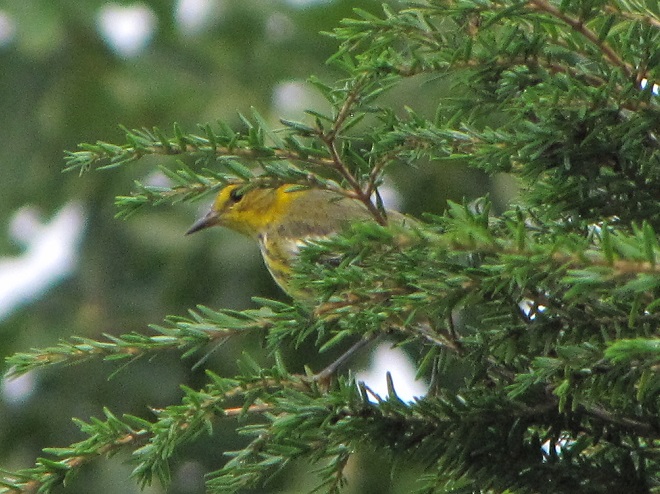
—or you can just keep an eye on the sky from wherever you happen to be. And don’t forget to check the trees and shrubs because warbler numbers are peaking too! During recent days…
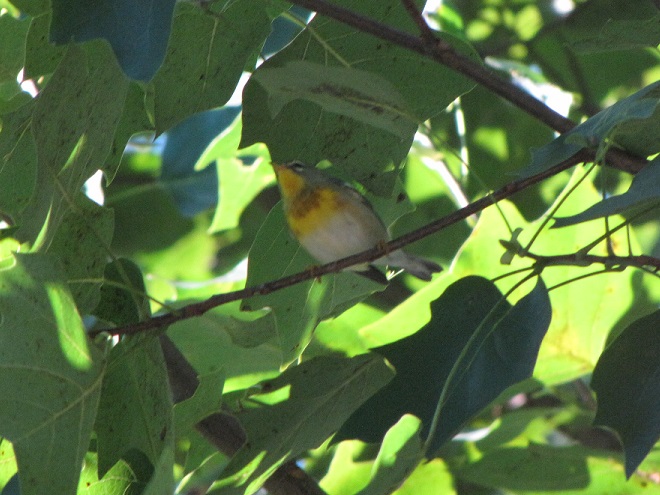
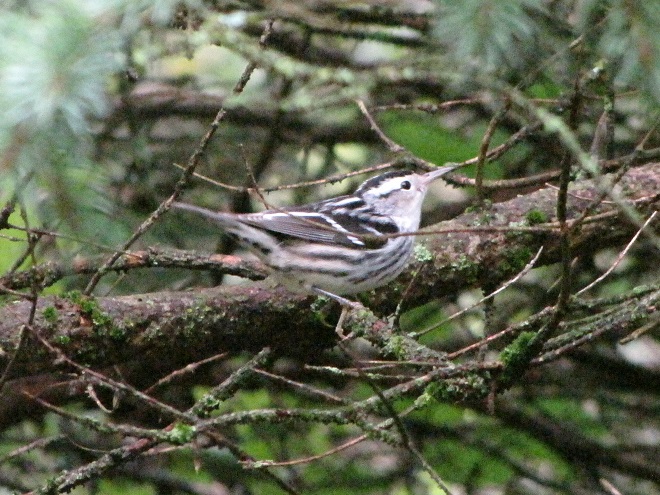
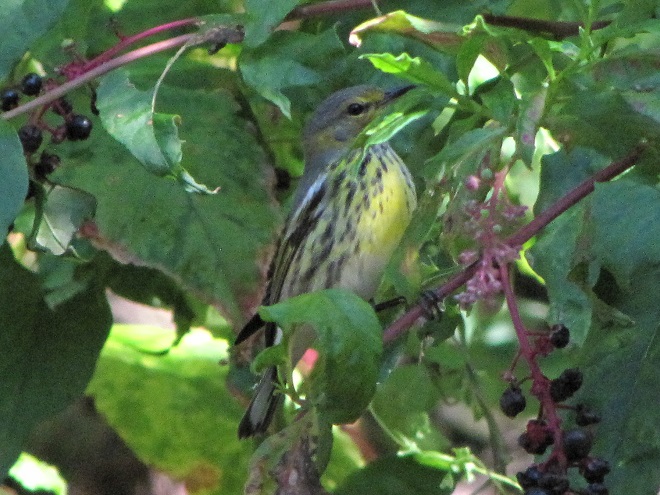
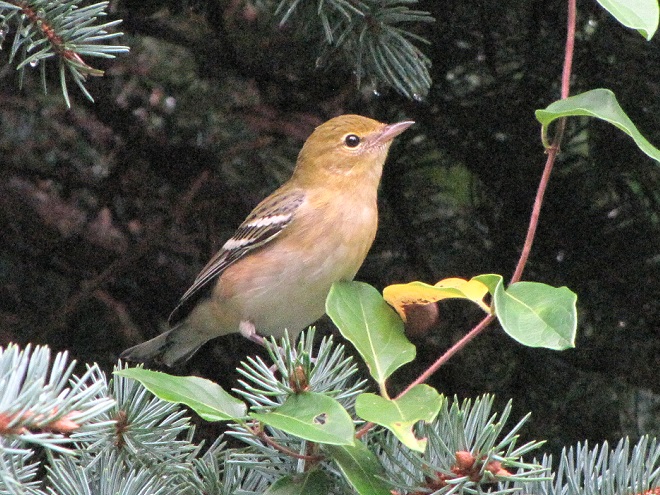




Some of of you may have been wondering why there has been no new content for a while. Well, rest assured that your editor has been replumbed and rewired by some of the best in the business during his recent stay at the Milton S. Hershey Medical Center and he is getting a little stronger every day. More field trips will be on the way soon!
In the meantime, have a look at some of the wide variety of dragonflies gathered along the shoreline at Gifford Pinchot State Park in York County, Pennsylvania. The lake was drained during the winter to perform some maintenance projects and has yet to refill because of the dry spring and early summer we’ve been experiencing. These photos show species seen mostly in the vegetated shallows near the dam.
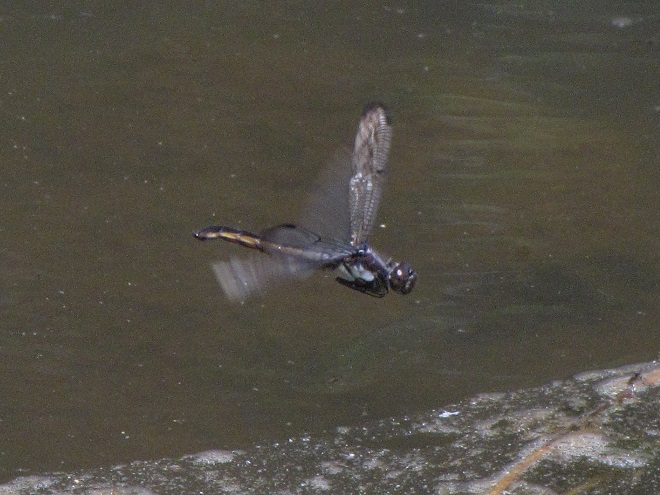
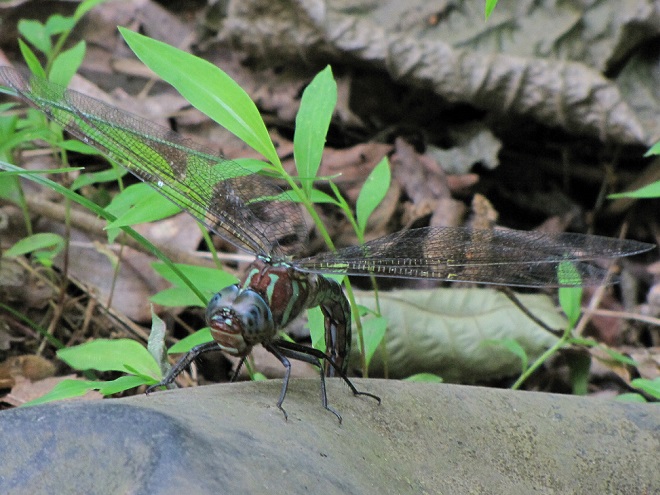
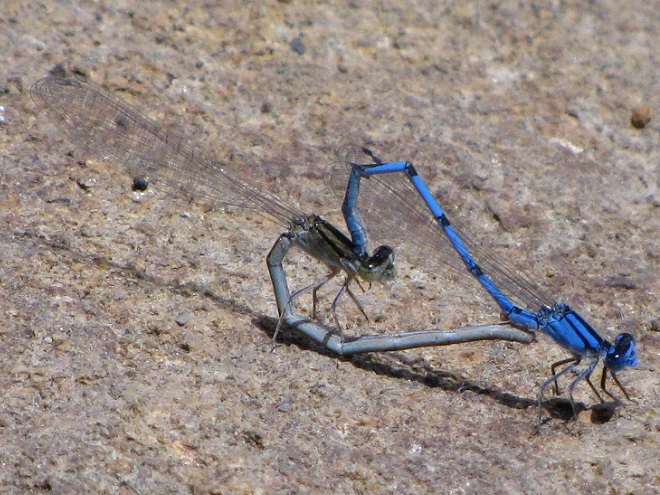
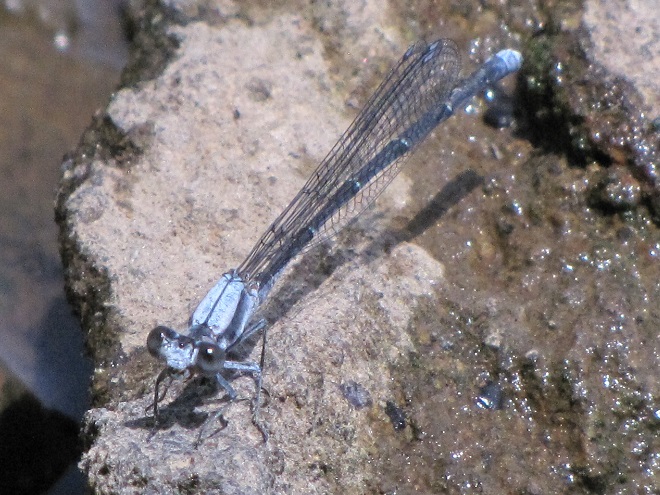
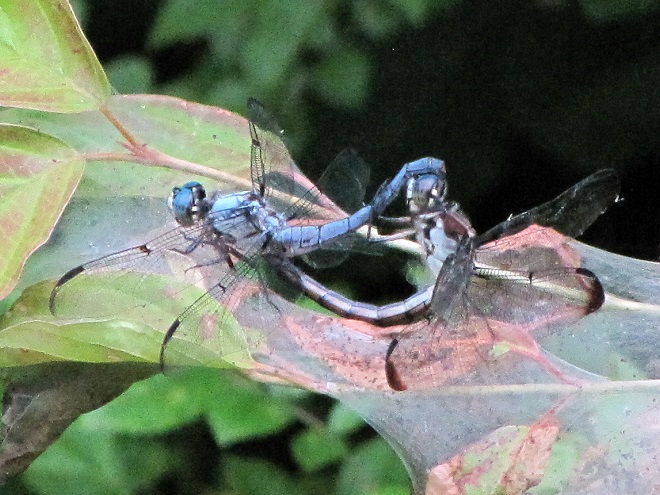
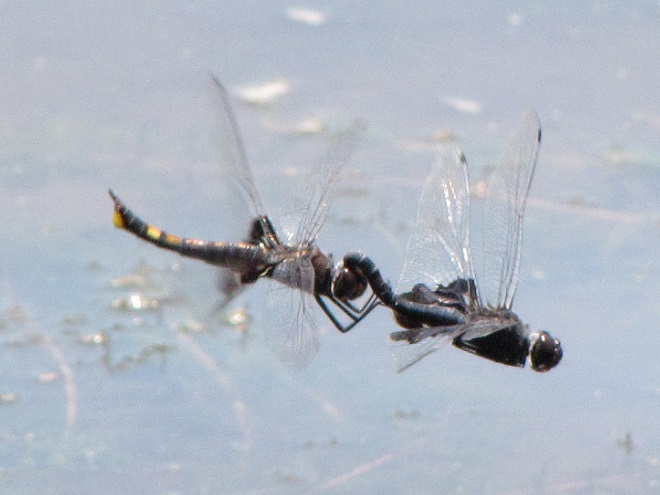












There are lots of others there too. Do have a look.
If it can fly, there’s a pretty good chance it was at Second Mountain today.
What follows is a photographic chronology of some of today’s sightings at Second Mountain Hawk Watch at Fort Indiantown Gap in Lebanon County, Pennsylvania. We begin with some of the hundreds of migratory songbirds found at the base of the mountain along Cold Spring Road near Indiantown Run during the early morning, then we continue to the lookout for the balance of the day.
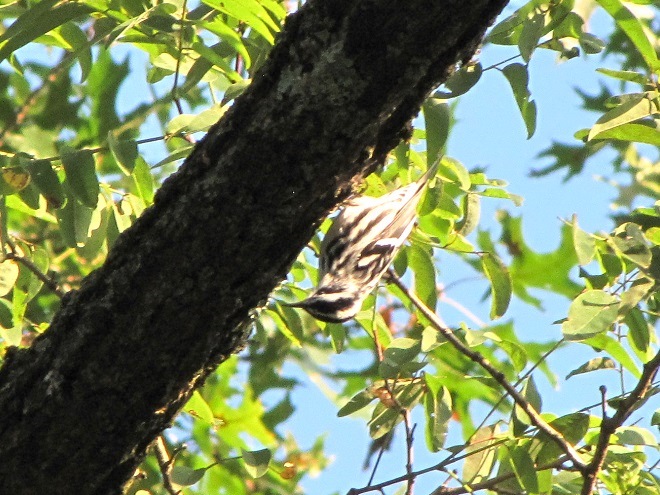
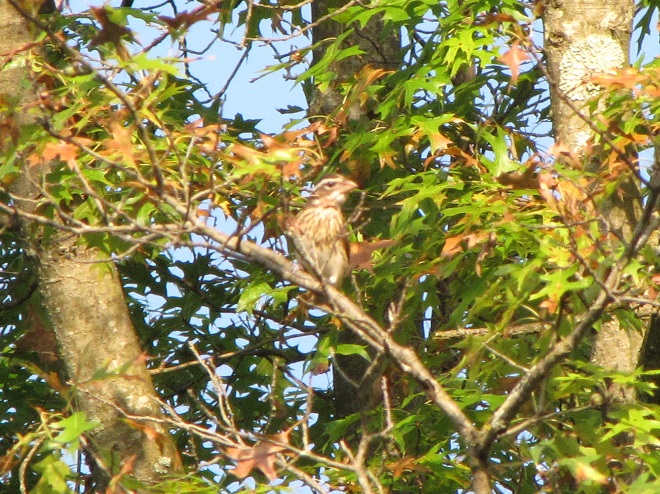
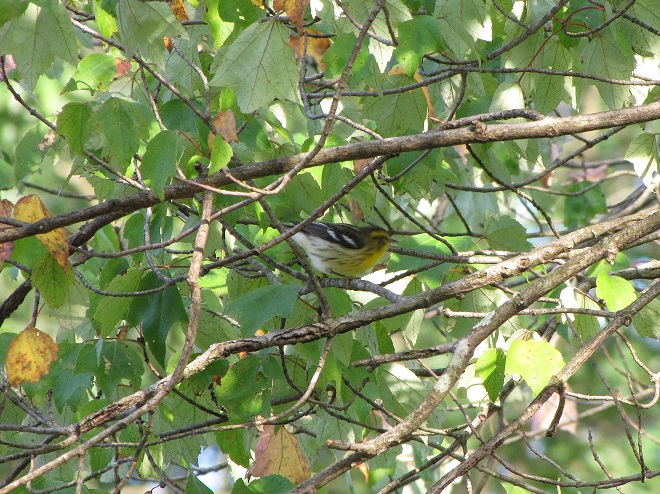
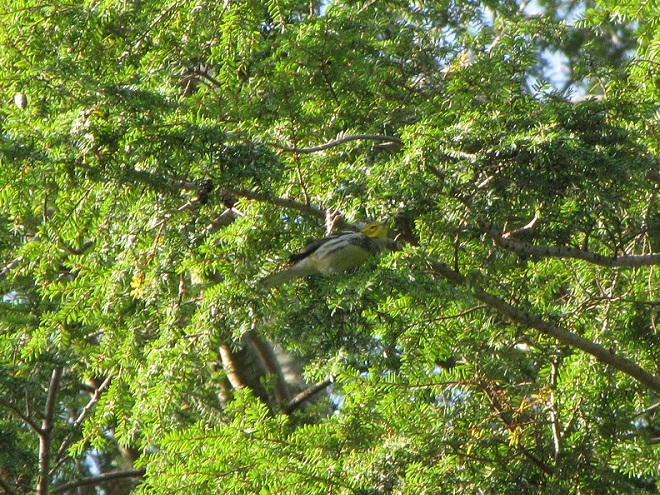
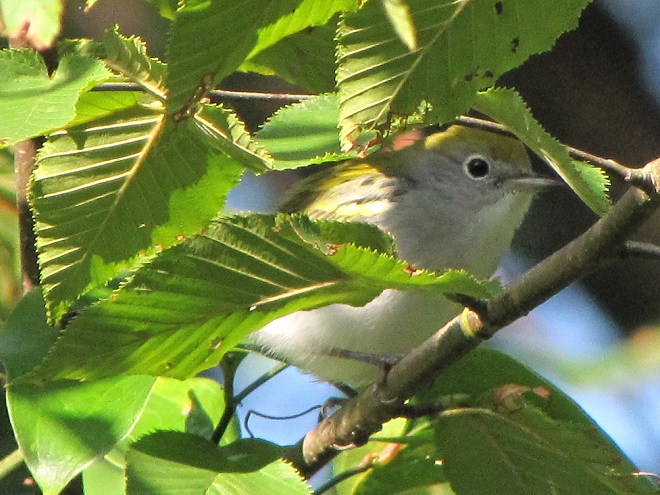
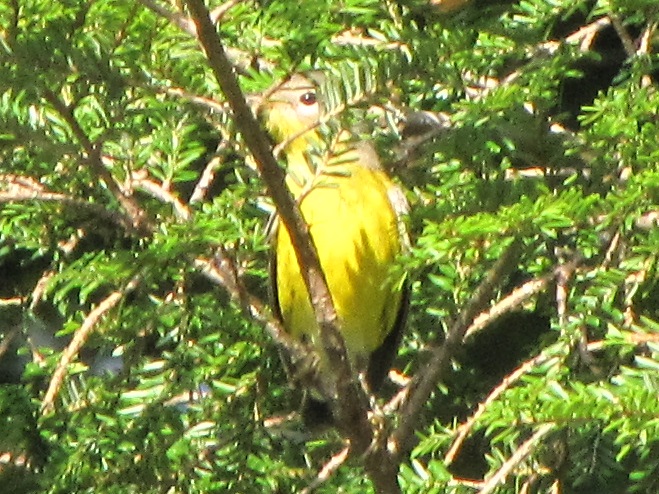
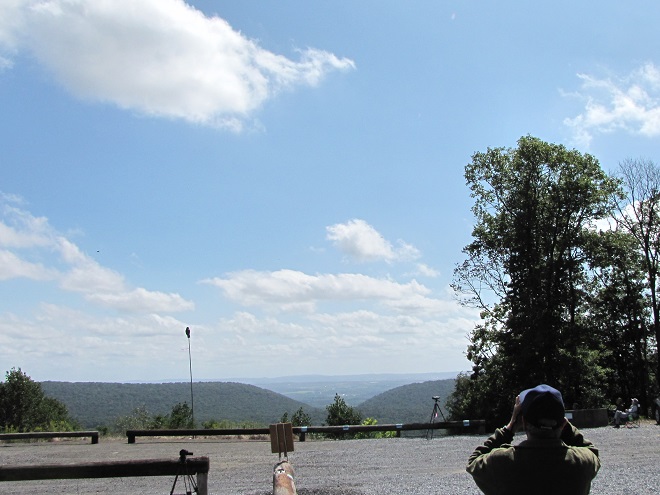
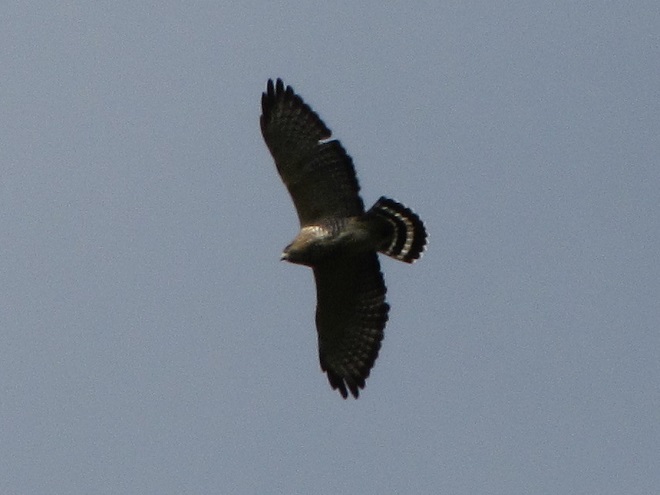
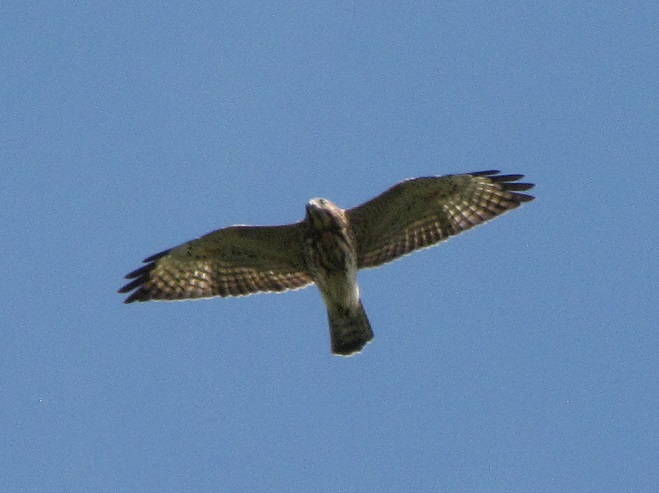
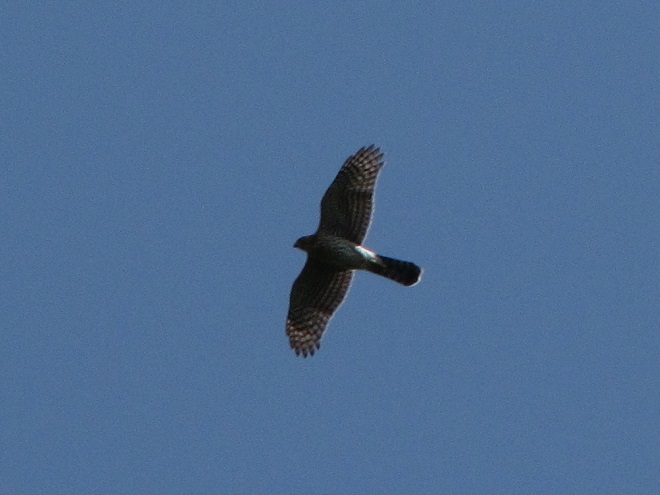
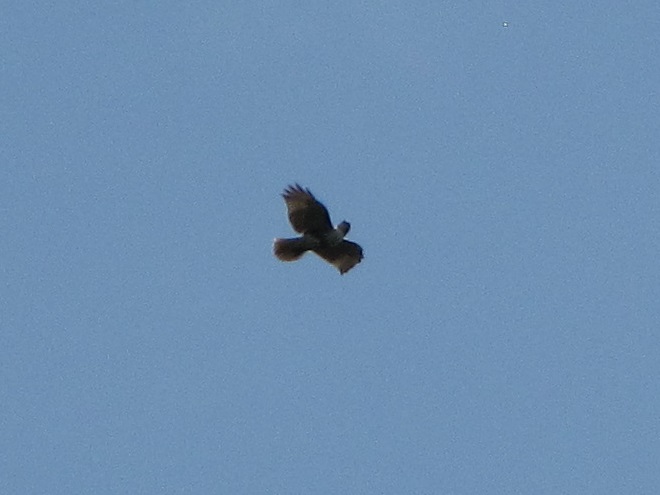
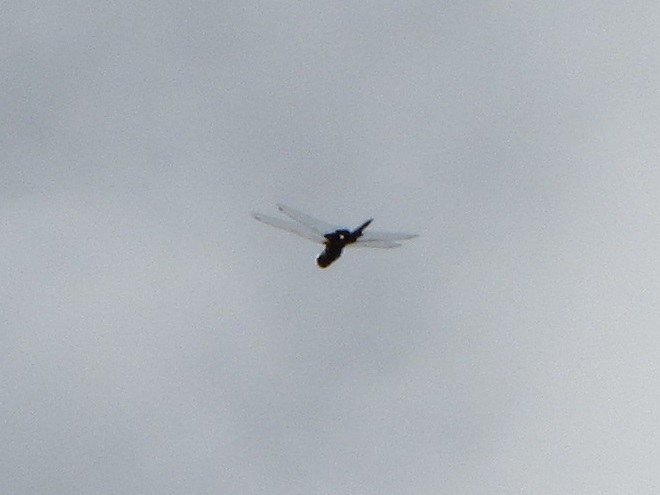
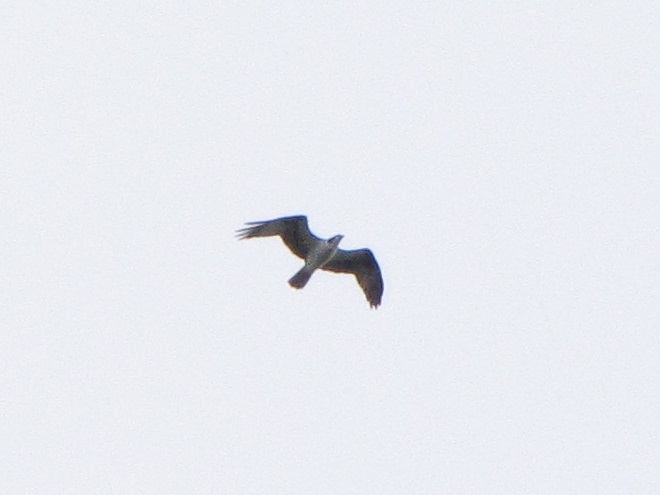
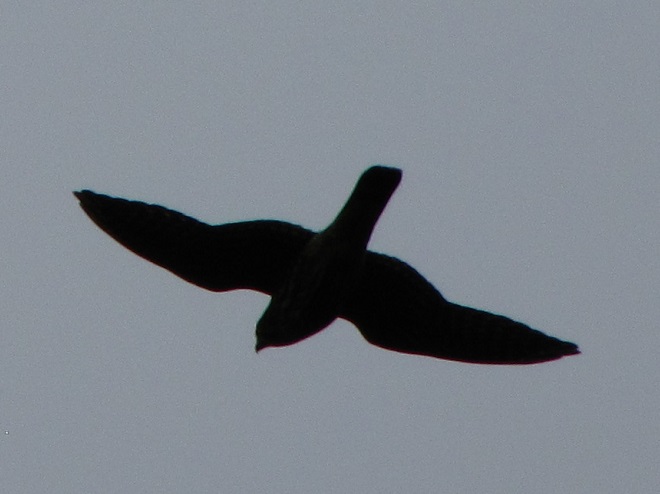
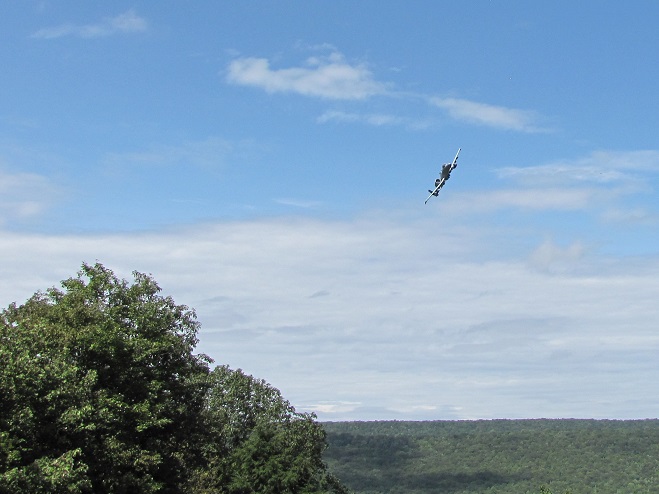
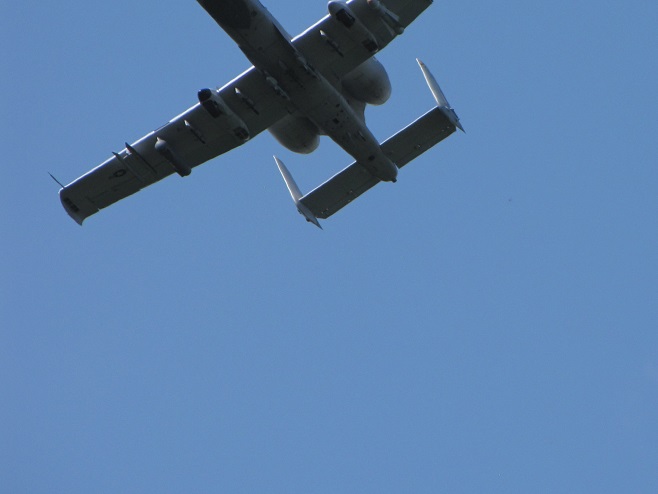
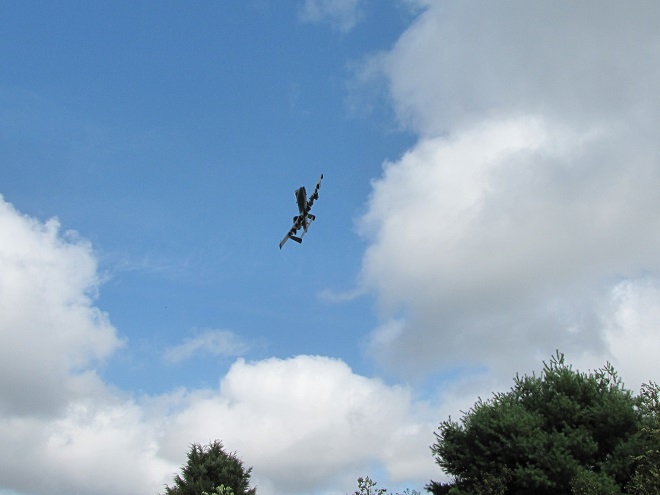
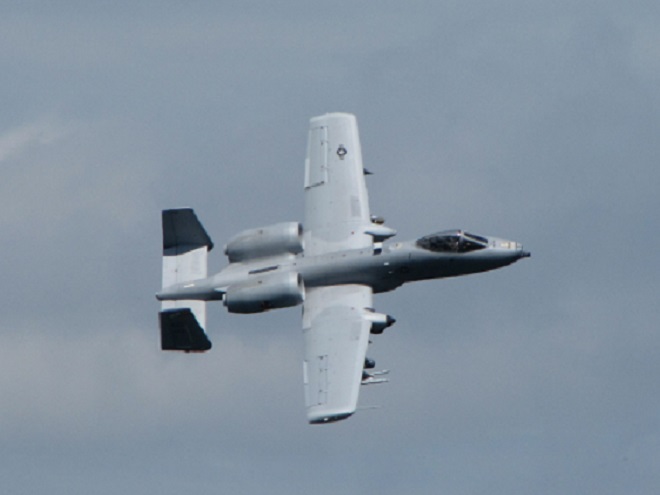

























The total number of Broad-winged Hawks observed migrating past the Second Mountain lookout today was 619. To see the daily raptor counts for Second Mountain and other hawk watches in North America, and to learn more about each site, be sure to visit hawkcount.org
Have the affairs of life got you down?
Feel like you’re not your normal self?
Feel unable to be happy?
Feel alone in your nightmare?
Well, nothing improves one’s demeanor better than seeing someone whose lot is worse than their own.
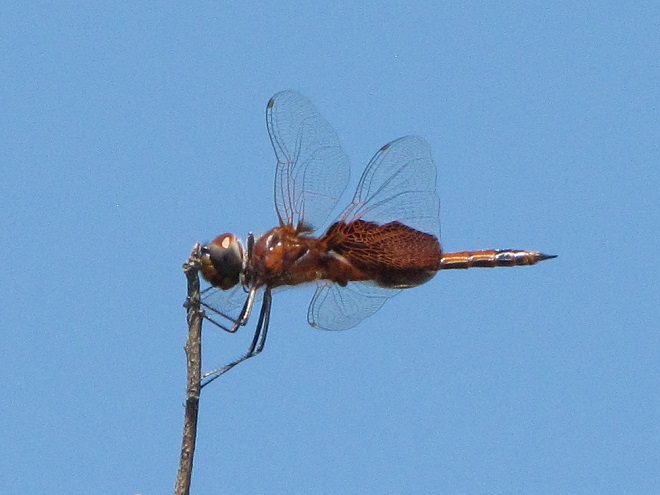
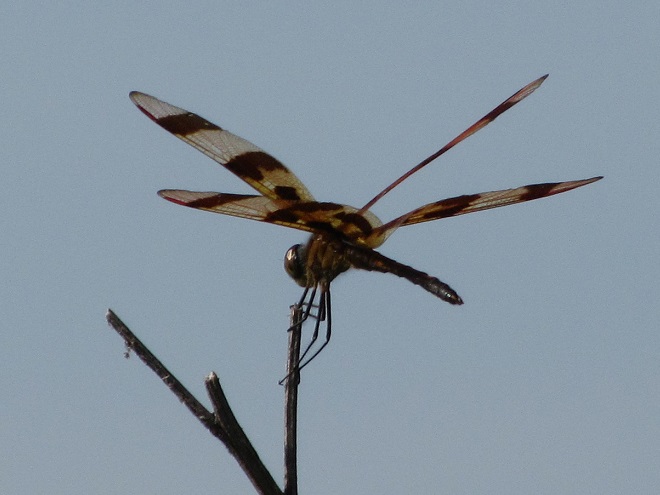
Have a look at this sad-looking Halloween Pennant.
All worn and torn—a shred of its former self. Pitiful. And Halloween is still two and a half months away.
Don’t you feel better now?
It’s been more than a week since Tropical Storm Isaias moved swiftly up the Atlantic seaboard leaving wind and flood damage in its wake. Here in the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed, the brevity of its presence minimized the effects.

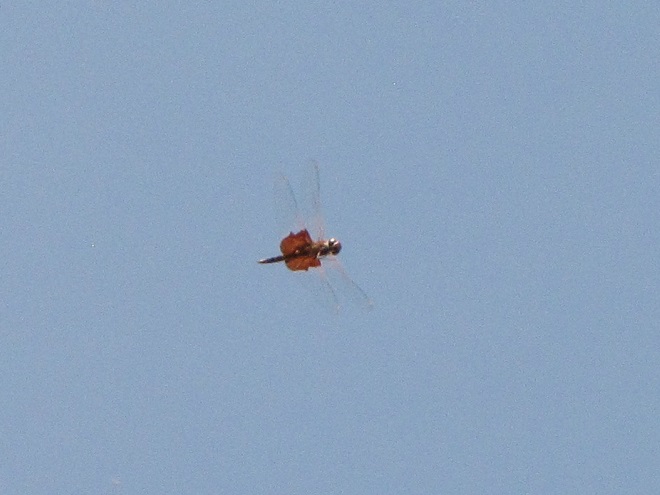
You may have noticed some summertime visitors flying about during these hot humid days that followed Isaias’ passing. They’re the dragonflies.
Our familiar friend the Wandering Glider is widespread throughout the valley right now—dropping eggs on shiny automobile hoods that look to them like a nice quiet puddle of water.
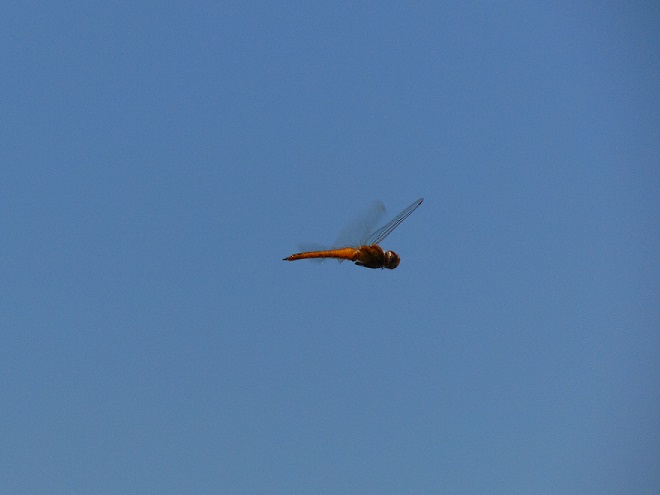

Each of the other common migratory species is here too. Look for them patrolling the skies over large bodies of water and over adjacent fallow land and meadows where tiny flying insects abound. Did these dragonflies arrive on the winds associated with the tropical storm, or did they move in with the waves of warm air that followed it? Probably a little of both.
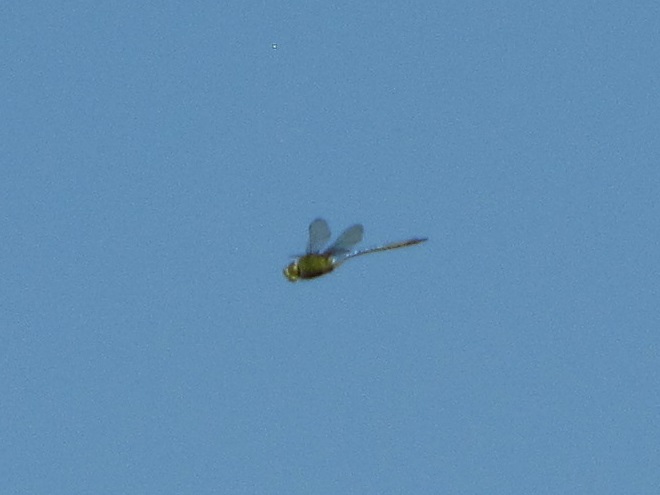
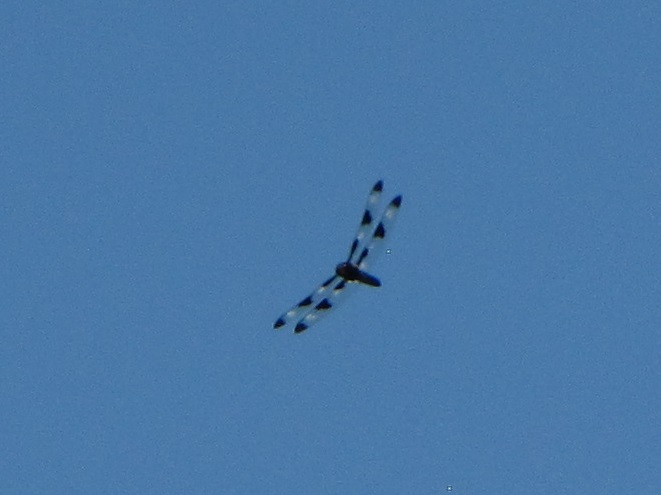
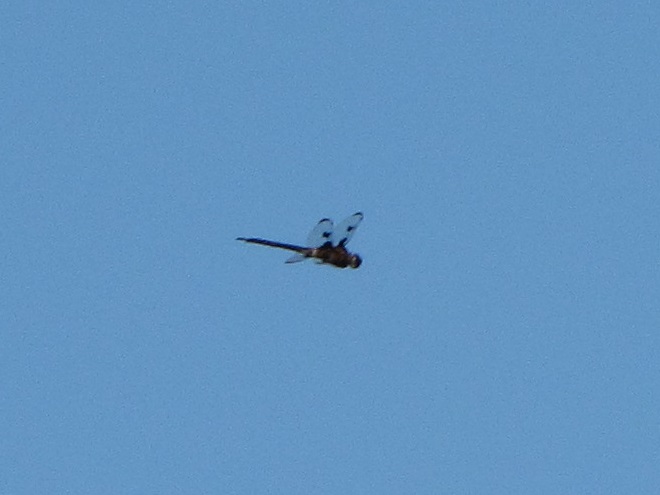




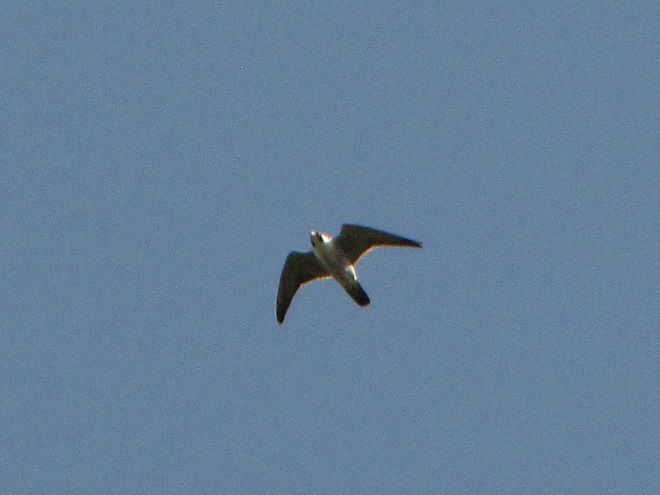
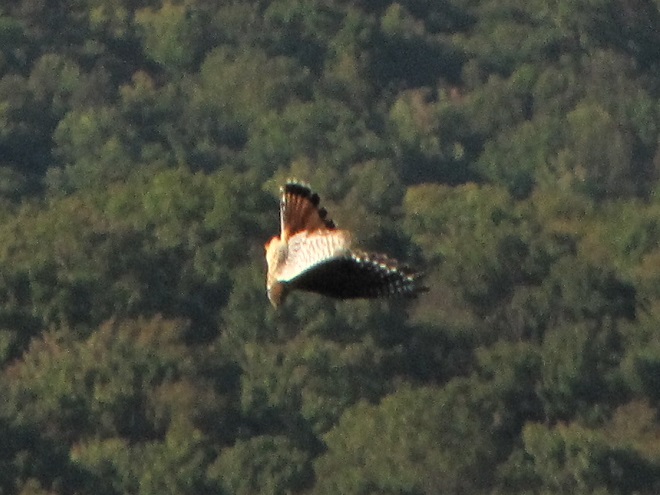
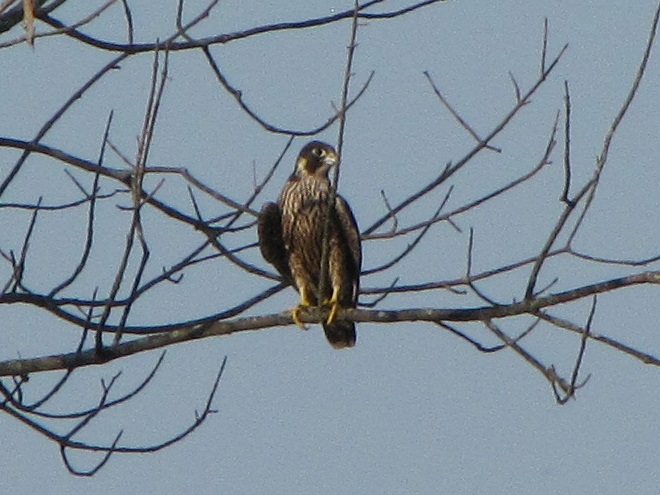
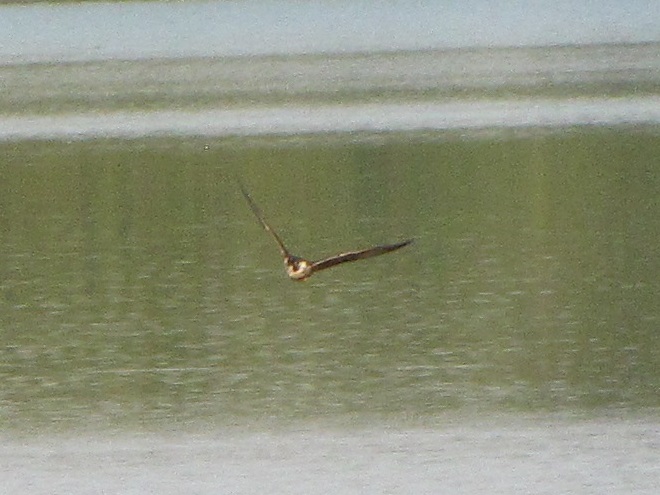
Big swarms of dragonflies don’t go unnoticed by predators—particularly birds. The southbound migration of kites, Broad-winged Hawks, American Kestrels, and Merlins often coincides with the swarming of migratory dragonflies in late summer. Each of these raptors will grab and feed upon these insects while on the wing—so keep an eye on the sky.


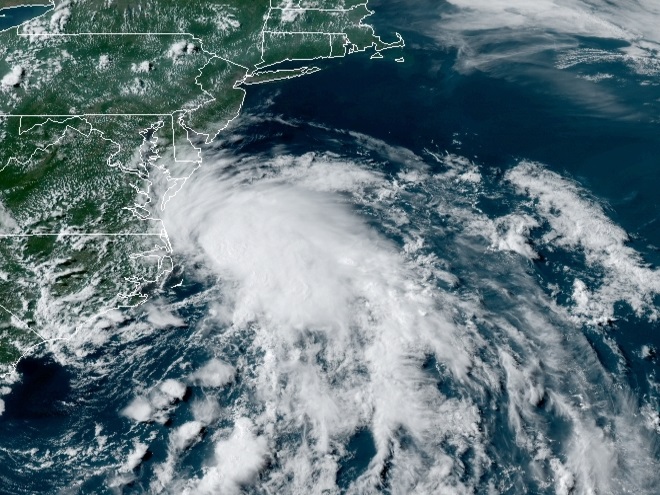
Dust continues to be carried aloft on dry updrafts over the Sahara Desert. The plume is presently stretching for thousands of miles due west across the tropical Atlantic into the Pacific, leaving the United States out of the loop—at least for now.

With no dry air to spoil the fun, the warm waters of the Gulf Stream off the coast of North Carolina are spawning some convective clouds in a low pressure system that could become tropical within the next day or so.

Now that the heat and humidity is upon us, why not get out and take a look at the damselflies and dragonflies that inhabit the ponds, wetlands, and waterways of the lower Susquehanna watershed? These flying insects thrive in sultry weather and some species will breed in a body of water as small as a garden pond—as long as it is free of large fish. Check out some of the species found locally by clicking on the “Damselflies and Dragonflies” tab at the top of this page. We’ll be adding more photos and species soon.

Second Mountain Hawk Watch is located on a ridge top along the northern edge of the Fort Indiantown Gap Military Reservation and the southern edge of State Game Lands 211 in Lebanon County, Pennsylvania. The valley on the north side of the ridge, also known as St. Anthony’s Wilderness, is drained to the Susquehanna by Stony Creek. The valley to the south is drained toward the river by Indiantown Run, a tributary of Swatara Creek.
The hawk watch is able to operate at this prime location for observing the autumn migration of birds, butterflies, dragonflies, and bats through the courtesy of the Pennsylvania Game Commission and the Garrison Commander at Fort Indiantown Gap. The Second Mountain Hawk Watch Association is a non-profit organization that staffs the count site daily throughout the season and reports data to the North American Hawk Watch Association (posted daily at hawkcount.org).
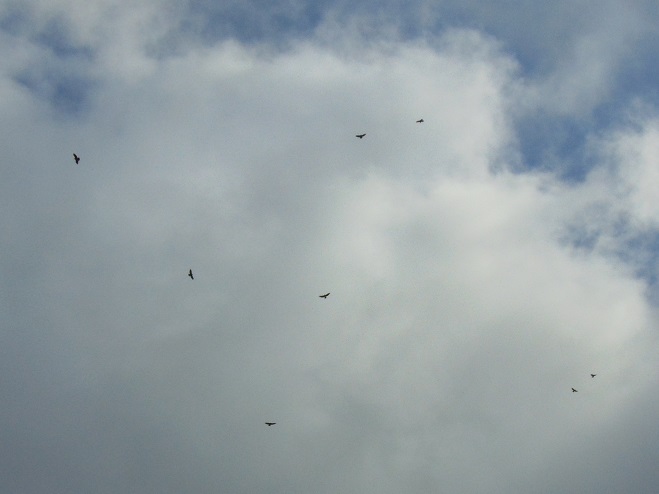
Today, Second Mountain Hawk Watch was populated by observers who enjoyed today’s break in the rainy weather with a visit to the lookout to see what birds might be on the move. All were anxiously awaiting a big flight of Broad-winged Hawks, a forest-dwelling Neotropical species that often travels back to its wintering grounds in groups exceeding one hundred birds. Each autumn, many inland hawk watches in the northeast experience at least one day in mid-September with a Broad-winged Hawk count exceeding 1,000 birds. They are an early-season migrant and today’s southeast winds ahead of the remnants of Hurricane Florence (currently in the Carolinas) could push southwest-heading “Broad-wings” out of the Piedmont Province and into the Ridge and Valley Province for a pass by the Second Mountain lookout.
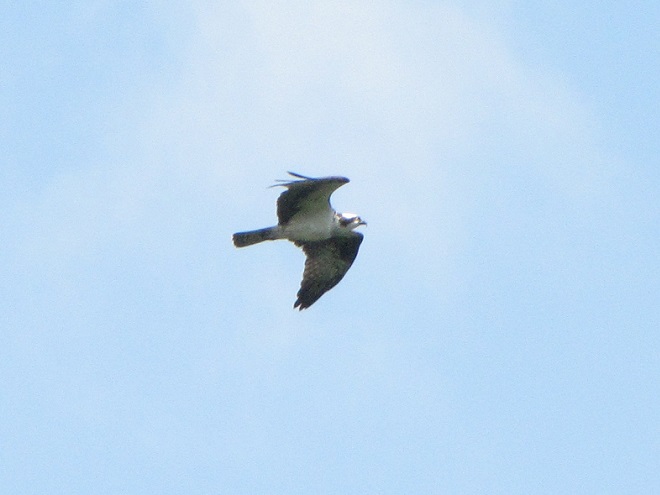
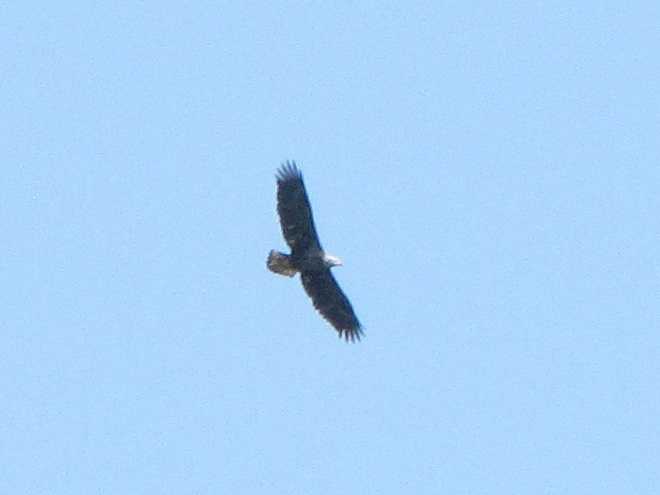
The flight turned out to be steady through the day with over three hundred Broad-winged Hawks sighted. The largest group consisted of several dozen birds. We would hope there are probably many more yet to come after the Florence rains pass through the northeast and out to sea by mid-week. Also seen today were Bald Eagles, Ospreys, American Kestrels, and a migrating Red-headed Woodpecker.

Migrating insects included Monarch butterflies, and the three commonest species of migratory dragonflies: Wandering Glider, Black Saddlebags, and Common Green Darner. The Common Green Darners swarmed the lookout by the dozens late in the afternoon and attracted a couple of American Kestrels, which had apparently set down from a day of migration. American Kestrels and Broad-winged Hawks feed upon dragonflies and often migrate in tandem with them for at least a portion of their journey.
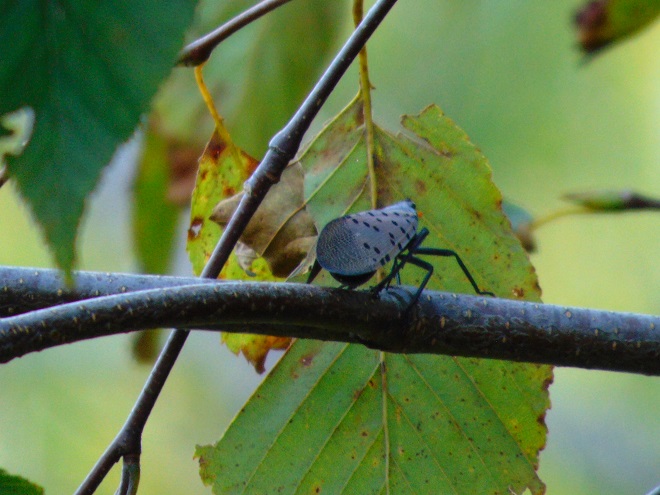
Still later, as the last of the Broad-winged Hawks descended from great heights and began passing by just above the trees looking for a place to settle down, a most unwelcome visitor arrived at the lookout. It glided in from the St. Anthony’s Wilderness side of the ridge on showy crimson-red wings, then became nearly indiscernible from gray tree bark when it landed on a limb. It was the dreaded and potentially invasive Spotted Lanternfly (Lycorma delicatula). This large leafhopper is native to Asia and was first discovered in North America in the Oley Valley of eastern Berks County, Pennsylvania in 2014. The larval stage is exceptionally damaging to cultivated grape and orchard crops. It poses a threat to forest trees as well. Despite efforts to contain the species through quarantine and other methods, it’s obviously spreading quickly. Here on the Second Mountain lookout, we know that wind has a huge influence on the movement of birds and insects. The east and southeast winds we’ve experienced for nearly a week may be carrying Spotted Lanternflies well out of their most recent range and into the forests of the Ridge and Valley Province. We do know for certain that the Spotted Lanternfly has found its way into the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed.

It’s been an atypical summer. The lower Susquehanna River valley has been in a cycle of heavy rains for over a month and stream flooding has been a recurring event. At Conewago Falls, the Pothole Rocks have been inundated for weeks. The location used as a lookout for the Autumn Migration Count last fall is at the moment submerged in ten feet of roaring water. Any attempt to tally the migrants which are passing thru in 2018 will thus be delayed indefinitely. Of greater import, the flooding at Conewago Falls is impacting many of the animals and plants there at a critical time in their annual life cycle. Having been displaced from its usual breeding sites on the river, one insect species in particular seems to be omnipresent in upland areas right now, and few people have ever heard of it.
So, you take a cruise in the motorcar to your favorite store and arrive at the sprawling parking lot. Not wishing to have your doors dented or paint chipped because you settled for a space tightly packed among other shopper’s conveyances, you park out there in the “boondocks”. You know the place, the lightly-used portion of the lot where sometimes brush grows from cracks in the asphalt and you must be on alert for impatient consumers who throttle-up to high speeds and dash diagonally across the carefully painted grids on the pavement to reach their favorite parking destination in the front row. Coming to a stop, you take the car out of gear, set the brake, disengage the safety belt, and gather your shopping list. You grasp the door handle and, not wanting to be flattened by one of the aforementioned motorists, you have a look around before exiting.
It was then that you saw the thing, hovering above your shiny bright hood. For a brief moment, it seemed to be peering right through the windshield at you with big reddish-brown eyes. In just a second or two, it turned its whole bronze body ninety degrees to the left and darted away on its cellophane wings. Maybe you didn’t really get a good look at it. It was so fast. But it certainly was odd. Oh well, time to walk inside a grab a few provisions. Away you go.
Upon completion of your shopping, you’re taking the long stroll back to your car and you notice more of these peculiar creatures. Two are coupled together and are hovering above someone’s automobile hood, then they drop down, and the lower of the two taps its abdomen on the paint. You ask yourself, “What are these bizarre things?”
Meet the Wandering Glider (Pantala flavescens), also known as the Globe Wanderer or Globe Skimmer, a wide-ranging dragonfly known to occur on every continent with the exception of Antarctica.
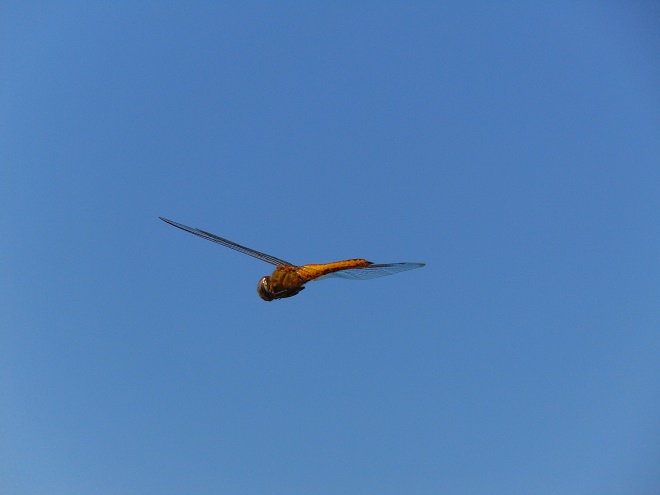

Wandering Gliders travel the globe, and as such are accomplished fliers. Adults spend most of the day on the wing, feeding upon a variety of flying insects. Days ago, I watched several intercepting a swarm of flying ants. As fast as ants left the ground they were grabbed and devoured by the gliders. Wandering Gliders are adept at taking day-flying mosquitos, often zipping stealthily past a person’s head or shoulders to grab one of the little pests—the would-be skeeter victim usually unaware of the whole affair.
Due to their nomadic life history, Wandering Gliders are opportunists when breeding and will lay eggs in most any body of freshwater. Their larvae do not overwinter prior to maturity; adults can be expected in a little more than one to two months. Repetitive flooding in the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed this summer may be reducing the availability of the best local breeding sites for this species—riverine, stream, and floodplain pools of standing water with prey. This may explain why thousands of Wandering Gliders are patrolling parking lots, farmlands, and urban areas this summer. And it’s the likely reason for their use of puddles on asphalt pavement, on rubber roofs, and in fields as places to try to deposit eggs. Unfortunately, they may be as likely to succeed there as they are on your motor vehicle hood.
At this time a year ago, the airspace above the Diabase Pothole Rocks at Conewago Falls was jammed with territorial male Wandering Gliders. Each male hovered at various locations around his breeding territory consisting of pools and water-filled potholes. Intruders would quickly be dispatched from the area, then the male would resume his patrols from a set of repetitively-used hovering positions about six feet above the rocks. Mating and egg-laying continued into late September. The larvae, also called nymphs or naiads, were readily observed in many pools and potholes in early October and the emergence of juveniles was noted in mid-October. The absence of flooding, the mild autumn weather, and the moderation of water temperatures in the pools and potholes courtesy of the sun-drenched diabase boulders helped to extend the 2017 breeding season for Wandering Gliders in Conewago Falls. They aren’t likely to experience the same favor this year, but their great ability to travel and adapt should overcome this momentary misfortune.
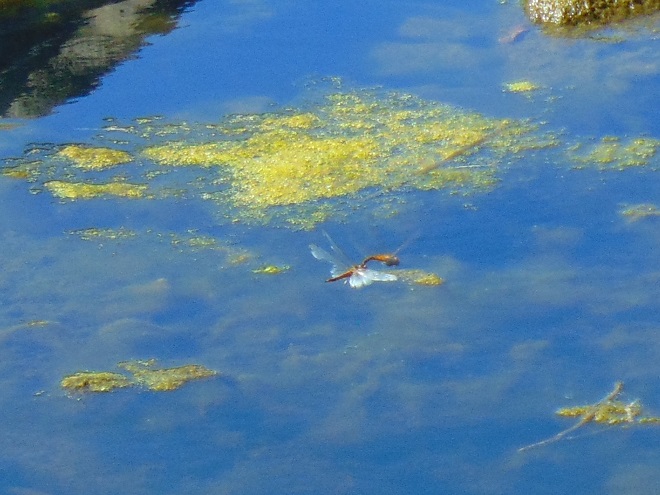
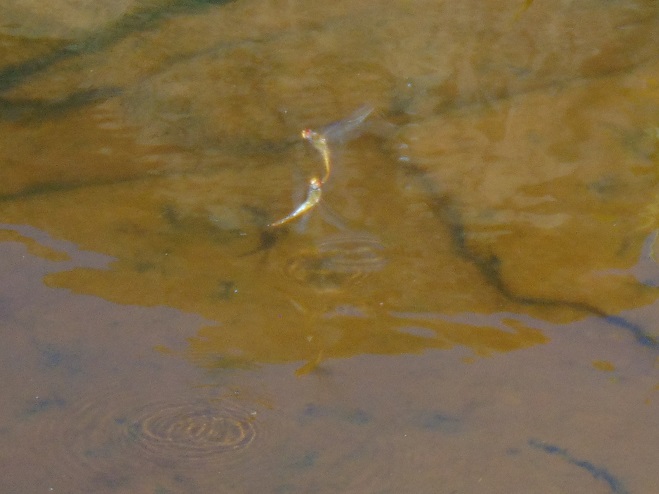
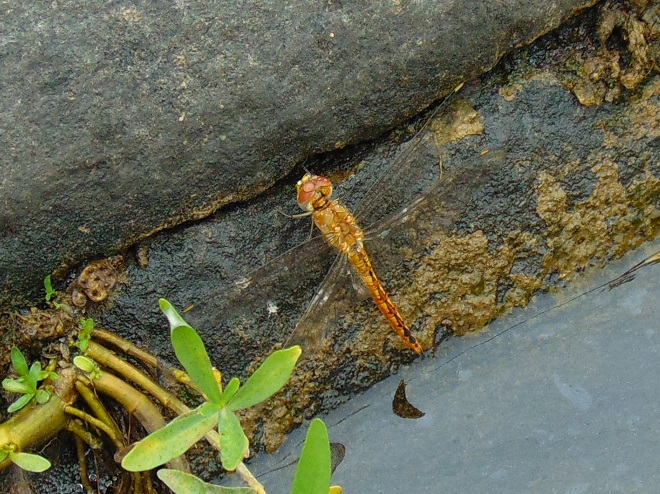






The humid rainy remains of Hurricane Nate have long since passed by Pennsylvania, yet mild wet weather lingers to confuse one’s sense of the seasons. This gloomy misty day was less than spectacular for watching migrating birds and insects, but some did pass by. Many resident animals of the falls are availing themselves of the opportunity to continue active behavior before the cold winds of autumn and winter force a change of lifestyle.
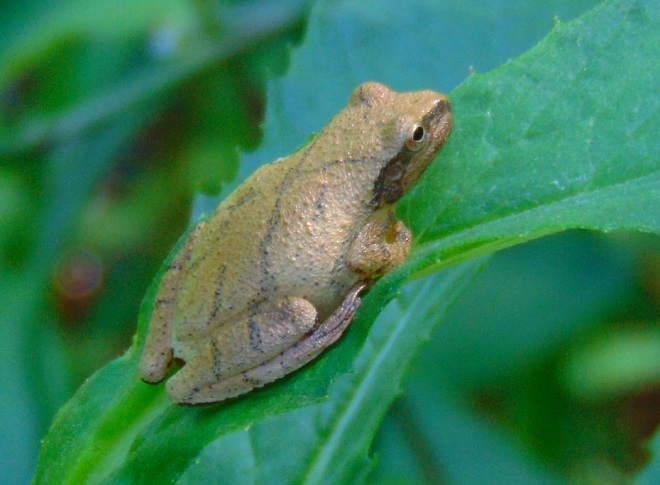
Warm drizzle at daybreak prompted several Northern Spring Peepers (Pseudacris crucifer crucifer) to begin calling from the wetlands in the Riparian Woodlands of Conewago Falls. An enormous chorus of these calls normally begins with the first warm rains of early spring to usher in this tiny frog’s mating season. Today, it was just a few “peeps” among anxious friends.

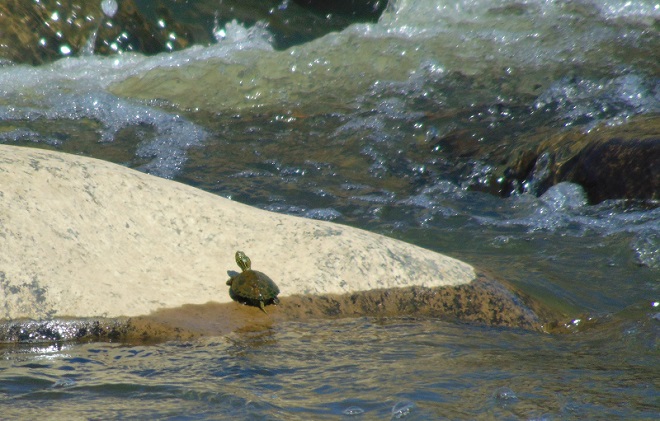
Any additional river flow that resulted from the rains of the previous week is scarcely noticeable among the Pothole Rocks. The water level remains low, the water column is fairly clear, and the water temperatures are in the 60s Fahrenheit.
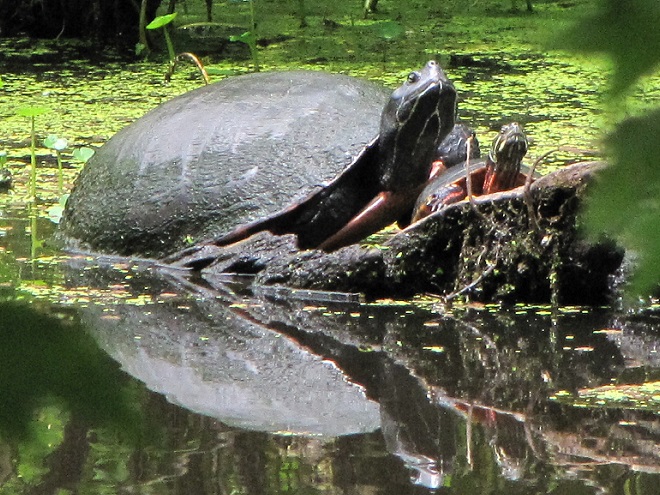
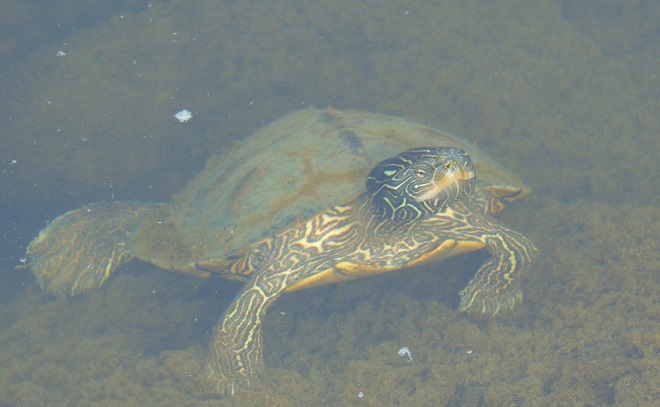
It’s no real surprise then to see aquatic turtles climbing onto the boulders in the falls to enjoy a little warmth, if not from the sun, then from the stored heat in the rocks. As usual, they’re quick to slide into the depths soon after sensing someone approaching or moving nearby. Seldom found anywhere but on the river, these skilled divers are Common Map Turtles (Graptemys geographica), also known as Northern Map Turtles. Their paddle-like feet are well adapted to swimming in strong current. They are benthic feeders, feasting upon a wide variety of invertebrates found among the stone and substrate of the river bottom.
Adult Common Map Turtles hibernate communally on the river bottom in a location protected from ice scour and turbulent flow, often using boulders, logs, or other structures as shelter from strong current. The oxygenation of waters tumbling through Conewago Falls may be critical to the survival of the turtles overwintering downstream. Dissolved oxygen in the water is absorbed by the nearly inactive turtles as they remain submerged at their hideout through the winter. Though Common Map Turtles, particularly males, may occasionally move about in their hibernation location, they are not seen coming to the surface to breathe.
The Common Map Turtles in the Susquehanna River basin are a population disconnected from that found in the main range of the species in the Great Lakes and upper Mississippi basin. Another isolated population exists in the Delaware River.



SOURCES
Committee on the Status of Endangered Wildlife in Canada. 2002. Status Report of the Northern Map Turtle. Canadian Wildlife Service. Ottawa, Ontario.
A moderate breeze from the south placed a headwind into the face of migrants trying to wing their way to winter quarters. The urge to reach their destination overwhelmed any inclination a bird or insect may have had to stay put and try again another day.
Blue Jays were joined by increasing numbers of American Robins crossing the river in small groups to continue their migratory voyages. Killdeer (Charadrius vociferous) and a handful of sandpipers headed down the river route. Other migrants today included a Cooper’s Hawk (Accipiter cooperii), Eastern Bluebirds (Sialia sialis), and a few Common Mergansers (Mergus merganser), House Finches (Haemorhous mexicanus), and Common Grackles (Quiscalus quiscula).
The afternoon belonged to the insects. The warm wind blew scores of Monarchs toward the north as they persistently flapped on a southwest heading. Many may have actually lost ground today. Painted Lady (Vanessa cardui) and Cloudless Sulphur butterflies were observed battling their way south as well. All three of the common migrating dragonflies were seen: Common Green Darner (Anax junius), Wandering Glider (Pantala flavescens), and Black Saddlebags (Tramea lacerata).
The warm weather and summer breeze are expected to continue as the rain and wind from Hurricane Nate, today striking coastal Alabama and Mississippi, progresses toward the Susquehanna River watershed during the coming forty-eight hours.


