Photo of the Day


LIFE IN THE LOWER SUSQUEHANNA RIVER WATERSHED
A Natural History of Conewago Falls—The Waters of Three Mile Island

To pass the afternoon, we sat quietly along the edge of a pond created recently by North American Beavers (Castor canadensis). They first constructed their dam on this small stream about five years ago. Since then, a flourishing wetland has become established. Have a look.
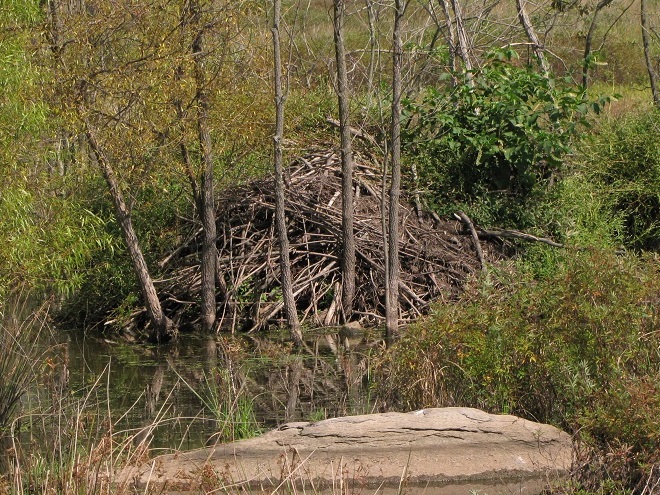















Isn’t that amazing? North American Beavers build and maintain what human engineers struggle to master—dams and ponds that reduce pollution, allow fish passage, and support self-sustaining ecosystems. Want to clean up the streams and floodplains of your local watershed? Let the beavers do the job!
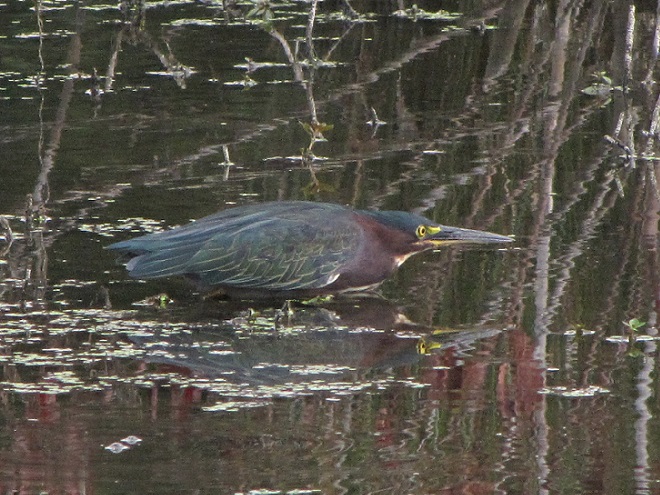
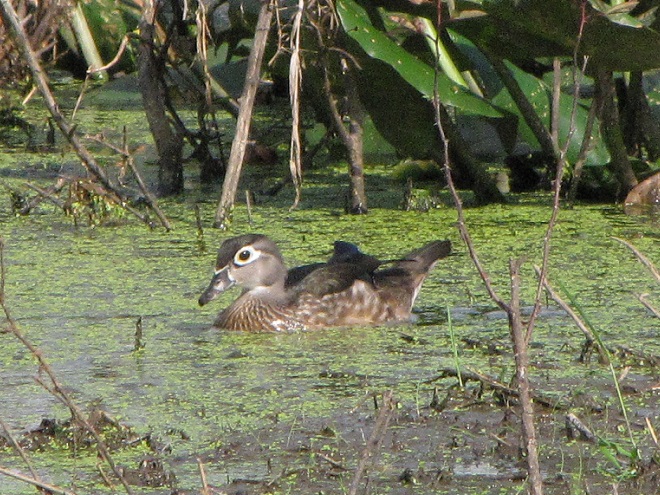
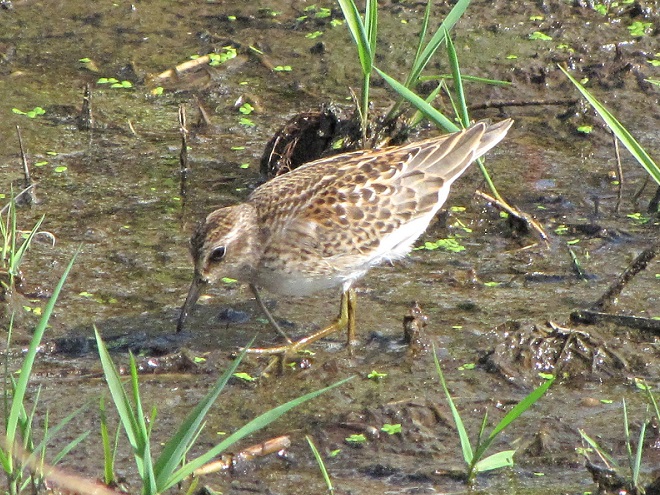
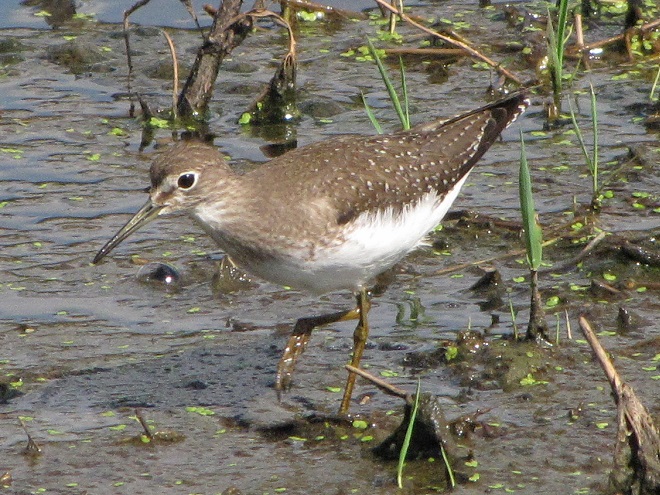
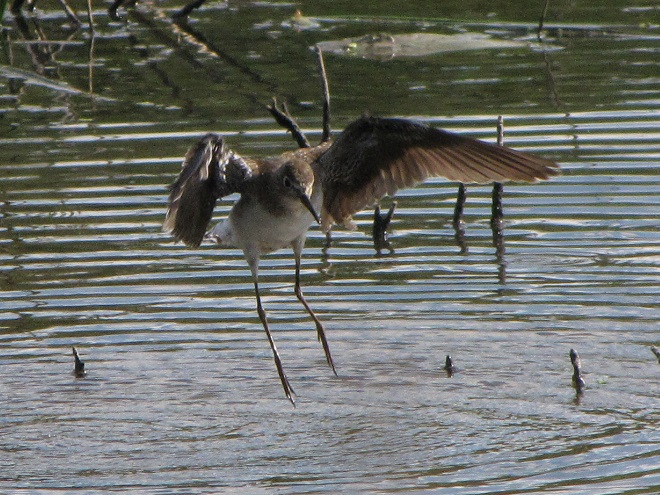
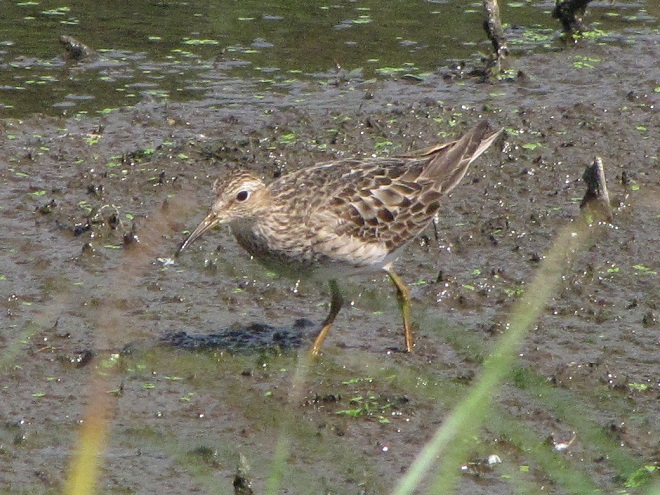
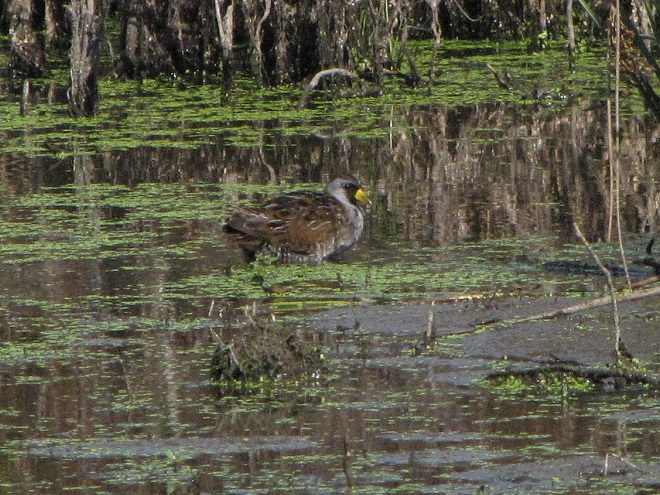
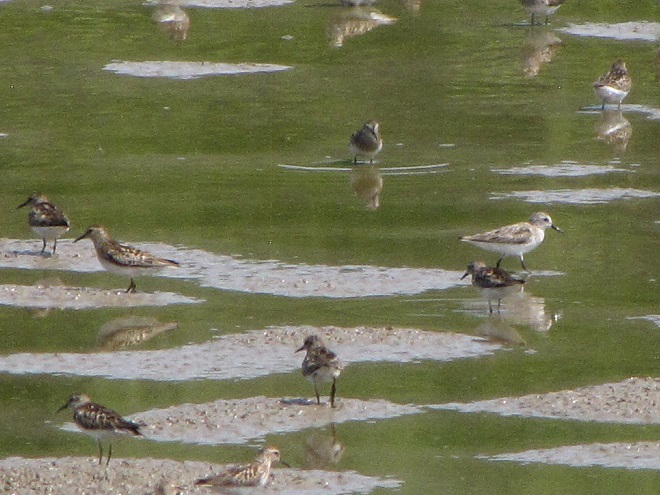
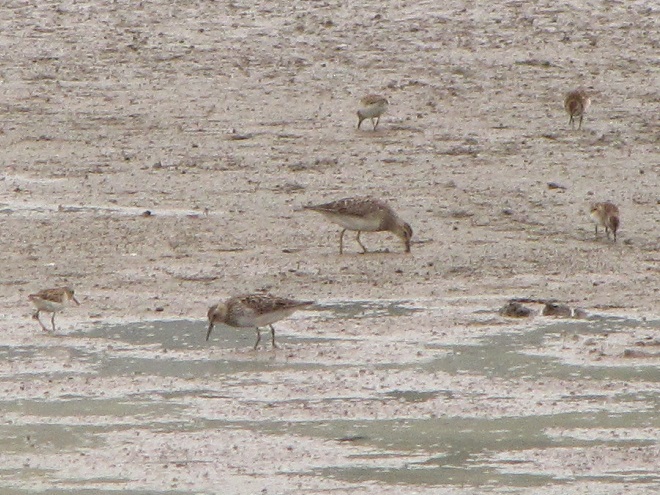
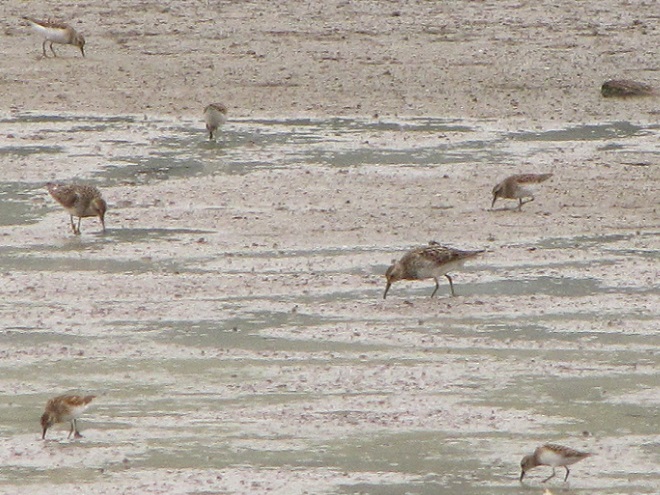
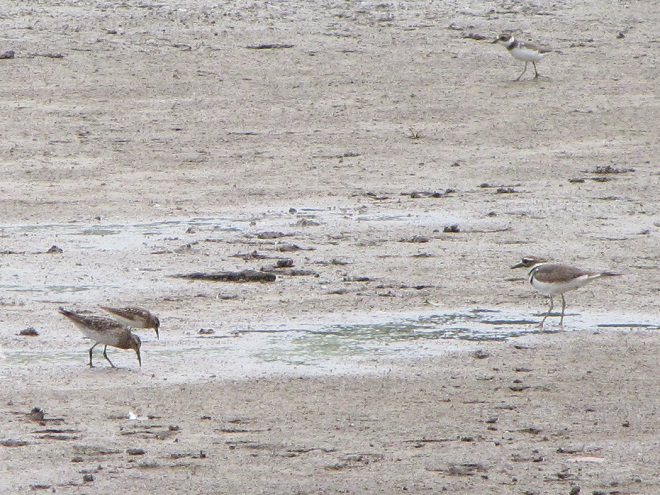
Your best bet for finding migrating shorebirds in the lower Susquehanna region is certainly a visit to a sandbar or mudflat in the river. The Conejohela Flats off Washington Boro just south of Columbia is a renowned location. Some man-made lakes including the one at Middle Creek Wildlife Management Area are purposely drawn down during the weeks of fall migration to provide exposed mud and silt for feeding and resting sandpipers and plovers. But with the Susquehanna running high due to recent rains and the cost of fuel trending high as well, maybe you want to stay closer to home to do your observing.
Fortunately for us, migratory shorebirds will drop in on almost any biologically active pool of shallow water and mud that they happen to find. This includes flooded portions of fields, construction sites, and especially stormwater retention basins. We stopped by a new basin just west of Hershey, Pennsylvania, and found more than two dozen shorebirds feeding and loafing there. We took each of these photographs from the sidewalk paralleling the south shore of the pool, thus never flushing or disturbing a single bird.
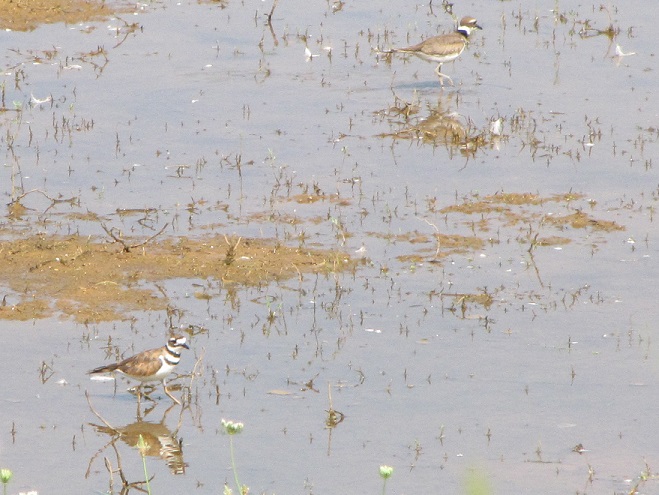
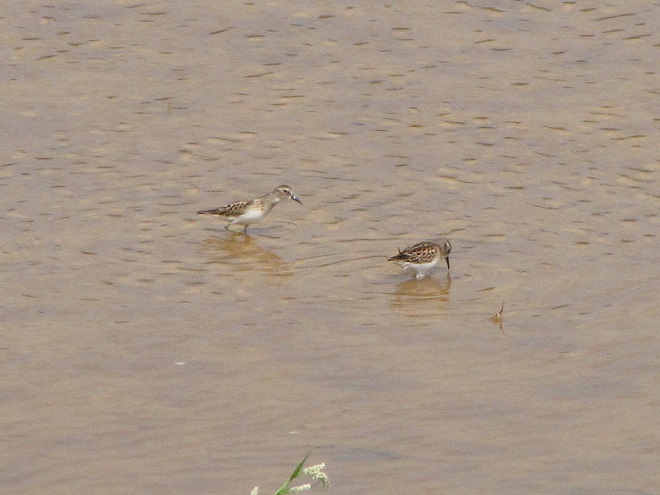
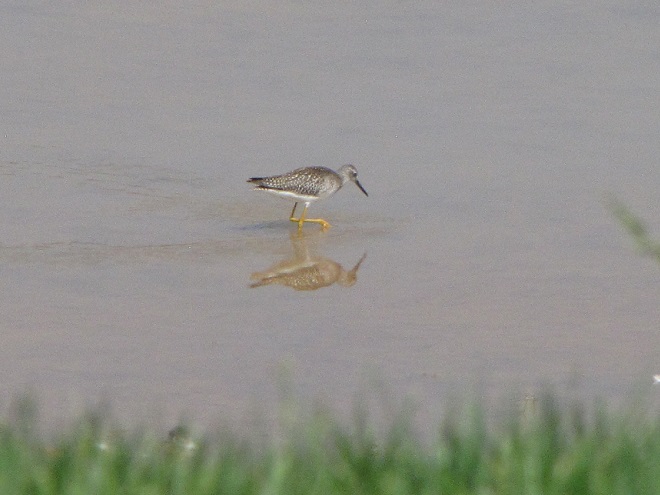
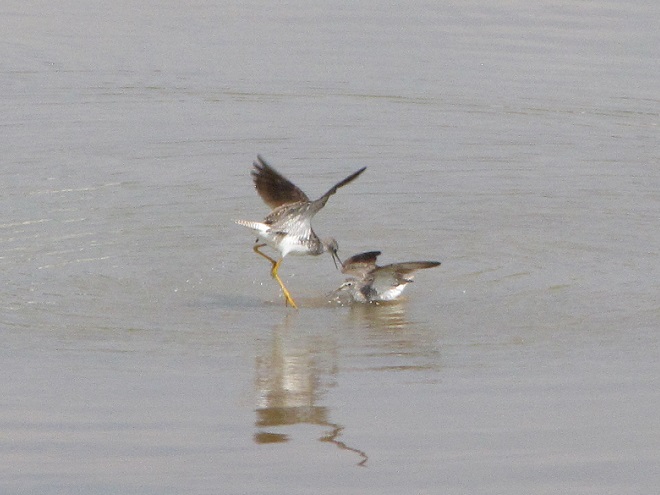
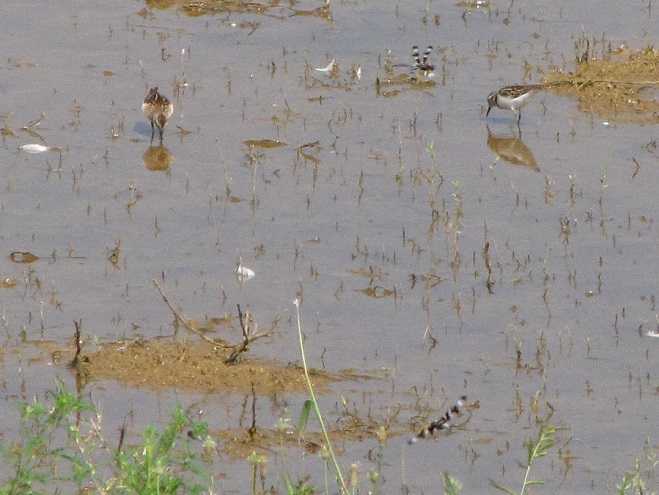






So don’t just drive by those big puddles, stop and have a look. You never know what you might find.




During the coming two weeks, peak numbers of migrating Neotropical birds will be passing through the northeastern United States including the lower Susquehanna valley. Hawk watches are staffed and observers are awaiting big flights of Broad-winged Hawks—hoping to see a thousand birds or more in a single day.
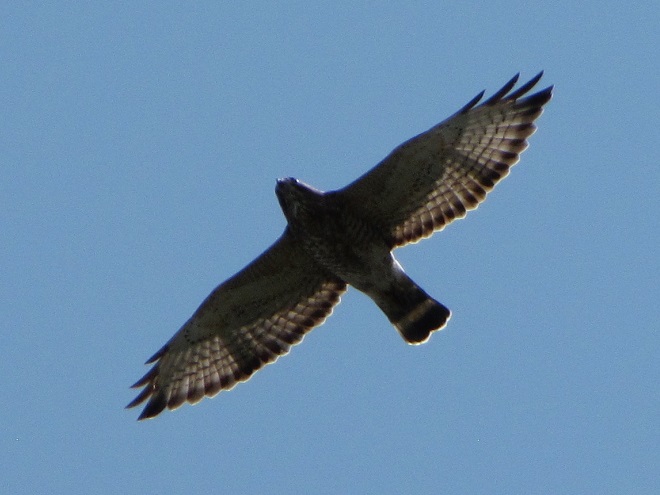
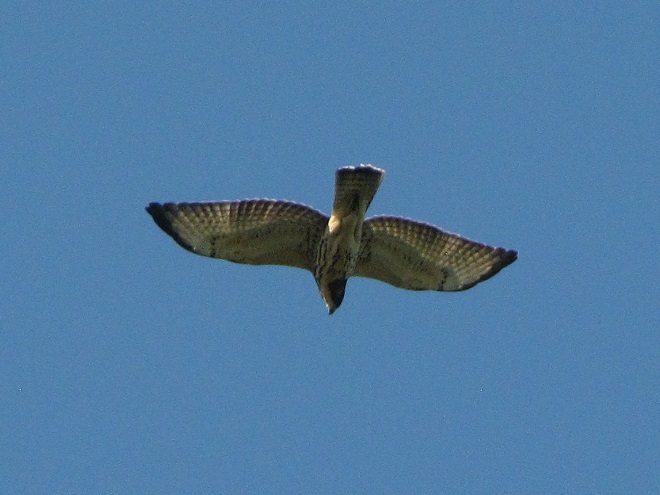


Broad-winged hawks feed on rodents, amphibians, and a variety of large insects while on their breeding grounds in the forests of the northern United States and Canada. They depart early, journeying to wintering areas in Central and South America before frost robs them of a reliable food supply.

While migrating, Broad-winged Hawks climb to great altitudes on thermal updrafts and are notoriously difficult to see from ground level. Bright sunny skies with no clouds to serve as a backdrop further complicate a hawk counter’s ability to spot passing birds. Throughout the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed, the coming week promises to be especially challenging for those trying to observe and census the passage of high-flying Broad-winged Hawks. The forecast of hot and humid weather is not so unusual, but the addition of smoke from fires in the western states promises to intensify the haze and create an especially irritating glare for those searching the skies for raptors.
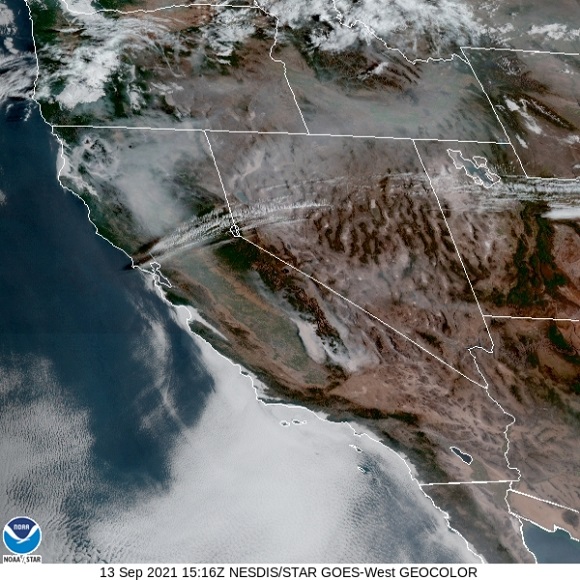
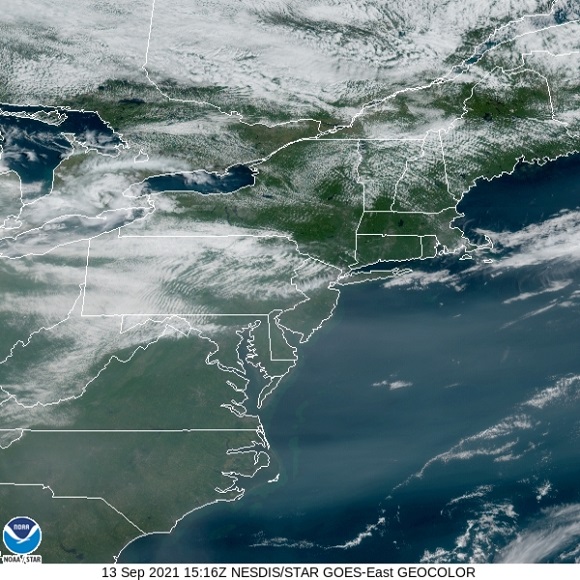

It may seem gloomy for the mid-September flights in 2021, but hawk watchers are hardy types. They know that the birds won’t wait. So if you want to see migrating “Broad-wings” and other species, you’ve got to get out there and look up while they’re passing through.
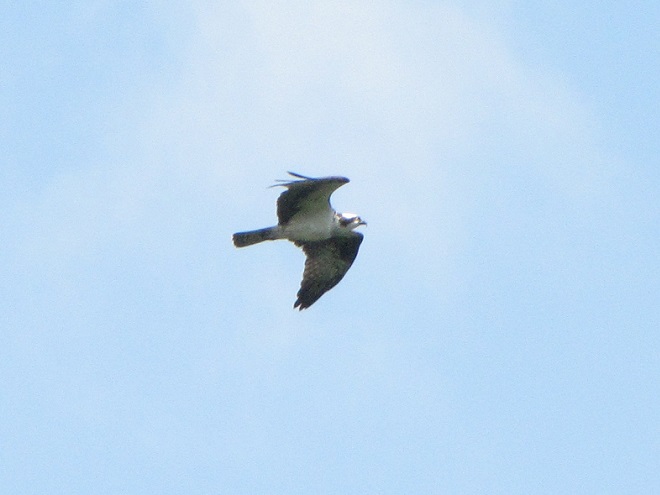
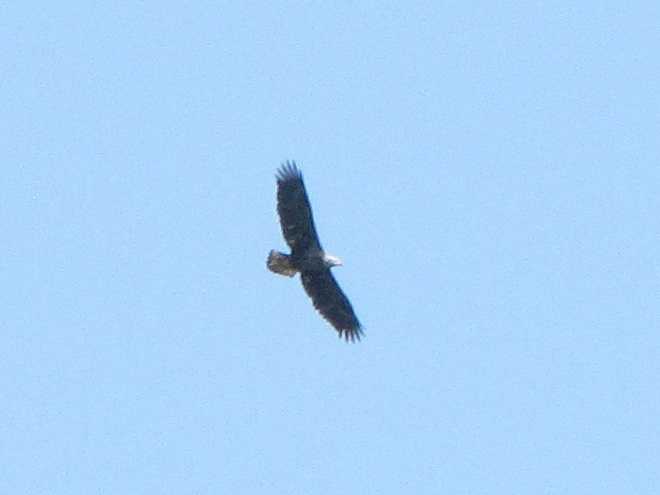



These hawk watches in the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed are currently staffed by official counters and all welcome visitors:
—or you can just keep an eye on the sky from wherever you happen to be. And don’t forget to check the trees and shrubs because warbler numbers are peaking too! During recent days…
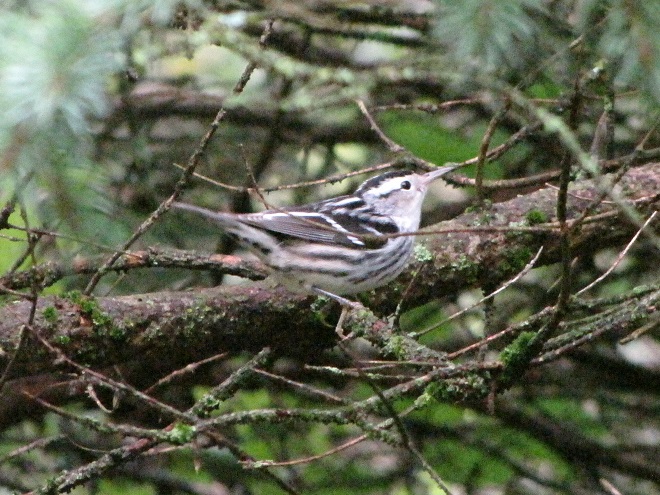
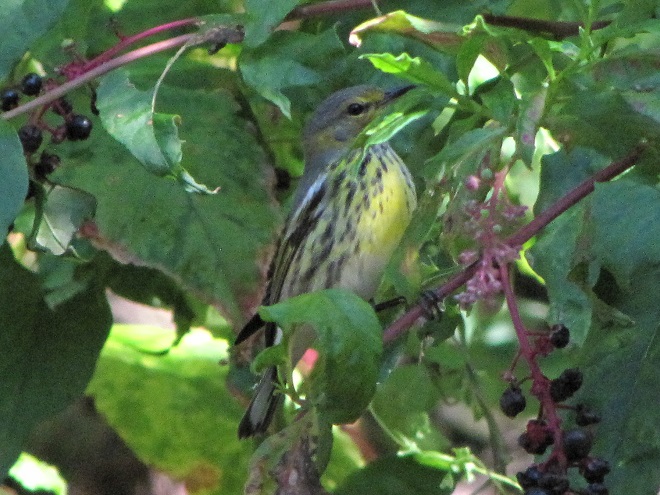
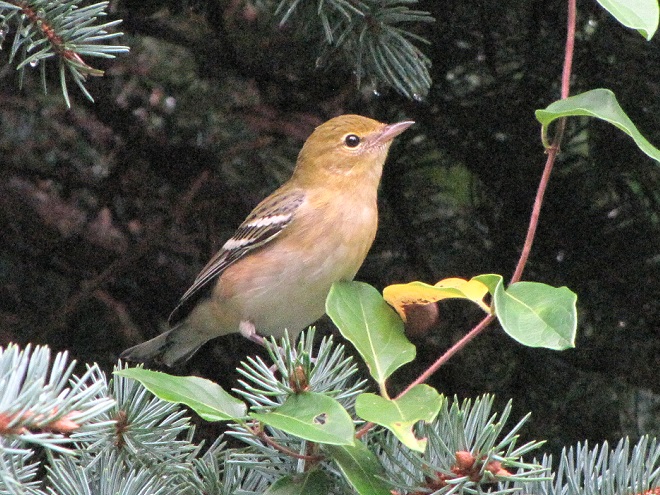




It’s been more than a week since Tropical Storm Isaias moved swiftly up the Atlantic seaboard leaving wind and flood damage in its wake. Here in the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed, the brevity of its presence minimized the effects.

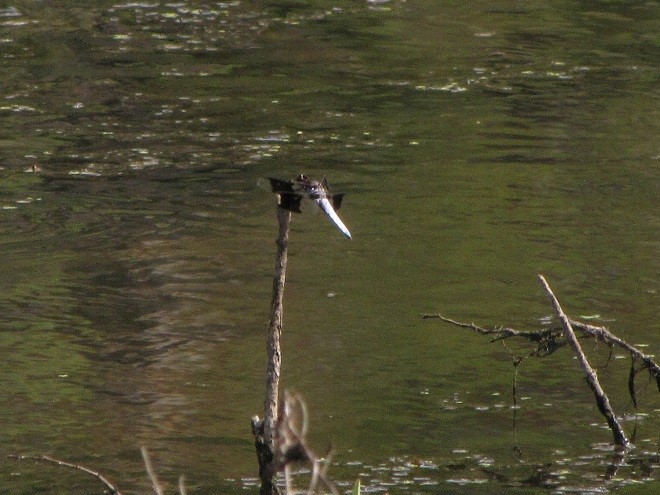
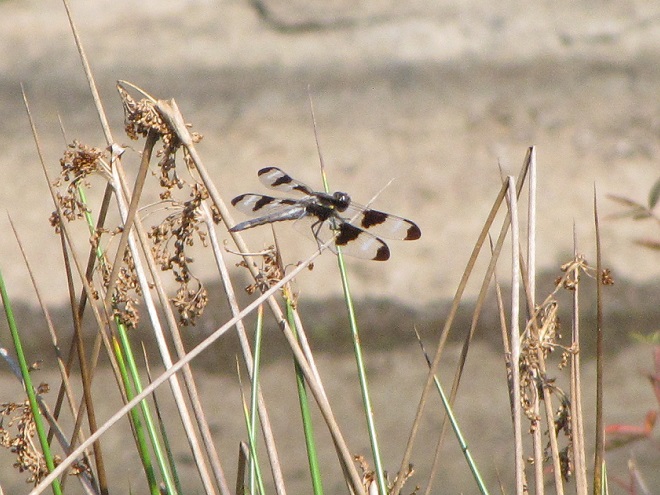
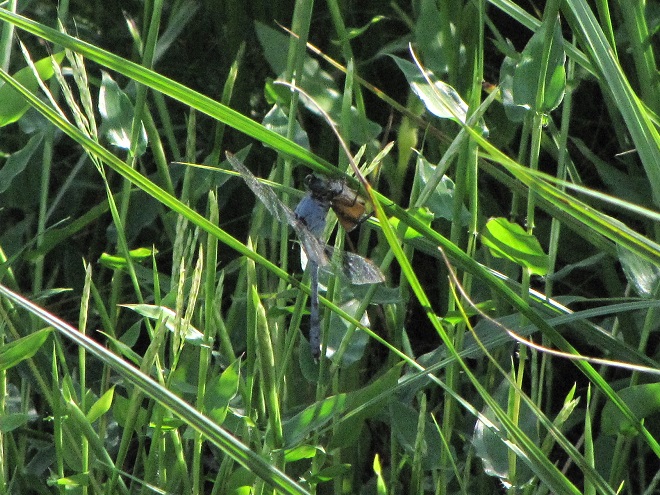
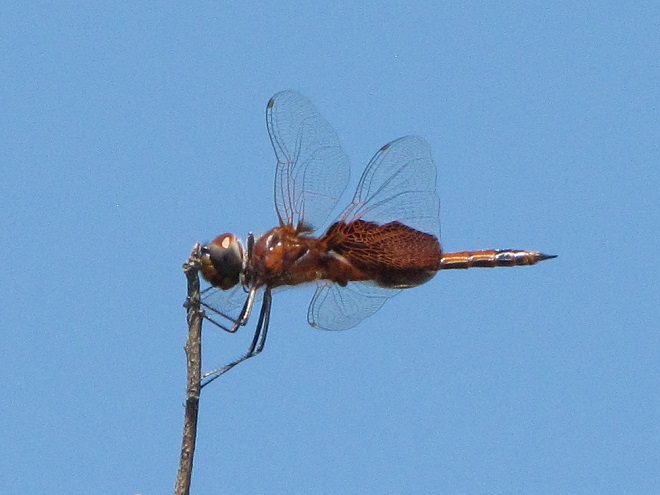
You may have noticed some summertime visitors flying about during these hot humid days that followed Isaias’ passing. They’re the dragonflies.
Our familiar friend the Wandering Glider is widespread throughout the valley right now—dropping eggs on shiny automobile hoods that look to them like a nice quiet puddle of water.
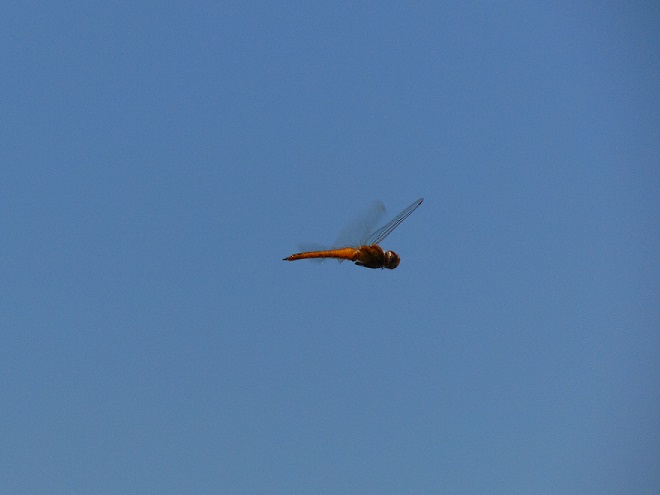

Each of the other common migratory species is here too. Look for them patrolling the skies over large bodies of water and over adjacent fallow land and meadows where tiny flying insects abound. Did these dragonflies arrive on the winds associated with the tropical storm, or did they move in with the waves of warm air that followed it? Probably a little of both.
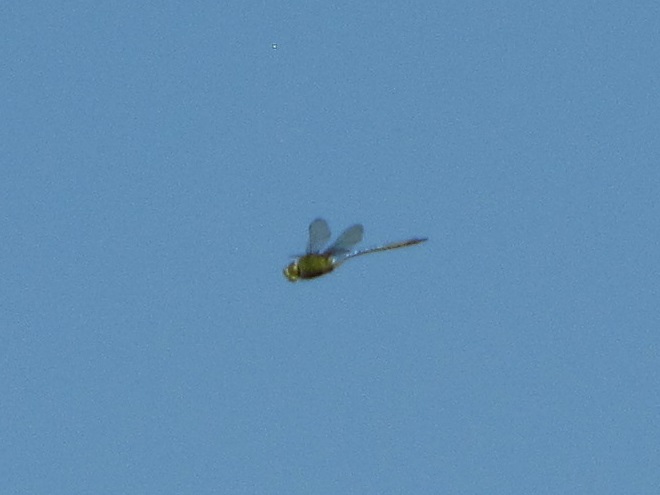
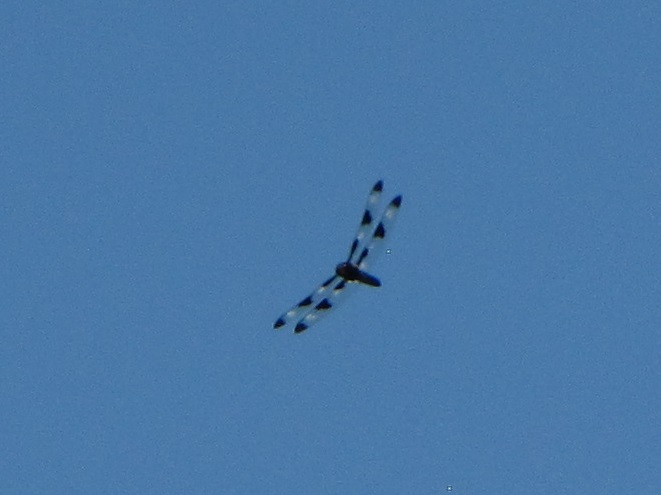
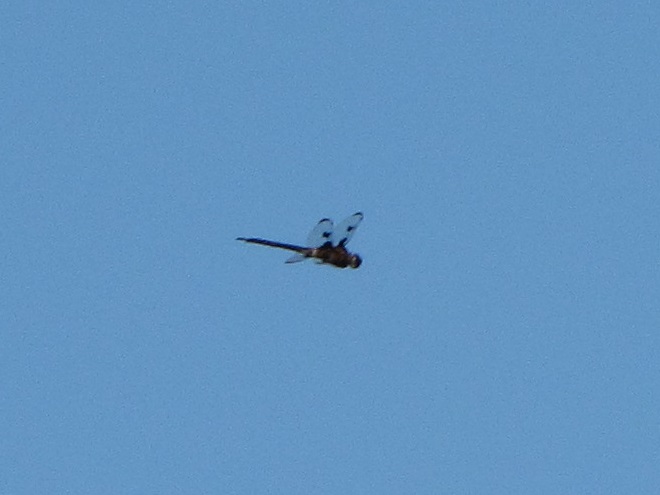




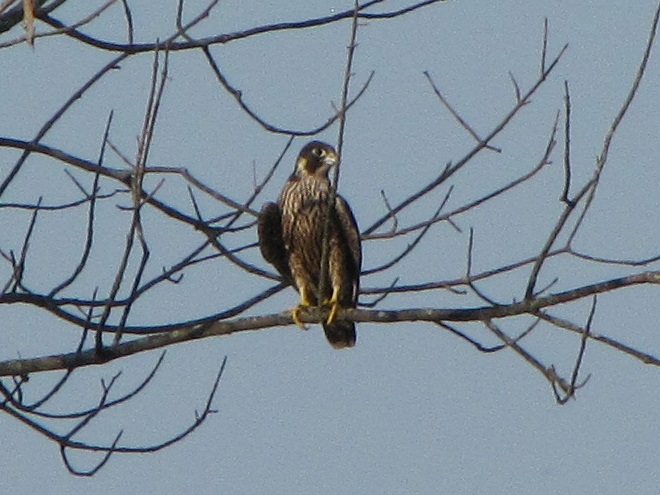
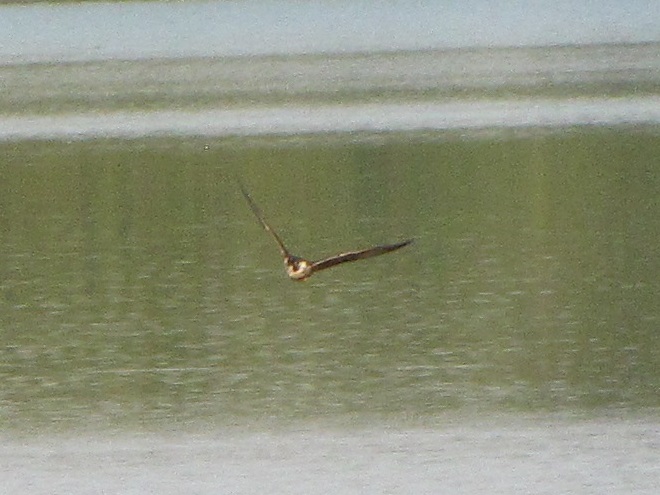
Big swarms of dragonflies don’t go unnoticed by predators—particularly birds. The southbound migration of kites, Broad-winged Hawks, American Kestrels, and Merlins often coincides with the swarming of migratory dragonflies in late summer. Each of these raptors will grab and feed upon these insects while on the wing—so keep an eye on the sky.

