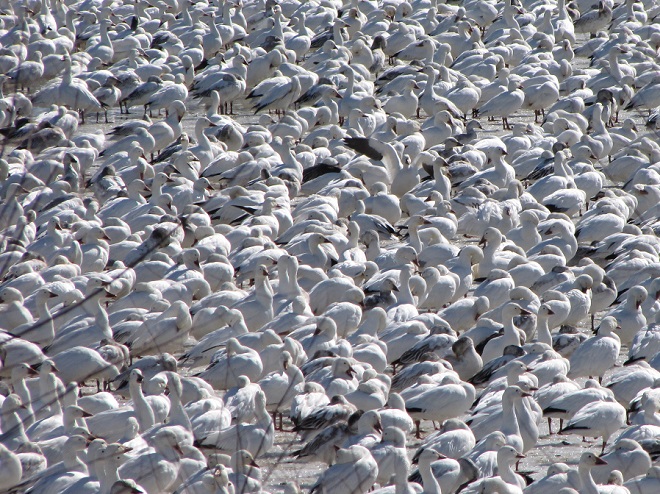
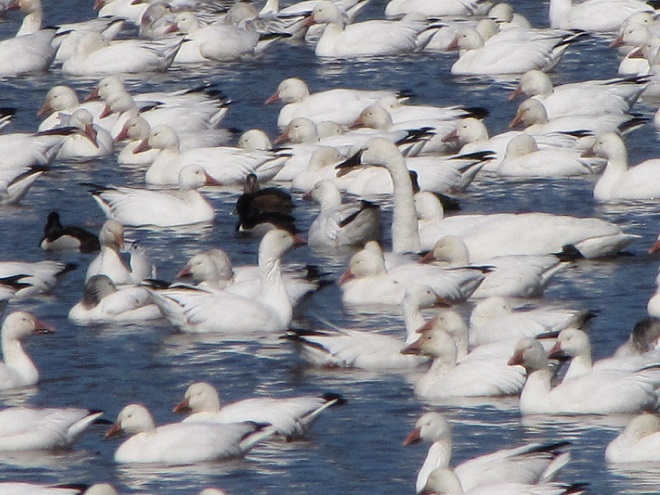
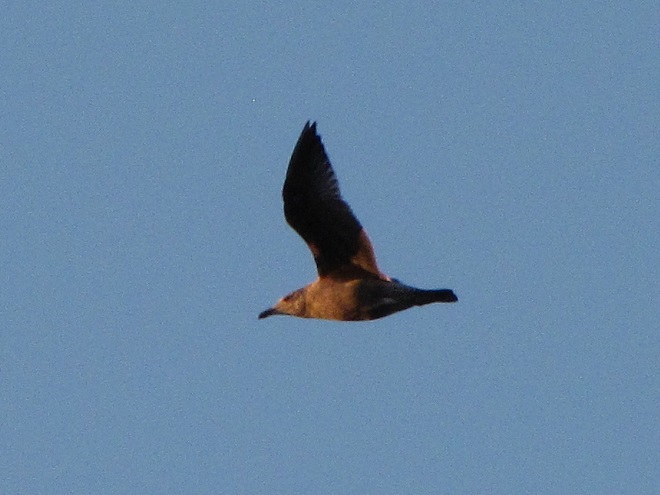
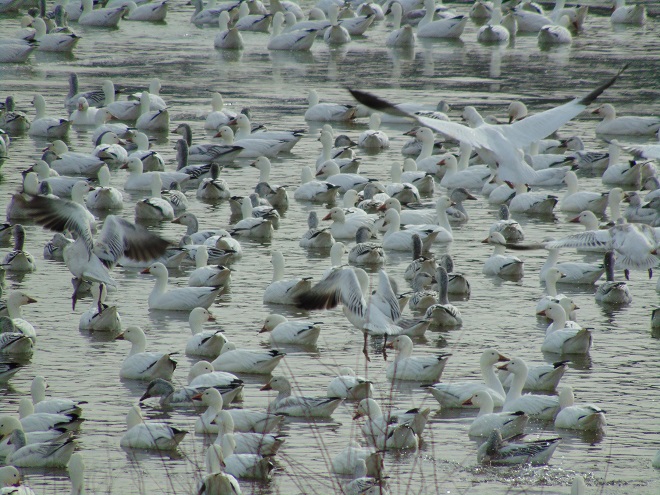
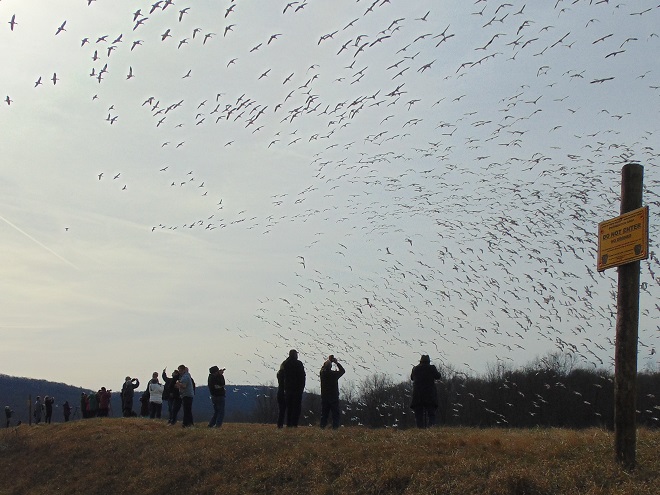
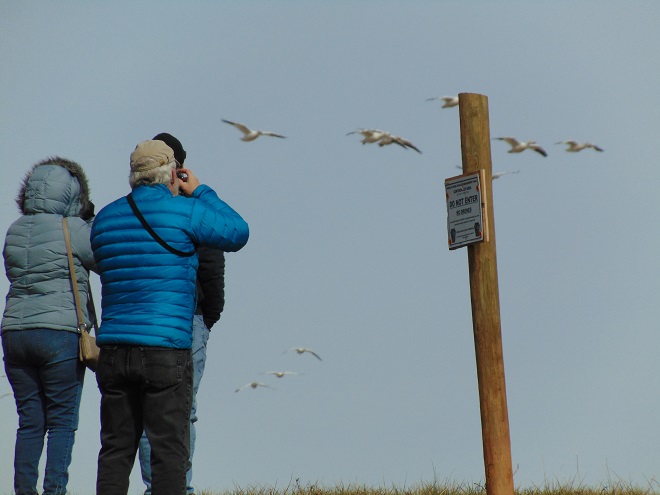
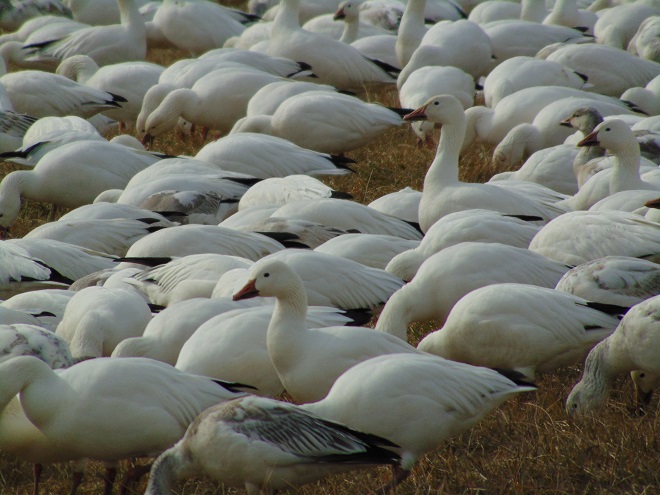
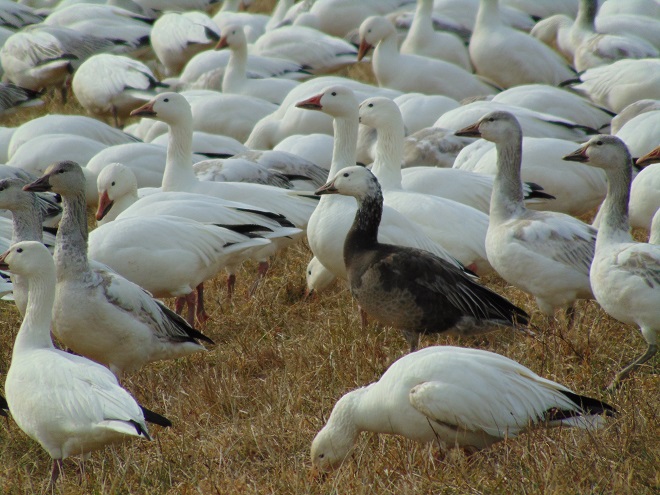
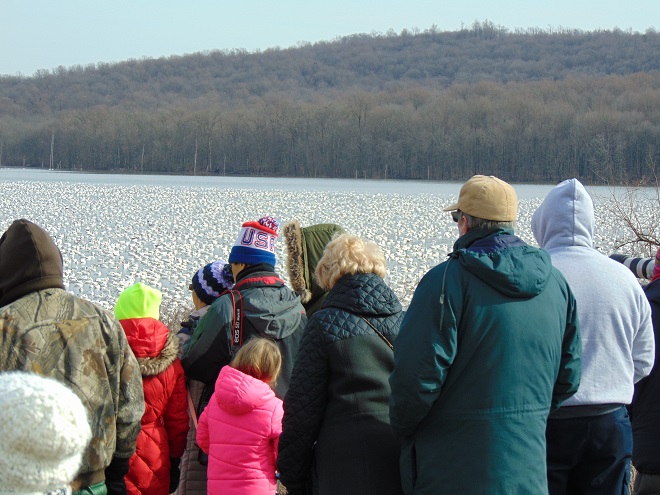
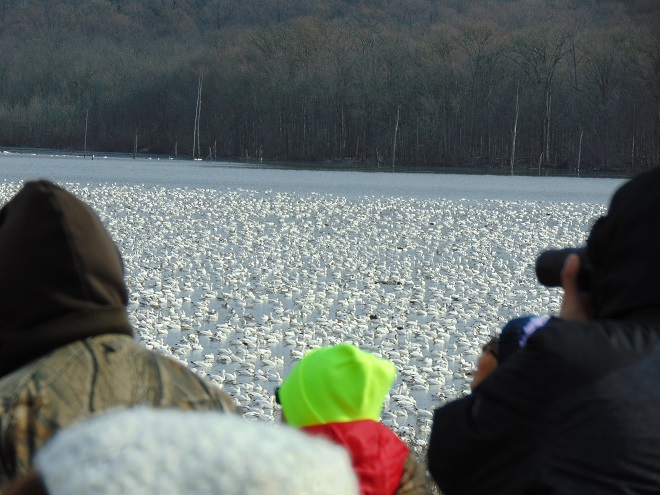
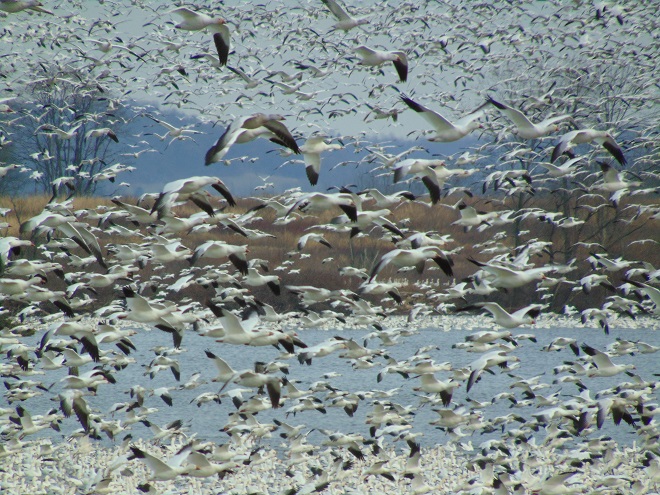
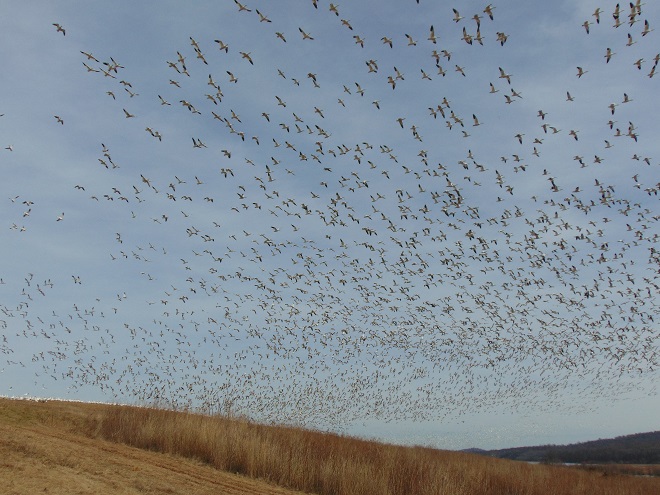
It’s that time—Snow Goose numbers are peaking at Middle Creek Wildlife Management Area in Lancaster/Lebanon Counties.






LIFE IN THE LOWER SUSQUEHANNA RIVER WATERSHED
A Natural History of Conewago Falls—The Waters of Three Mile Island
It’s that time—Snow Goose numbers are peaking at Middle Creek Wildlife Management Area in Lancaster/Lebanon Counties.





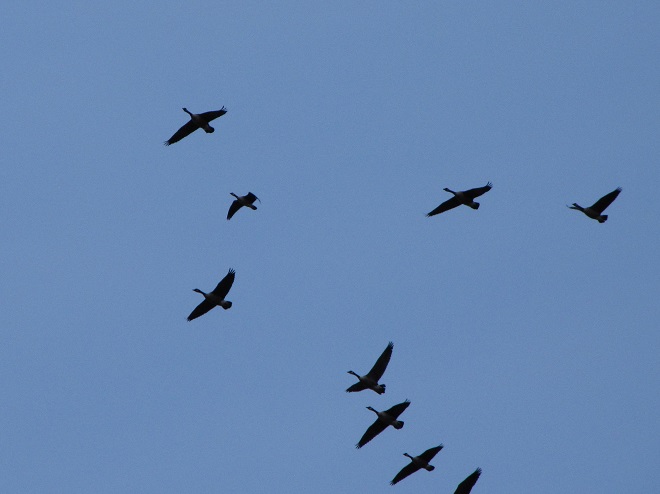
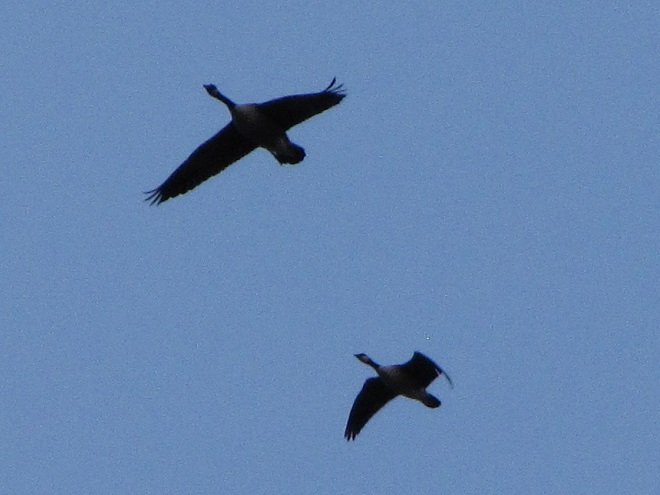
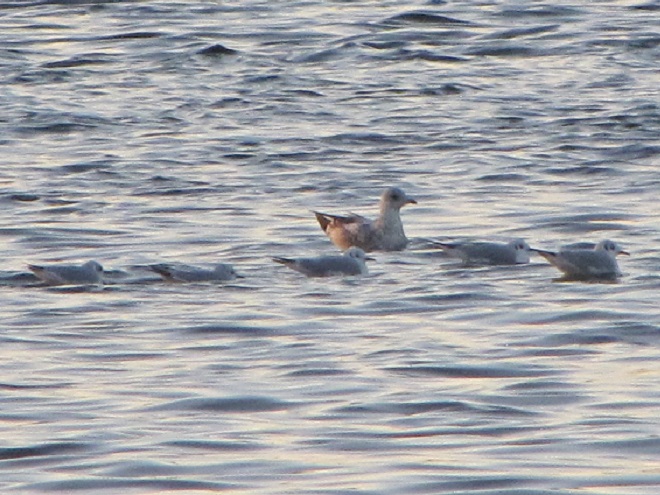
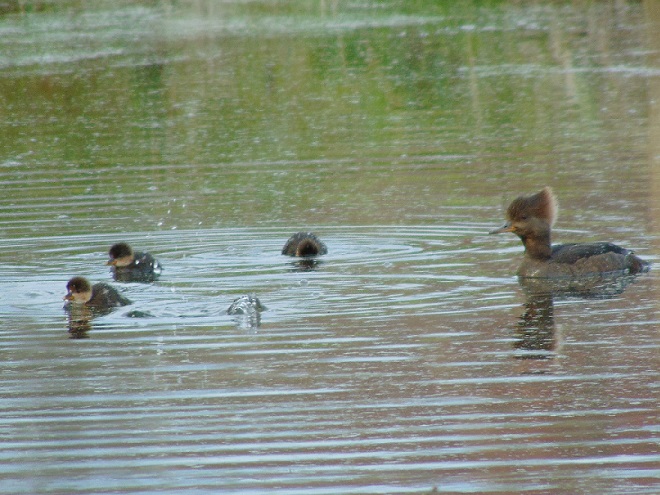
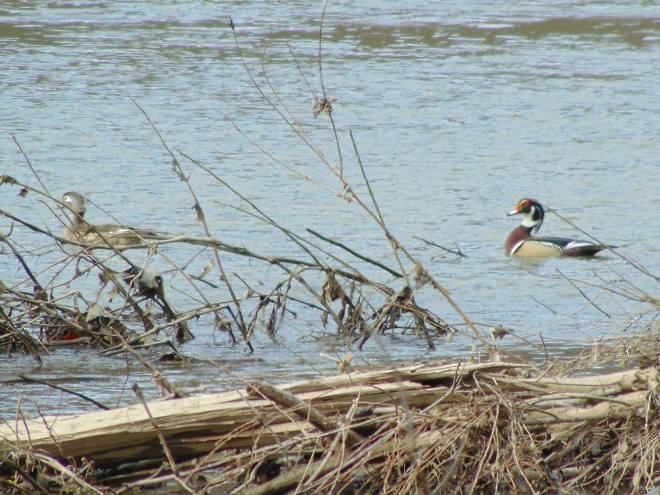
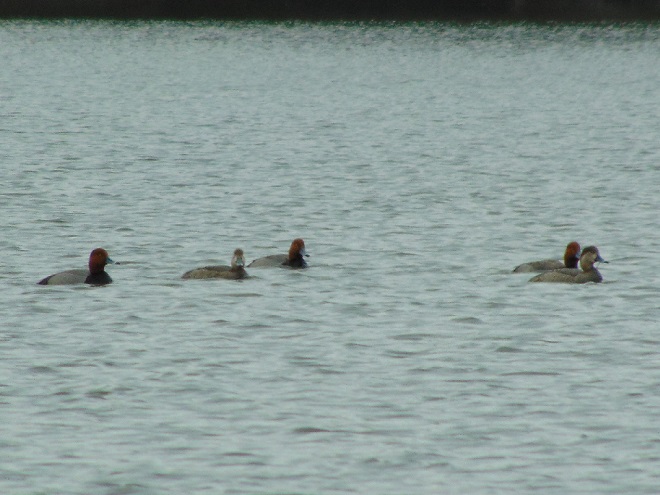
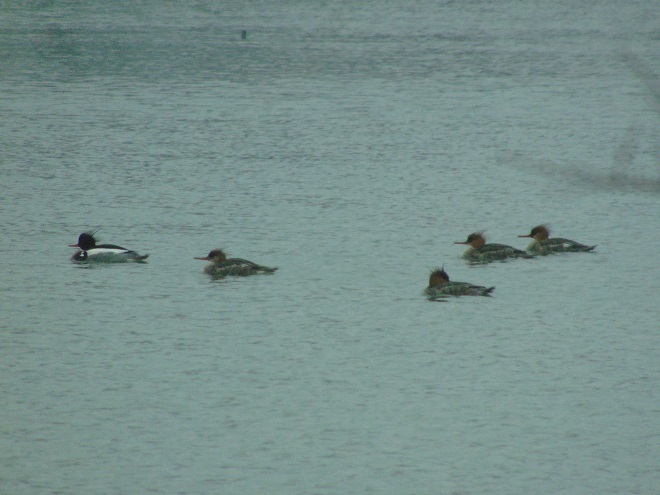
Spring migration is underway and waterfowl are on the move along the lower Susquehanna River. Here is a sample of sightings collected during a walk across the Veteran’s Memorial Bridge at Columbia-Wrightsville this morning.
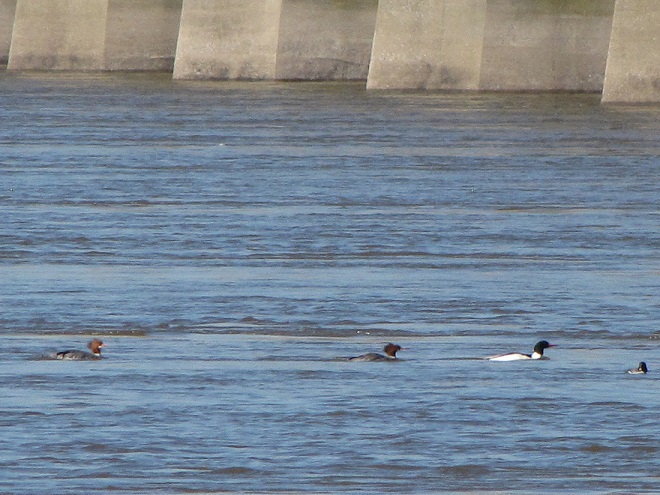
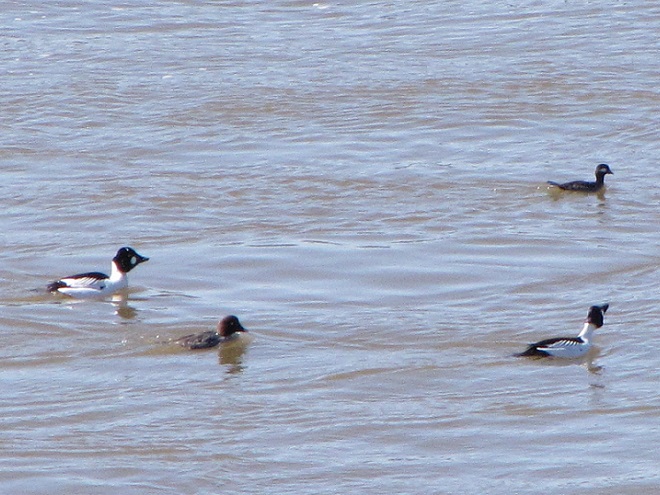
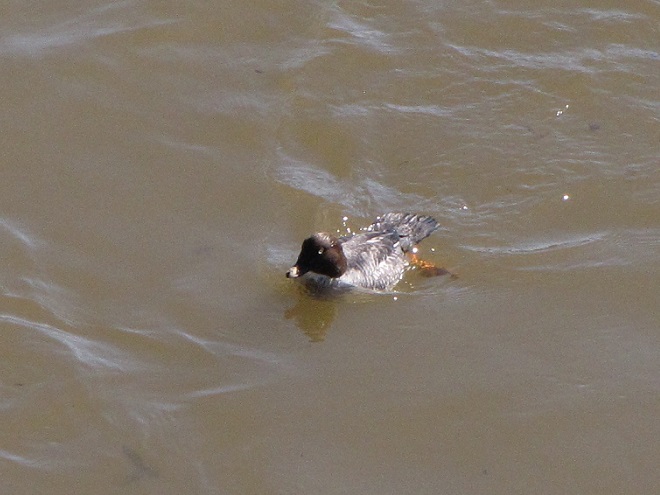
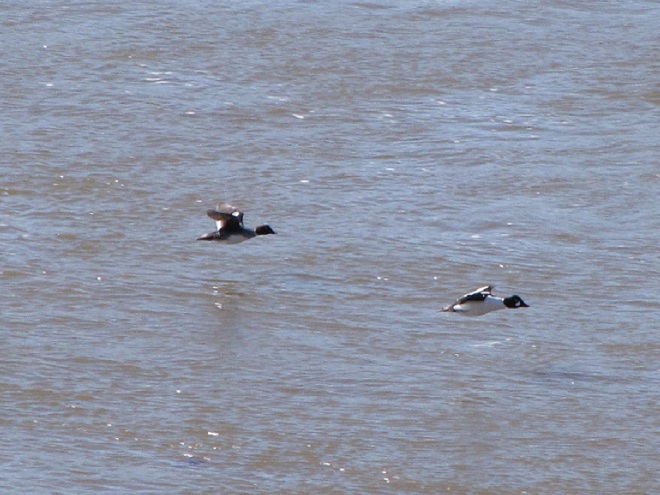
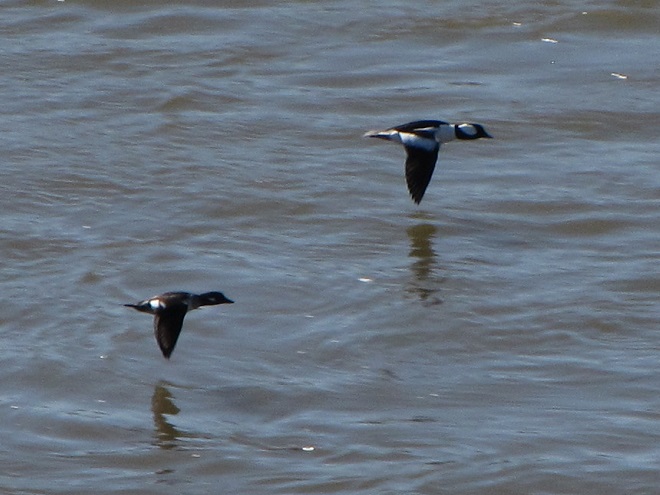
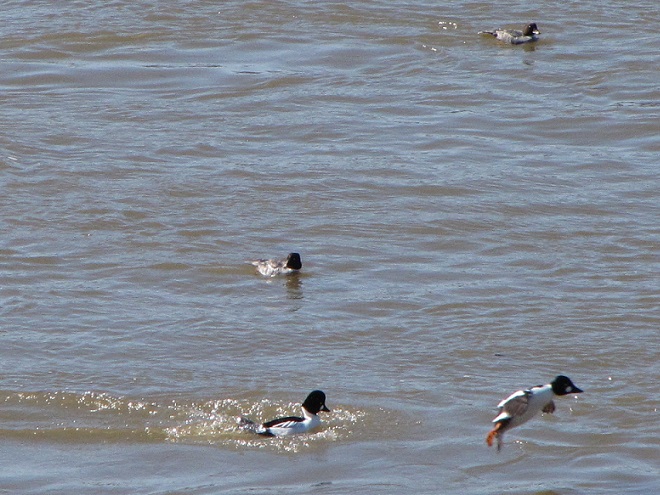
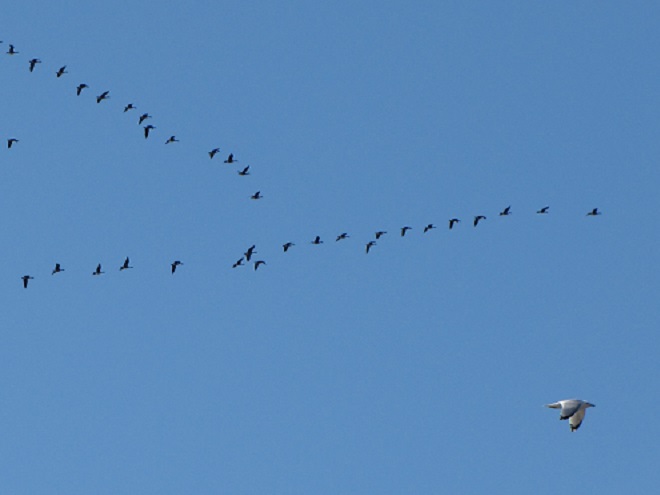











This is, of course, just the beginning of the great spring migration. Do make a point of getting out to observe the spectacle. And remember, keep looking up—you wouldn’t want to miss anything.
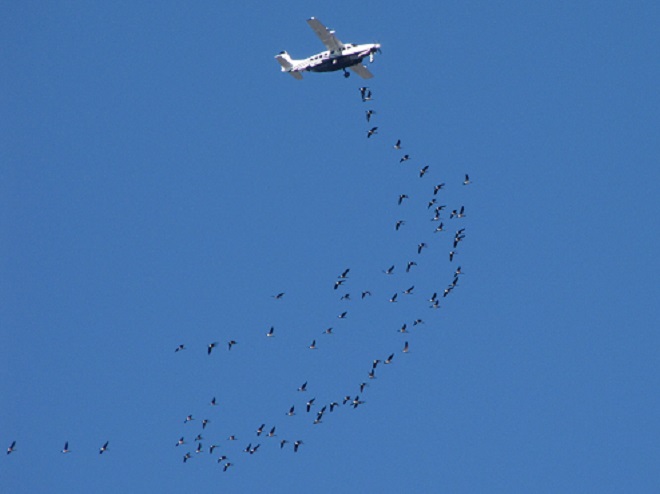
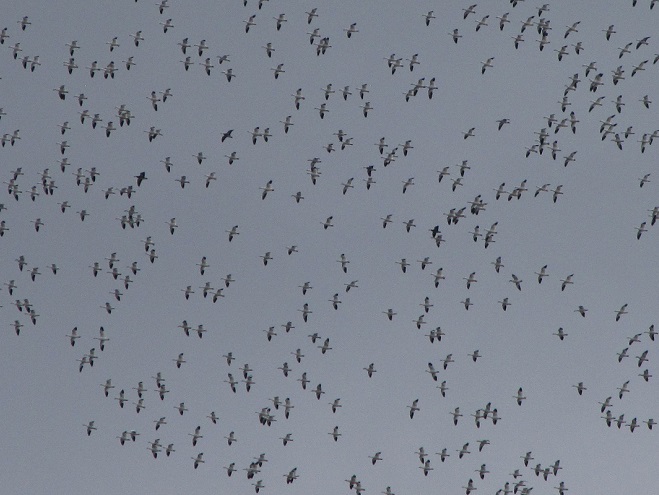
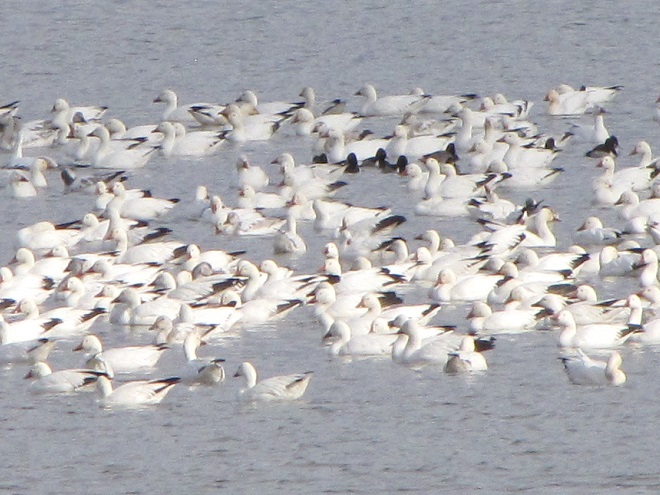
With plenty of open water on the main lake and no snow cover on the fields where they graze, Snow Geese have begun arriving at Middle Creek Wildlife Management Area in Lancaster/Lebanon Counties. As long as our mild winter weather continues, more can be expected to begin moving inland from coastal areas to prepare for their spring migration and a return to arctic breeding grounds.
You probably need a break from being indoors all month, so why not get out and have a look?
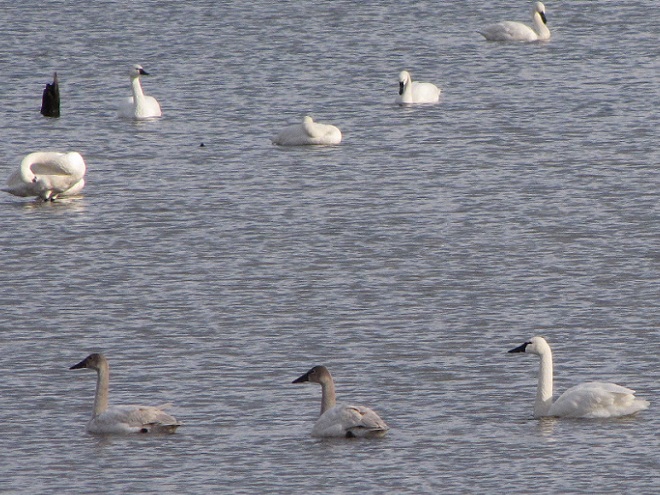
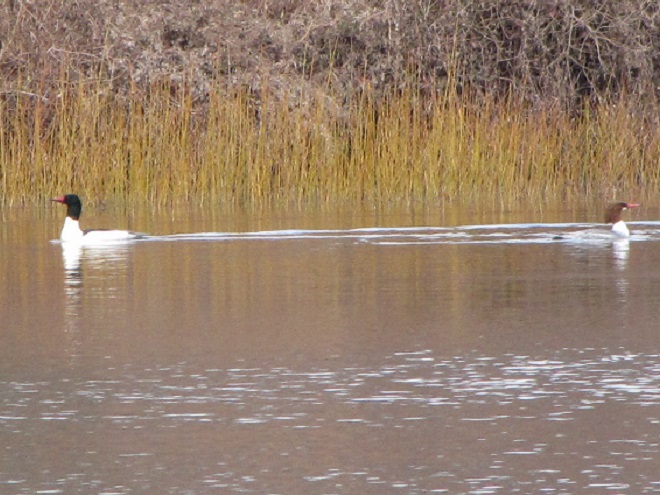
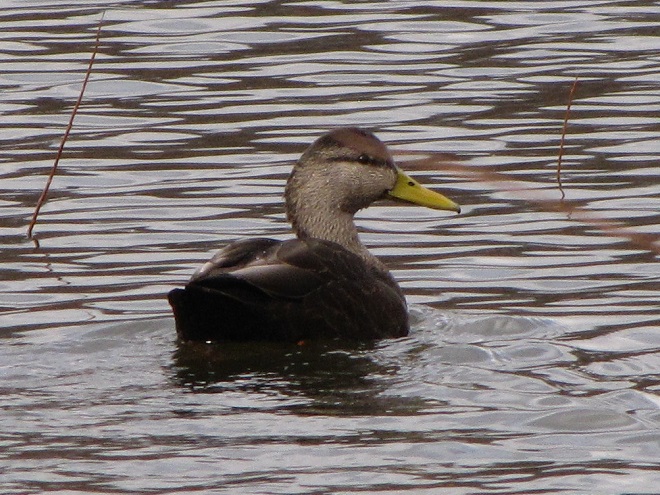
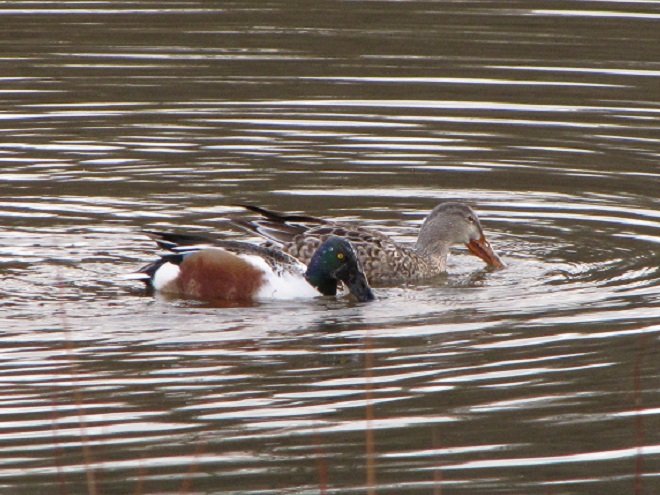








Don’t just sit there—don your coat, grab a pair of binoculars, and get out and have a gander!
You say you really don’t want to take a look back at 2020? Okay, we understand. But here’s something you may find interesting, and it has to do with the Susquehanna River in 2020.
As you may know, the National Weather Service has calculated the mean temperature for the year 2020 as monitored just upriver from Conewago Falls at Harrisburg International Airport. The 56.7° Fahrenheit value was the highest in nearly 130 years of monitoring at the various stations used to register official climate statistics for the capital city. The previous high, 56.6°, was set in 1998.
Though not a prerequisite for its occurrence, record-breaking heat was accompanied by a drought in 2020. Most of the Susquehanna River drainage basin experienced drought conditions during the second half of the year, particularly areas of the watershed upstream of Conewago Falls. A lack of significant rainfall resulted in low river flows throughout late summer and much of the autumn. Lacking water from the northern reaches, we see mid-river rocks and experience minimal readings on flow gauges along the lower Susquehanna, even if our local precipitation happens to be about average.
Back in October, when the river was about as low as it was going to get, we took a walk across the Susquehanna at Columbia-Wrightsville atop the Route 462/Veteran’s Memorial Bridge to have a look at the benthos—the life on the river’s bottom.
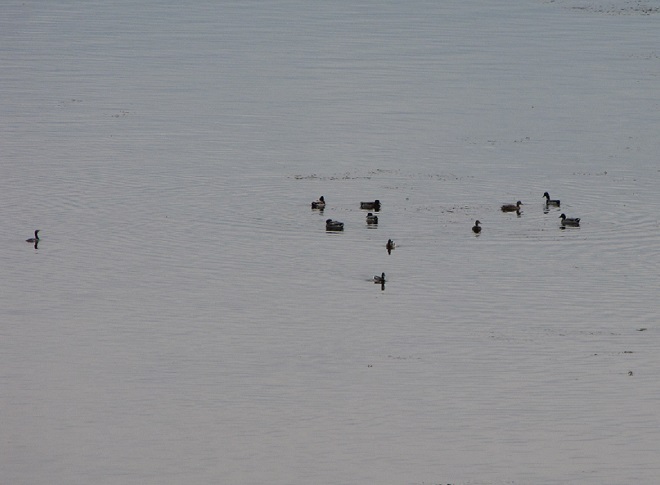







These improvements in water quality and wildlife habitat can have a ripple effect. In 2020, the reduction in nutrient loads entering Chesapeake Bay from the low-flowing Susquehanna may have combined with better-than-average flows from some of the bay’s lesser-polluted smaller tributaries to yield a reduction in the size of the bay’s oxygen-deprived “dead zones”. These dead zones typically occur in late summer when water temperatures are at their warmest, dissolved oxygen levels are at their lowest, and nutrient-fed algal blooms have peaked and died. Algal blooms can self-enhance their severity by clouding water, which blocks sunlight from reaching submerged aquatic plants and stunts their growth—making quantities of unconsumed nutrients available to make more algae. When a huge biomass of algae dies in a susceptible part of the bay, its decay can consume enough of the remaining dissolved oxygen to kill aquatic organisms and create a “dead zone”. The Chesapeake Bay Program reports that the average size of this year’s dead zone was 1.0 cubic miles, just below the 35-year average of 1.2 cubic miles.
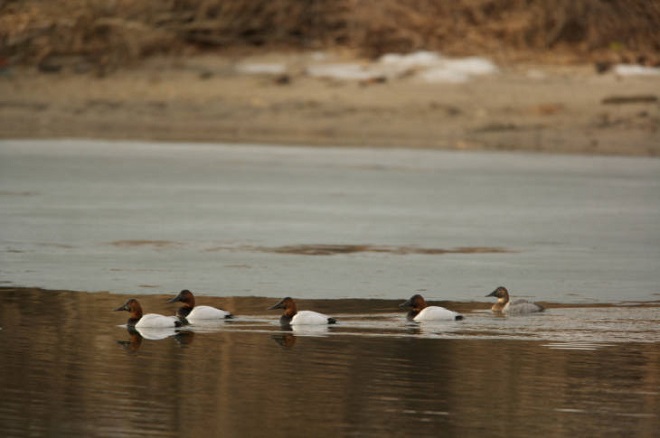
Back on a stormy day in mid-November, 2020, we took a look at the tidal freshwater section of Chesapeake Bay, the area known as Susquehanna Flats, located just to the southwest of the river’s mouth at Havre de Grace, Maryland. We wanted to see how the restored American Eelgrass beds there might have fared during a growing season with below average loads of nutrients and life-choking sediments spilling out of the nearby Susquehanna River. Here’s what we saw.
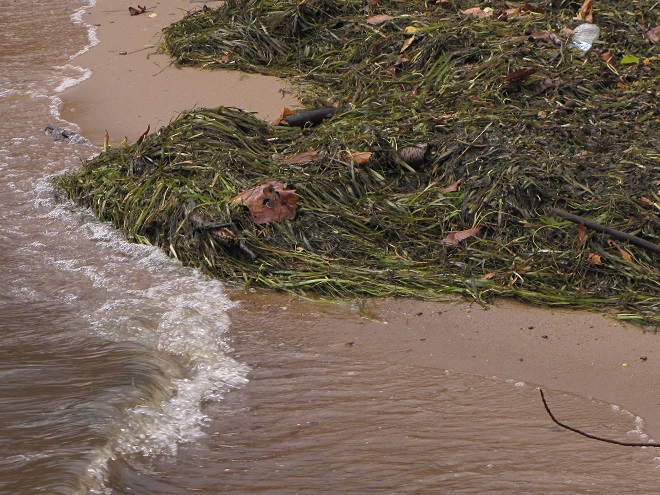
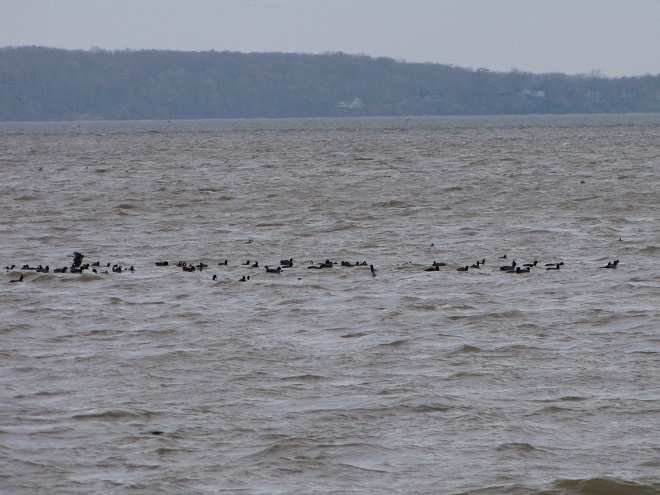
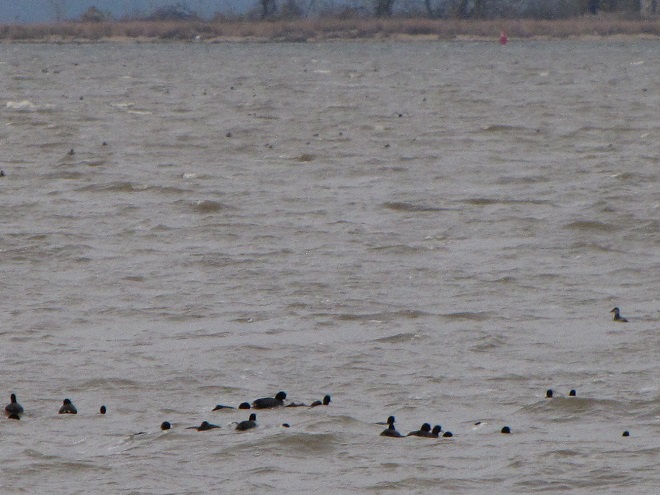







We noticed a few Canvasbacks (Aythya valisineria) on the Susquehanna Flats during our visit. Canvasbacks are renowned as benthic feeders, preferring the tubers and other parts of submerged aquatic plants (a.k.a. submersed aquatic vegetation or S.A.V.) including eelgrass, but also feeding on invertebrates including bivalves. The association between Canvasbacks and eelgrass is reflected in the former’s scientific species name valisineria, a derivitive of the genus name of the latter, Vallisneria.

The plight of the Canvasback and of American Eelgrass on the Susquehanna River was described by Herbert H. Beck in his account of the birds found in Lancaster County, Pennsylvania, published in 1924:
“Like all ducks, however, it stops to feed within the county less frequently than formerly, principally because the vast beds of wild celery which existed earlier on broads of the Susquehanna, as at Marietta and Washington Borough, have now been almost entirely wiped out by sedimentation of culm (anthracite coal waste). Prior to 1875 the four or five square miles of quiet water off Marietta were often as abundantly spread with wild fowl as the Susquehanna Flats are now.”
Beck quotes old Marietta resident and gunner Henry Zink:
“Sometimes there were as many as 500,000 ducks of various kinds on the Marietta broad at one time.”
The abundance of Canvasbacks and other ducks on the Susquehanna Flats would eventually plummet too. In the 1950s, there were an estimated 250, 000 Canvasbacks wintering on Chesapeake Bay, primarily in the area of the American Eelgrass, a.k.a. Wild Celery, beds on the Susquehanna Flats. When those eelgrass beds started disappearing during the second half of the twentieth century, the numbers of Canvasbacks wintering on the bay took a nosedive. As a population, the birds moved elsewhere to feed on different sources of food, often in saltier estuarine waters.
Canvasbacks were able to eat other foods and change their winter range to adapt to the loss of habitat on the Susquehanna River and Chesapeake Bay. But not all species are the omnivores that Canvasbacks happen to be, so they can’t just change their diet and/or fly away to a better place. And every time a habitat like the American Eelgrass plant community is eliminated from a region, it fragments the range for each species that relied upon it for all or part of its life cycle. Wildlife species get compacted into smaller and smaller suitable spaces and eventually their abundance and diversity are impacted. We sometimes marvel at large concentrations of birds and other wildlife without seeing the whole picture—that man has compressed them into ever-shrinking pieces of habitat that are but a fraction of the widespread environs they once utilized for survival. Then we sometimes harass and persecute them on the little pieces of refuge that remain. It’s not very nice, is it?
By the end of 2020, things on the Susquehanna were getting back to normal. Near normal rainfall over much of the watershed during the final three months of the year was supplemented by a mid-December snowstorm, then heavy downpours on Christmas Eve melted it all away. Several days later, the Susquehanna River was bank full and dishing out some minor flooding for the first time since early May. Isn’t it great to get back to normal?




SOURCES
Beck, Herbert H. 1924. A Chapter on the Ornithology of Lancaster County, Pennsylvania. The Lewis Historical Publishing Company. New York, NY.
White, Christopher P. 1989. Chesapeake Bay, Nature of the Estuary: A Field Guide. Tidewater Publishers. Centreville, MD.
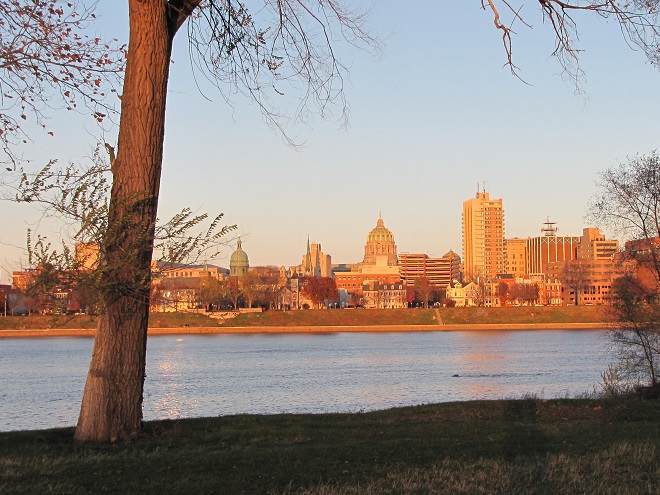
So you aren’t particularly interested in a stroll through the Pennsylvania woods during the gasoline and gunpowder gang’s second-biggest holiday of the year—the annual sacrifice-of-the-White-tailed-Deity ritual. I get it. Two weeks and nothing to do. Well, why not try a hike through the city instead? I’m not kidding. You might be surprised at what you see. Here are some photographs taken today during several strolls in Harrisburg, Pennsylvania.
First stop was City Island in the Susquehanna River—accessible from downtown Harrisburg or the river’s west shore by way of the Market Street Bridge.
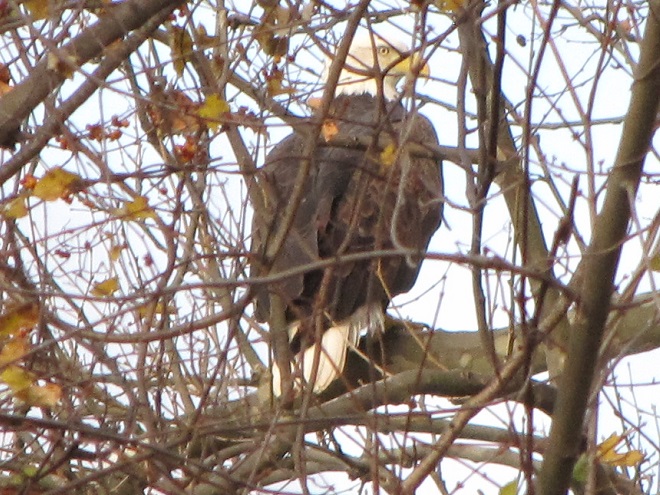
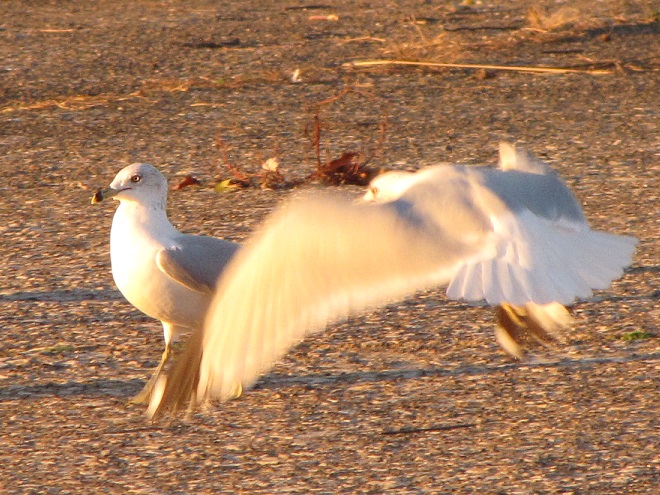






Okay, City Island was worth the effort. Next stop is Wildwood Park, located along Industrial Road just north of the Pennsylvania Farm Show complex and the Harrisburg Area Community College (HACC) campus. There are six miles of trails surrounding mile-long Wildwood Lake within this marvelous Dauphin County Parks Department property.
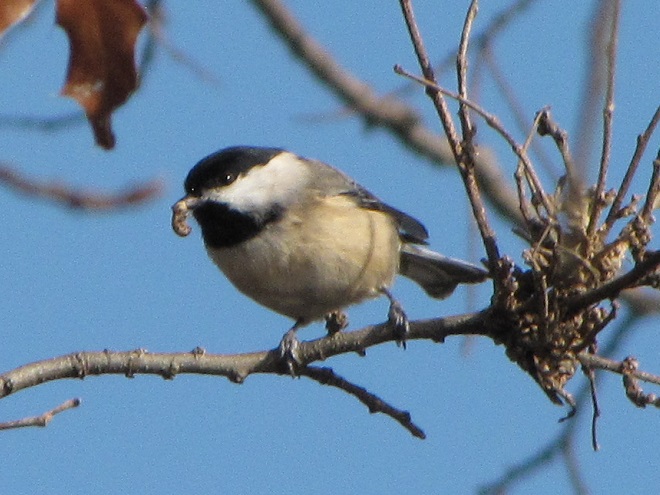
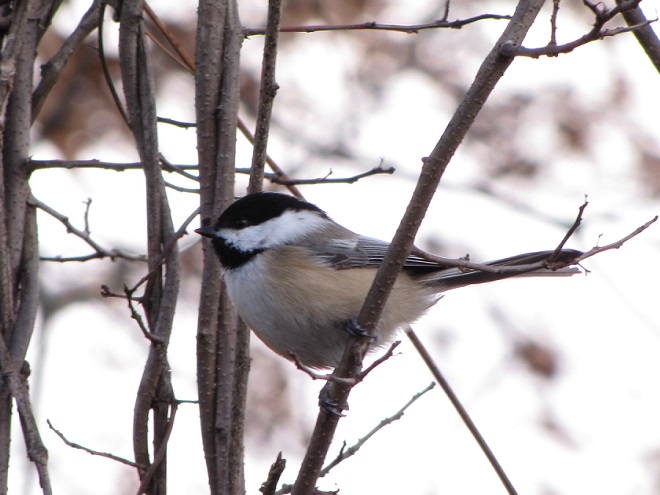
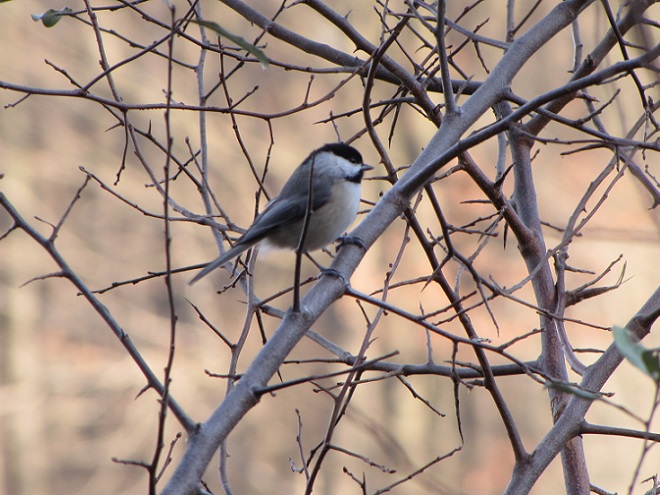
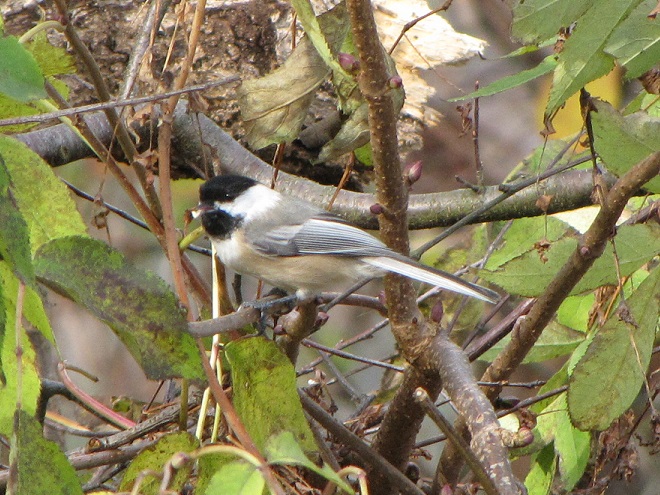
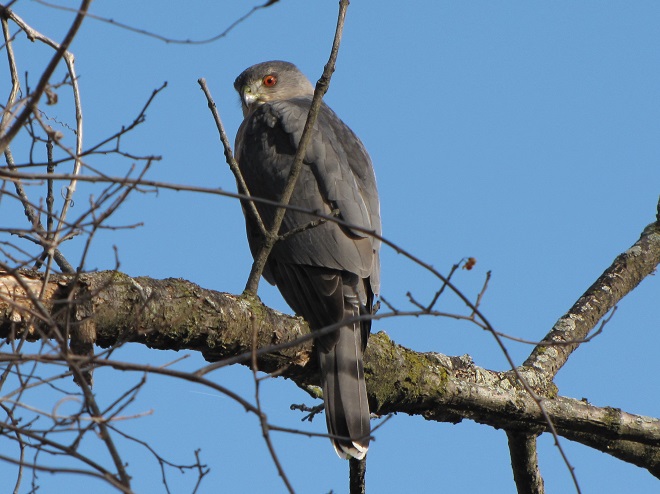
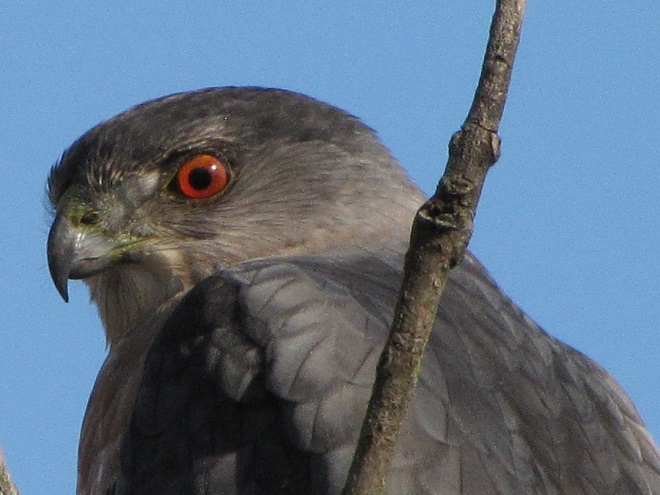
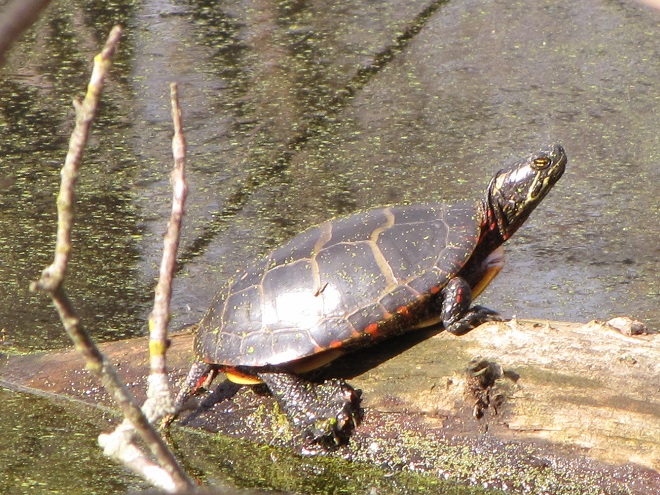








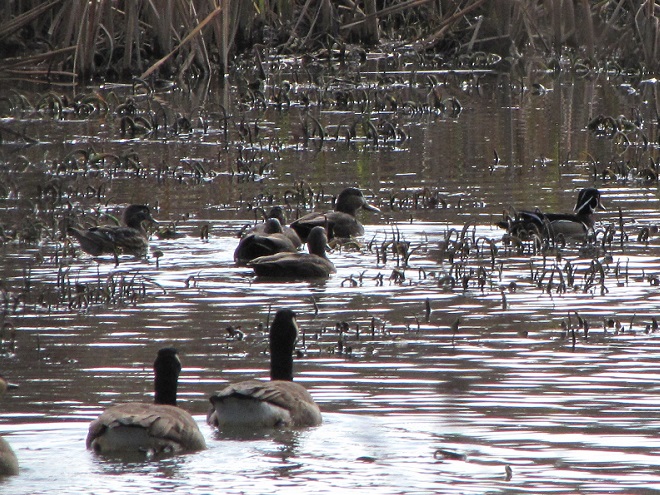
And now, without further ado, it’s time for the waterfowl of Wildwood Lake—in order of their occurrence.
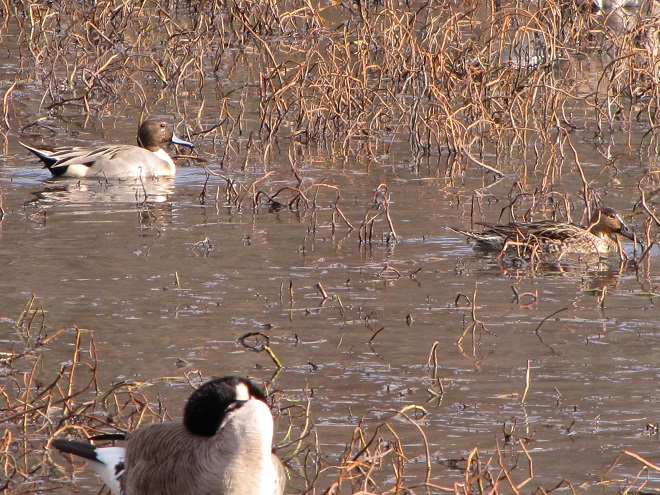
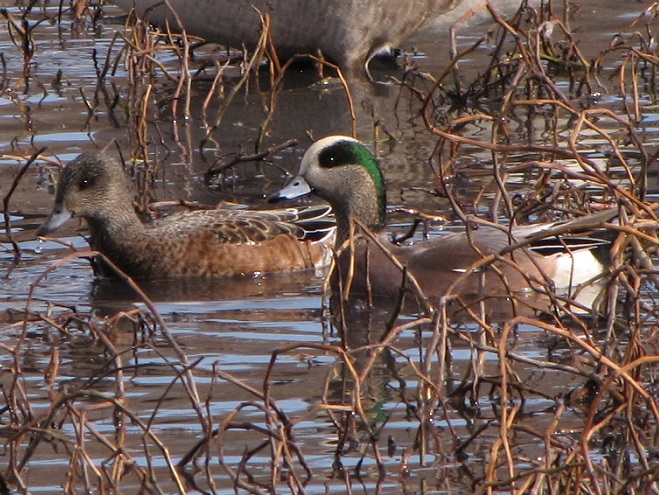
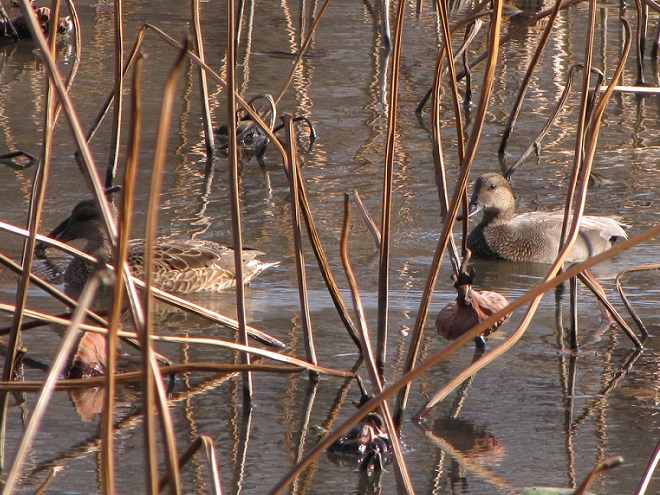
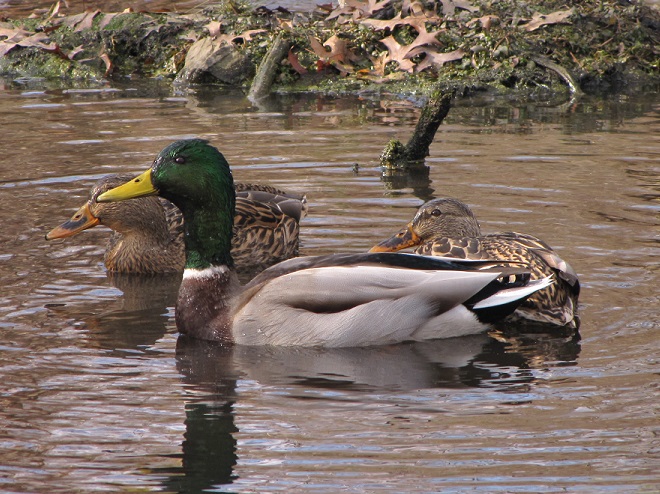
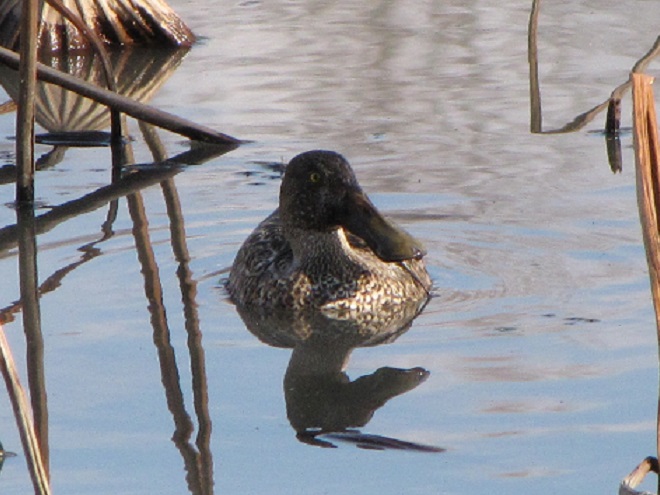
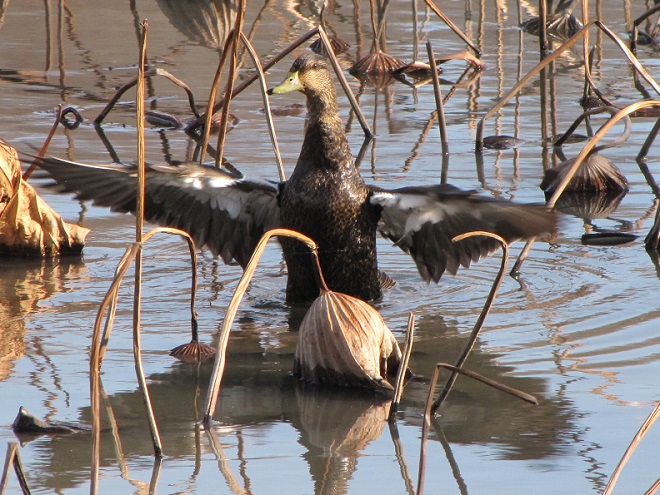
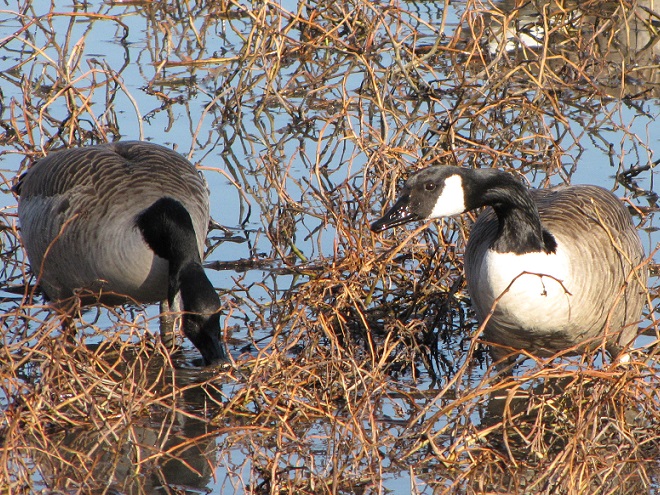
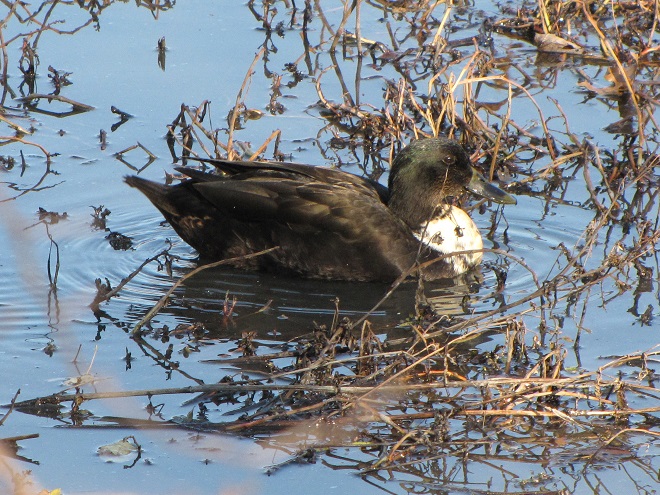











See, you don’t have to cloak yourself in bright orange ceremonial garments just to go for a hike. Go put on your walking shoes and a warm coat, grab your binoculars and/or camera, and have a look at wildlife in a city near you. You never know what you might find.
SOURCES
Taylor, Scott A., Thomas A. White, Wesley M. Hochachka, Valentina Ferretti, Robert L. Curry, and Irby Lovette. 2014. “Climate-Mediated Movement of an Avian Hybrid Zone”. Current Biology. 24:6 pp.671-676.
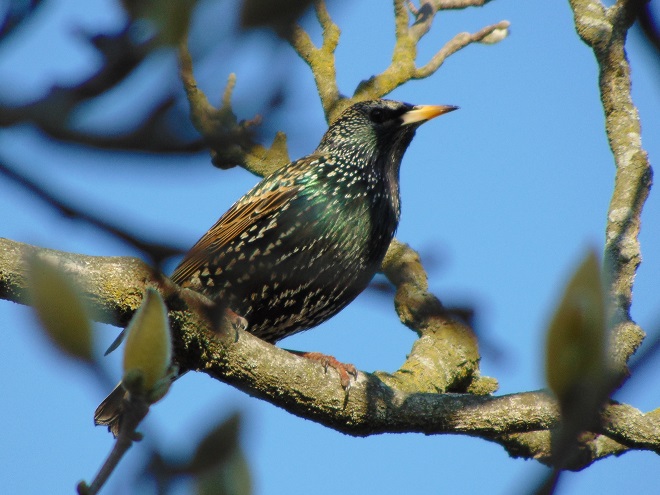
The southbound bird migration of 2020 is well underway. With passage of a cold front coming within the next 48 hours, the days ahead should provide an abundance of viewing opportunities.
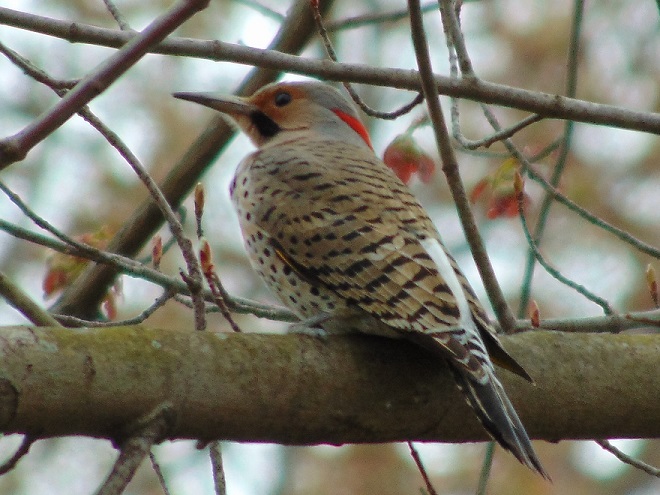
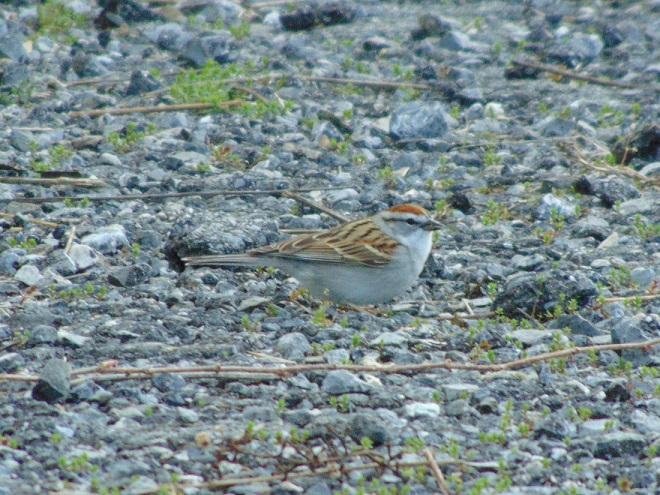
Here are some of the species moving through the lower Susquehanna valley right now.
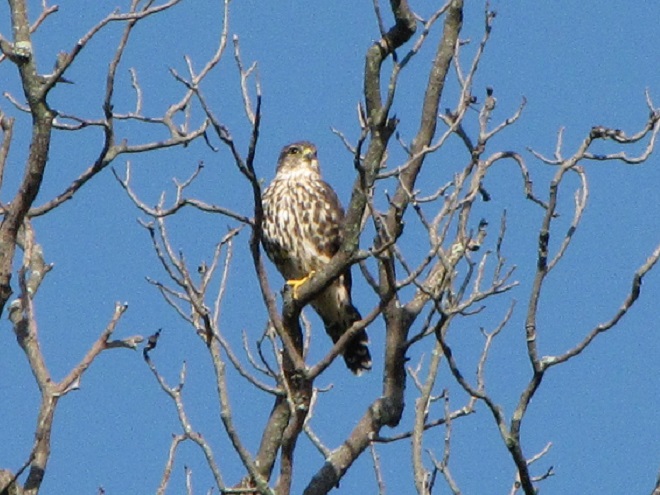
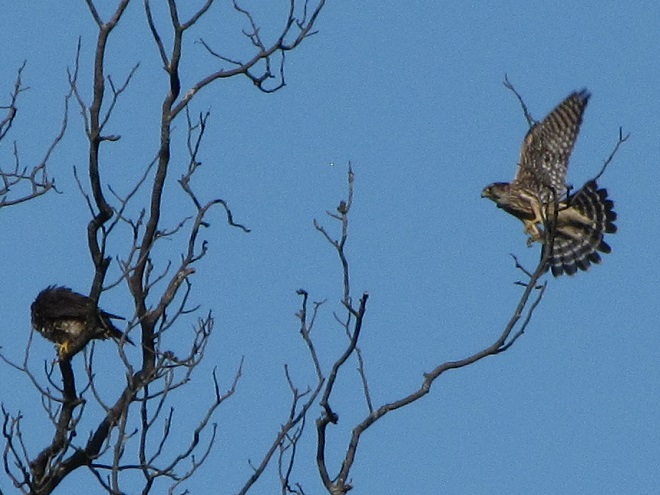
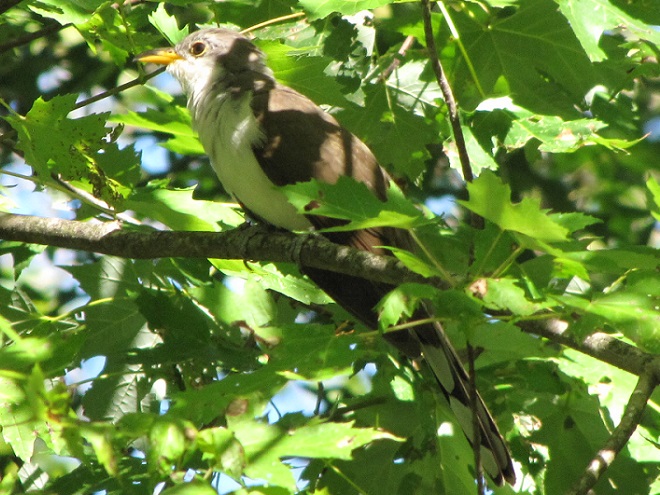
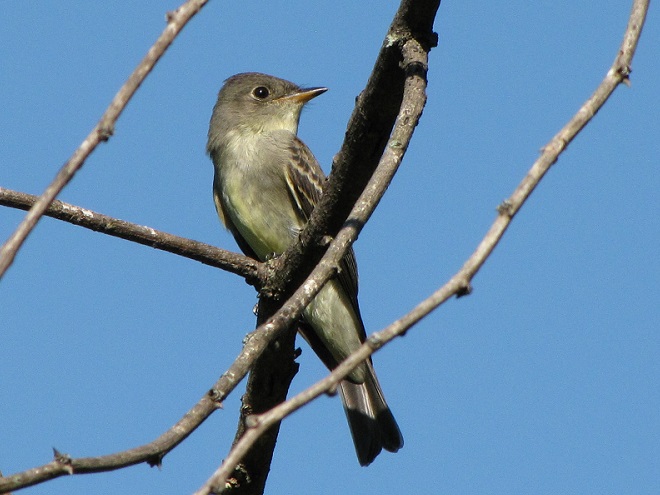
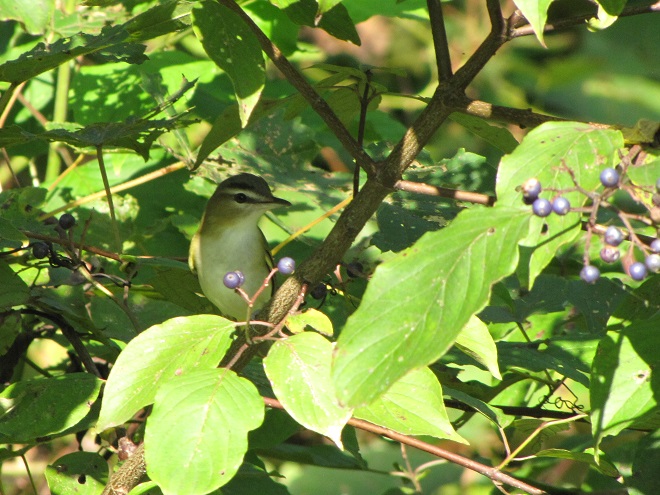
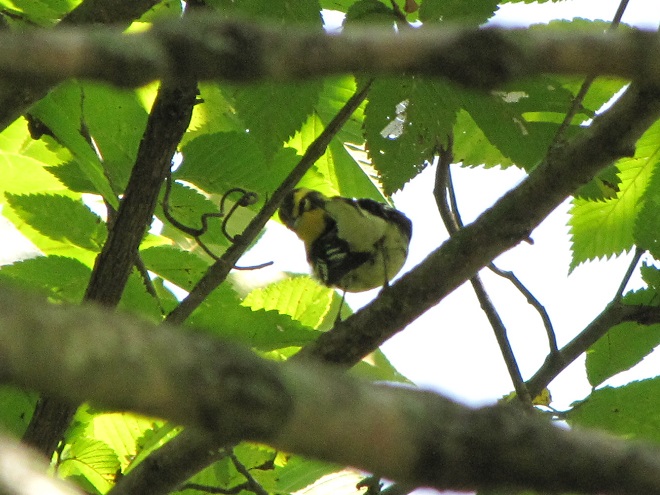
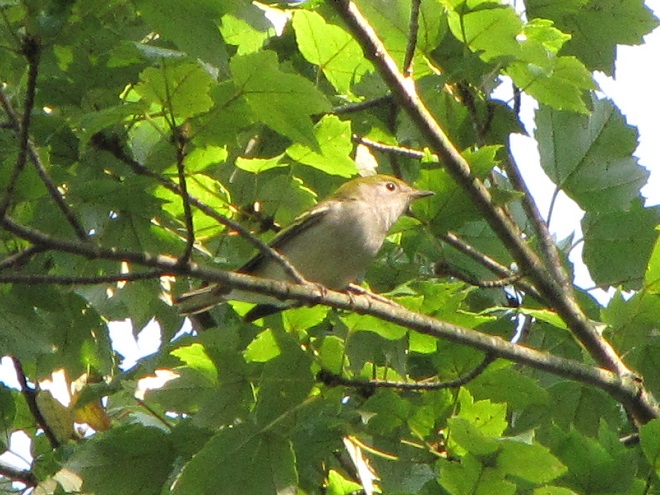
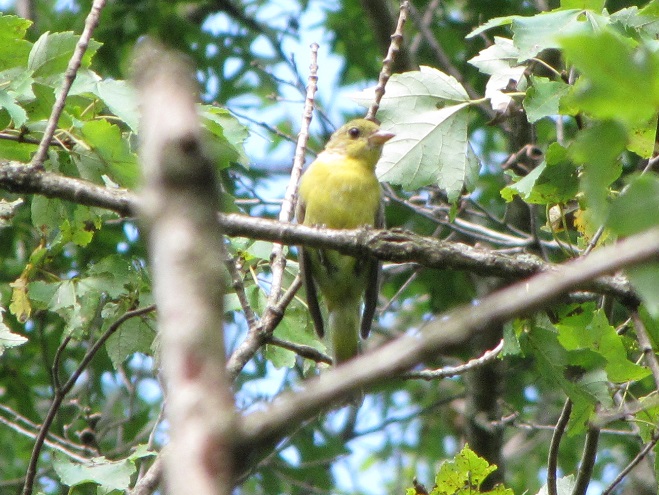
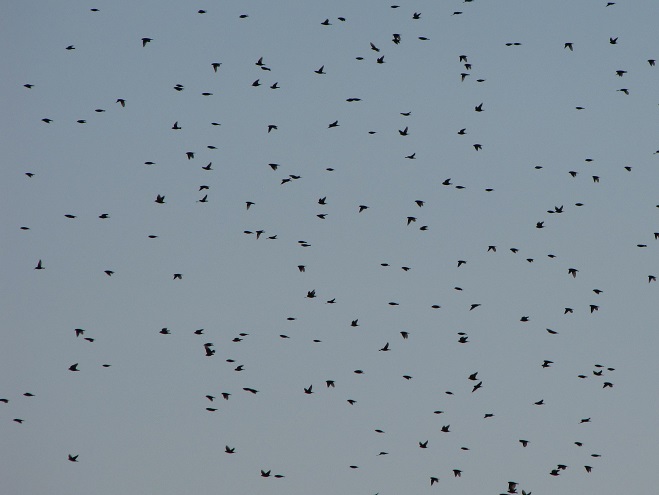
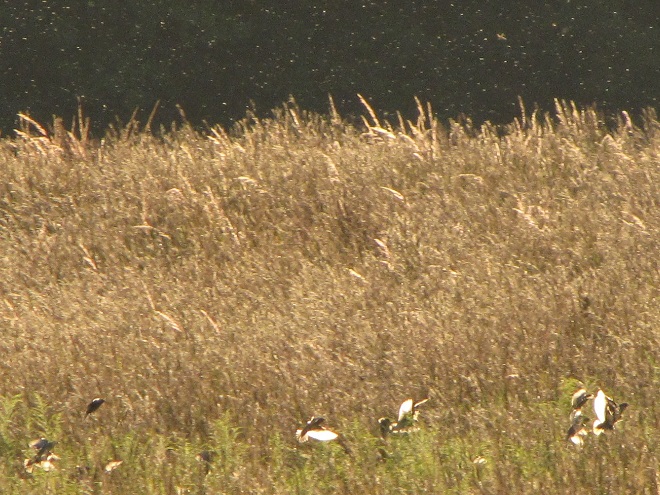
















Some of the newest mothers in the lower Susquehanna valley—nurturing their young.
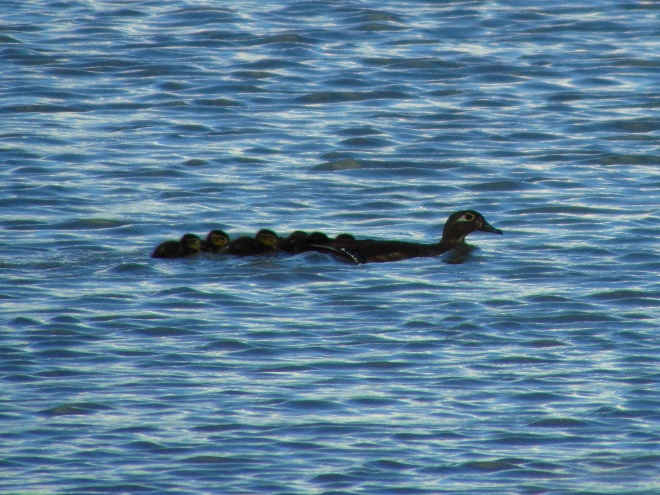



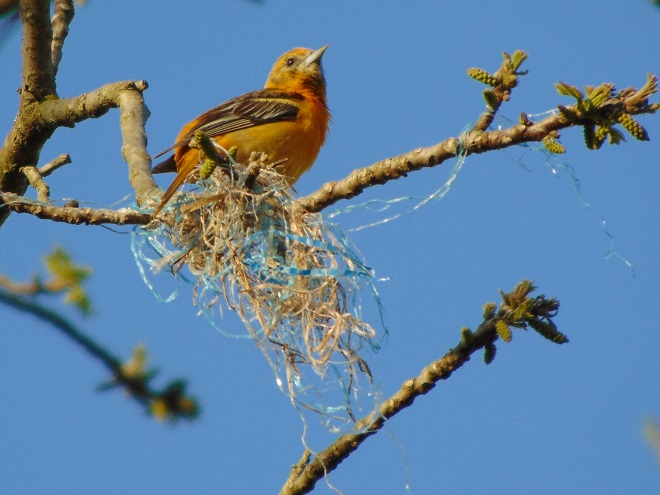
And a soon-to-be mother making the necessary preparations to bring a new generation into the world.

Have a Happy Mother’s Day!
For those of you who dare to shed that filthy contaminated rag you’ve been told to breathe through so that you might instead get out and enjoy some clean air in a cherished place of solitude, here’s what’s around—go have a look.
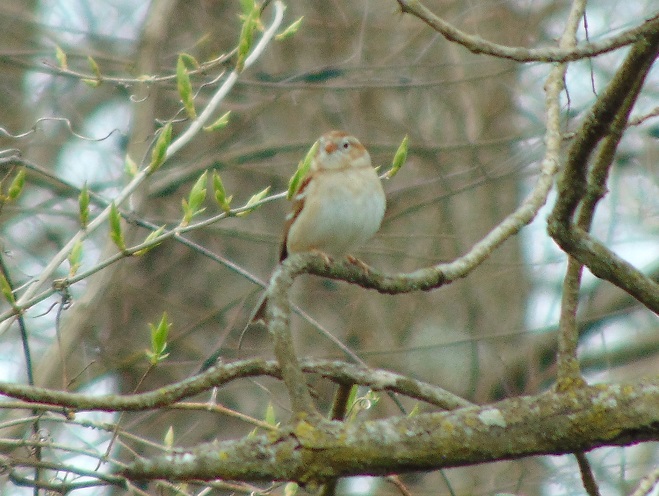
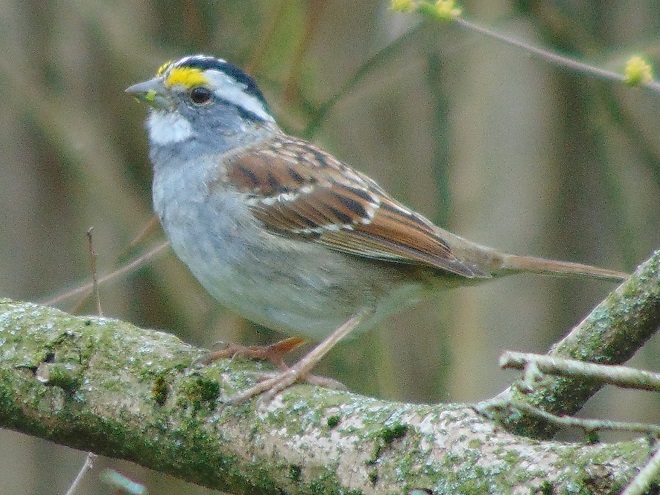
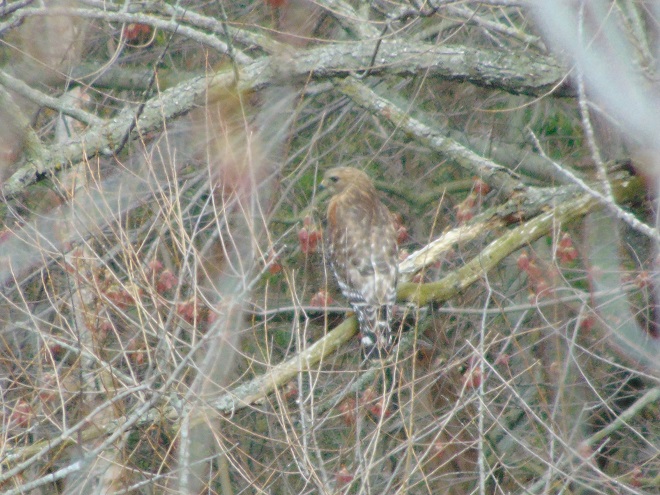
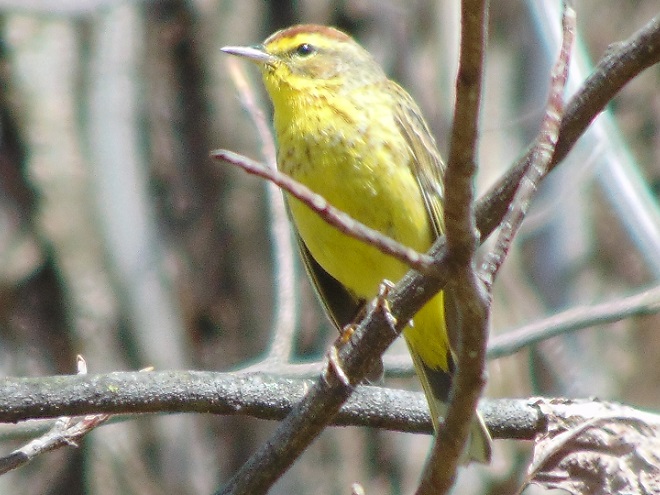







The springtime show on the water continues…







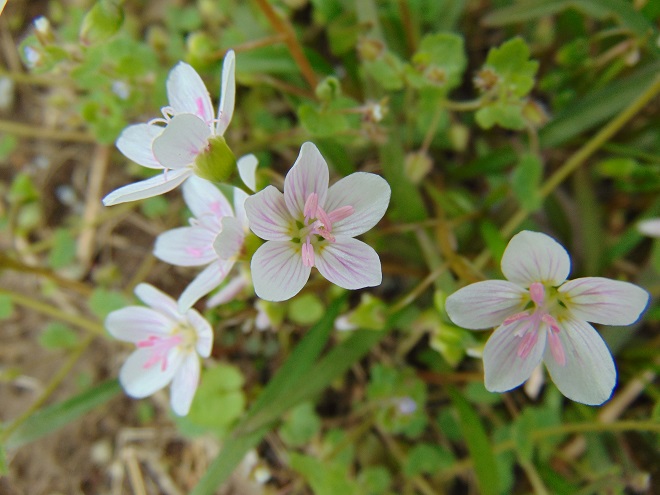
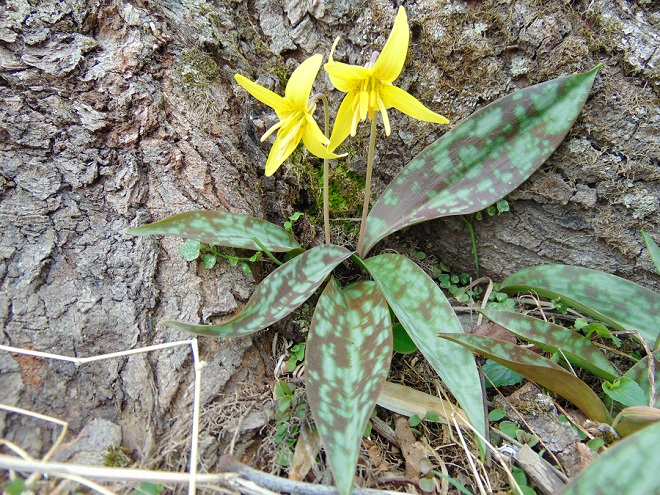
Hey, what are those showy flowers?





Wasn’t that refreshing? Now go take a walk.
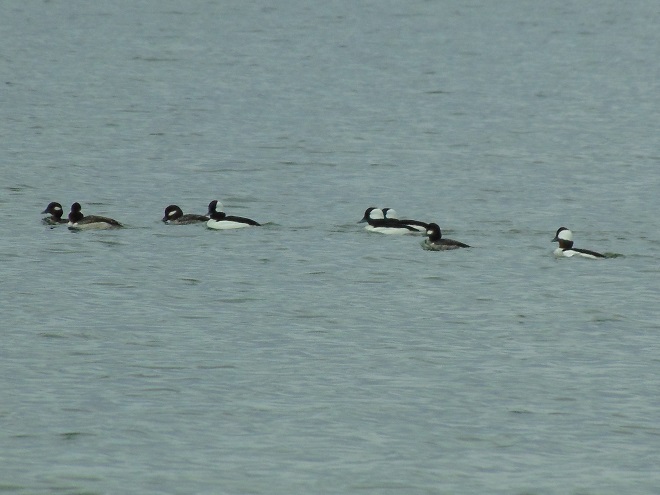
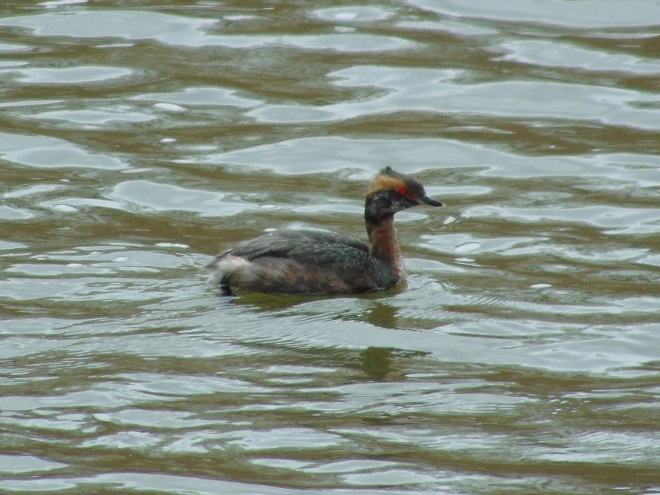
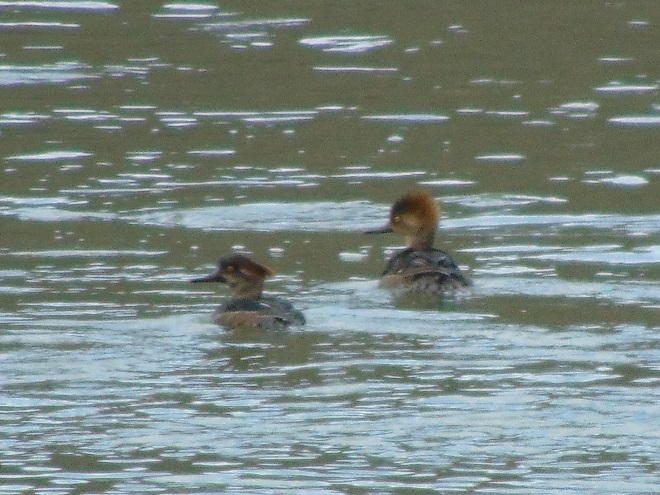
Fog and mist lingered throughout the day, as did the migratory water birds on the river and lakes in the lower Susquehanna valley. As a continuation of yesterday’s post on the fallout, here’s a photo tour of some of the sites where ducks, loons, grebes, and other birds have gathered.
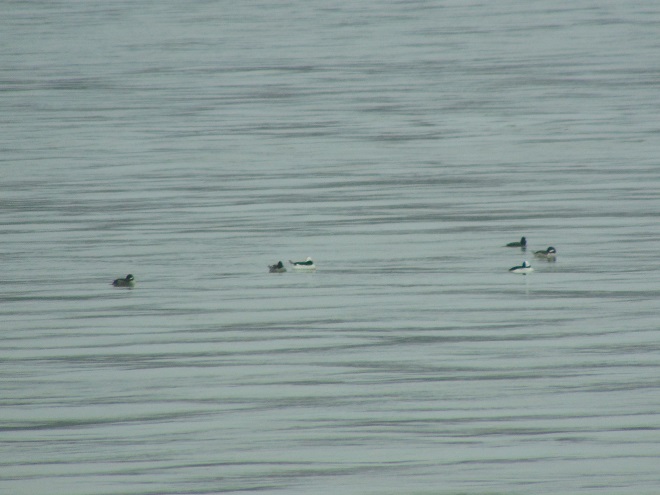
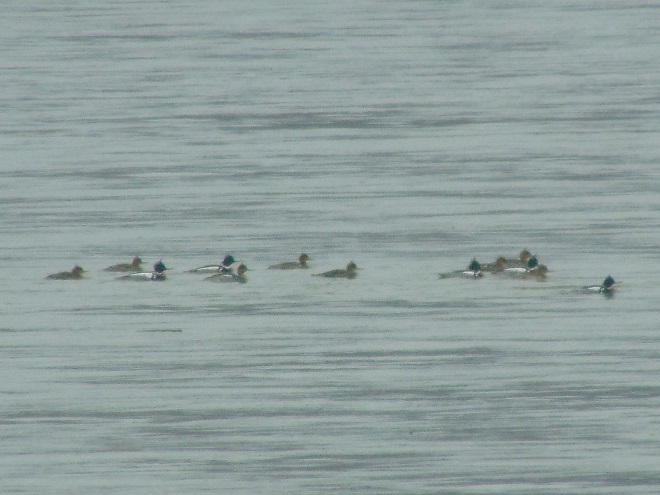
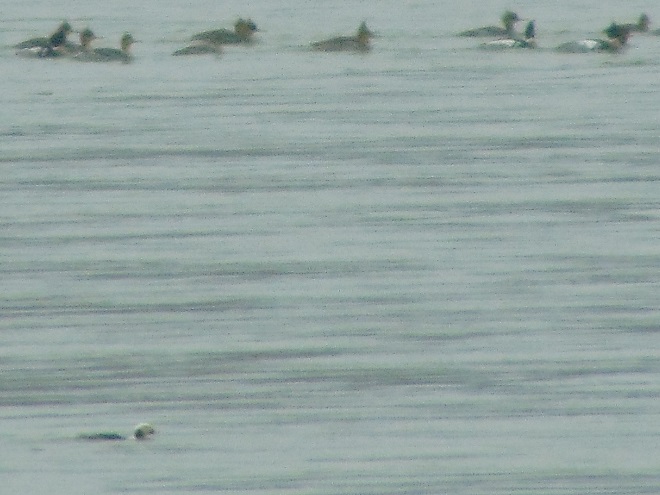
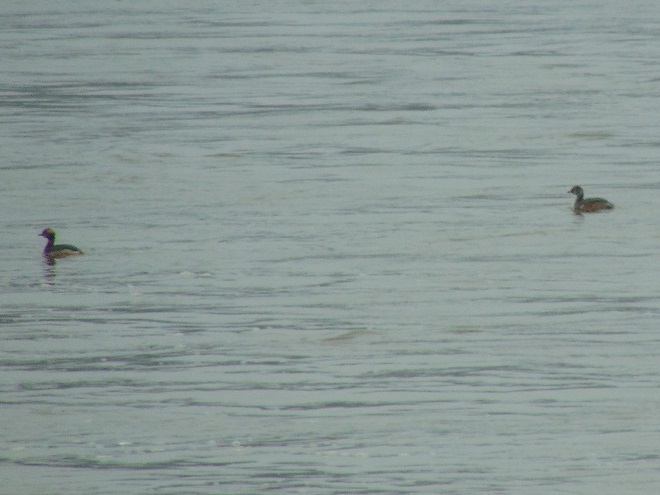
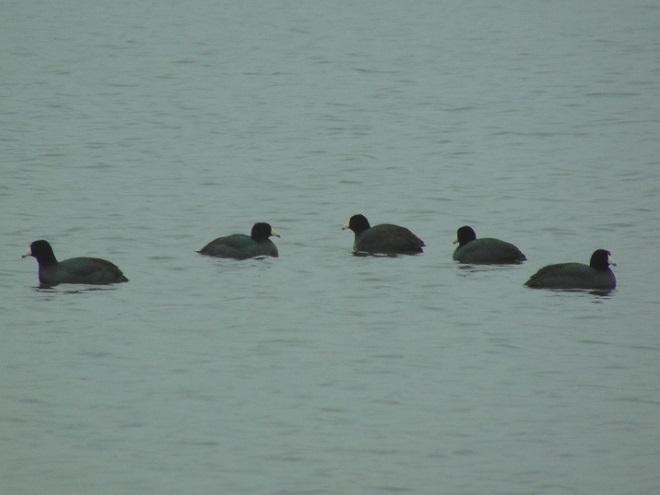
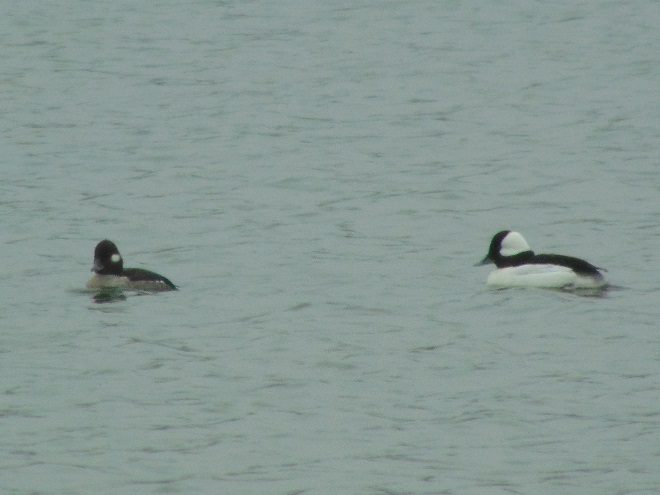
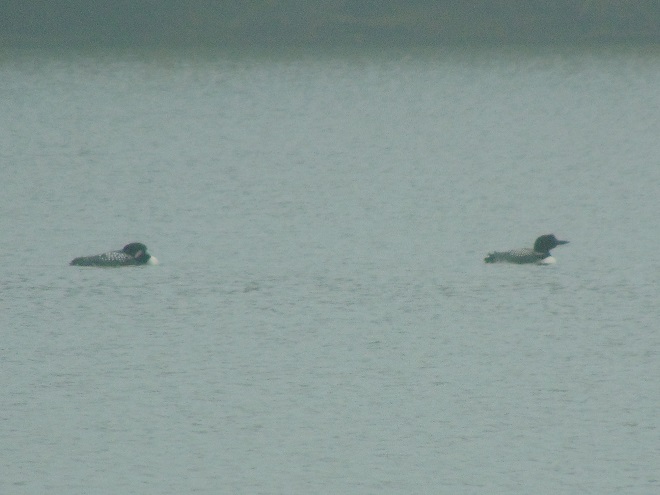
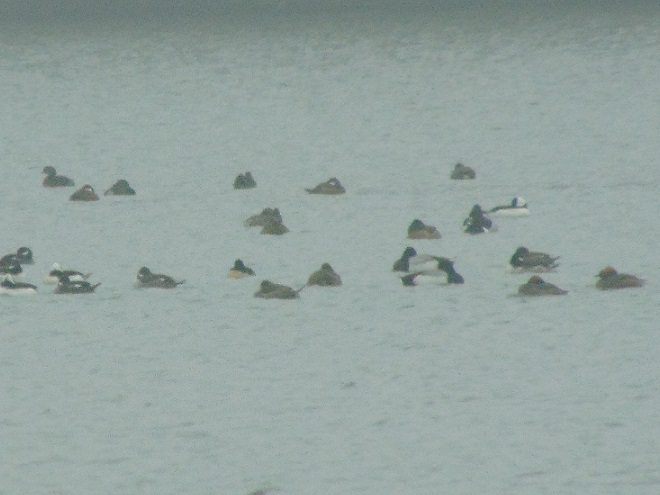











Stormy weather certainly is a birder’s delight.
Local birders enjoy going to the Atlantic coast of New Jersey and Delmarva in the winter. The towns and beaches host far fewer people than birds, and many of the species seen are unlikely to be found anywhere else in the region. Unusual rarities add to the excitement.
The regular seaside attraction in winter is the variety of diving ducks and similar water birds that feed in the ocean surf and in the saltwater bays. Most of these birds breed in Canada and many stealthily cross over the landmass of the northeastern United States during their migrations. If an inland birder wants to see these coastal specialties, a trip to the shore in winter or a much longer journey to Canada in the summer is normally necessary—unless there is a fallout.
Migrating birds can show up in strange places when a storm interrupts their flight. Forest songbirds like thrushes and warblers frequently take temporary refuge in a wooded backyard or even in a city park when forced down by inclement weather. Loons have been found in shopping center parking lots after mistaking the wet asphalt for a lake. Fortunately though, loons, ducks, and other water birds usually find suitable ponds, lakes, and rivers as places of refuge when forced down. For inland birders, a fallout like this can provide an opportunity to observe these coastal species close to home.
Not so coincidentally, it has rained throughout much of today in the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed, apparently interrupting a large movement of migrating birds. There is, at the time of this writing, a significant fallout of coastal water birds here. Hundreds of diving ducks and other benthic feeders are on the Susquehanna River and on some of the clearer lakes and ponds in the region. They can be expected to remain until the storm passes and visibility improves—then they’ll promptly commence their exodus.
The following photographs were taken during today’s late afternoon thundershower at Memorial Lake State Park at Fort Indiantown Gap, Lebanon County.






Migrating land birds have also been forced down by the persistent rains.

Why not get out and take a slow quiet walk on a rainy day. It may be the best time of all for viewing certain birds and other wildlife.


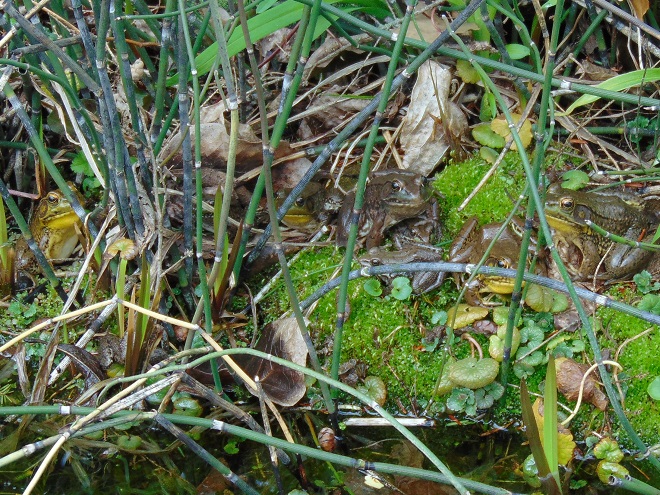
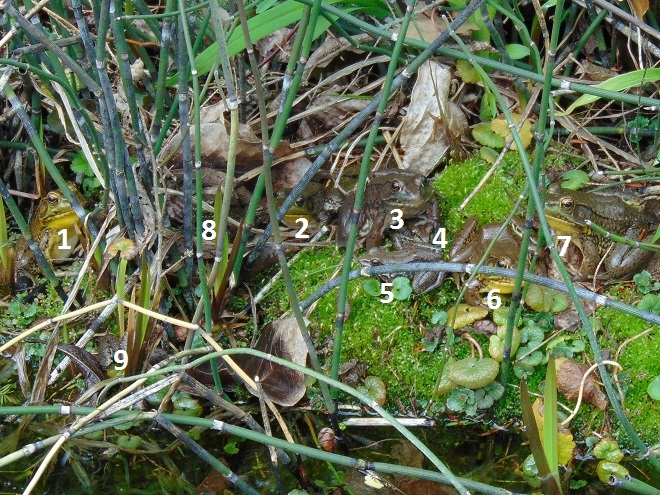
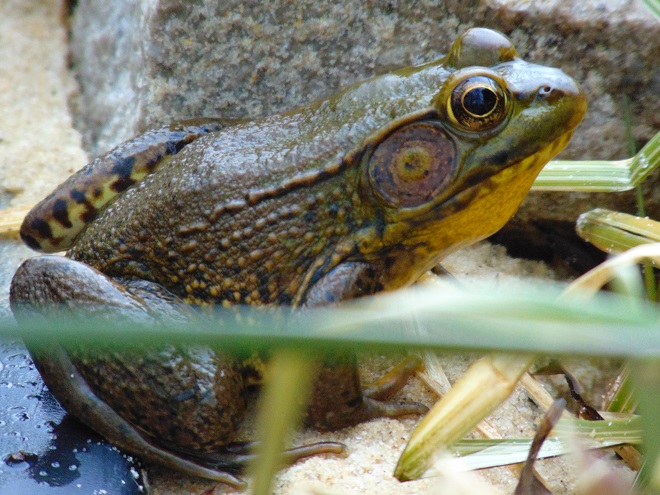
The mild winter has apparently minimized weather-related mortality for the local Green Frog population. With temperatures in the seventies throughout the lower Susquehanna valley for this first full day of spring, many recently emerged adults could be seen and, on occasion, heard. Yellow-throated males tested their mating calls—reminding the listener of the sound made by the plucking of a loose banjo string.

If you venture out, keep alert for the migrating birds of late winter and early spring.
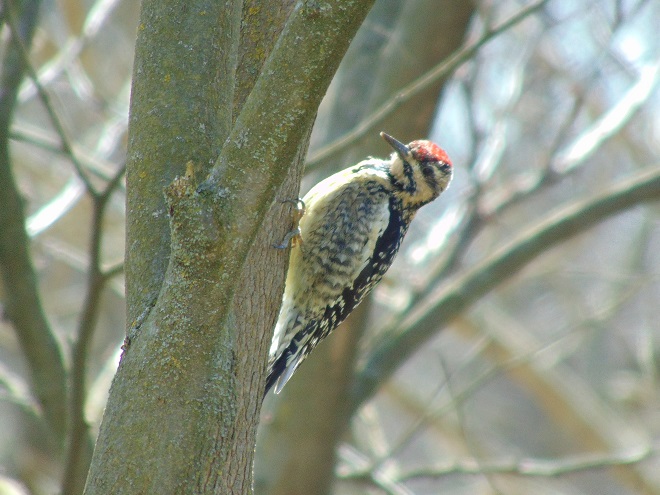
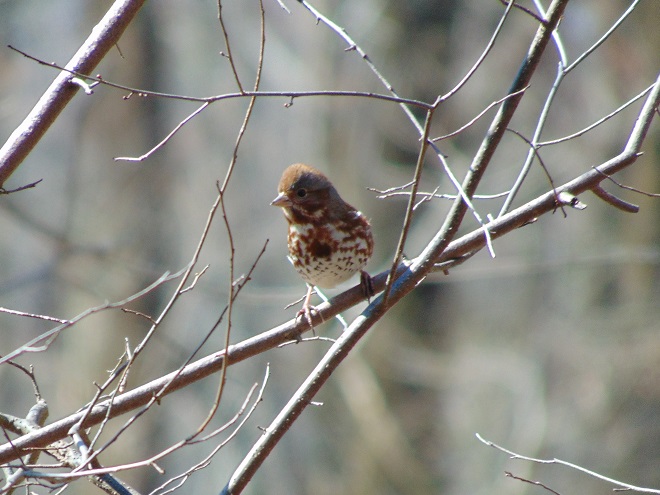
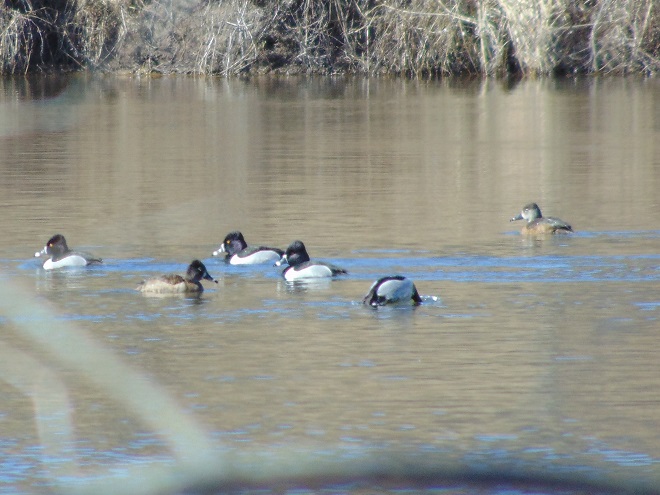
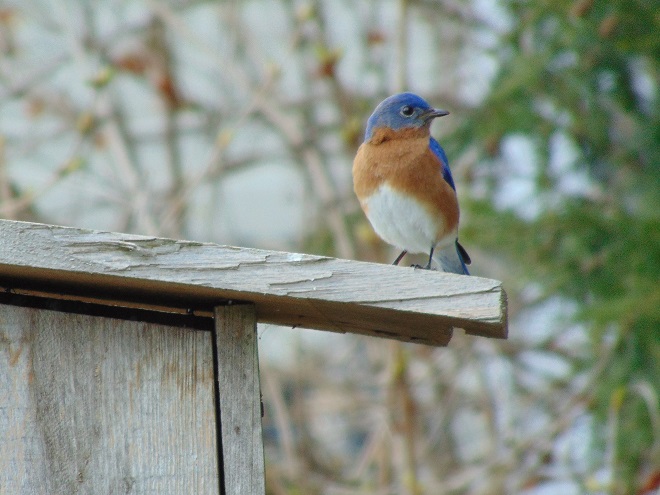
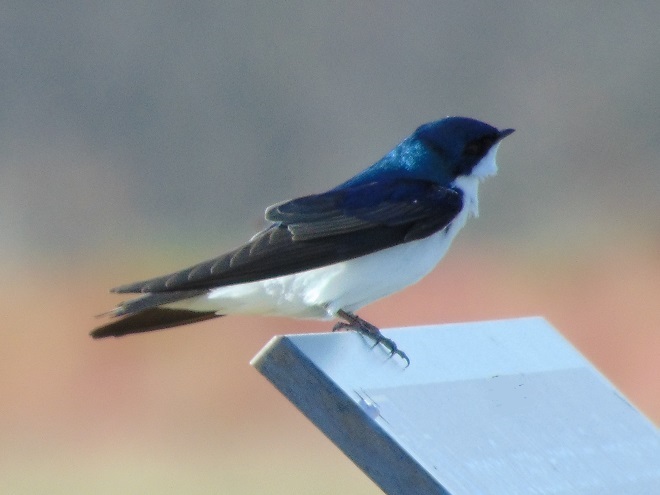
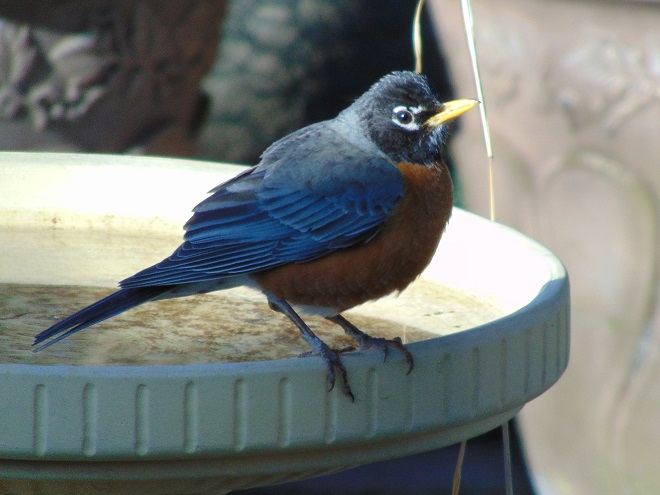
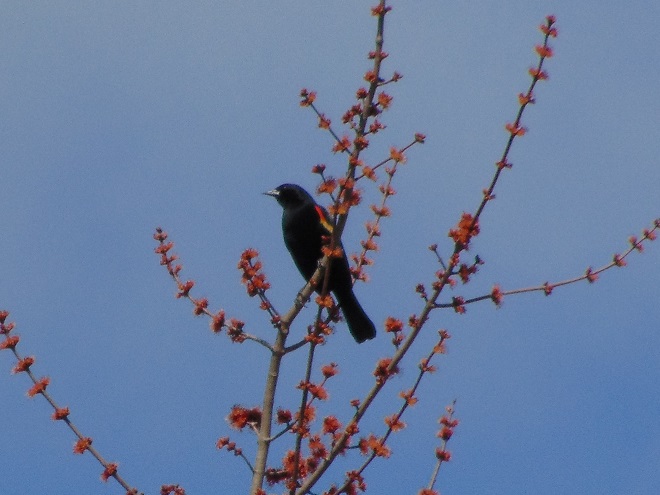








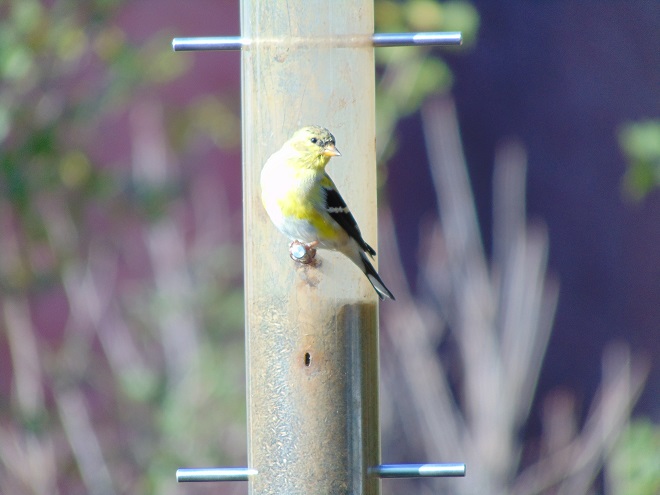
If you’re staying close to home, be sure to check out the changing appearance of the birds you see nearby. Some species are losing their drab winter basic plumage and attaining a more colorful summer breeding alternate plumage.


So just how many Green Frogs were there in that first photograph? Here’s the answer.

Happy Spring. For the benefit of everyone’s health, let’s hope that it’s a hot and humid one!
According to the most recent Pennsylvania Game Commission estimate, there are presently more than 100,000 Snow Geese at the Middle Creek Wildlife Management Area (W.M.A.) in Lancaster and Lebanon Counties. It’s a spectacular sight.
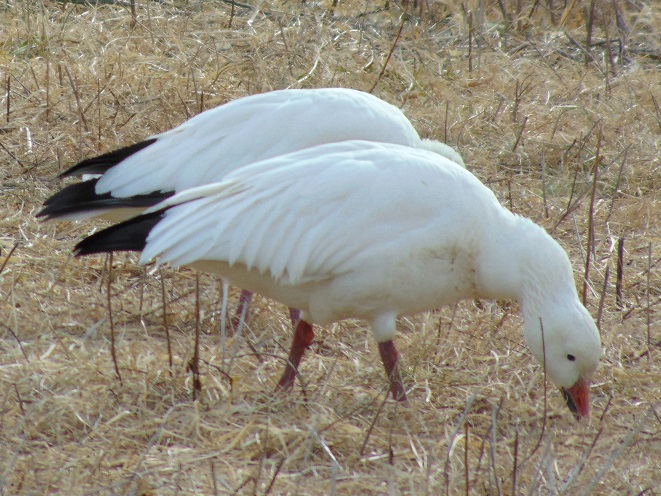


If you go to see these and other birds at Middle Creek, it’s important to remember that you are visiting them in a “wildlife refuge” set aside for, believe it or not, wildlife. “Wildlife refuge”, many would be surprised to learn, is short for “terrestrial or aquatic habitat where wildlife can find refuge and protection from all the meddlesome and murderous things people do”.










Nothing says Happy Valentine’s Day like a really bad poem, so here it is…
FOR THE LOVE OF DUCKS
I like to feed the duckies
Try it and you’ll see
Aren’t they really lucky?
Relying just on me
My neighbors are complainin’
I can hear them talk
The mallards eat their garden
Let surprises on their walk
Dung stains on the carpets
They tracked it in the house
It’s from those ducks and not the pets
Can’t blame it on the spouse
I like to feed the duckies
Try it and you’ll see
Aren’t they really lucky?
Relying just on me
Tamed with bread and crackers
I gave them as a treat
I soon found maimed dead quackers
Lying in the street
A driver who intended
To miss the hens and drakes
Had their car rear-ended
When they hit the brakes
I like to feed the duckies
Try it and you’ll see
Aren’t they really lucky?
Relying just on me
The flock is very wasteful
Each bird a pound a day
Web-foots in a cesspool
Pollute the waterway
There are some kids playing
In that filthy ditch
Soon they’ll be displaying
The rash of Swimmer’s Itch
I like to feed the duckies
Try it and you’ll see
Aren’t they really lucky?
Relying just on me
These ducks they do not migrate
They’re here day in, day out
Aquatic life they decimate
No plants, no fish, no trout
Hurry! Hurry! Heed my call
Before it starts to rain
Ten more ducklings took a fall
And are stranded in a drain
I like to feed the duckies
Try it and you’ll see
Aren’t they really lucky?
Relying just on me
Have you people lost your minds?
I see you by your fence
These ducks are cute and I am kind
It’s you who’ve lost your sense
Beggars from the handouts
My God what have I done?
Their senseless habits leave no doubt
Their instincts are all gone
I like to feed the duckies
Try it and you’ll see
Aren’t they really lucky?
Relying just on me
Now I know just what to do
Like one would teach a child
I’ll feed the ducks at the zoo
And let the rest live wild
So if you feed the duckies
Beware of the spell
Or you will do the same as me
Loving ducks to death as well
—Ducks Anonymous, LLC

Inside the doorway that leads to your editor’s 3,500 square foot garden hangs a small chalkboard upon which he records the common names of the species of birds that are seen there—or from there—during the year. If he remembers to, he records the date when the species was first seen during that particular year. On New Year’s Day, the results from the freshly ended year are transcribed onto a sheet of notebook paper. On the reverse, the names of butterflies, mammals, and other animals that visited the garden are copied from a second chalkboard that hangs nearby. The piece of paper is then inserted into a folder to join those from previous New Year’s Days. The folder then gets placed back into the editor’s desk drawer beneath a circular saw blade and an old scratched up set of sunglasses—so that he knows exactly where to find it if he wishes to.
A quick glance at this year’s list calls to mind a few recollections.
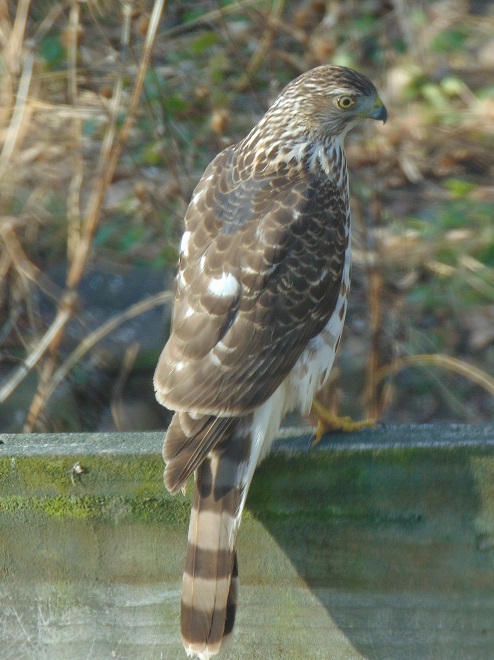
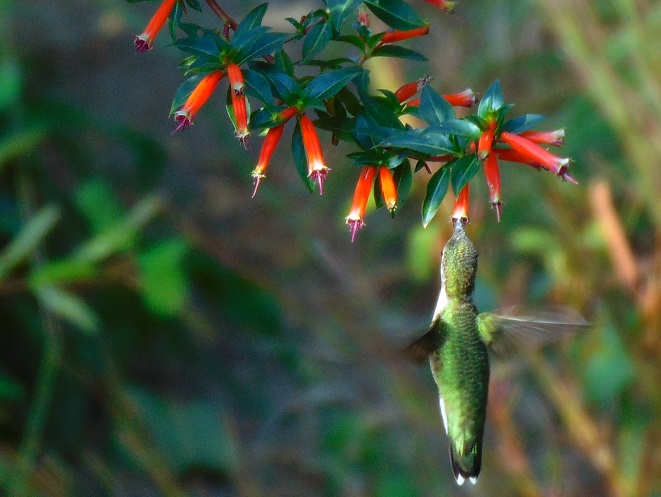
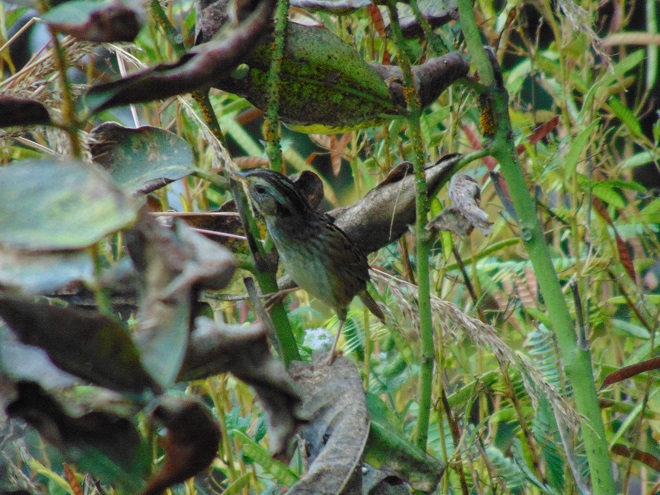






Before putting the folder back into the drawer for another year, the editor decided to count up the species totals on each of the sheets and load them into the chart maker in the computer.
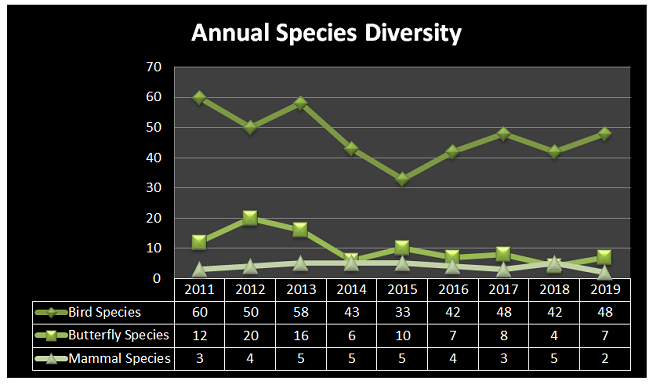 Despite the habitat improvements in the garden, the trend is apparent. Bird diversity has not cracked the 50 species mark in 6 years. Despite native host plants and nectar species in abundance, butterfly diversity has not exceeded 10 species in 6 years.
Despite the habitat improvements in the garden, the trend is apparent. Bird diversity has not cracked the 50 species mark in 6 years. Despite native host plants and nectar species in abundance, butterfly diversity has not exceeded 10 species in 6 years.
It appears that, at the very least, the garden habitat has been disconnected from the home ranges of many species by fragmentation. His little oasis is now isolated in a landscape that becomes increasingly hostile to native wildlife with each passing year. The paving of more parking areas, the elimination of trees, shrubs, and herbaceous growth from the large number of rental properties in the area, the alteration of the biology of the nearby stream by hand-fed domestic ducks, light pollution, and the outdoor use of pesticides have all contributed to the separation of the editor’s tiny sanctuary from the travel lanes and core habitats of many of the species that formerly visited, fed, or bred there. In 2019, migrants, particularly “fly-overs”, were nearly the only sightings aside from several woodpeckers, invasive House Sparrows (Passer domesticus), and hardy Mourning Doves. Even rascally European Starlings became sporadic in occurrence—imagine that! It was the most lackluster year in memory.
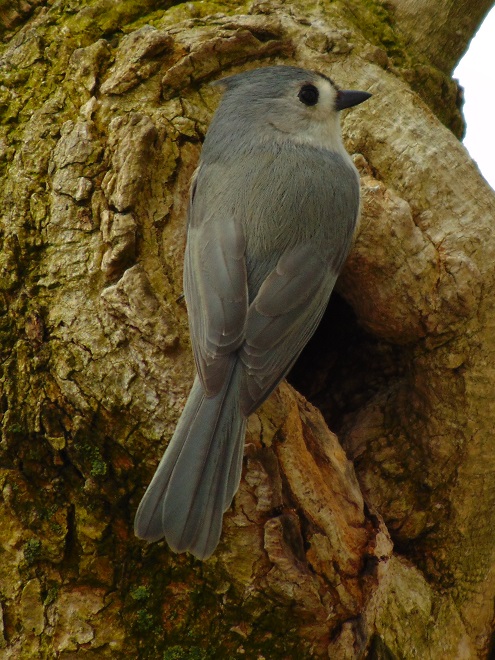
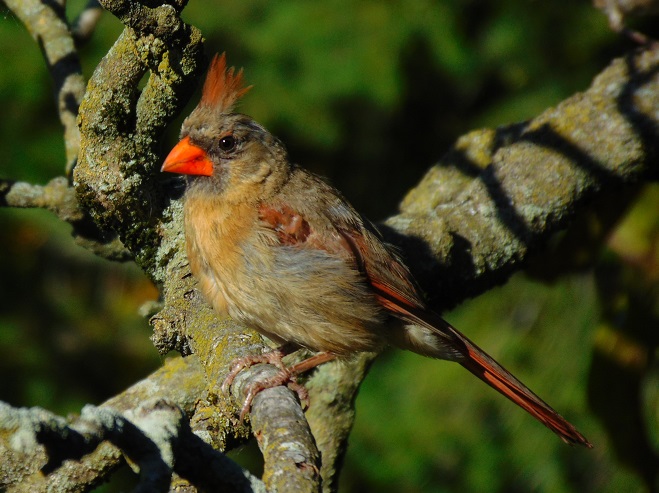


If habitat fragmentation were the sole cause for the downward trend in numbers and species, it would be disappointing, but comprehendible. There would be no cause for greater alarm. It would be a matter of cause and effect. But the problem is more widespread.
Although the editor spent a great deal of time in the garden this year, he was also out and about, traveling hundreds of miles per week through lands on both the east and the west shores of the lower Susquehanna. And on each journey, the number of birds seen could be counted on fingers and toes. A decade earlier, there were thousands of birds in these same locations, particularly during the late summer.
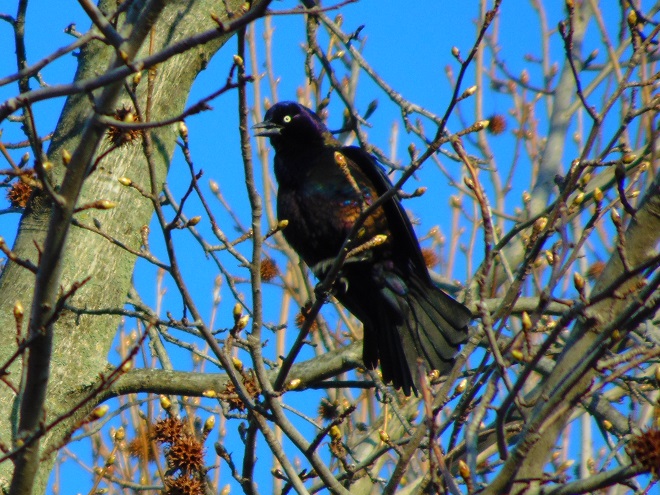

In the lower Susquehanna valley, something has drastically reduced the population of birds during breeding season, post-breeding dispersal, and the staging period preceding autumn migration. In much of the region, their late-spring through summer absence was, in 2019, conspicuous. What happened to the tens of thousands of swallows that used to gather on wires along rural roads in August and September before moving south? The groups of dozens of Eastern Kingbirds (Tyrannus tyrannus) that did their fly-catching from perches in willows alongside meadows and shorelines—where are they?
Several studies published during the autumn of 2019 have documented and/or predicted losses in bird populations in the eastern half of the United States and elsewhere. These studies looked at data samples collected during recent decades to either arrive at conclusions or project future trends. They cite climate change, the feline infestation, and habitat loss/degradation among the factors contributing to alterations in range, migration, and overall numbers.
There’s not much need for analysis to determine if bird numbers have plummeted in certain Lower Susquehanna Watershed habitats during the aforementioned seasons—the birds are gone. None of these studies documented or forecast such an abrupt decline. Is there a mysterious cause for the loss of the valley’s birds? Did they die off? Is there a disease or chemical killing them or inhibiting their reproduction? Is it global warming? Is it Three Mile Island? Is it plastic straws, wind turbines, or vehicle traffic?
The answer might not be so cryptic. It might be right before our eyes. And we’ll explore it during 2020.

In the meantime, Uncle Ty and I going to the Pennsylvania Farm Show in Harrisburg. You should go too. They have lots of food there.
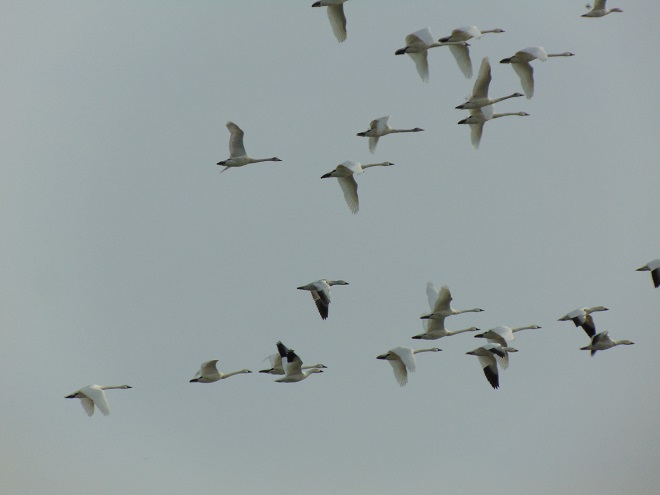
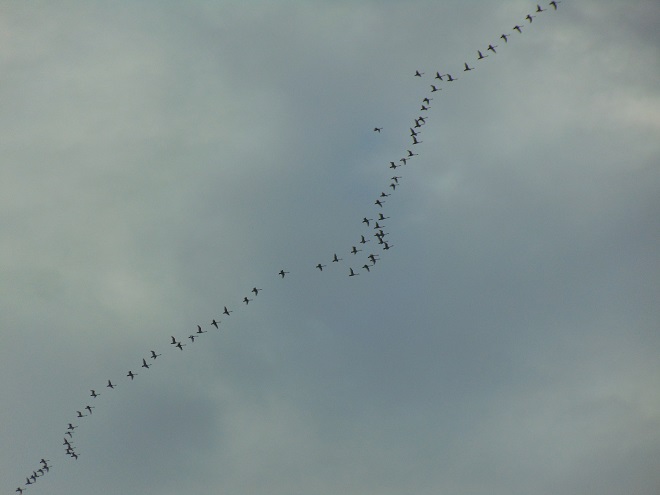
There was a hint of what was to come. If you were out and about before dawn this morning, you may have been lucky enough to hear them passing by high overhead. It was 5:30 A.M. when I opened the door and was greeted by that distinctive nasal whistle. Stepping through the threshold and into the cold, I peered into the starry sky and saw them, their feathers glowing orange in the diffused light from the streets and parking lots below. Their size and snow-white plumage make Tundra Swans one of the few species of migrating birds you’ll ever get to visibly discern in a dark moonless nighttime sky.
The calm air at daybreak and through the morning transitioned to a steady breeze from the south in the afternoon. Could this be it? Would this be that one day in late February or the first half of March each year when waterfowl (and other birds too) seem to take advantage of the favorable wind to initiate an “exodus” and move in conspicuous numbers up the lower Susquehanna valley on their way to breeding grounds in the north? Well, indeed it would be. And with the wind speeding up the parade, an observer at a fixed point on the ground gets to see more birds fly by.
In the late afternoon, an observation location in the Gettysburg Basin about five miles east of Conewago Falls in Lancaster County seemed to be well-aligned with a northwesterly flight path for migrating Tundra Swans. At about 5:30 P.M., the clear sky began clouding over, possibly pushing high-flying birds more readily into view. During the next several hours, over three thousand Tundra Swans passed overhead, flocks continuing to pass for a short time after nightfall. There were more than one thousand Canada Geese, the most numerous species on similar days in previous years. Sometimes on such a day there are numerous ducks. Not today. The timing, location, and conditions put Tundra Swans in the spotlight for this year’s show.
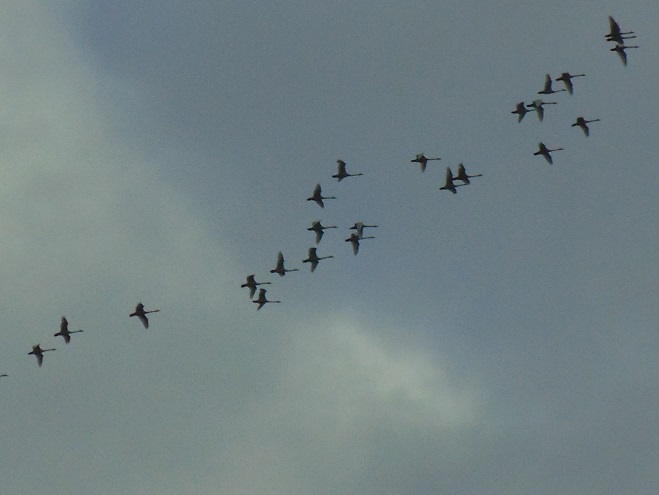
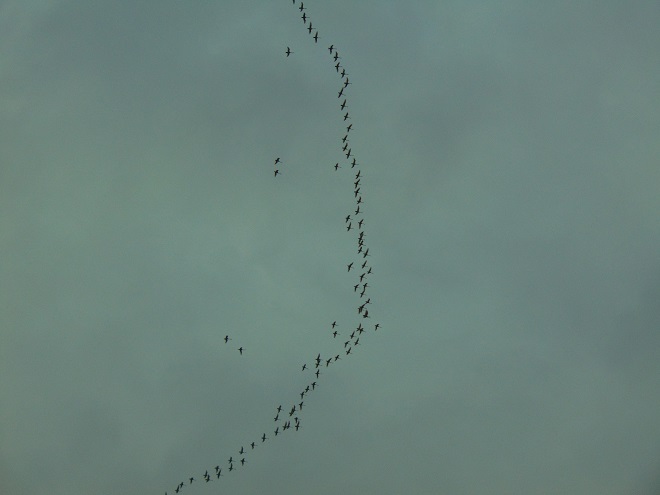
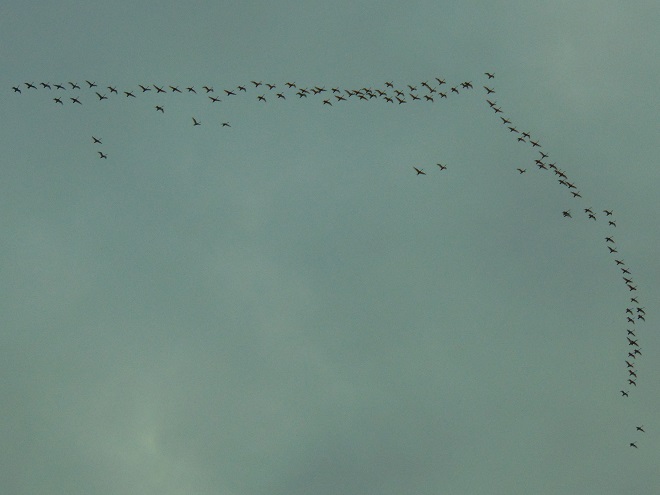
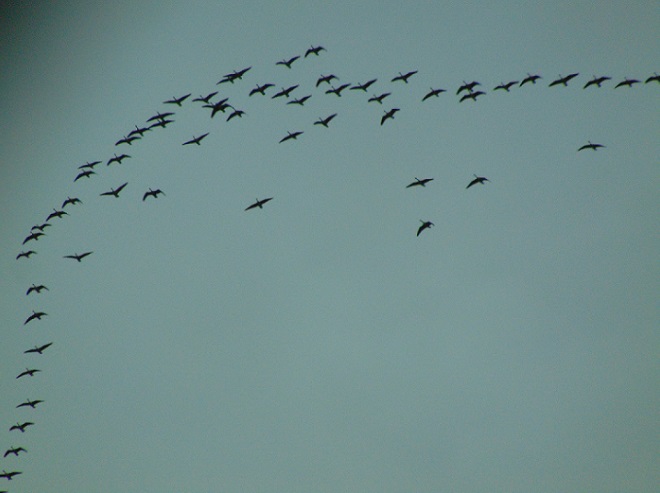






Other migrants moving concurrently with the waterfowl included Ring-billed Gulls, Herring Gulls (6+), American Robins (50+), Red-winged Blackbirds (500+), and Common Grackles (100+).
Though I’ve only seen such a spectacle only once during a season in recent years, there certainly could be another large flight of ducks, geese, or swans yet to come. The breeze is forecast to continue from southerly directions for at least another day. Keep you eyes skyward, no matter where you might happen to be in the lower Susquehanna valley. These or other migratory species may put on another show, a “big day”, just for you.
One can get a stiff neck looking up at the flurry of bird activity in the treetops at this time of year. Many of the Neotropical migrants favor rich forests as daytime resting sites after flying through the night. For others, these forests are a destination where they will nest and raise their young.
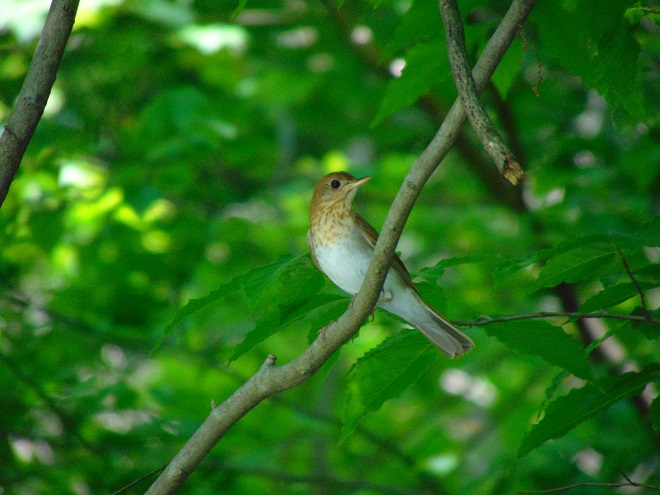
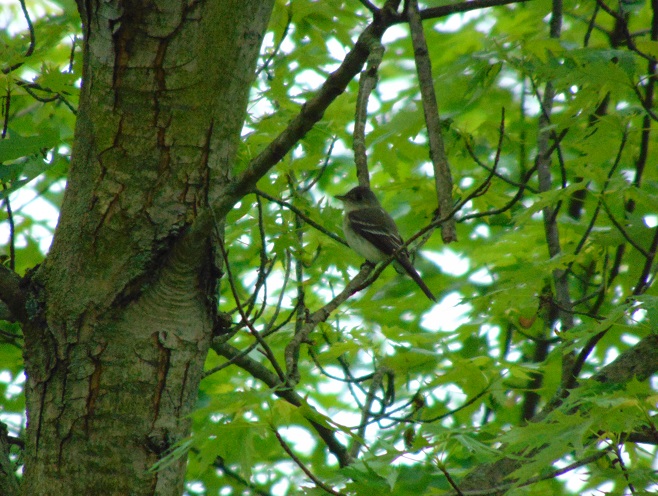
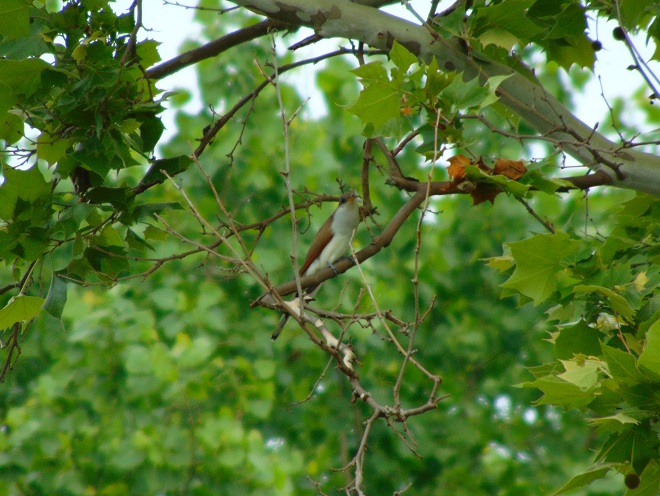
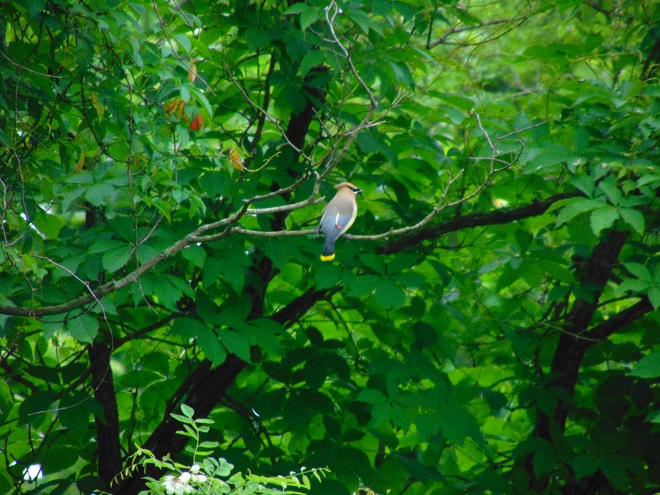
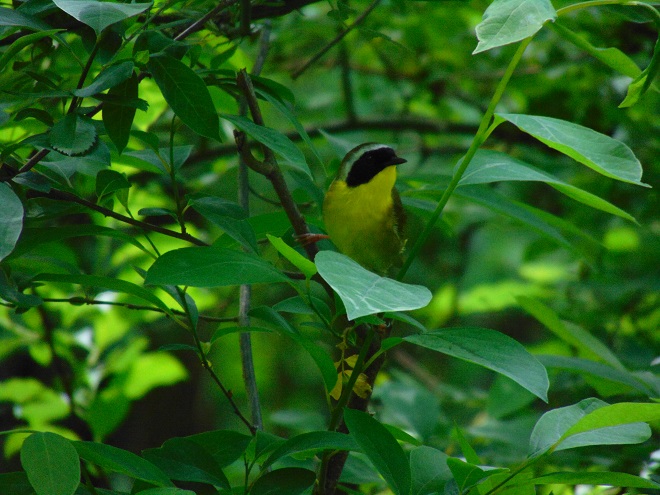







For the birds that arrive earlier in spring than the Neotropical migrants, the breeding season is well underway. The wet weather may be impacting the success of the early nests.



So long for now, if you’ll excuse me please, I have a sore neck to tend to.
You remember the signs of an early spring, don’t you? It was a mild, almost balmy, February. The earliest of the spring migrants such as robins and blackbirds were moving north through the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed. The snow had melted and ice on the river had passed. Everyone was outdoors once again. At last, winter was over and only the warmer months lie ahead…beginning with March.

Ah yes, March, the cold windy month of March. We remember February fondly, but this March has startled us out of our vernal daydreams to wrestle with the reality of the season. And if you’re anywhere near the Mid-Atlantic states on this first full day of spring, you know that a long winter’s nap and visions of sugar peas would be time better spent than a stroll outdoors. Presently it’s dusk, and the snow from the 4th “Nor’easter” in a month is a foot deep and still falling.
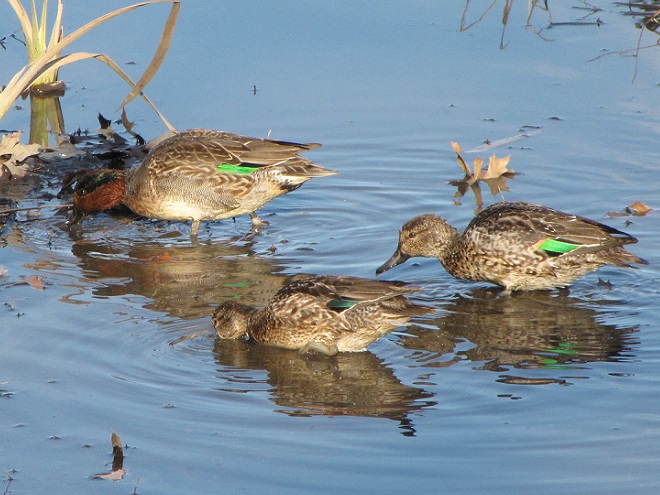
In honor of “The Spring That Was”, here then is a sampling of some of the migratory waterfowl that have found their way to the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed during March. Some are probably lingering and feeding for a while. All will move along to their breeding grounds within a couple of weeks, regardless of the weather.
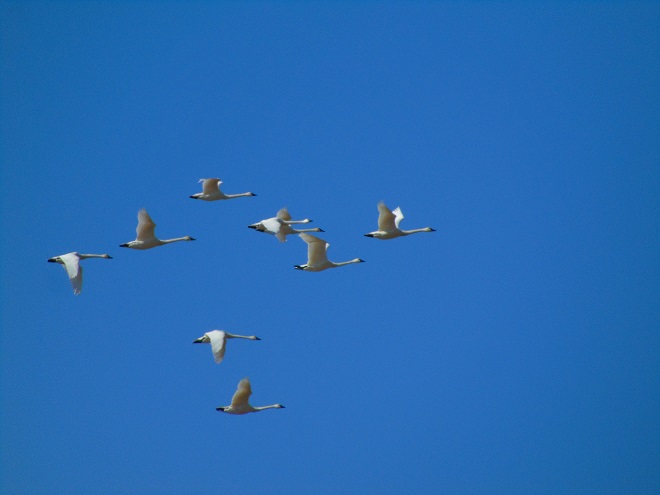
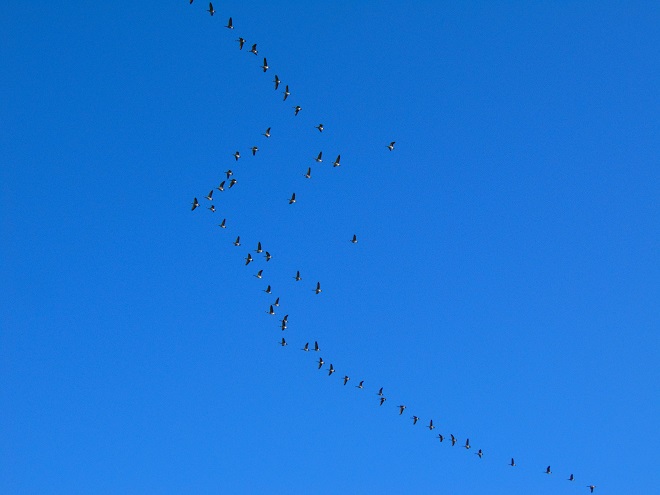
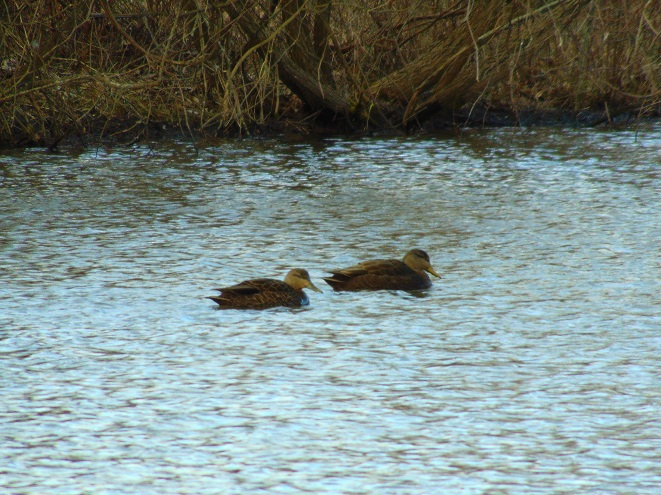
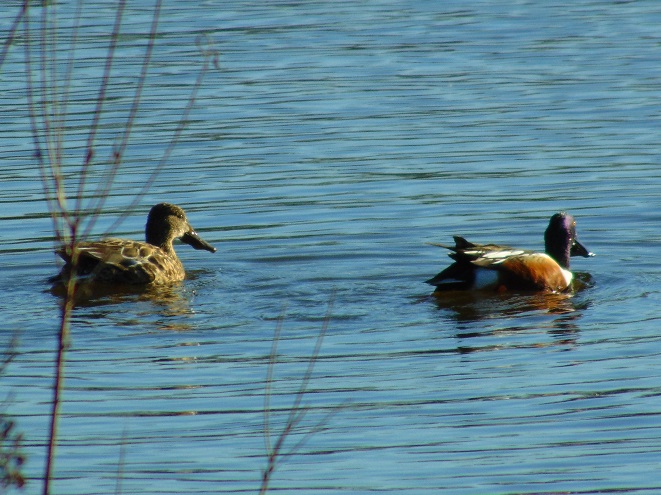
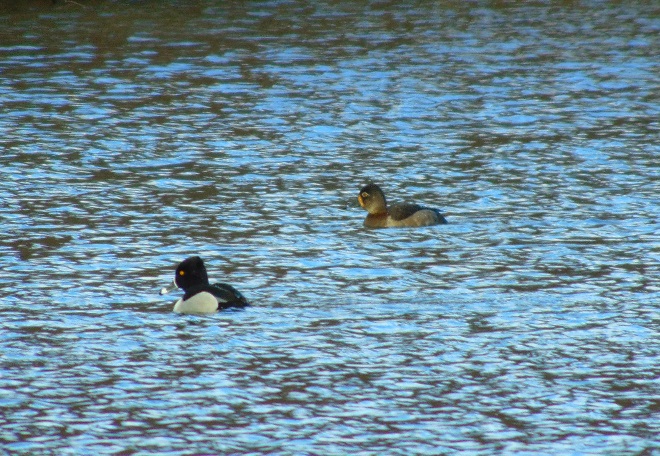
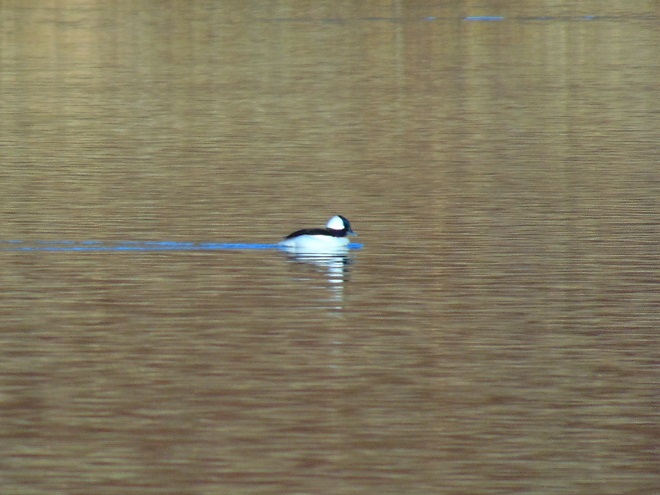









At the moment there is a heavy snow falling, not an unusual occurrence for mid-February, nevertheless, it is a change in weather. Forty-eight hours ago we were in the midst of a steady rain and temperatures were in the sixties. The snow and ice had melted away and a touch of spring was in the air.
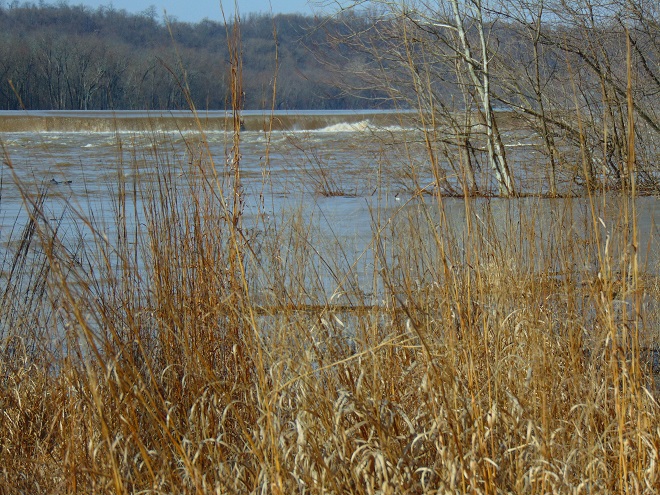

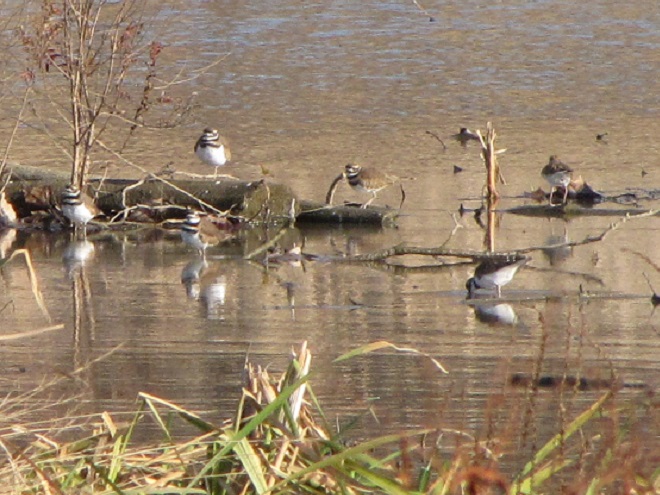
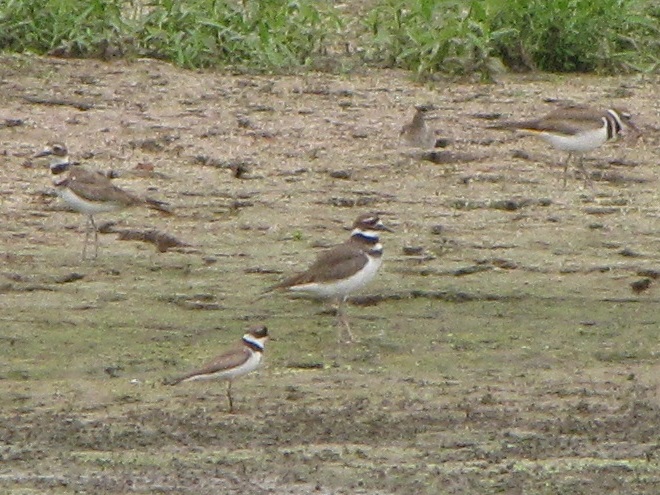
Anyone casually looking about while outdoors during these last several days may have noticed that birds are indeed beginning to migrate north in the lower Susquehanna valley. Killdeer, American Robins, Eastern Bluebirds, Red-winged Blackbirds, and Common Grackles are easily seen or heard in most of the area now.
Just hours ago, between nine o’clock this morning and one o’clock this afternoon, there was a spectacular flight of birds following the river north, their spring migration well underway. In the blue skies above Conewago Falls, a steady parade of Ring-billed Gulls was utilizing thermals and riding a tailwind from the south-southeast to cruise high overhead on a course toward their breeding range.
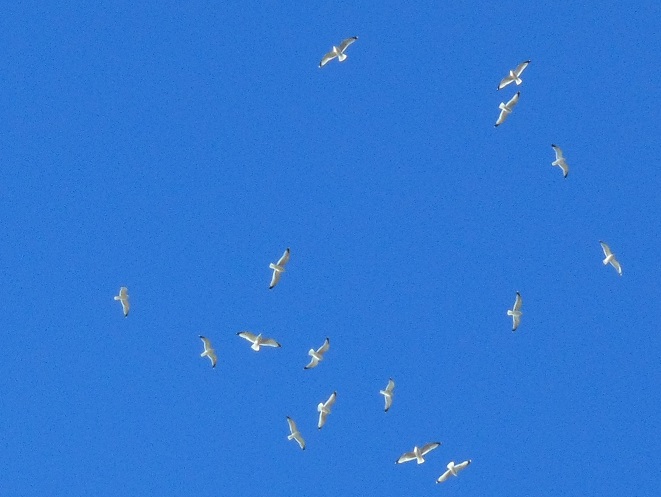


The swirling hoards of Ring-billed Gulls attracted other migrants to take advantage of the thermals and glide paths on the breeze. Right among them were 44 Herring Gulls, 3 Great Black-backed Gulls, 12 Tundra Swans (Cygnus columbianus), 10 Canada Geese, 3 Northern Pintails (Anas acuta), 6 Common Mergansers, 3 Red-tailed Hawks, a Red-shouldered Hawk, 6 Bald Eagles (non-adults), 8 Black Vultures, and 5 Turkey Vultures.


In the afternoon, the clouds closed in quickly, the flight ended, and by dusk more than an inch of snow was on the ground. Looks like spring to me.

A steady stream of birds was on the move this morning over Conewago Falls. There were hundreds of Ring-billed Gulls, scores of Herring Gulls, and a few Great Black-backed Gulls to dominate the flight. Then too there were thirteen Mallards, Turkey Vultures and a Black Vulture, twenty or more American Robins, a half a dozen Bald Eagles (juvenile and immature birds), a couple of Red-winged Blackbirds, and, perhaps most unusual of all, a flock of a dozen Scoters (Melanitta species), a waterfowl typical of the Mid-Atlantic surf in winter. All of these birds were diligently following the river, and into a headwind no less.
“Hold on just a minute there, buster,” you may say, “I’ve looked at the migration count by dutifully clicking on the logo above and there is nothing but zeroes on the count sheet for today. The season totals have not changed since the previous count day!”
Ah-ha, my dedicated friend, correct you are. It seems that today’s bird flight was solely in one direction. And that direction was upriver, moving north into a north breeze, on a heading which conflicts with all logic for creatures that should still be headed south for winter. As a result, none of the birds observed today were counted on the “Autumn Migration Count”.
You might say, “Don’t you know that Winter Solstice was three days ago, so autumn and autumn migration is over.”
Okay, point well taken. I should therefore clarify that what we title as “Autumn Migration Count” is more accurately a census of birds, insects, and other creatures transiting from northerly latitudes to more favorable latitudes to the south for winter. This transit can begin as early as late June and extend into the first weeks of winter. While most of this movement is motivated by the reduced hours of daylight during the period, late season migrants are often responding to ice, bad weather, or lack of food to prompt a journey further south. Migration south in late December and January occurs even while the amount of daylight is increasing slightly in the days following the Winter Solstice.
So what of the birds seen flying north today? There was some snow cover that has melted away, and the ice that formed on the river a week ago is gone due to the milder than normal temperatures this week.
One may ask, “Were the birds seen today migrating north?”
Let’s look at the species seen moving upriver today a try to determine their motivation.
First, and perhaps most straight-forward, is the huge flight of gulls. Wintering gulls on the Susquehanna River near Conewago Falls tend to spend their nights in flocks on the water or on treeless islands and rocky outcrops in the river. Many hundreds, sometimes thousands, find such favorable sites along the fifteen mile stretch of river from Conewago Falls downstream to Lake Clarke and the Conejohela Flats at Washington Boro. Each morning most of these gulls venture out to suburbia, farmland, landfill, hydroelectric dams, and other sections of river in search of food. Gulls are very able fliers and easily cover dozens of miles outbound and inbound each day in search of food. Many of the gulls seen this morning were probably on their way to the Harrisburg metropolitan area to eat trash. Barring any extraordinary buildups of ice on this section of river, one would expect these gulls to remain and make these daily excursions to food sources through early spring.
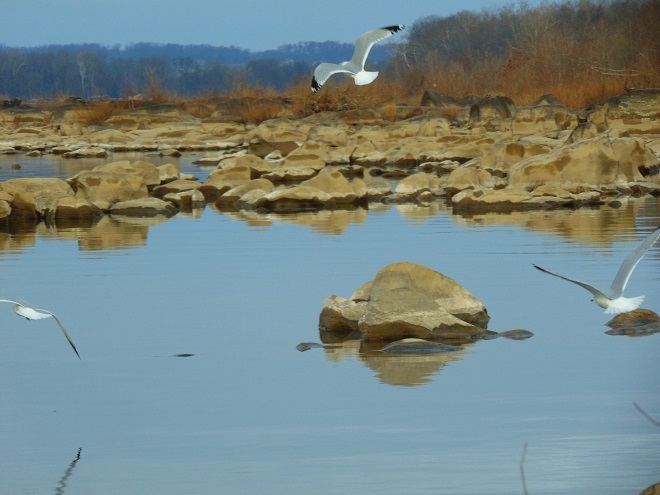


Second, throughout the season Bald Eagles have been tallied on the migration count with caution. Flight altitude, behavior, plumage, and the reaction of the “local” eagles to these transients was carefully considered before counting an eagle as a migrant. They roam a lot, particularly when young, and range widely to feed. The movement of eagles up the river today was probably food related. A gathering of adult, juvenile, and immature Bald Eagles could be seen more than a half mile upstream from the migration count lookout. Those moving up the river seemed to assemble with the “locals” there throughout the morning. White-tailed Deities occasionally drown, particularly when there is thin or unstable ice on the river (as there was last week) and they attempt to tread upon it. Then, their bodies are often stranded among rocks, in trees, or on the crown of the dam. After such a mishap, their carcasses become meals for carrion-eaters in the falls. Such an unfortunate deity, or another source of food, may have been attracting the eagles in numbers today.

Next, Black and Turkey Vultures often roam widely in search of food. The small numbers seen headed up-river today would tend to mean very little when trying to determine if there is a trend or population shift. Again, food may have been luring them upriver from nearby roosts.
And finally, the scoters, Mallards, American Robins, and Red-winged Blackbirds may have been wandering as well. Toward mid-day, the wind speed picked up and the direction changed to the east. This raises the possibility that these and others of the birds seen today may sense a change in weather, and may seek to take flight from the inclement conditions. Prompted by the ocean breeze and in an attempt to avoid a storm, was there some movement away from the Atlantic Coastal Plain to the upper Piedmont today? Many species may make these types of reactive movements. Is it possible that some birds flee or avoid ever-changing storm tracks and alter there wintering locations based on jet streams, water currents, and other climatic conditions? Probably. These are interesting dynamics and something worthy of study outside the simpler methods of a migration count.

…And if it snows that stretch down south won’t ever stand the strain… –Jimmy Webb
The lower Susquehanna valley’s first snowfall of the season arrived yesterday. By this morning it measured just an inch in depth at Conewago Falls, more to the south and east, less to the west and north. By mid-morning a cold fresh to moderate breeze from the northwest was blowing through the falls and stirring up ripples on the river.

Gulls sailed high overhead on the wind, taking a speedy ride downriver toward Chesapeake Bay, the Atlantic coast, and countless fast-food restaurant parking lots where surviving winter weather is more of a sure thing. Nearly a thousand Ring-billed Gulls soared past the migration count lookout today. Thirteen Herring Gulls and four Great Black-backed Gulls were among them.
Other migrants today included a Mallard, twenty-nine American Black Ducks, two Bald Eagles, eleven Black Vultures, fifteen Turkey Vultures, five American Goldfinches, and fifteen Red-winged Blackbirds. The wintery weather seems to be prompting these late-season travelers to be on their way.

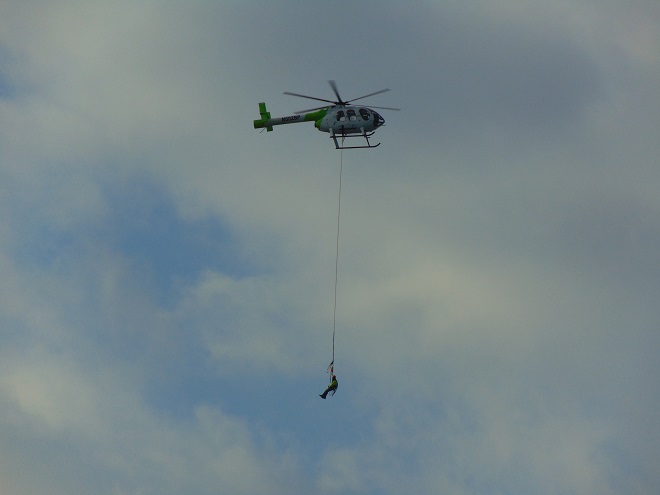
You know, today was like many other days at the falls. As I arrive, I have the habit of checking all the power line towers on both river shorelines to see what may be there awaiting discovery. More often than not, something interesting is perched on one or more of the structures…
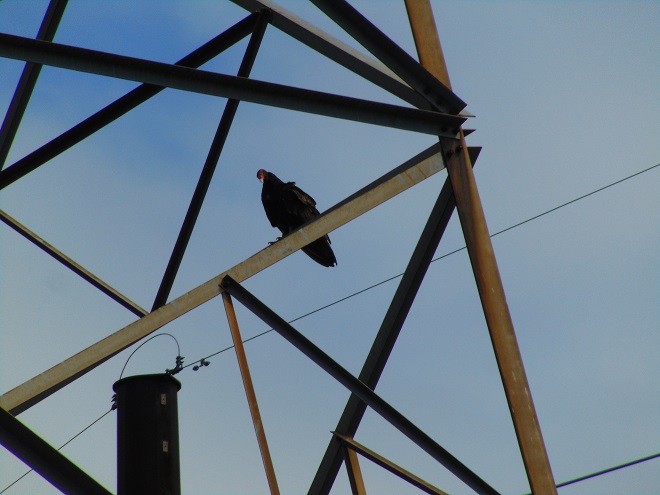
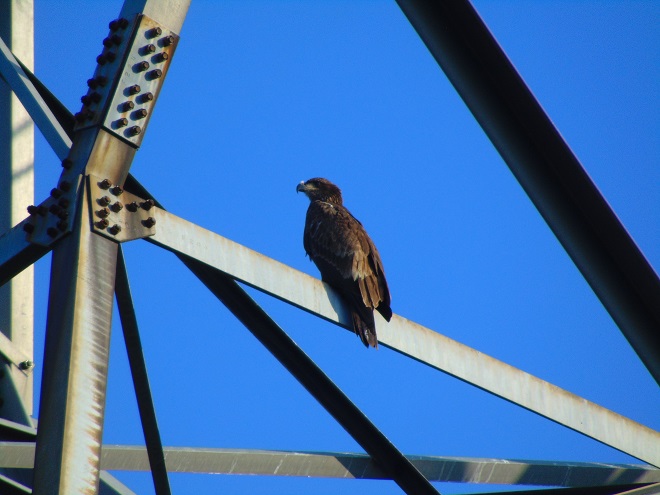
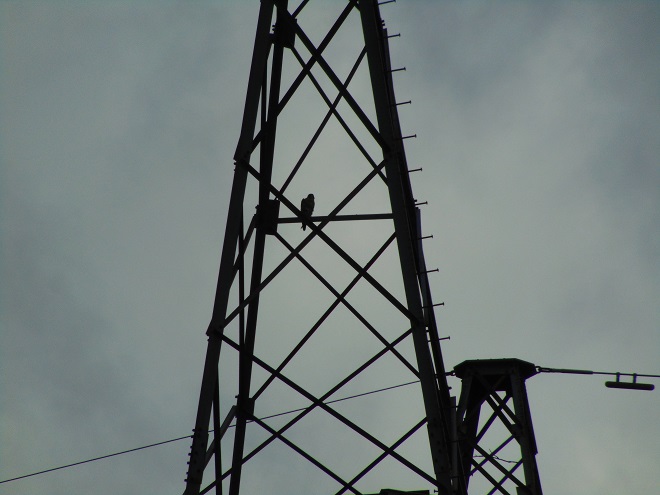
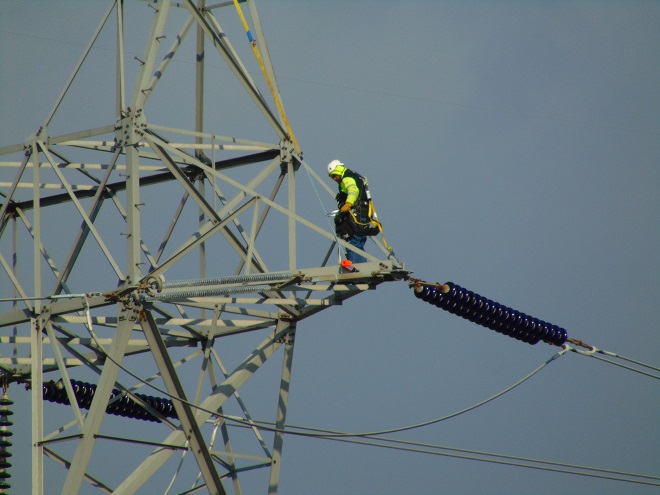





Yes friends, while the birds migrated through high above, down below a coordinated effort was underway to replace some of the electric transmission cable that stretches across the Susquehanna River at Conewago Falls. As you’ll see, this project requires precise planning, preparation, and skill. And it was fascinating to watch!
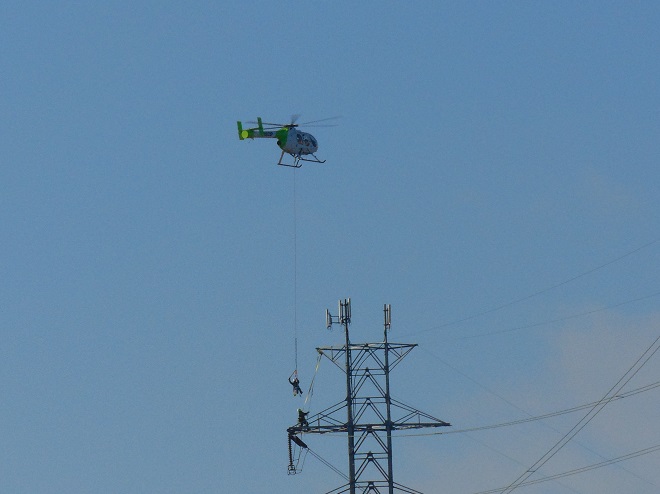
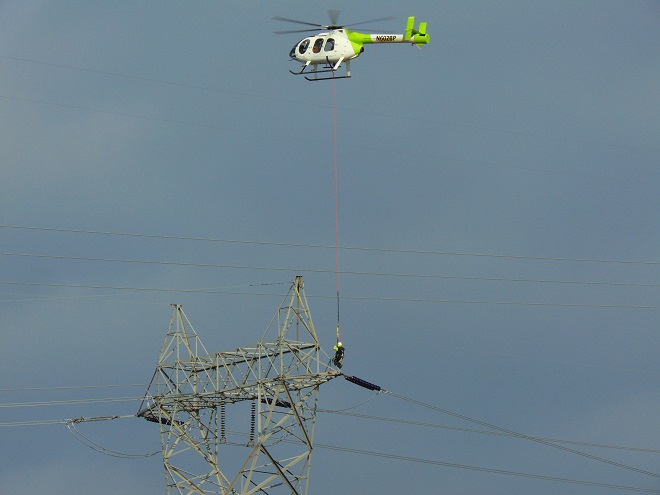









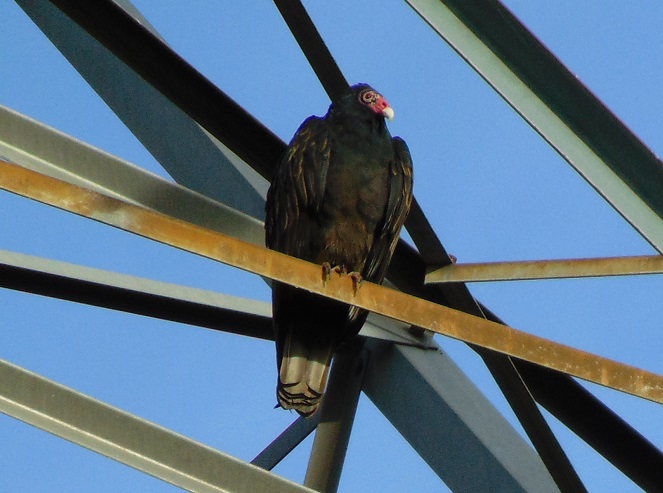
It was a crisp clear morning with birdless blue skies. The migration has mostly drawn to a close; very little was seen despite a suitable northwest breeze to support a flight. There were no robins and no blackbirds. Not even a starling was seen today. The only highlights were a Bufflehead (Bucephala albeola) and a couple of Swamp Sparrows.


And now ladies and gentlemen, boys and girls, it’s time for a Thanksgiving Day culinary reminder from the local Conewago Falls Turkey…

The NOAA National Weather Service radar images from last evening provided an indication that there may be a good fallout of birds at daybreak in the lower Susquehanna valley. The moon was bright, nearly full, and there was a gentle breeze from the north to move the nocturnal migrants along. The conditions were ideal.

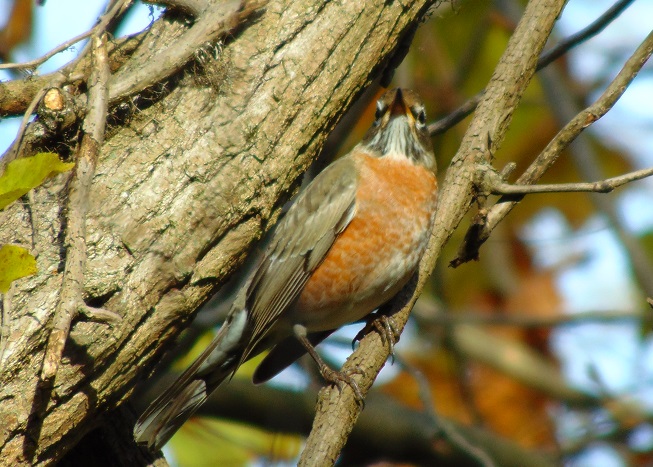
The Riparian Woodlands at Conewago Falls were alive with migrants this morning. American Robins and White-throated Sparrows were joined by new arrivals for the season: Brown Creeper (Certhia americana), Ruby-crowned Kinglets (Regulus calendula), Golden-crowned Kinglets (Regulus satrapa), Dark-eyed Junco (Junco hyemalis), and Yellow-rumped Warbler (Setophaga coronata). These are the perching birds one would expect to have comprised the overnight flight. While the individuals that will remain may not yet be among them, these are the species we will see wintering in the Mid-Atlantic states. No trip to the tropics for these hardy passerines.
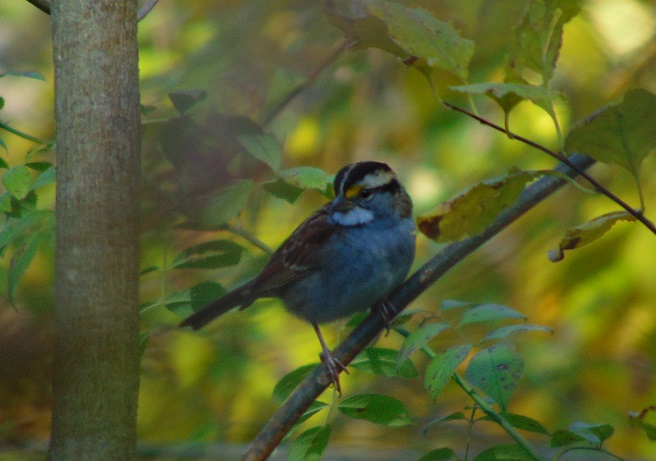
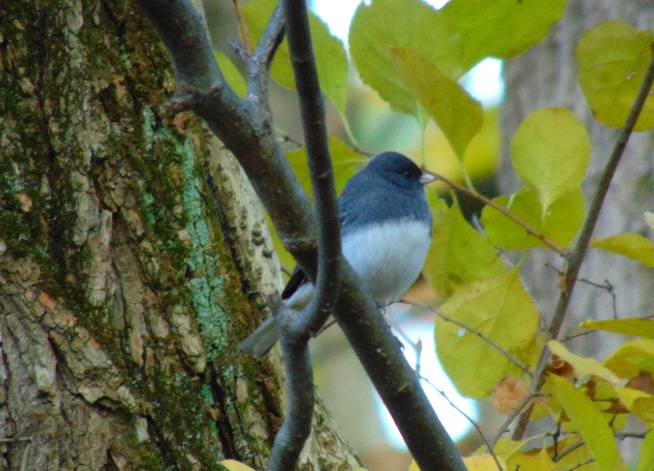





It was a placid morning on Conewago Falls with blue skies dotted every now and then by a small flock of migrating robins or blackbirds. The jumbled notes of a singing Winter Wren (Troglodytes hiemalis) in the Riparian Woodland softly mixed with the sounds of water spilling over the dam. The season’s first Wood Ducks (Aix sponsa), Blue-winged Teal (Spatula discors), Herring Gull (Larus argentatus), Horned Larks (Eremophila alpestris), and White-throated Sparrows (Zonotrichia albicollis) were seen.
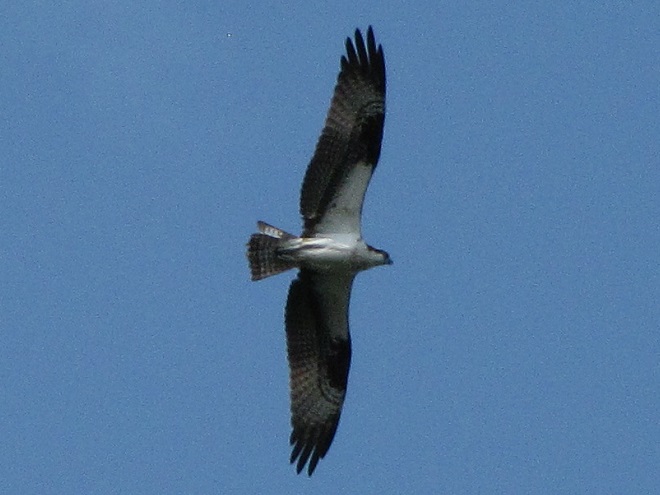
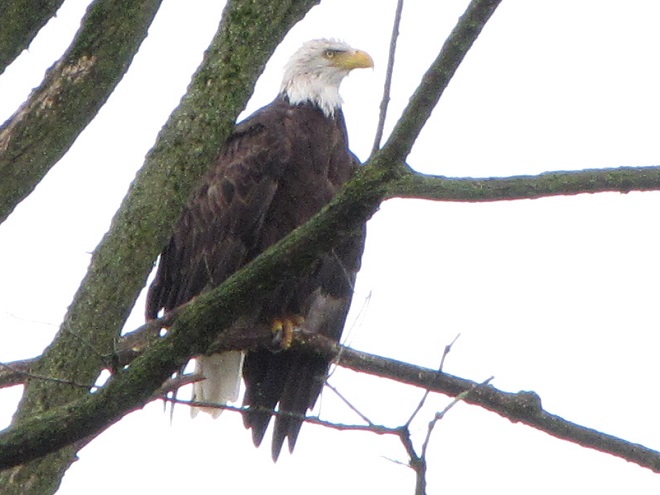
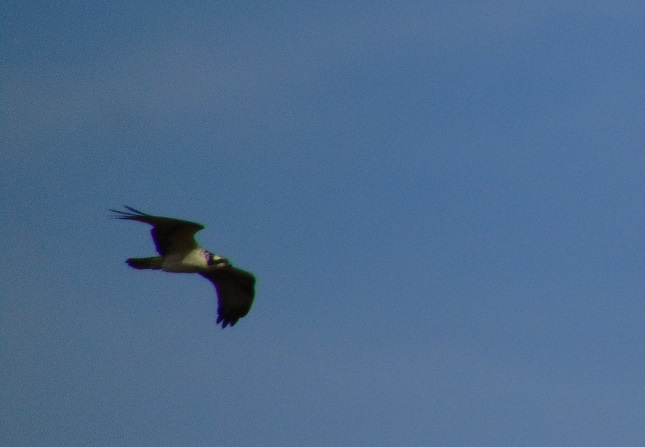
There was a small ruckus when one of the adult Bald Eagles from a local pair spotted an Osprey passing through carrying a fish. This eagle’s effort to steal the Osprey’s catch was soon interrupted when an adult eagle from a second pair that has been lingering in the area joined the pursuit. Two eagles are certainly better than one when it’s time to hustle a skinny little Osprey, don’t you think?
But you see, this just won’t do. It’s a breach of eagle etiquette, don’t you know? Soon both pairs of adult eagles were engaged in a noisy dogfight. It was fussing and cackling and the four eagles going in every direction overhead. Things calmed down after about five minutes, then a staring match commenced on the crest of the dam with the two pairs of eagles, the “home team” and the “visiting team”, perched about 100 feet from each other. Soon the pair which seems to be visiting gave up and moved out of the falls for the remainder of the day. The Osprey, in the meantime, was able to slip away.
In recent weeks, the “home team” pair of Bald Eagles, seen regularly defending territory at Conewago Falls, has been hanging sticks and branched tree limbs on the cross members of the power line tower where they often perch. They seem only to collect and display these would-be nest materials when the “visiting team” pair is perched in the nearby tower just several hundred yards away…an attempt to intimidate by homesteading. It appears that with winter and breeding time approaching, territorial behavior is on the increase.

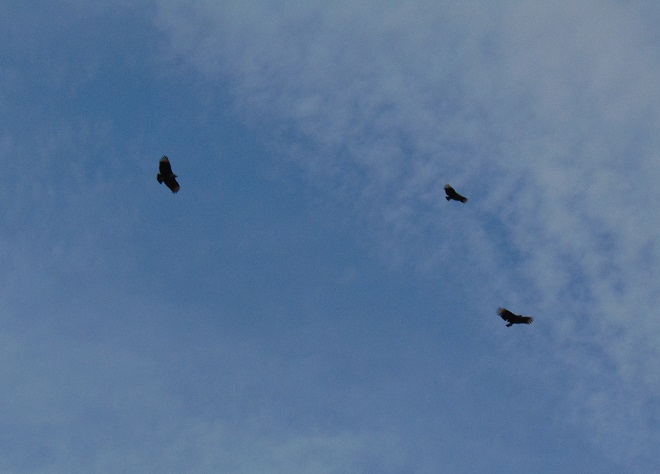
In the afternoon, a fresh breeze from the south sent ripples across the waters among the Pothole Rocks. The updraft on the south face of the diabase ridge on the east shore was like a highway for some migrating hawks, falcons, and vultures. Black Vultures (Coragyps atratus) and Turkey Vultures streamed off to the south headlong into the wind after leaving the ridge and crossing the river. A male and female Northern Harrier (Circus hudsonius), ten Red-tailed Hawks, two Red-shouldered Hawks (Buteo lineatus), six Sharp-shinned Hawks, and two Merlins crossed the river and continued along the diabase ridge on the west shore, accessing a strong updraft along its slope to propel their journey further to the southwest. Four high-flying Bald Eagles migrated through, each following the east river shore downstream and making little use of the ridge except to gain a little altitude while passing by.

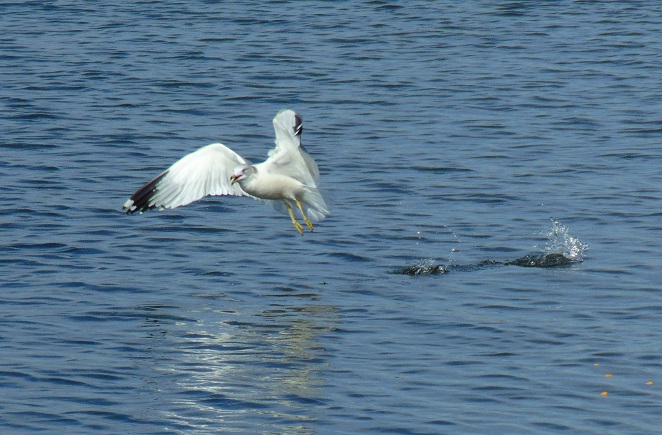
Late in the afternoon, the local Bald Eagles were again airborne and cackling up a storm. This time they intercepted an eagle coming down the ridge toward the river and immediately forced the bird to climb if it intended to pass. It turned out to be the best sighting of the day, and these “home team” eagles found it first. It was a Golden Eagle (Aquila chrysaetos) in crisp juvenile plumage. On its first southward voyage, it seemed to linger after climbing high enough for the Bald Eagles to loose concern, then finally selected the ridge route and crossed the river to head off to the southwest.


The humid rainy remains of Hurricane Nate have long since passed by Pennsylvania, yet mild wet weather lingers to confuse one’s sense of the seasons. This gloomy misty day was less than spectacular for watching migrating birds and insects, but some did pass by. Many resident animals of the falls are availing themselves of the opportunity to continue active behavior before the cold winds of autumn and winter force a change of lifestyle.
Warm drizzle at daybreak prompted several Northern Spring Peepers (Pseudacris crucifer crucifer) to begin calling from the wetlands in the Riparian Woodlands of Conewago Falls. An enormous chorus of these calls normally begins with the first warm rains of early spring to usher in this tiny frog’s mating season. Today, it was just a few “peeps” among anxious friends.
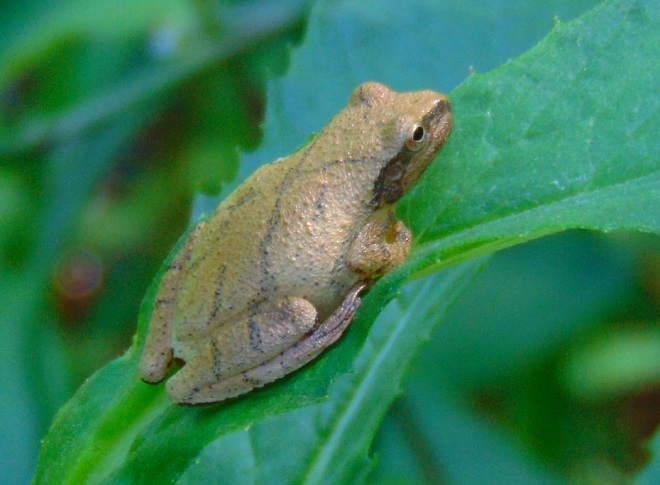

Any additional river flow that resulted from the rains of the previous week is scarcely noticeable among the Pothole Rocks. The water level remains low, the water column is fairly clear, and the water temperatures are in the 60s Fahrenheit.
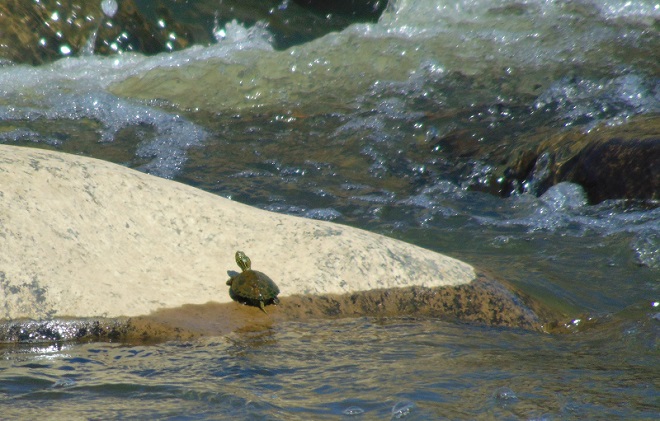
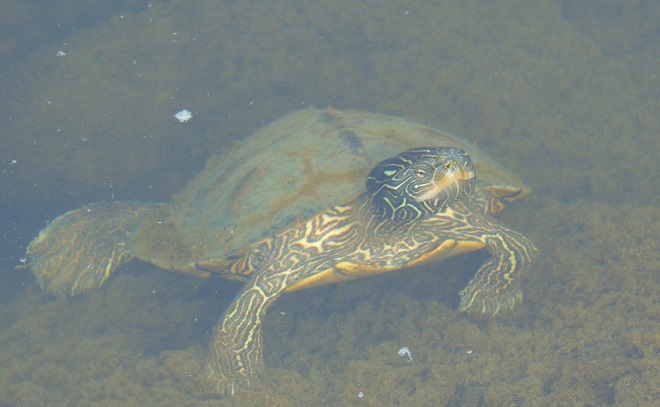
It’s no real surprise then to see aquatic turtles climbing onto the boulders in the falls to enjoy a little warmth, if not from the sun, then from the stored heat in the rocks. As usual, they’re quick to slide into the depths soon after sensing someone approaching or moving nearby. Seldom found anywhere but on the river, these skilled divers are Common Map Turtles (Graptemys geographica), also known as Northern Map Turtles. Their paddle-like feet are well adapted to swimming in strong current. They are benthic feeders, feasting upon a wide variety of invertebrates found among the stone and substrate of the river bottom.
Adult Common Map Turtles hibernate communally on the river bottom in a location protected from ice scour and turbulent flow, often using boulders, logs, or other structures as shelter from strong current. The oxygenation of waters tumbling through Conewago Falls may be critical to the survival of the turtles overwintering downstream. Dissolved oxygen in the water is absorbed by the nearly inactive turtles as they remain submerged at their hideout through the winter. Though Common Map Turtles, particularly males, may occasionally move about in their hibernation location, they are not seen coming to the surface to breathe.
The Common Map Turtles in the Susquehanna River basin are a population disconnected from that found in the main range of the species in the Great Lakes and upper Mississippi basin. Another isolated population exists in the Delaware River.



SOURCES
Committee on the Status of Endangered Wildlife in Canada. 2002. Status Report of the Northern Map Turtle. Canadian Wildlife Service. Ottawa, Ontario.
A moderate breeze from the south placed a headwind into the face of migrants trying to wing their way to winter quarters. The urge to reach their destination overwhelmed any inclination a bird or insect may have had to stay put and try again another day.
Blue Jays were joined by increasing numbers of American Robins crossing the river in small groups to continue their migratory voyages. Killdeer (Charadrius vociferous) and a handful of sandpipers headed down the river route. Other migrants today included a Cooper’s Hawk (Accipiter cooperii), Eastern Bluebirds (Sialia sialis), and a few Common Mergansers (Mergus merganser), House Finches (Haemorhous mexicanus), and Common Grackles (Quiscalus quiscula).
The afternoon belonged to the insects. The warm wind blew scores of Monarchs toward the north as they persistently flapped on a southwest heading. Many may have actually lost ground today. Painted Lady (Vanessa cardui) and Cloudless Sulphur butterflies were observed battling their way south as well. All three of the common migrating dragonflies were seen: Common Green Darner (Anax junius), Wandering Glider (Pantala flavescens), and Black Saddlebags (Tramea lacerata).
The warm weather and summer breeze are expected to continue as the rain and wind from Hurricane Nate, today striking coastal Alabama and Mississippi, progresses toward the Susquehanna River watershed during the coming forty-eight hours.



A fresh breeze from the north brought cooler air and a reminder that summer is gone and autumn has arrived.
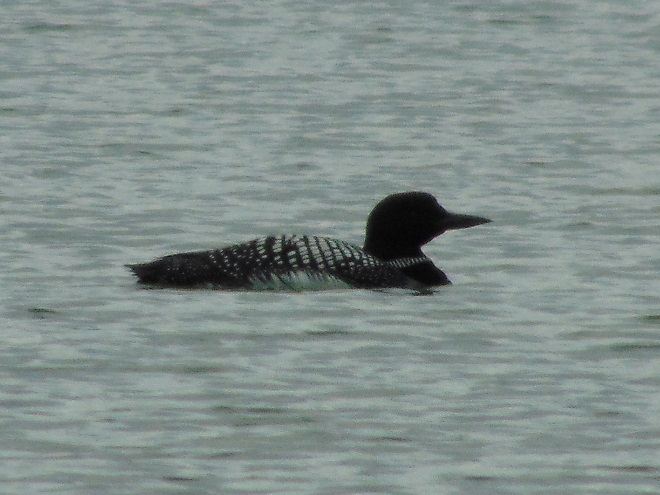
Fast-moving dark clouds provided a perfect backdrop for viewing passing diurnal migrants. Bald Eagles utilized the tail wind to cruise down the Susquehanna toward Chesapeake Bay and points further south. A migrating Merlin began a chase from which a Northern Flicker narrowly escaped by finding shelter among Pothole Rocks and a few small trees. The season’s first American Black Duck (Anas rubripes), Common Loon (Gavia immer), Yellow-bellied Sapsucker (Sphyrapicus varia), and American Pipits (Anthus rubescens) moved through.
Blue Jays continued their hesitant crossings of the river at Conewago Falls. The majority completed the journey by forming groups of a dozen or more birds and following the lead of a lone American Robin, a Northern Flicker, or, odd as it appeared, a small warbler.
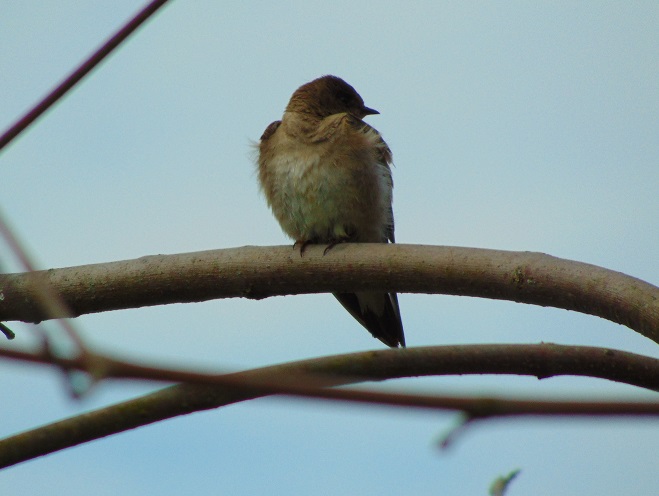
By far the most numerous migrants today were swallows. Thousands of Northern Rough-winged Swallows and hundreds of Tree Swallows were on the wing in search of what was suddenly a sparse flying insect supply. To get out of the brisk wind, some of the more resourceful birds landed on the warm rocks. To satisfy their appetite, many were able to pick crawling arthropods from the surface of the boulders. They swallow them whole.


The Neotropical birds that raised their young in Canada and in the northern United States have now logged many miles on their journey to warmer climates for the coming winter. As their density decreases among the masses of migrating birds, a shift to species with a tolerance for the cooler winter weather of the temperate regions will be evident.
Though it is unusually warm for this late in September, the movement of diurnal migrants continues. This morning at Conewago Falls, five Broad-winged Hawks (Buteo platypterus) lifted from the forested hills to the east, then crossed the river to continue a excursion to the southwest which will eventually lead them and thousands of others that passed through Pennsylvania this week to wintering habitat in South America. Broad-winged Hawks often gather in large migrating groups which swarm in the rising air of thermal updrafts, then, after gaining substantial altitude, glide away to continue their trip. These ever-growing assemblages from all over eastern North America funnel into coastal Texas where they make a turn to south around the Gulf of Mexico, then continue on toward the tropics. In the coming weeks, a migration count at Corpus Christi in Texas could tally 100,000 or more Broad-winged Hawks in a single day as a large portion of the continental population passes by. You can track their movement and that of other diurnal raptors as recorded at sites located all over North America by visiting hawkcount.org on the internet. Check it out. You’ll be glad you did.
Nearly all of the other migrants seen today have a much shorter flight ahead of them. Red-bellied Woodpeckers (Melanerpes carolinus), Red-headed Woodpeckers (Melanerpes erythrocephalus), and Northern Flickers (Colaptes auratus) were on the move. Migrating American Robins (Turdus migratorius) crossed the river early in the day, possibly leftovers from an overnight flight of this primarily nocturnal migrant. The season’s first Great Black-backed Gulls (Larus marinus) arrived. American Goldfinches are easily detected by their calls as they pass overhead. Look carefully at the goldfinches visiting your feeder, the birds of summer are probably gone and are being replaced by migrants currently passing through.
By far, the most conspicuous migrant today was the Blue Jay. Hundreds were seen as they filtered out of the hardwood forests of the diabase ridge to cautiously cross the river and continue to the southwest. Groups of five to fifty birds would noisily congregate in trees along the river’s edge, then begin flying across the falls. Many wary jays abandoned their small crossing parties and turned back. Soon, they would try the trip again in a larger flock.
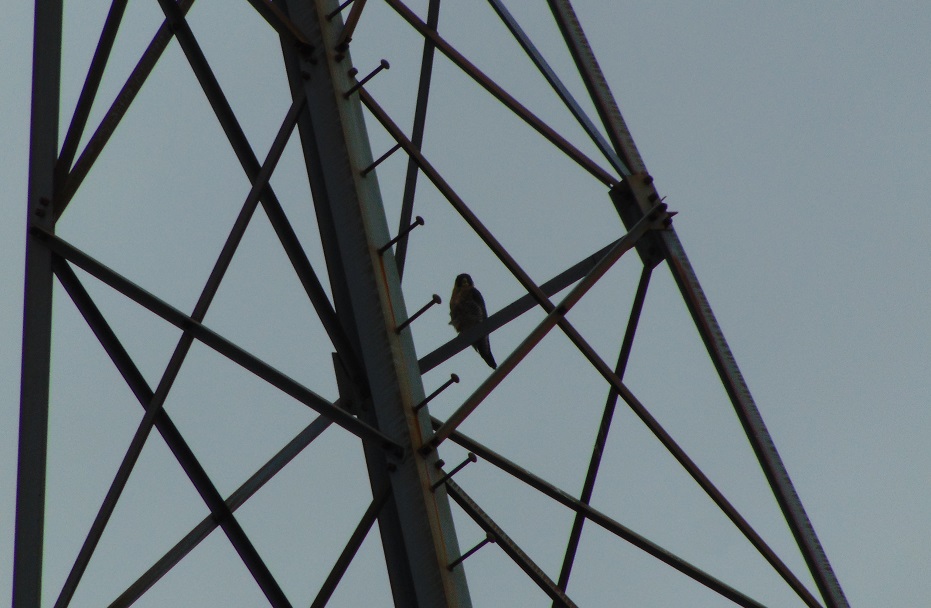

A look at this morning’s count reveals few Neotropical migrants. With the exception of the Broad-winged Hawks and warblers, the migratory species seen today will winter in a sub-tropical temperate climate, primarily in the southern United States, but often as far north as the lower Susquehanna River valley. The individual birds observed today will mostly continue to a winter home a bit further south. Those that will winter in the area of Conewago Falls will arrive in October and later.
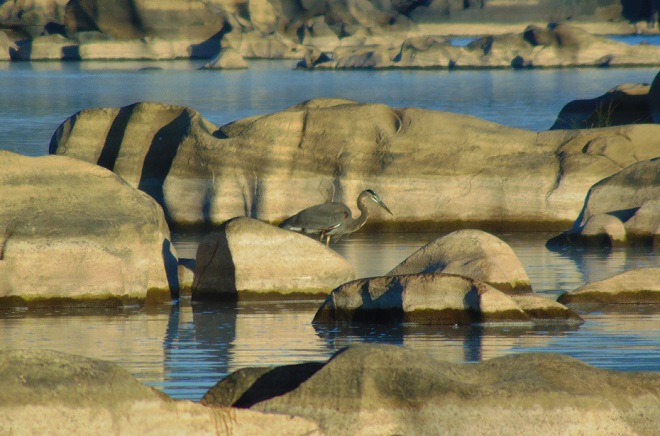
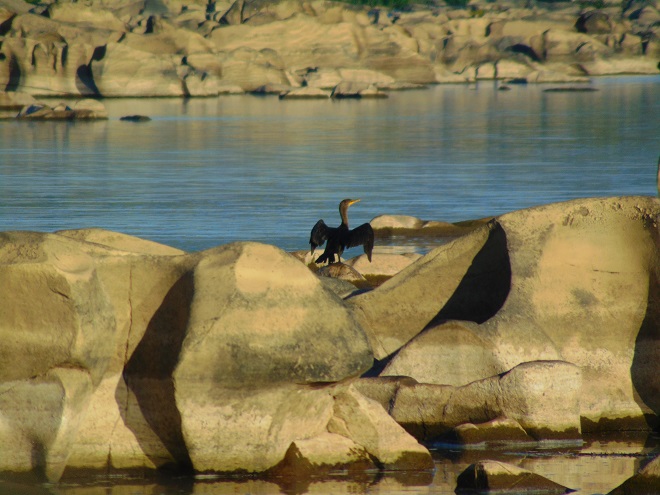


The long-distance migrating insect so beloved among butterfly enthusiasts shows signs of improving numbers. Today, more than two dozen Monarchs were seen crossing the falls and slowly flapping and gliding their way to Mexico.

A couple of inches of rain this week caused a small increase in the flow of the river, just a burp, nothing major. This higher water coincided with some breezy days that kicked up some chop on the open waters of the Susquehanna upstream of Conewago Falls. Apparently it was just enough turbulence to uproot some aquatic plants and send them floating into the falls.
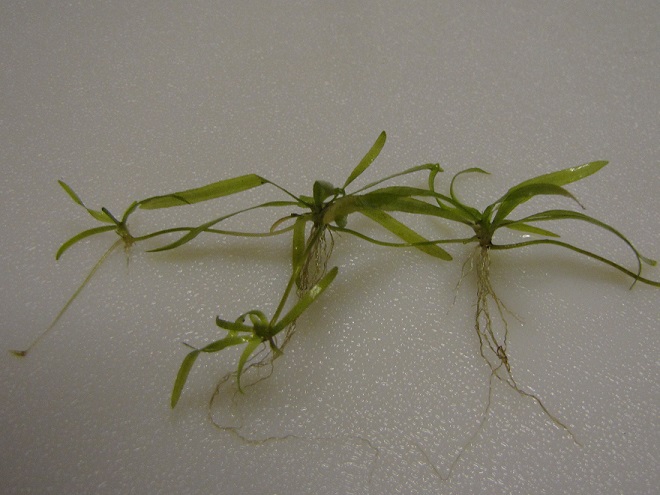
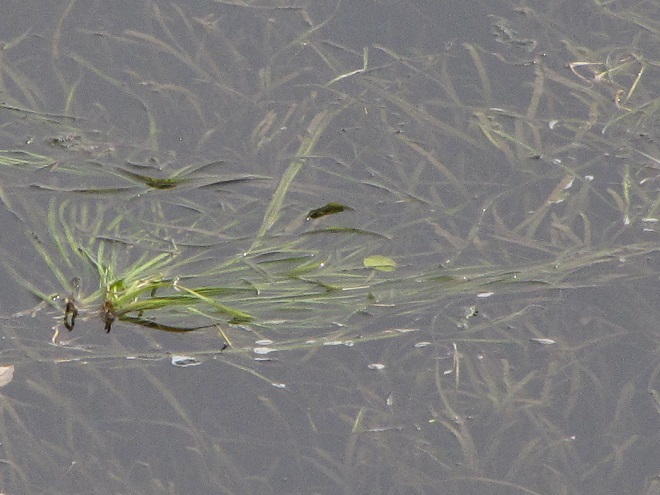
Piled against and upon the upstream side of many of the Pothole Rocks were thousands of two to three feet-long flat ribbon-like opaque green leaves of Tapegrass, also called Wild Celery, but better known as American Eelgrass (Vallisneria americana). Some leaves were still attached to a short set of clustered roots. It appears that most of the plants broke free from creeping rootstock along the edge of one of this species’ spreading masses which happened to thrive during the second half of the summer. You’ll recall that persistent high water through much of the growing season kept aquatic plants beneath a blanket of muddy current. The American Eelgrass colonies from which these specimens originated must have grown vigorously during the favorable conditions in the month of August. A few plants bore the long thread-like pistillate flower stems with a fruit cluster still intact. During the recent few weeks, there have been mats of American Eelgrass visible, the tops of their leaves floating on the shallow river surface, near the east and west shorelines of the Susquehanna where it begins its pass through the Gettysburg Basin near the Pennsylvania Turnpike bridge at Highspire. This location is a probable source of the plants found in the falls today.
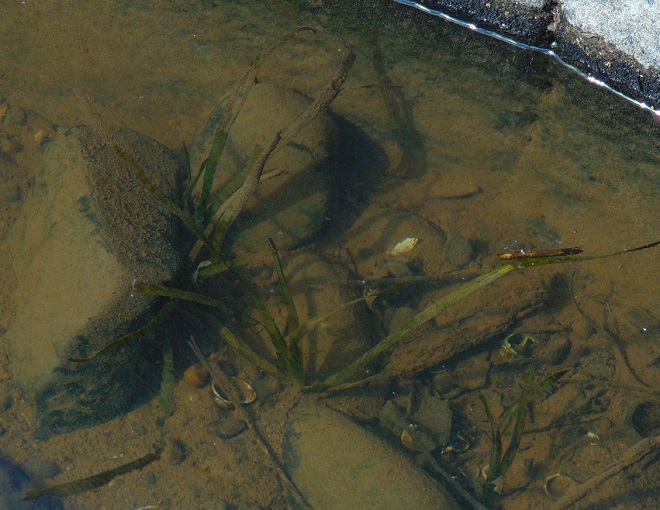


The cool breeze from the north was a perfect fit for today’s migration count. Nocturnal migrants settling down for the day in the Riparian Woodlands at sunrise included more than a dozen warblers and some Gray Catbirds (Dumetella carolinensis). Diurnal migration was underway shortly thereafter.
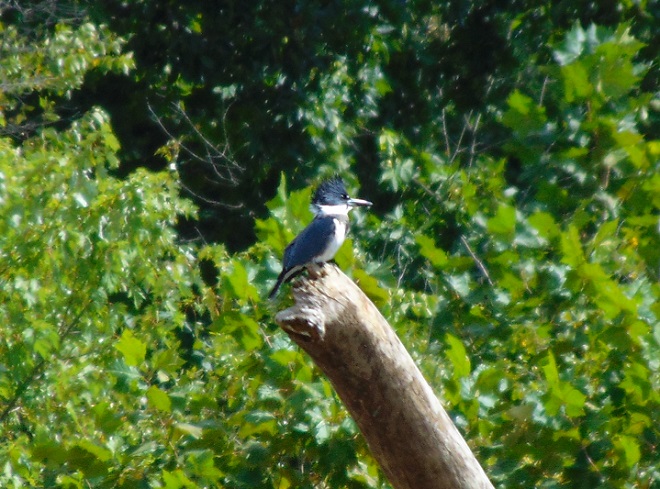
Four Bald Eagles were counted as migrants this morning. Based on plumage, two were first-year eagles (Juvenile) seen up high and flying the river downstream, one was a second-year bird (Basic I) with a jagged-looking wing molt, and a third was probably a fourth year (Basic III) eagle looking much like an adult with the exception of a black terminal band on the tail. These birds were the only ones which could safely be differentiated from the seven or more Bald Eagles of varying ages found within the past few weeks to be lingering at Conewago Falls. There were as many as a dozen eagles which appeared to be moving through the falls area that may have been migrating, but the four counted were the only ones readily separable from the locals.
Red-tailed Hawks (Buteo jamaicensis) were observed riding the wind to journey not on a course following the river, but flying across it and riding the updraft on the York Haven Diabase ridge from northeast to southwest.
Bank Swallows (Riparia riparia) seem to have moved on. None were discovered among the swarms of other species today.
Ruby-throated Hummingbirds, Caspian Terns, Cedar Waxwings (Bombycilla cedrorum), and Chimney Swifts (Chaetura pelagica) were migrating today, as were Monarch butterflies.
Not migrating, but always fun to have around, all four wise guys were here today. I’m referring to the four members of the Corvid family regularly found in the Mid-Atlantic states: Blue Jay (Cyanocitta cristata), American Crow (Corvus brachyrhynchos), Fish Crow (Corvus ossifragus), and Common Raven (Corvus corax).


SOURCES
Klots, Elsie B. 1966. The New Field Book of Freshwater Life. G. P. Putnam’s Sons. New York, NY.
We all know that birds (and many other animals) migrate. It’s a survival phenomenon which, above all, allows them to utilize their mobility to translocate to a climate which provides an advantage for obtaining food, enduring seasonal weather, and raising offspring.
In the northern hemisphere, most migratory birds fly north in the spring to latitudes with progressively greater hours of daylight to breed, nest, and provide for their young. In the southern hemisphere there are similar movements, these to the south during their spring (our autumn). The goal is the same, procreation, though the landmass offering sustenance for species other than seabirds is limited “down under”. Interestingly, there are some seabirds that breed in the southern hemisphere during our winter and spend our summer (their winter) feeding on the abundant food sources of the northern oceans.
Each autumn, migratory breeding birds leave their nesting grounds as the hours of sunlight slowly recede with each passing day. They fly to lower latitudes where the nights aren’t so long and the climate is less brutal. There, they pass their winter season.
Food supply, weather, the start/finish of the nesting cycle, and other factors motivate some birds to begin their spring and autumn journeys. But overall, the hours of daylight and the angle of the sun prompt most species to get going.
But what happens after birds begin their trips to favorable habitats? Do they follow true north and south routes? Do they fly continuously, day and night? Do they ease their way from point to point, stopping to feed along the way? Do they all migrate in flocks? Well, the tactics of migration differ widely from bird species to species, from population to population, and sometimes from individual to individual. The variables encountered when examining the dynamics of bird migration are seemingly endless, but fascinatingly so. Bird migration is well-studied, but most of its intricacies and details remain a mystery.
Consider for a moment that just 10,000 years ago, an Ice Age was coming to an end, with the southernmost edge of the most recent glaciers already withdrawn into present-day Canada from points as near as the upper Susquehanna River watershed. Back then, the birds migrating to the lower portion of the drainage basin each spring probably weren’t forest-dwelling tropical warblers, orioles, and other songbirds. The migratory birds that nested in the lower Susquehanna River valley tens of millennia ago were probably those species found nesting today in taiga and tundra much closer to the Arctic Circle. And the ancestors of most of the tropical migrants that nest here now surely spent their entire lives much closer to the Equator, finding no advantage by journeying to the frigid Susquehanna valley to nest. It’s safe to say that since those times, and probably prior to them, migration patterns have been in a state of flux.
During the intervening years since the great ice sheets, birds have been able to adapt to the shifts in their environment on a gradual basis, often using their unmatched mobility to exploit new opportunities. Migration patterns change slowly, but continuously, resulting in differences that can be substantial over time. If the natural transformations of habitat and climate have kept bird migration evolving, then man’s impact on the planet shows great potential to expedite future changes, for better or worse.
Now, let’s look at two different bird migration strategies, that of day-fliers or diurnal migrants, and that of night-fliers, the nocturnal migrants.
Diurnal migrants are the most familiar to people who notice birds on the move. The majority of these species have one thing in common, some form of defense to lessen the threat of becoming the victim of a predator while flying in daylight. Of course the vultures, hawks, and eagles fly during the day. Swallows and swifts employ speed and agility on the wing to avoid becoming prey, as do hummingbirds. Finches have an undulating flight, never flying on a horizontal plane, which makes their capture more difficult. Other songbirds seen migrating by day, Red-winged Blackbirds for example, congregate into flocks soon after breeding season to avoid being alone. Defense flocks change shape constantly as birds position themselves toward the center and away from the vulnerable fringes of the swarm. The larger the flock, the safer the individual. For a lone bird, large size can be a form of protection against all but the biggest of predators. Among the more unusual defenses is that of birds like Indigo Buntings and other tropical migrants that fly across the Gulf of Mexico each autumn (often completing a portion of the flight during the day), risking exhaustion at sea to avoid the daylight hazards, including numerous predators, found in the coastal and arid lands of south Texas. Above all, diurnal migrants capture our attention and provide a spectacle which fascinates us. Perhaps diurnal migrants attract our favor because we can just stand or sit somewhere and watch them go by. We can see, identify, and even count them. It’s fantastic.
What about a bird like the Canada Goose (Branta canadensis)? It is often seen migrating in flocks during the day (the truly migratory ones flying much higher than the local year-round resident “transplants”), but then, during the big peak movements of spring and fall, they can be heard overhead all through the night. Perhaps the Canada Goose and related waterfowl bridge the gap between day and night, introducing us to the secretive starlight and moonshine commuters, the nocturnal migrants.

The skies are sometimes filled with thousands of them, mostly small perching birds and waders. These strangers in the night fly inconspicuously in small groups or individually, and most can be detected when passing above us only when heard making short calls to remain in contact with their travel partners. They need not worry about predators, but instead must have a method of finding their way. Many, like the Indigo Bunting, can navigate by the stars, a capability which certainly required many generations to refine. The nocturnal migrants begin moving just after darkness falls and ascend without delay to establish a safe flight path void of obstacles (though lights and tall structures can create a deadly counter to this tactic). Often, the only clue we have that a big overnight flight has occurred is the sudden appearance of new bird species or individuals, on occasion in great numbers, in a place where we observe regularly. Just days ago, the arrival of various warbler species at Conewago Falls indicated that there was at least a small to moderate movement of these birds during previous nights.
In recent years, the availability of National Weather Service radar has brought the capability to observe nocturnal migrants into easy reach. Through the night, you can log on to your local National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s National Weather Service radar page (State College for the Conewago Falls area) and watch on the map as the masses of migrating bird pass through the sweep of the radar beam. As they lift off just after nightfall, rising birds will create an echo as they enter the sweeping beam close to the radar site. Then, due to the incline of the transmitted signal and the curvature of the earth, migrants will be displayed as an expanding donut-like ring around the radar’s map location as returns from climbing birds are received from progressively higher altitudes at increasing distances from the center of the site’s coverage area. On a night with a local or regional flight, several radar locations may show signs of birds in the air. On nights with a widespread flight, an exodus of sorts, the entire eastern half of the United States may display birds around the sites. You’ll find the terrain in the east allows it to be well-covered while radars in the west are less effective due to the large mountains. At daybreak, the donut-shaped displays around each radar site location on the map contract as birds descend out of the transmitted beam and are no longer detected.
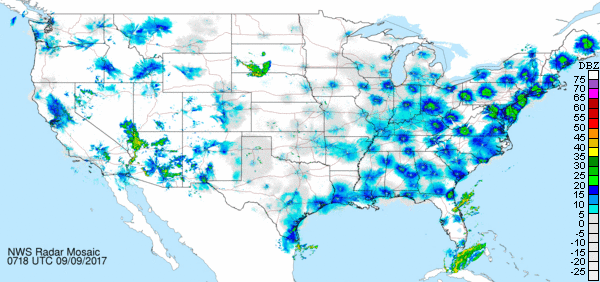
Weather systems sometimes seem to motivate some flights and stifle others. The first example seen below is a northbound spring exodus, the majority of which is probably migrants from the tropics, the Neotropical migrants, including our two dozen species of warblers. A cold front passing into the northeastern United States appears to have stifled any flight behind it, while favorable winds from the southwest are motivating a heavy concentration ahead of the front.
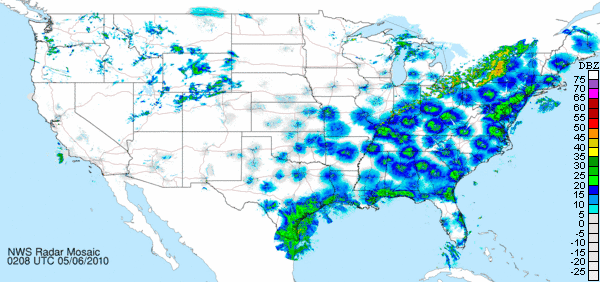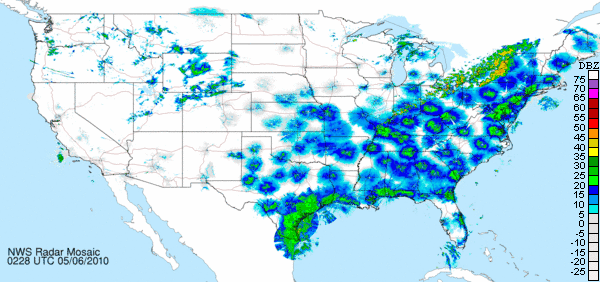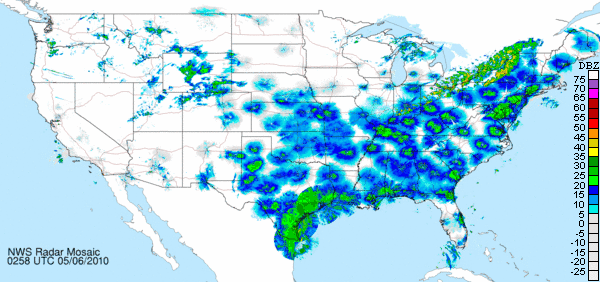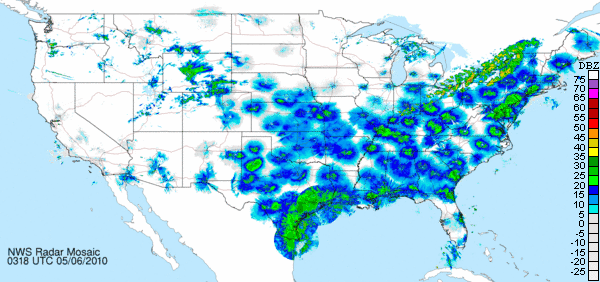
The second and third examples seen below are an autumn nocturnal migration movement, probably composed of many of the same tropics-bound species which were on the way north in the previous example. Note that during autumn, the cold front seems to motivate the flight following its passage. Ahead of the front, there is a reduced and, in places, undetectable volume of birds. The two images below are separated by about 42 hours.
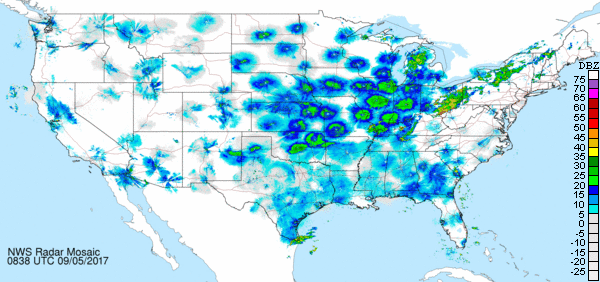

You can easily learn much more about birds (and insects and bats) on radar, including both diurnal and nocturnal migrants, by visiting the Clemson University Radar Ornithology Laboratory (CUROL) website. There you’ll find information on using the various mode settings on NEXRAD (Next-Generation Radar) to differentiate between birds, other flying animals, and inanimate airborne or grounded objects. It’s superbly done and you’ll be glad you gave it a try.
SOURCES
Clemson University Radar Ornithology Laboratory (CUROL) website: http://virtual.clemson.edu/groups/birdrad/ as accessed September 6, 2017.