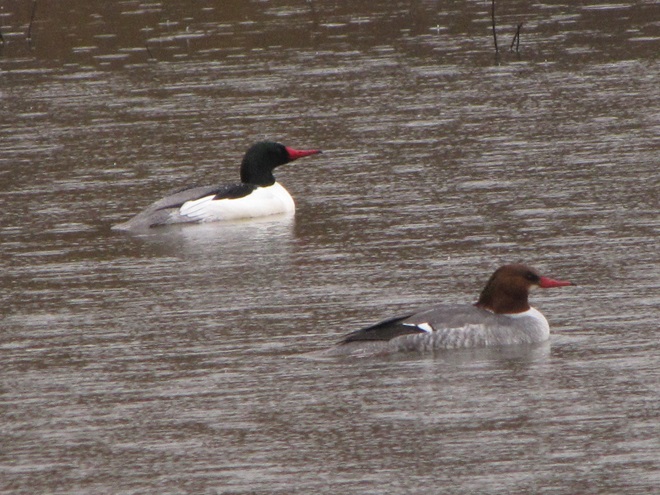
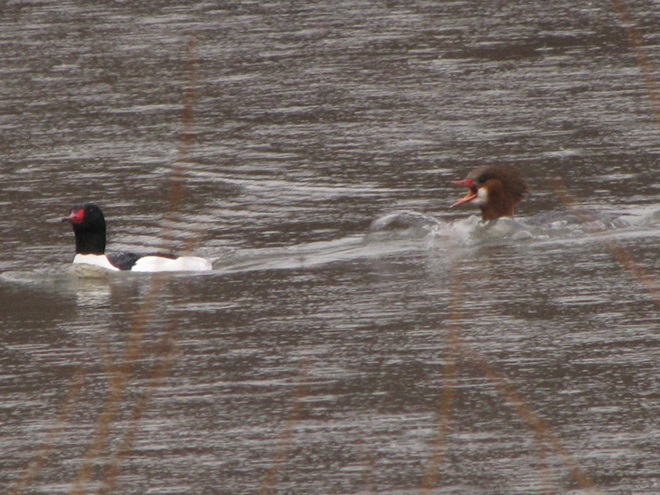
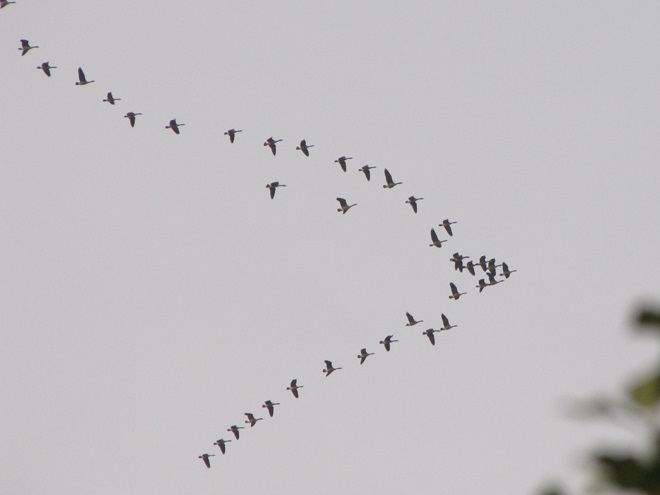
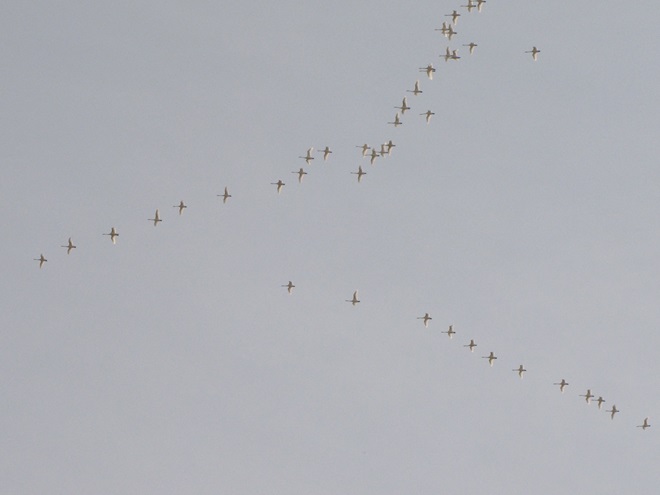
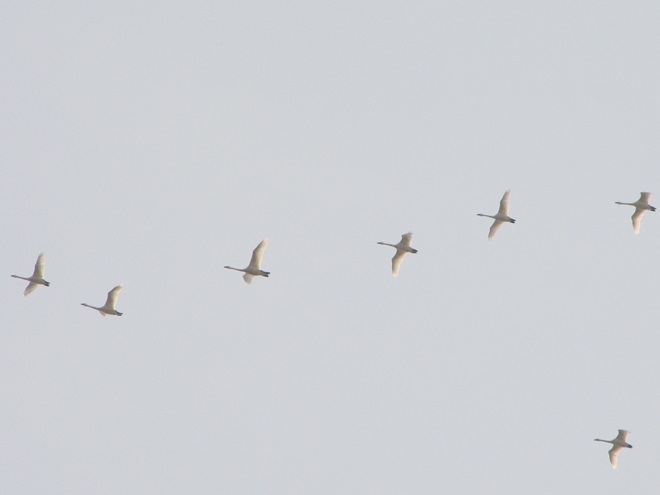
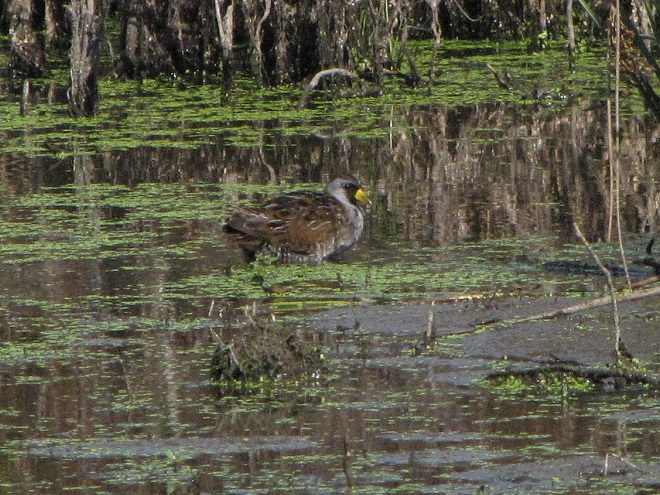
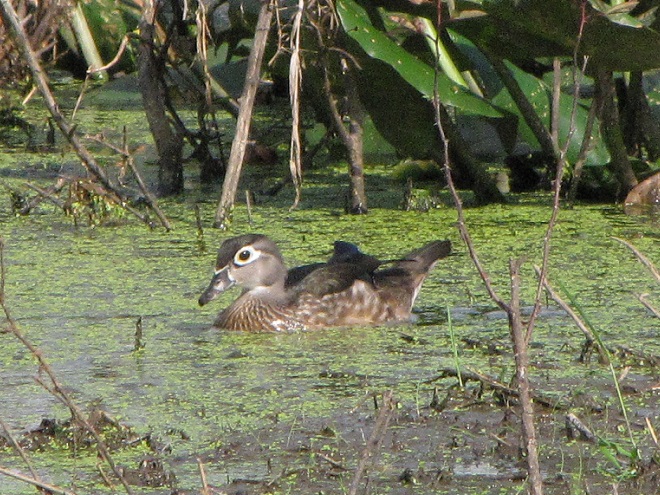
Though soggy, windy, and rainy, it happened to be a delightfully mild day to search for migrating waterfowl in the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed. Here’s a look at what we found temporarily grounded by the poor flight conditions…








A Natural History of Conewago Falls—The Waters of Three Mile Island
Though soggy, windy, and rainy, it happened to be a delightfully mild day to search for migrating waterfowl in the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed. Here’s a look at what we found temporarily grounded by the poor flight conditions…







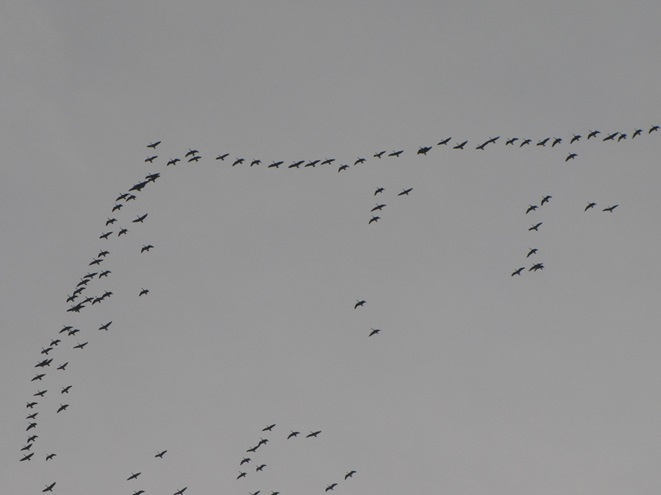
With a southerly breeze and warm front rolling through the region, migratory Canada Geese and other waterfowl are taking advantage of the tail wind to depart Chesapeake Bay and stream through the lower Susquehanna valley to begin a trek that will ultimately take them to nesting grounds far to our north.






It’s that time of year. Your local county conservation district is taking orders for their annual tree sale and it’s a deal that can’t be beat. Order now for pickup in April.
The prices are a bargain and the selection includes the varieties you need to improve wildlife habitat and water quality on your property. For species descriptions and more details, visit each tree sale web page (click the sale name highlighted in blue). And don’t forget to order packs of evergreens for planting in mixed clumps and groves to provide winter shelter and summertime nesting sites for our local native birds. They’re only $12.00 for a bundle of 10.

Cumberland County Conservation District Annual Tree Seedling Sale—
Orders due by: Friday, March 22, 2024
Pickup on: Thursday, April 18, 2024 or Friday, April 19, 2024



Dauphin County Conservation District Seedling Sale—
Orders due by: Monday, March 18, 2024
Pickup on: Thursday, April 18, 2024 or Friday, April 19, 2024

Lancaster County Annual Tree Seedling Sale—
Orders due by: Friday, March 8, 2024
Pickup on: Friday, April 12, 2024






Lebanon County Conservation District Tree and Plant Sale—
Orders due by: Friday, March 8, 2024
Pickup on: Friday, April 19, 2024




Perry County Conservation District Tree Sale—
Orders due by: Sunday, March 24, 2024
Pickup on: Thursday, April 11, 2024

Again this year, Perry County is offering bluebird nest boxes for sale. The price?—just $12.00.

York County Conservation District Seedling Sale—
Orders due by: Friday, March 15, 2024
Pickup on: Thursday, April 11, 2024

To get your deciduous trees like gums, maples, oaks, birches, and poplars off to a safe start, conservation district tree sales in Cumberland, Dauphin, Lancaster, and Perry Counties are offering protective tree shelters. Consider purchasing these plastic tubes and supporting stakes for each of your hardwoods, especially if you have hungry deer in your neighborhood.

There you have it. Be sure to check out each tree sale’s web page to find the selections you like, then get your order placed. The deadlines will be here before you know it and you wouldn’t want to miss values like these!
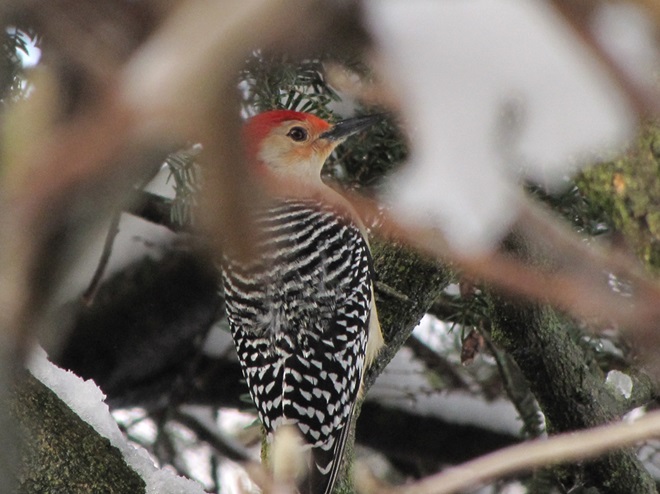
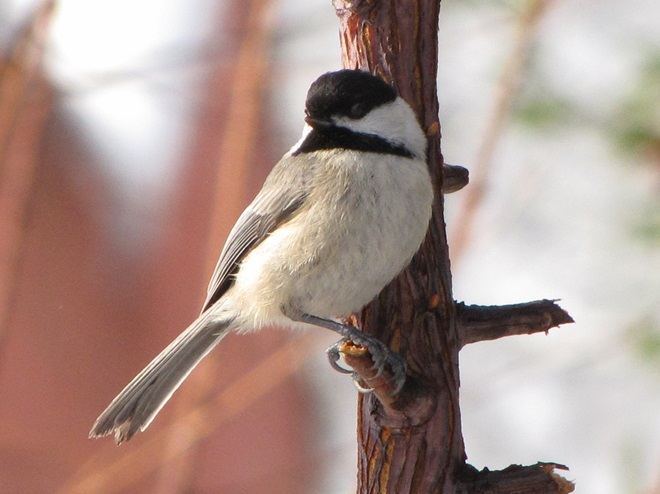
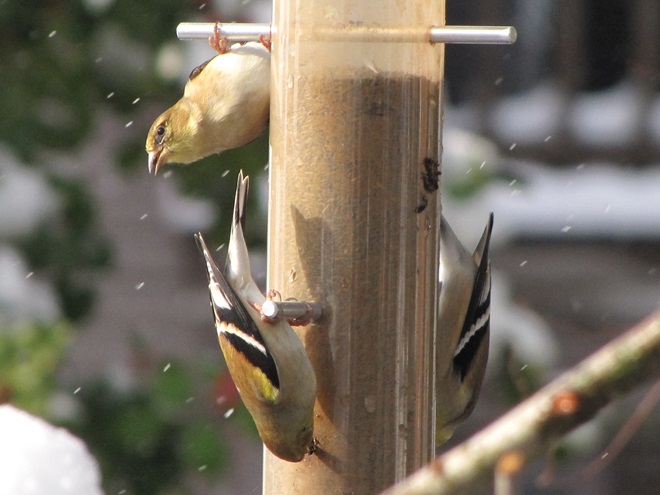
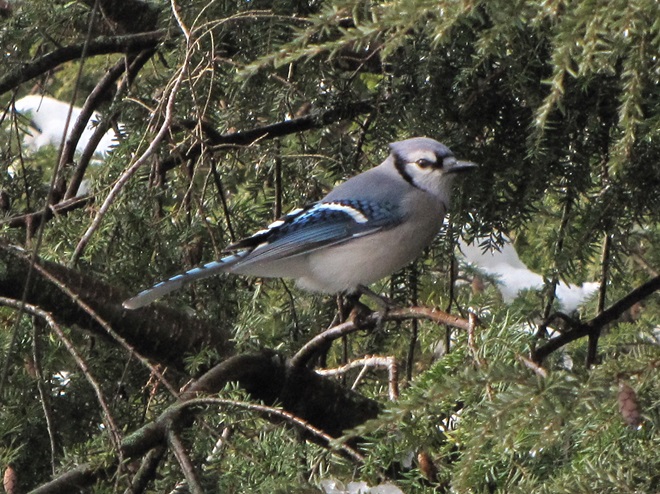
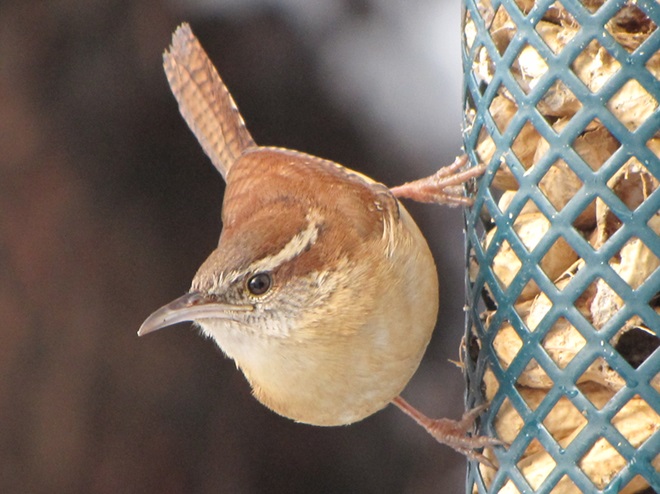
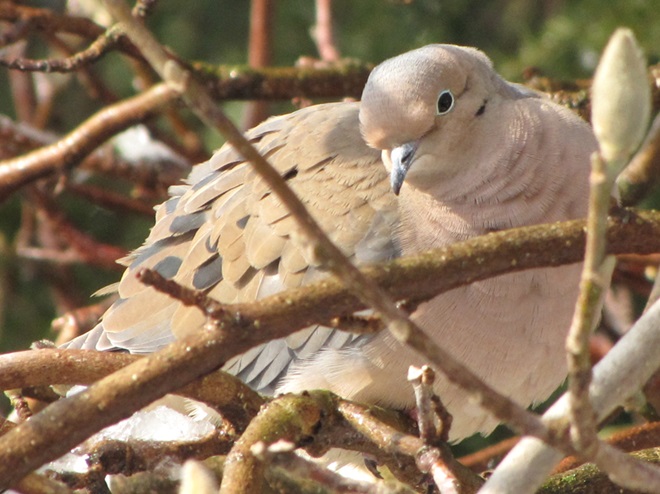
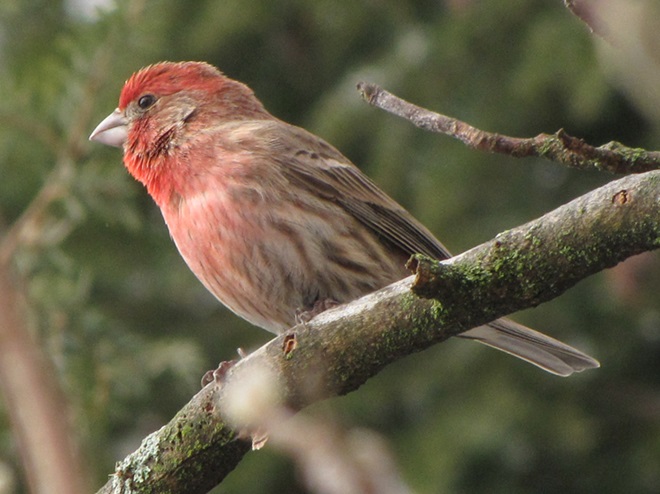
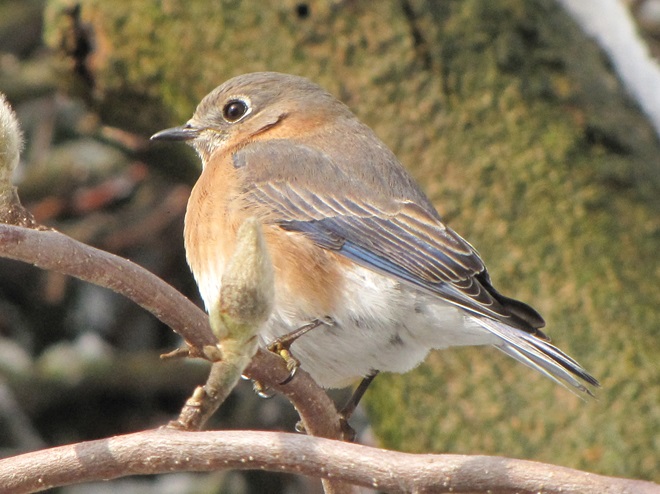
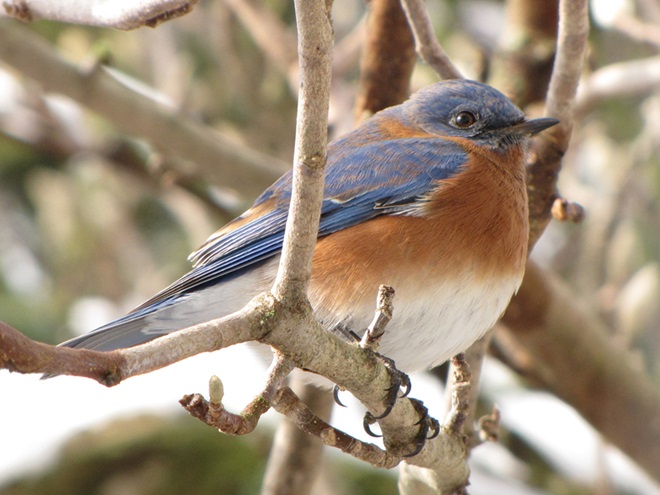
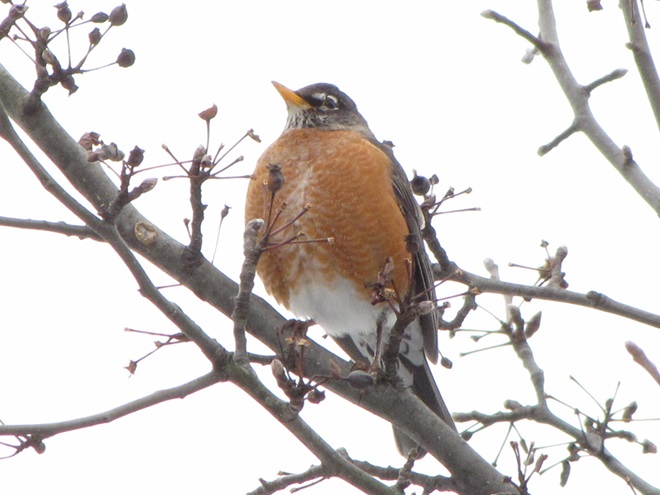
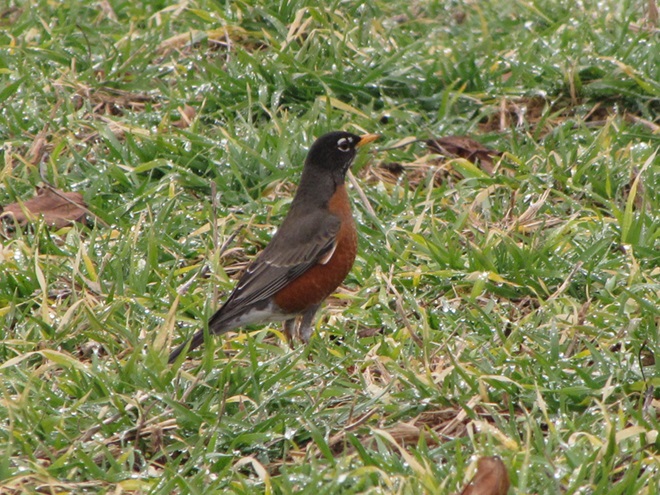
Since Tuesday’s snow storm, the susquehannawiildlife.net headquarters garden continues to bustle with bird activity.
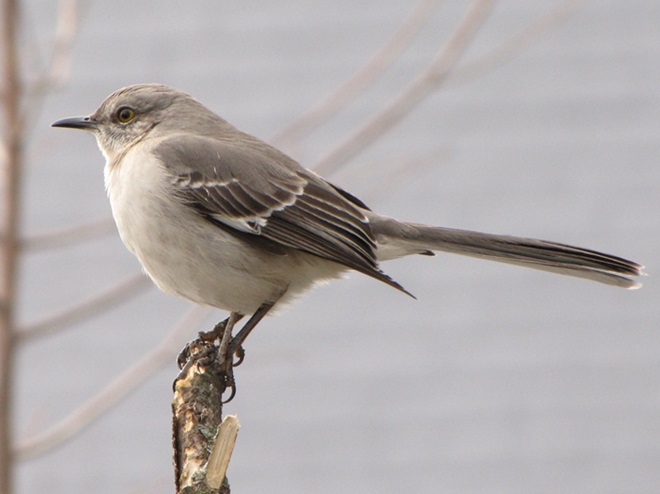
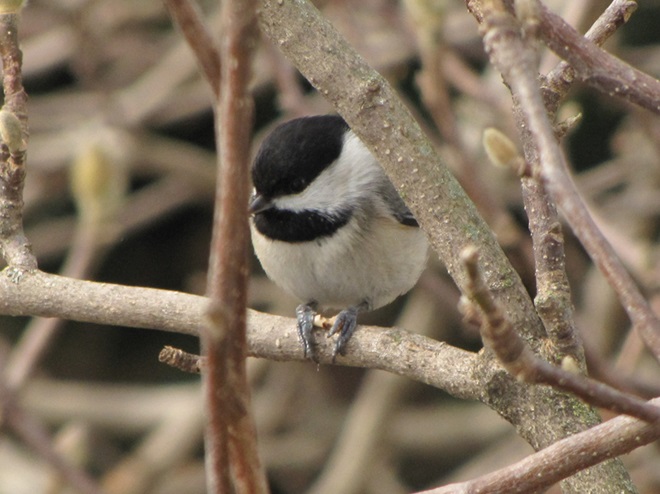
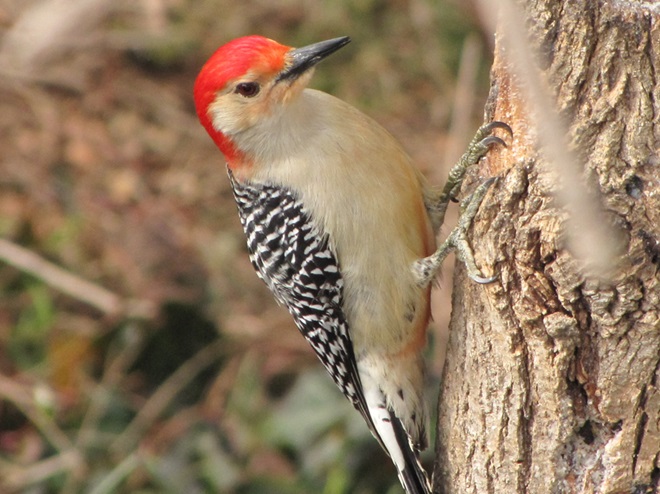
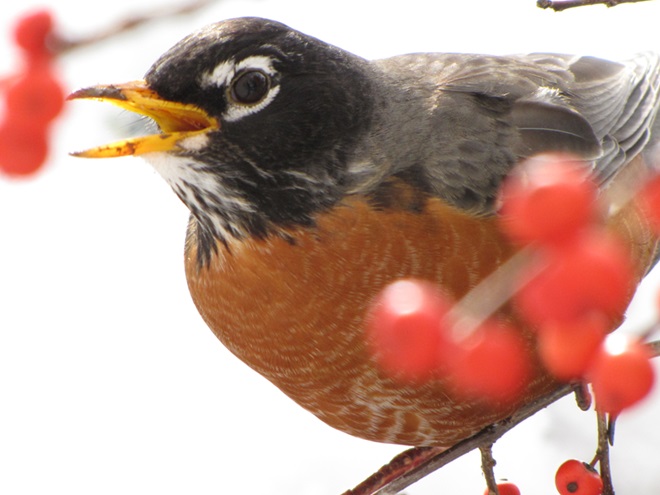




Today, there arrived three species of birds we haven’t seen here since autumn. These birds are, at the very least, beginning to wander in search of food. Then too, these may be individuals creeping slowly north to secure an advantage over later migrants by being the first to establish territories on the most favorable nesting grounds.
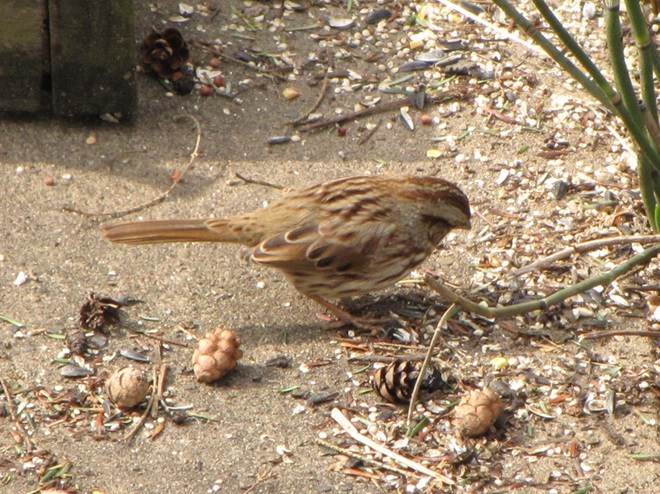
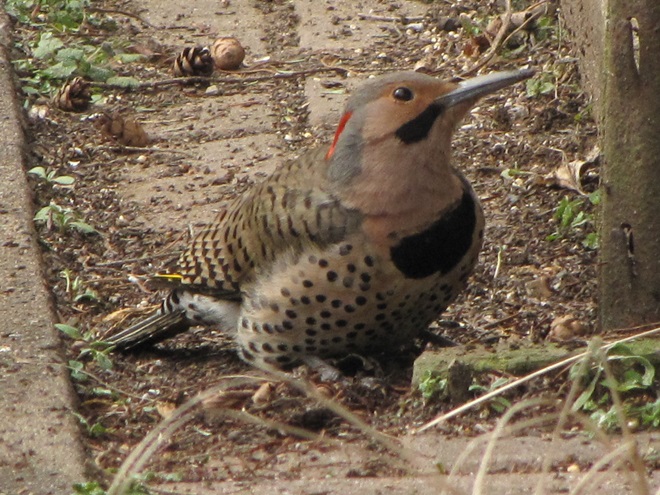
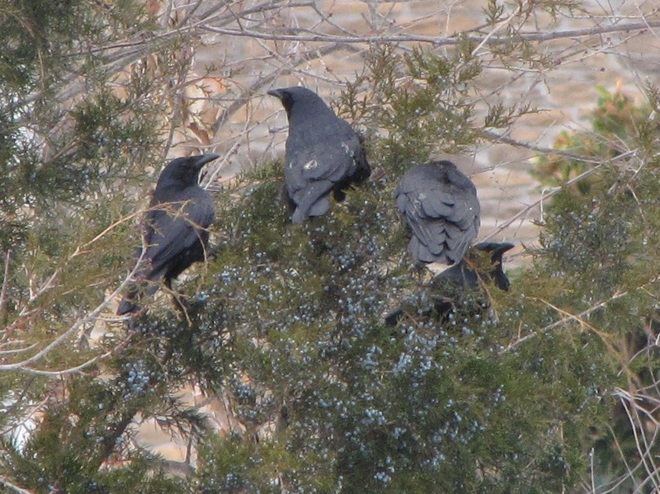



They say the early bird gets the worm. More importantly, it gets the most favorable nesting spot. What does the early birder get? He or she gets out of the house and enjoys the action as winter dissolves into the miracle of spring. Do make time to go afield and marvel a bit, won’t you? See you there!
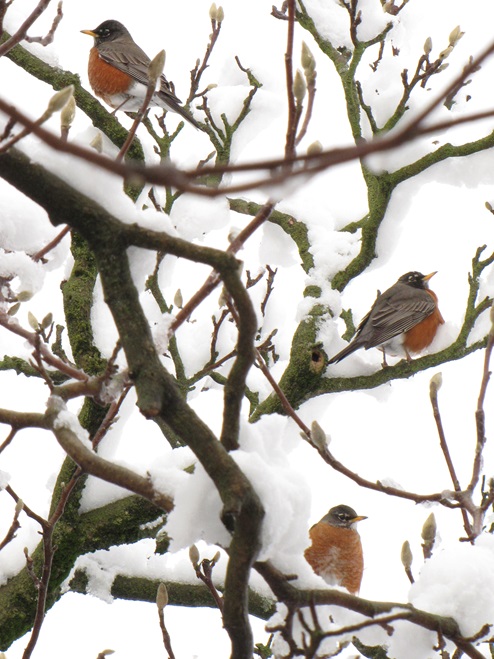
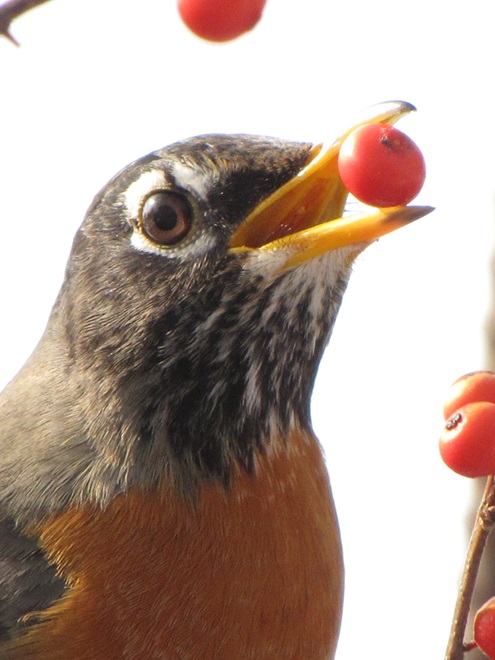
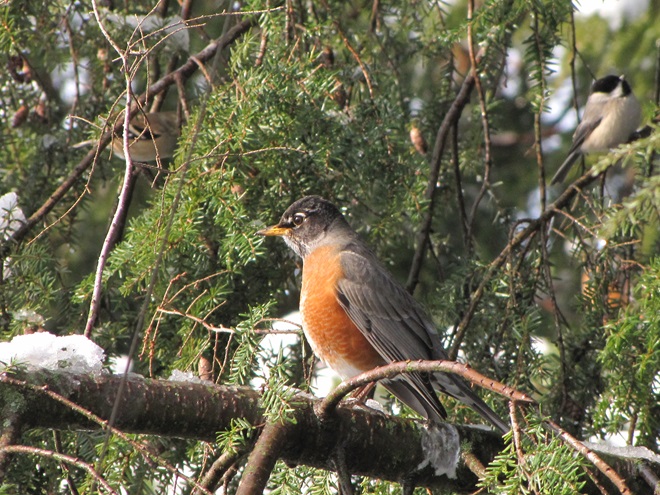
In mid-February each year, large numbers of American Robins descend upon the susquehannawildlife.net headquarters garden to feast on the ripe fruits that adorn several species of our native shrubs and trees. This morning’s wet snowfall provided the needed motivation for these birds and others to make today the big day for the annual feeding frenzy.
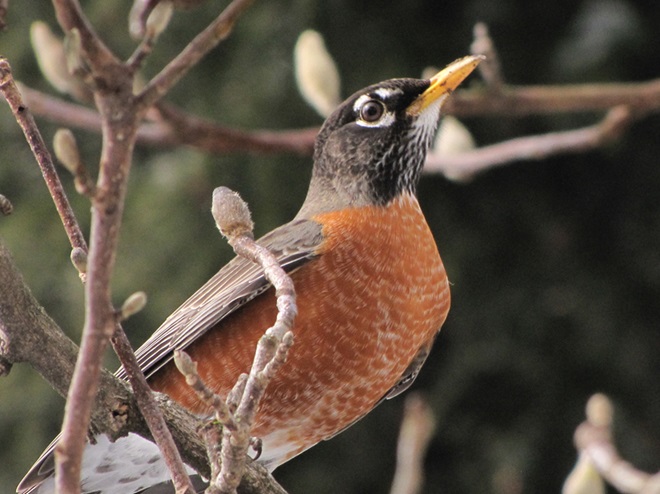
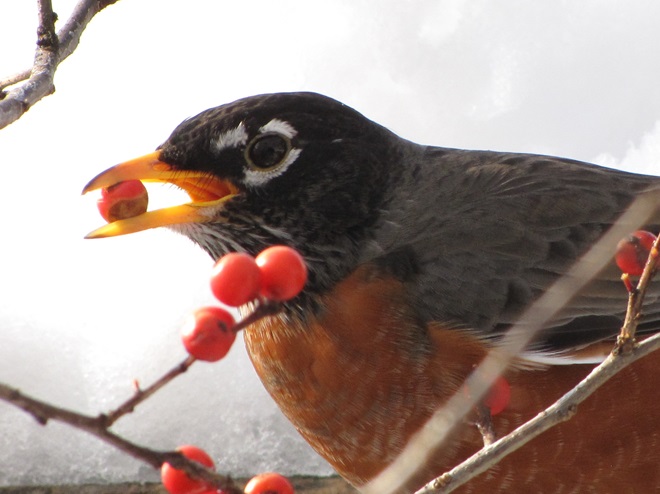
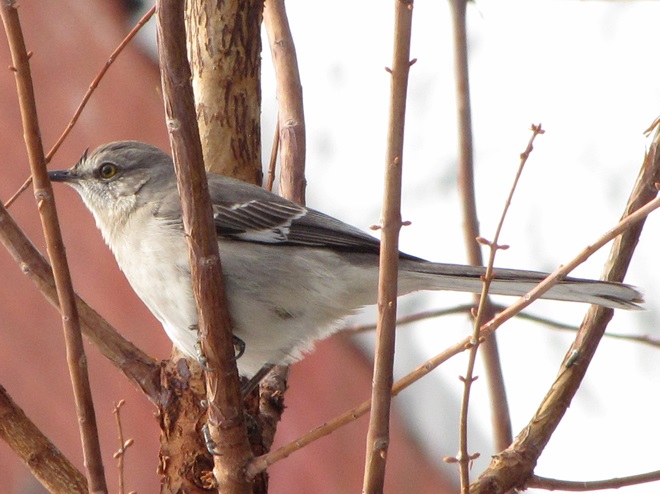
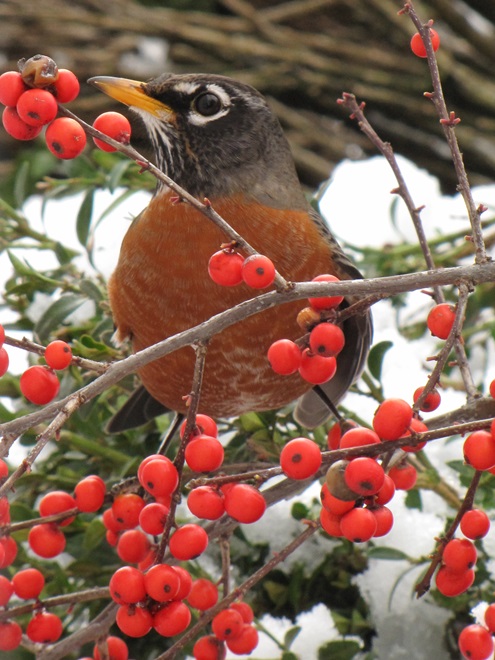

















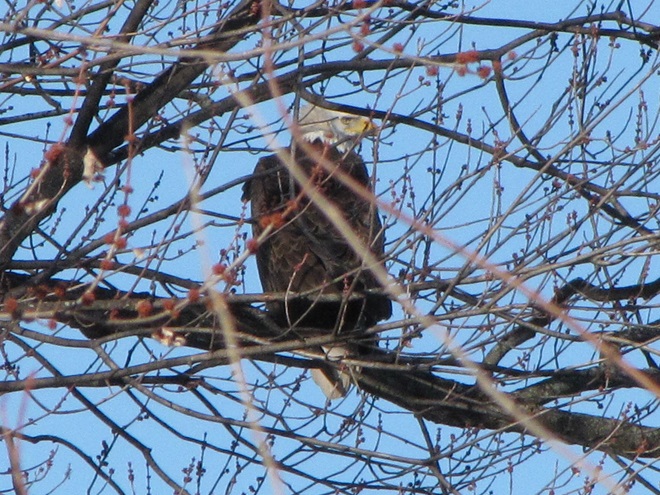
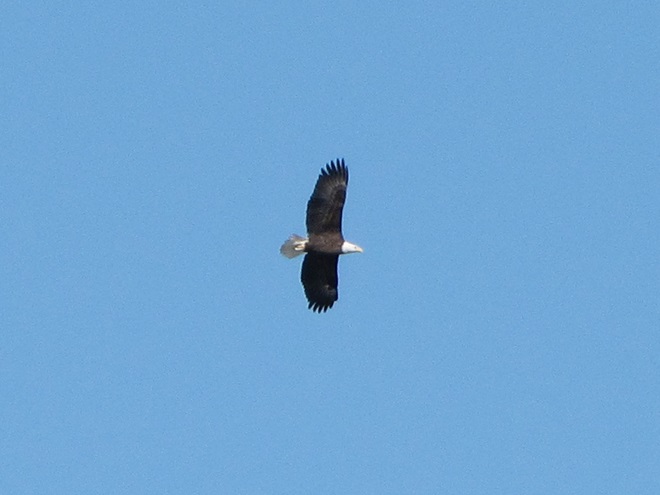
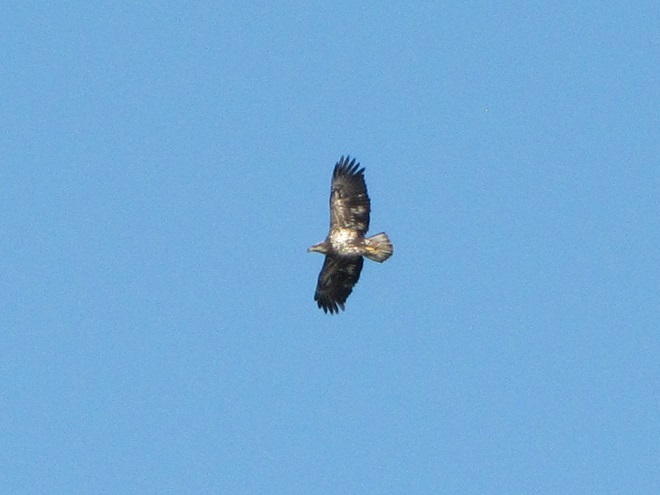
Now is a great time of year to see Bald Eagles in the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed. For the population that breeds here in our region, it’s nesting season. These birds are defending territories and some of them can get pretty aggressive towards the other eagles that happen to be wintering in the Susquehanna valley or will be migrating north through the area in coming weeks. All that competition has these birds spending a lot of time in the air, so no matter where you happen to be, keeping an eye on the sky may provide you with an opportunity for a memorable glimpse of one or more eagles in action. Skeptical? Well, just an hour ago, we spotted these eagles high above the susquehannawildlife.net headquarters garden.
So do spend some time outdoors soon and while you’re there, don’t forget to look up. You might turn some of your time into Bald Eagle time too!
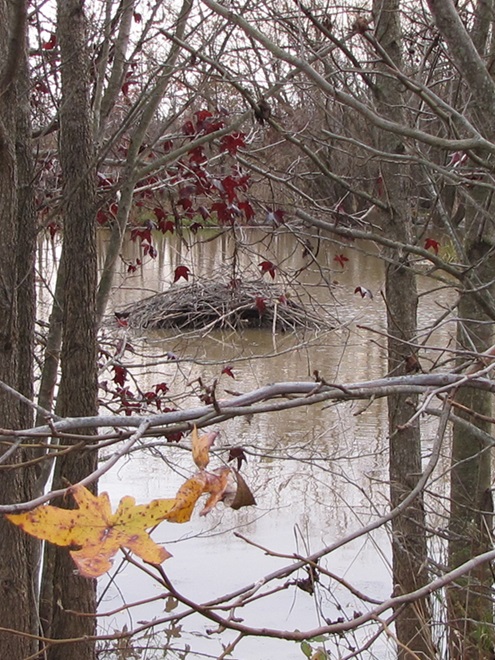
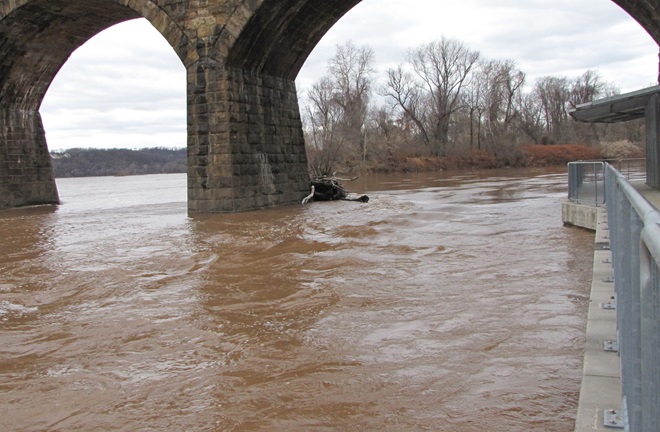
As week-old snow and ice slowly disappears from the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed landscape, we ventured out to see what might be lurking in the dense clouds of fog that for more than two days now have accompanied a mid-winter warm spell.
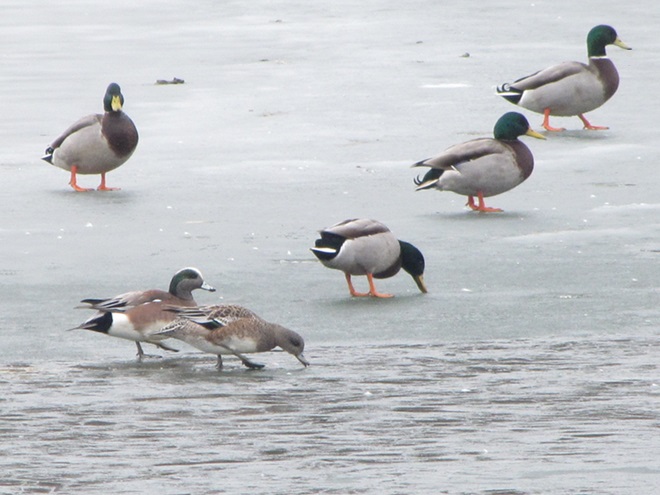
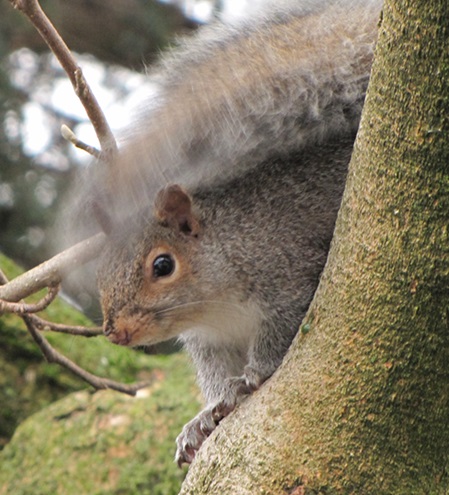
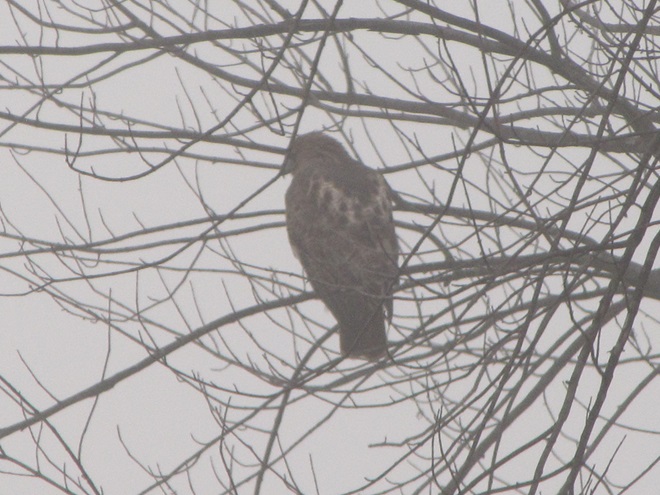
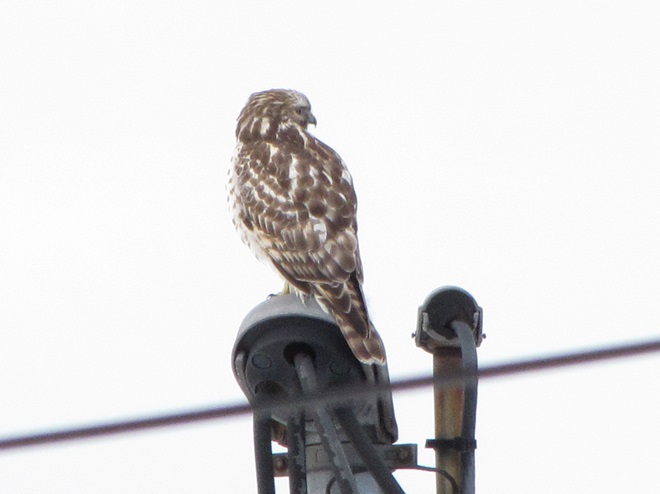
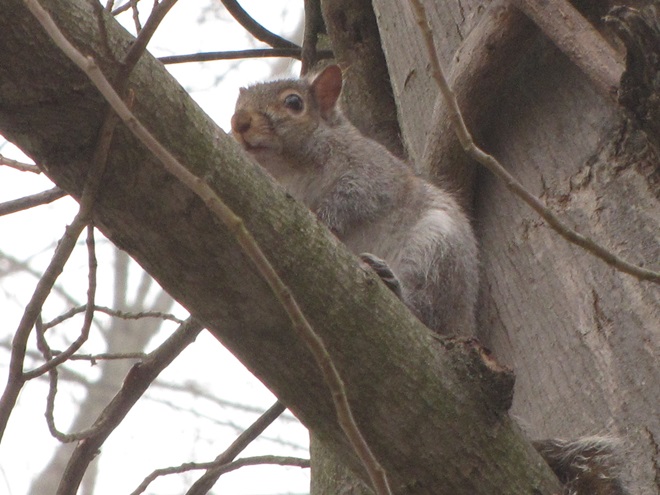
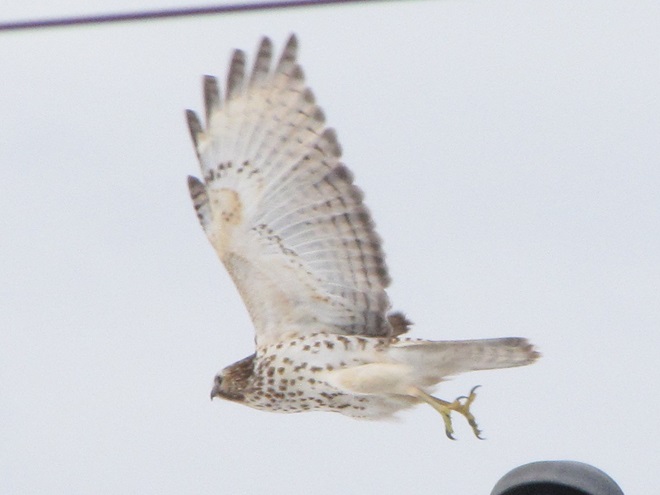
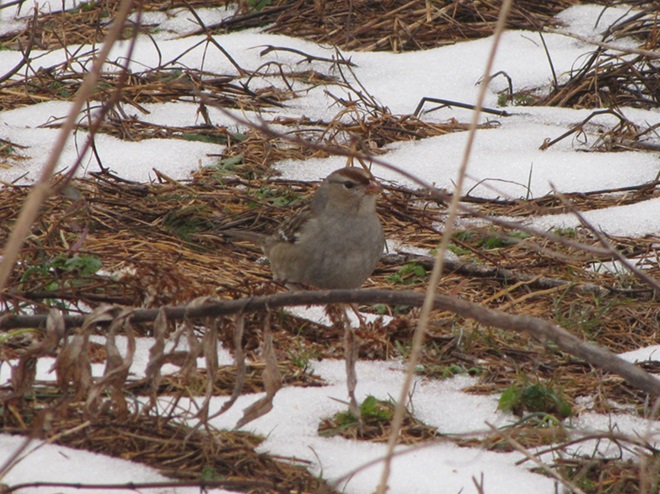
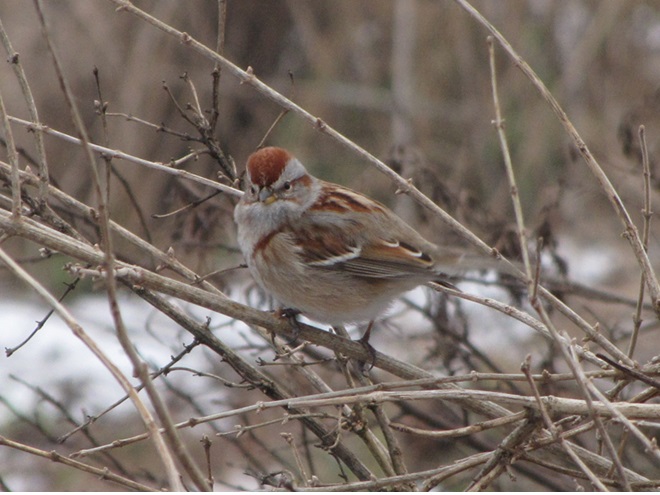
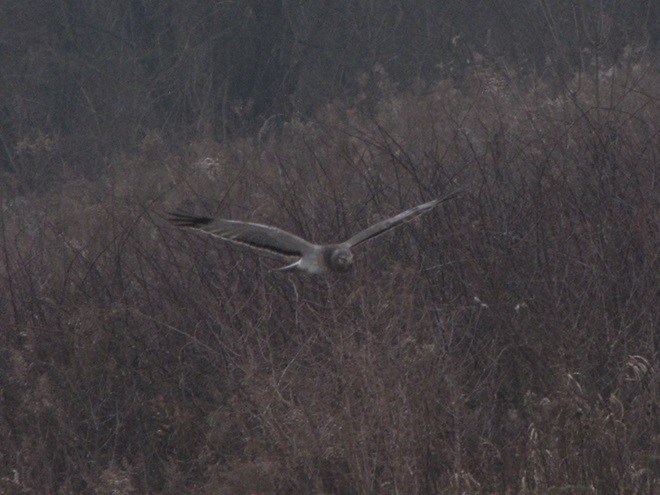















If scenes of a January thaw begin to awaken your hopes and aspirations for all things spring, then you’ll appreciate this pair of closing photographs…
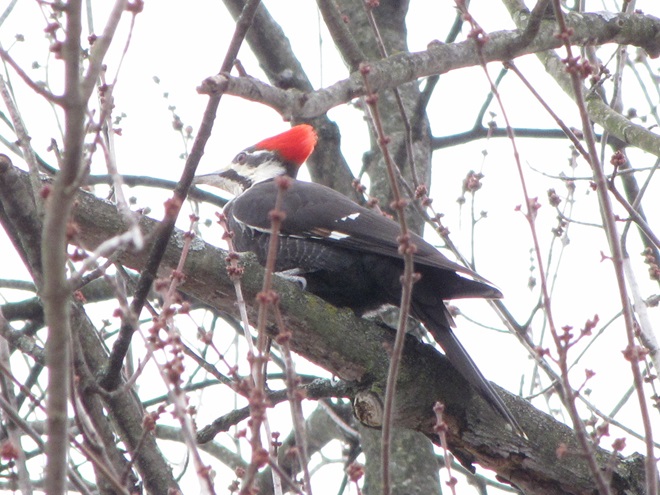
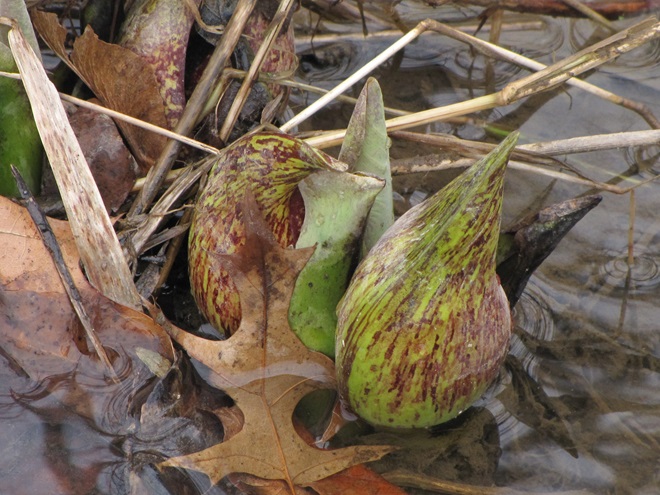


Just as bare ground along a plowed road attracts birds in an otherwise snow-covered landscape, a receding river or large stream can provide the same benefit to hungry avians looking for food following a winter storm.
Here is a small sample of some of the species seen during a brief stop along the Susquehanna earlier this week.
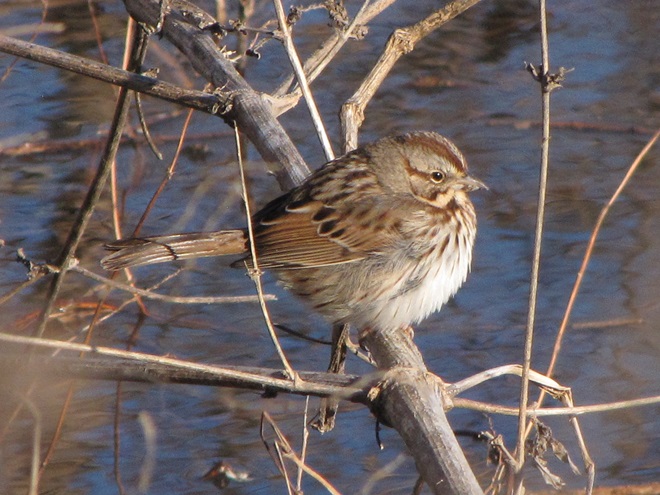
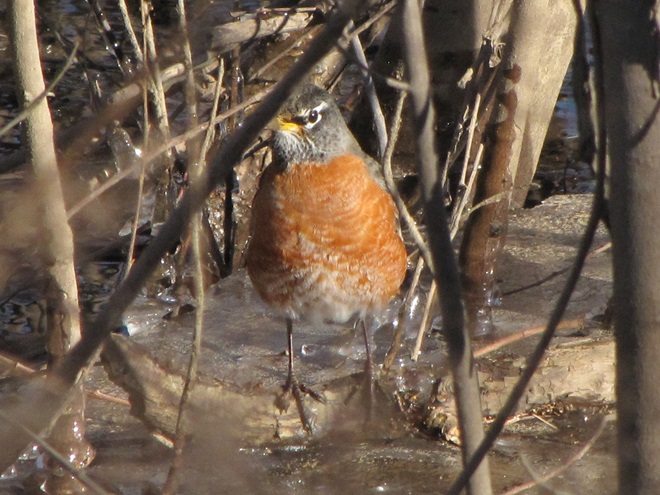
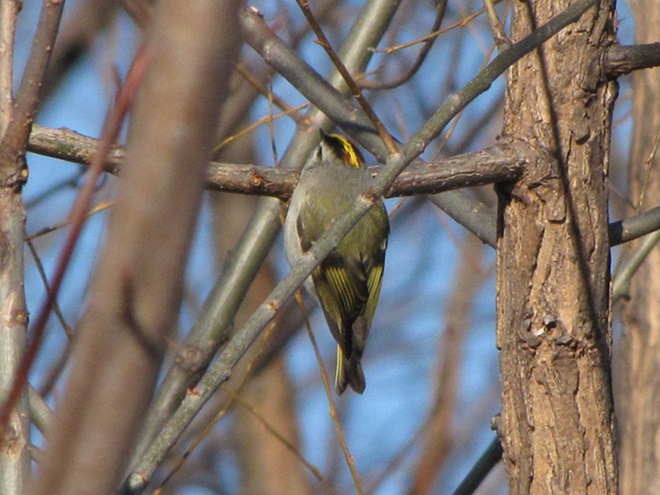
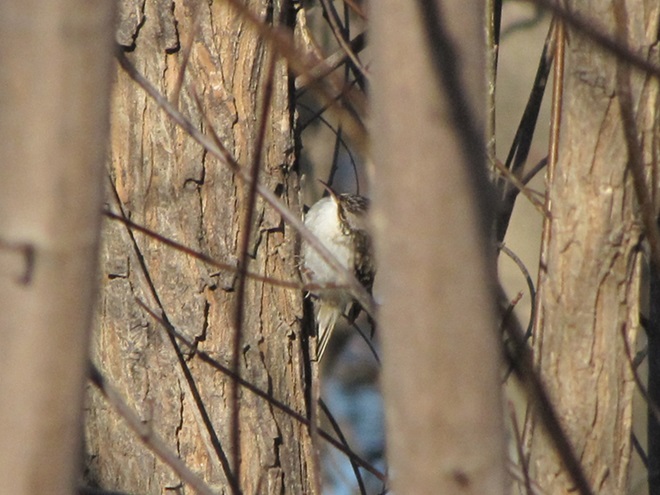
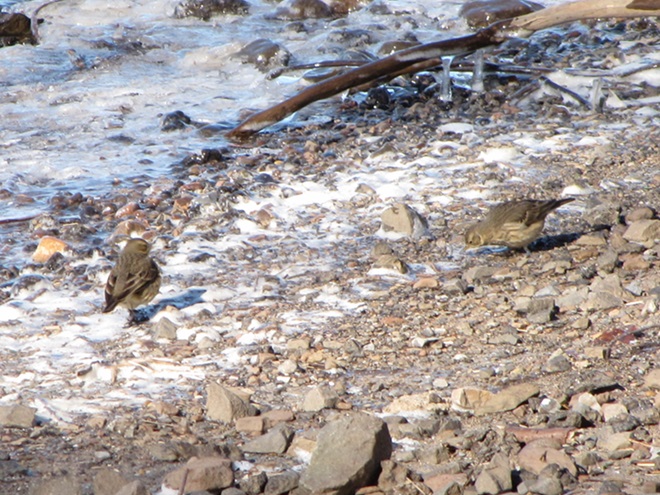
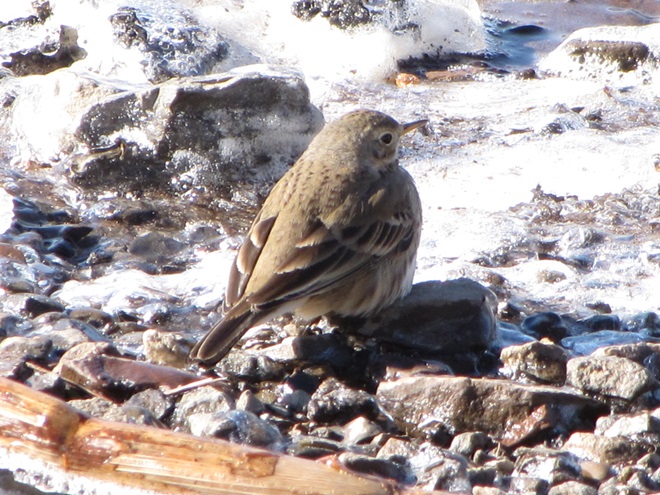






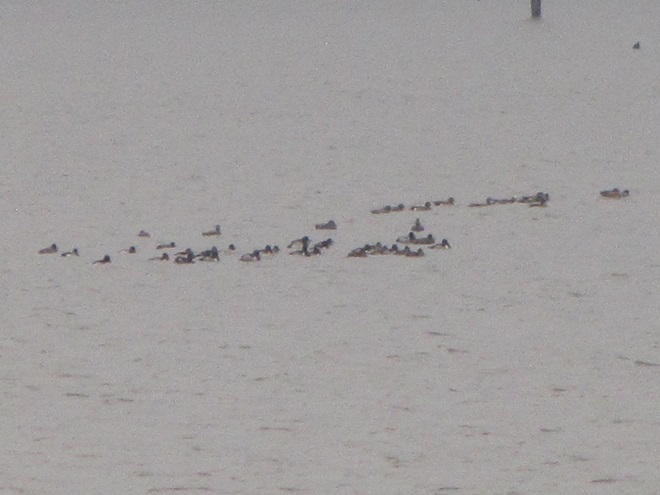
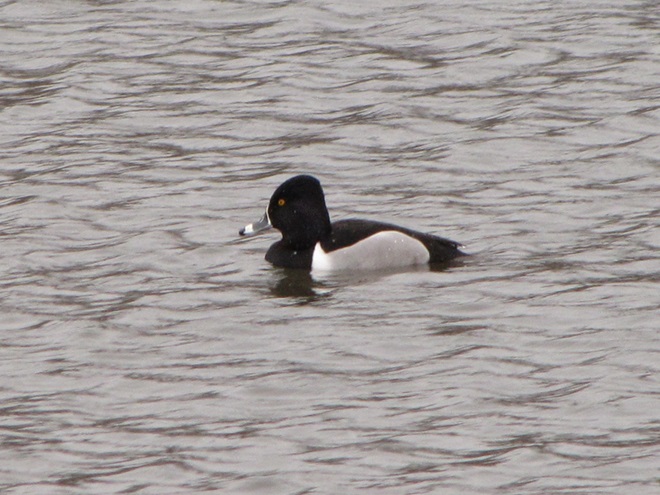
As anticipated, lakes and ponds throughout the lower Susquehanna basin are beginning to freeze. Fortunately for the waterfowl thereon, particularly diving ducks, the rain-swollen river is slowly receding and water clarity is improving to provide a suitable alternative to life on the man-made impoundments.
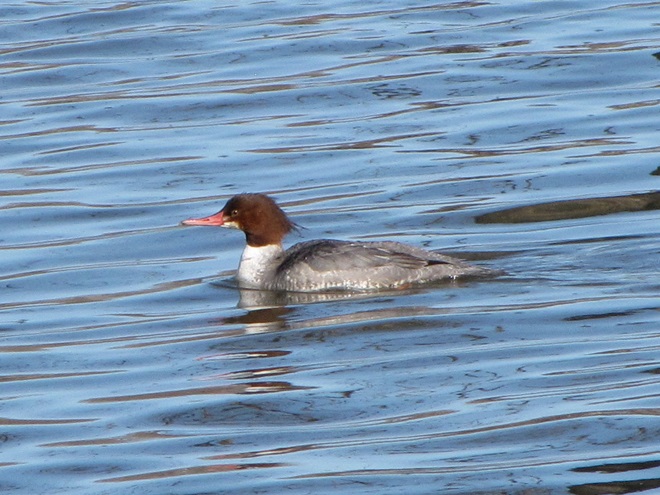


The deep freeze is not only impacting ponds and lakes in the lower Susquehanna valley, but is evidently affecting the larger bodies of water to our north and northwest. During Tuesday’s snow event, thousands of diving ducks arrived on the main stem of the river—apparently forced down by the inclement weather while en route to the Atlantic Coast from the Great Lakes and its connected waterways, which are currently beginning to freeze.
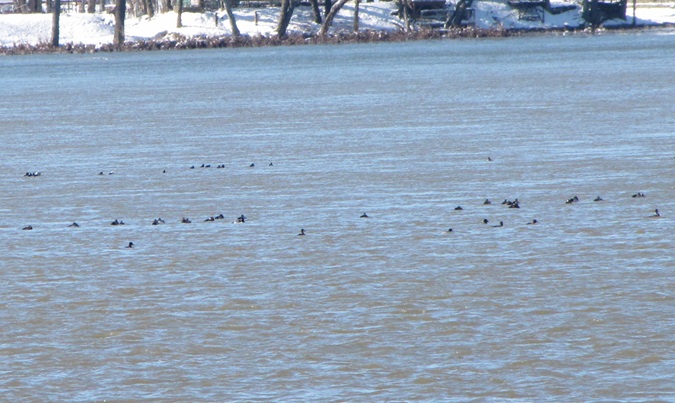
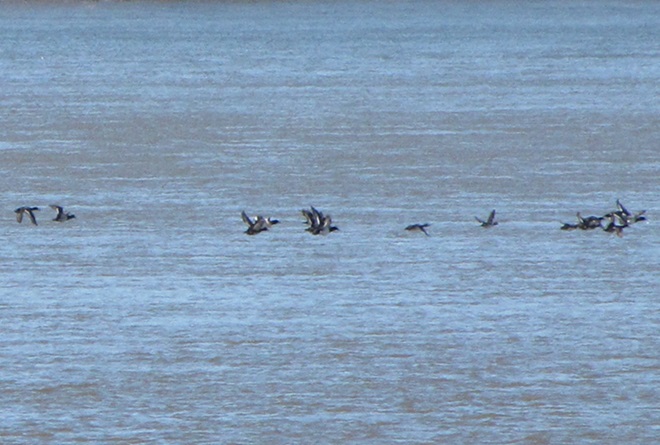
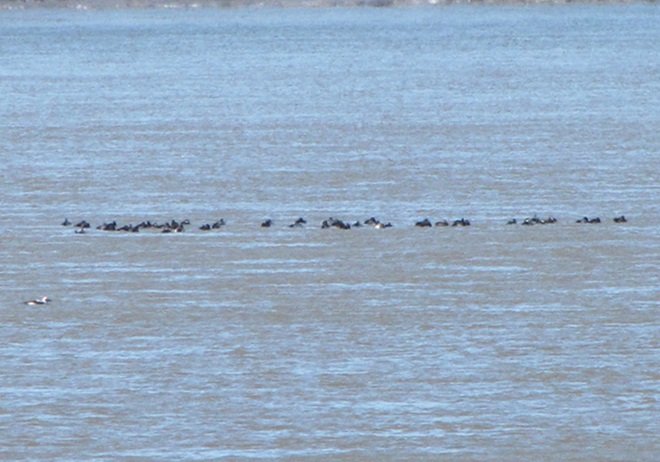
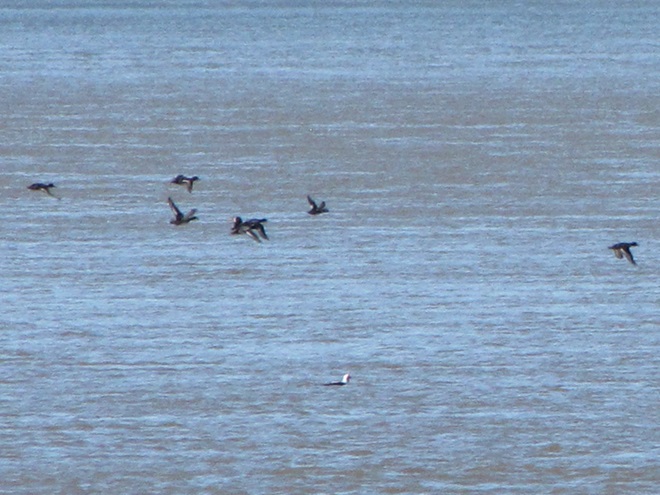
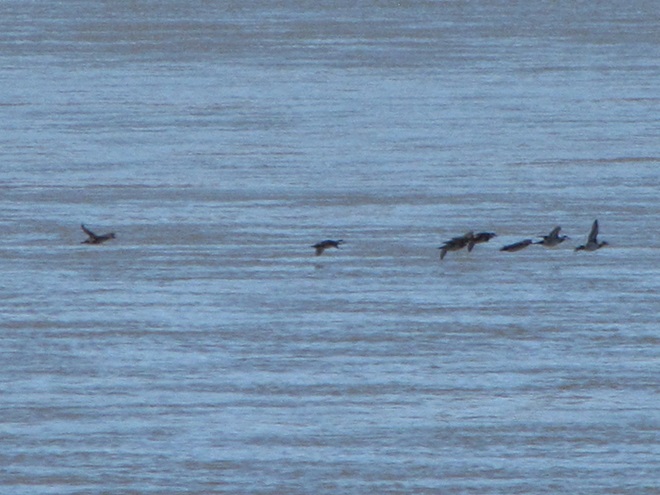
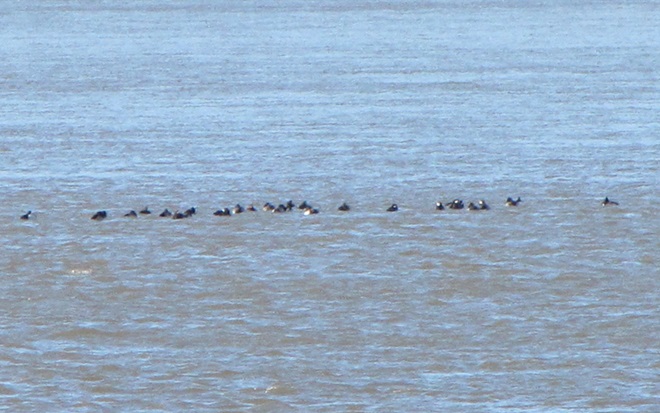
















With more snow on the way for tomorrow, you may be wondering if another fallout like this could be in the works. The only way to find out is to get out there and have a look. Good luck! And be good!
Heavy rains and snow melt have turned the main stem of the Susquehanna and its larger tributaries into a muddy torrent. For fish-eating (piscivorous) ducks, the poor visibility in fast-flowing turbid waters forces them to seek better places to dive for food. With man-made lakes and ponds throughout most of the region still ice-free, waterfowl are taking to these sources of open water until the rivers and streams recede and clear.
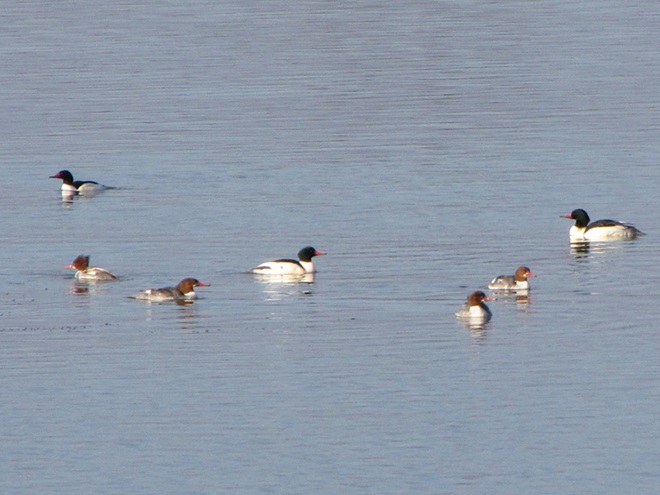
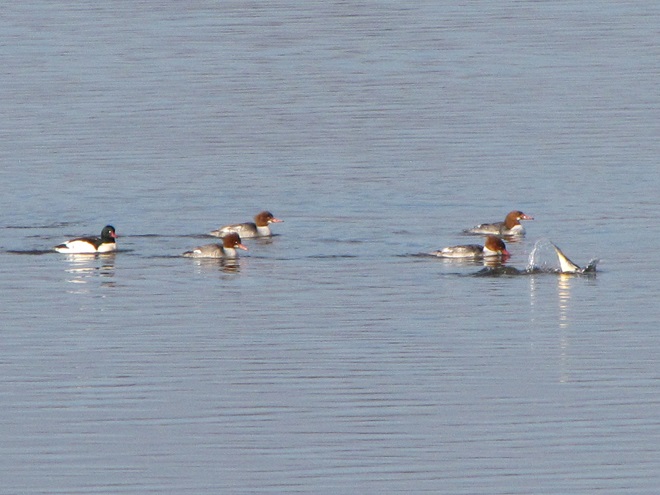
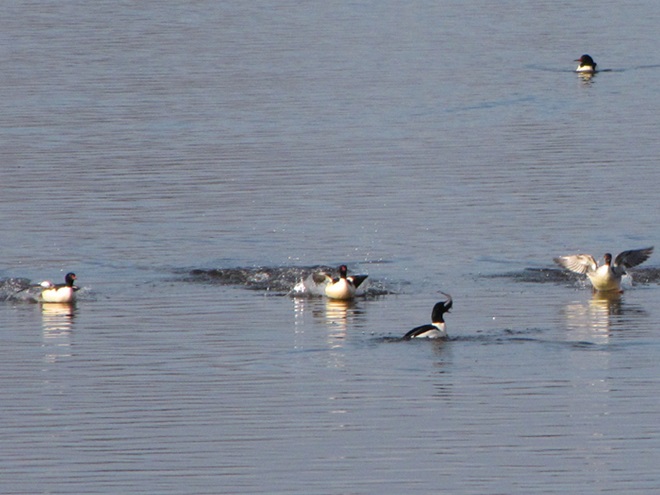



With a hard freeze on the way, the fight for life will get even more desperate in the coming weeks. Lakes will ice over and the struggle for food will intensify. Fortunately for mergansers and other piscivorous waterfowl, high water on the Susquehanna is expected to recede and clarify, allowing them to return to their traditional environs. Those with the most suitable skills and adaptations to survive until spring will have a chance to breed and pass their vigor on to a new generation of these amazing birds.
When the ground becomes snow covered, it’s hard to imagine anything lives in the vast wide-open expanses of cropland found in the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed’s fertile valleys.

Yet, there is one group of birds that can be found scrounging a living from what little exists after a season of high-intensity farming. Meet the Horned Lark.
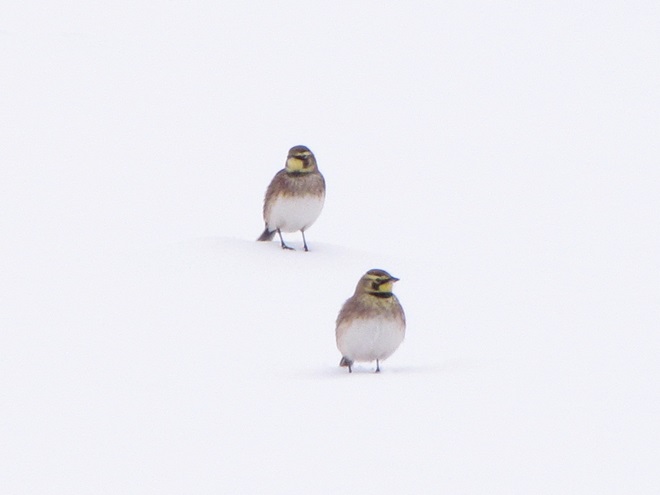
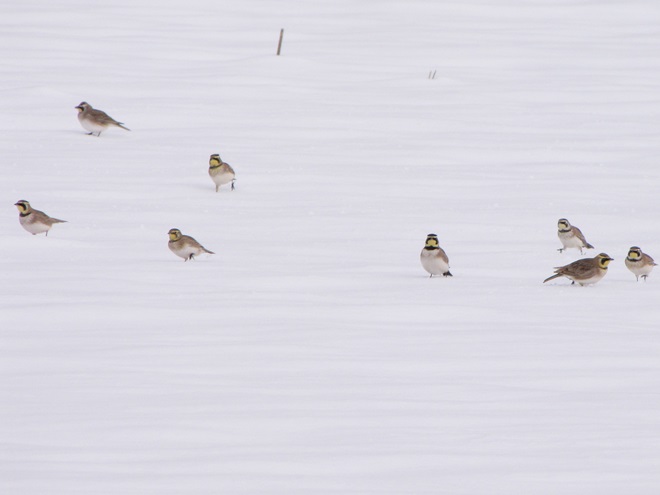
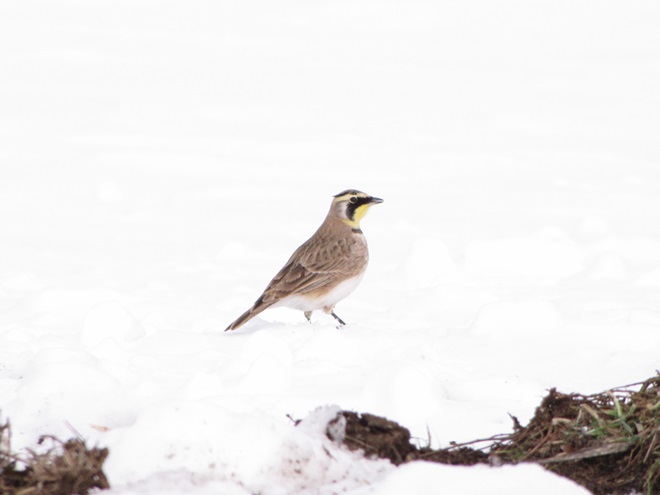
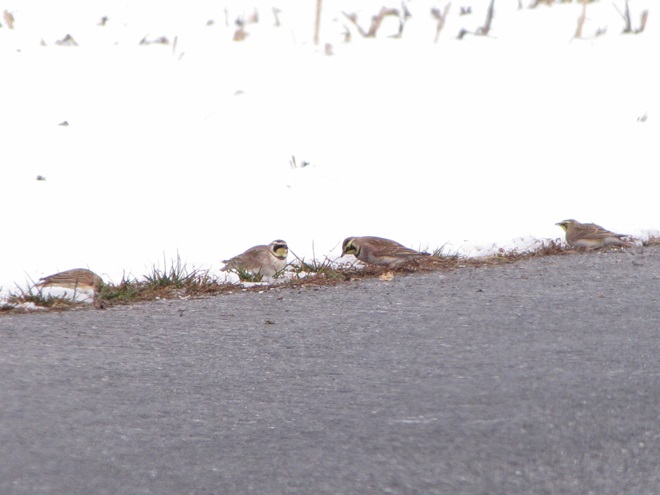
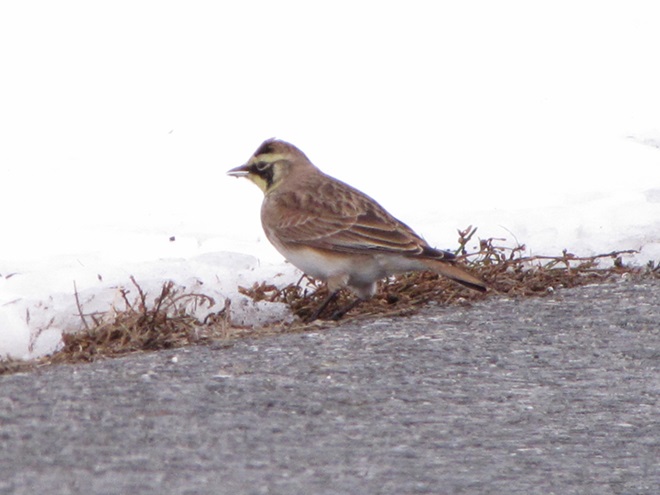
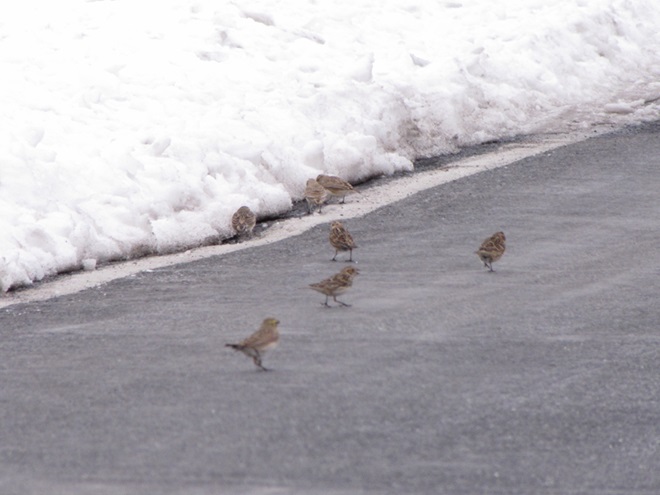
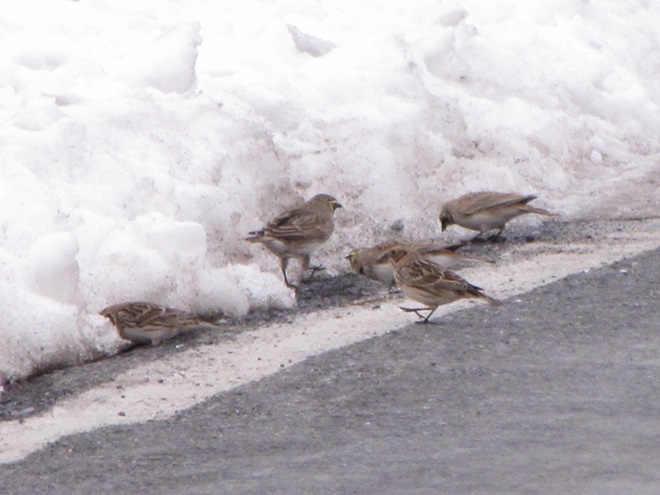
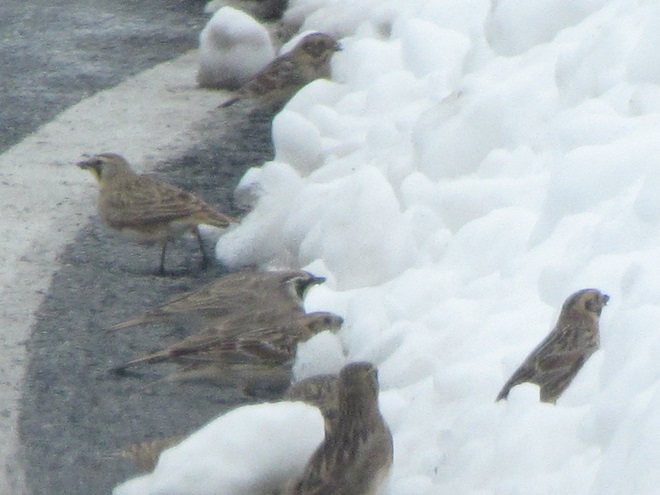










If you decide to take a little post-storm trip to look for Horned Larks and Lapland Longspurs, be sure to drive carefully. Do your searching on quiet rural roads with minimal traffic. Stop and park only where line-of-sight and other conditions allow it to be done safely. Use your flashers and check your mirrors often. Think before you stop and park—don’t get stuck or make a muddy mess. And most important of all, be aware that you’re on a roadway—get out of the way of traffic.

If you’re not going out to look for larks and longspurs, we do have a favor to ask of you. Please remember to slow down while you’re driving. Not only is this an accident-prone time of year for people in cars and trucks, it’s a dangerous time for birds and other wildlife too. They’re at greatest peril of getting run over while concentrated along roadsides looking for food following snow storms.
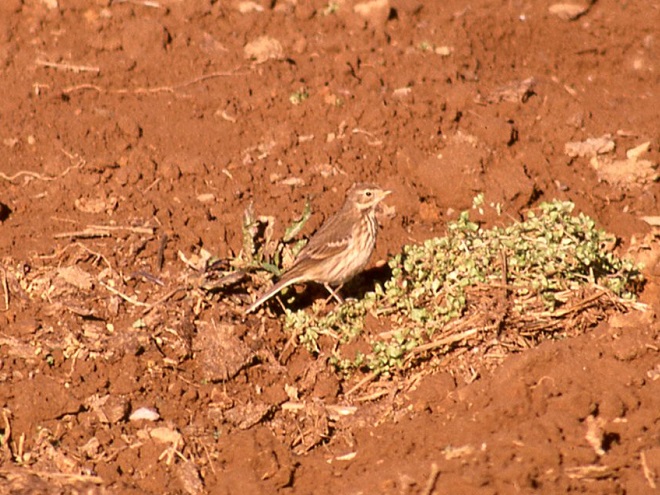
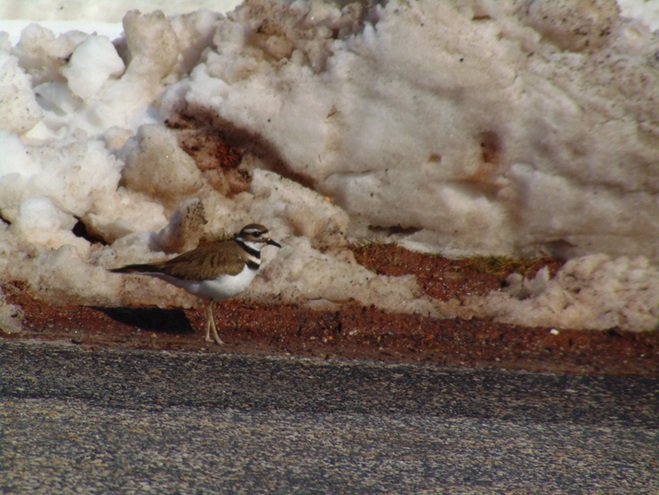



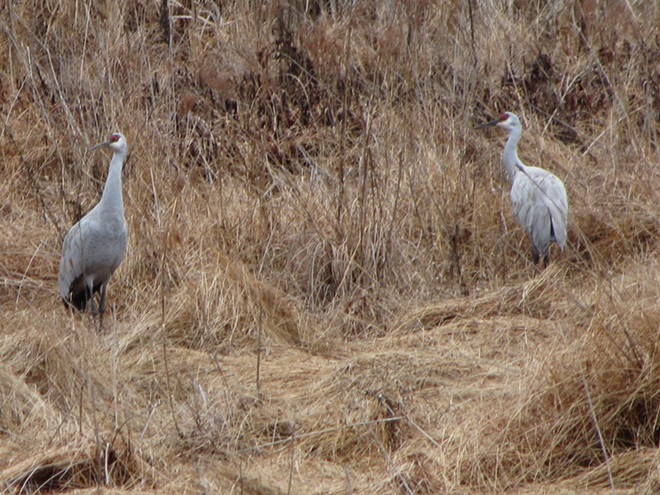
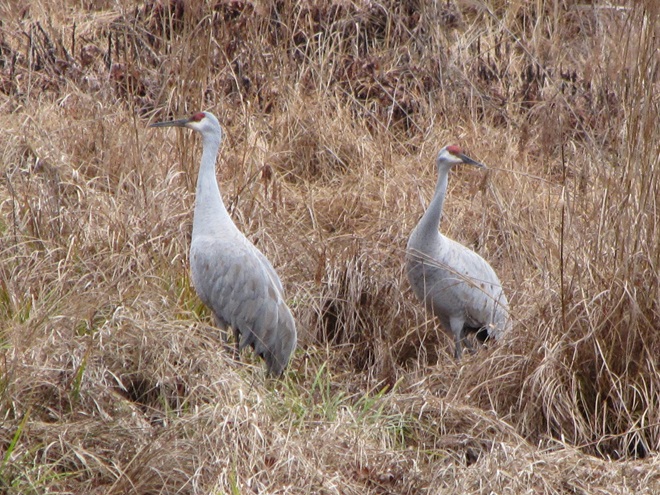
With the earth at perihelion (its closest approach to the sun) and with our home star just 27 degrees above the horizon at midday, bright low-angle light offered the perfect opportunity for doing some wildlife photography today. We visited a couple of grasslands managed by the Pennsylvania Game Commission to see what we could find…
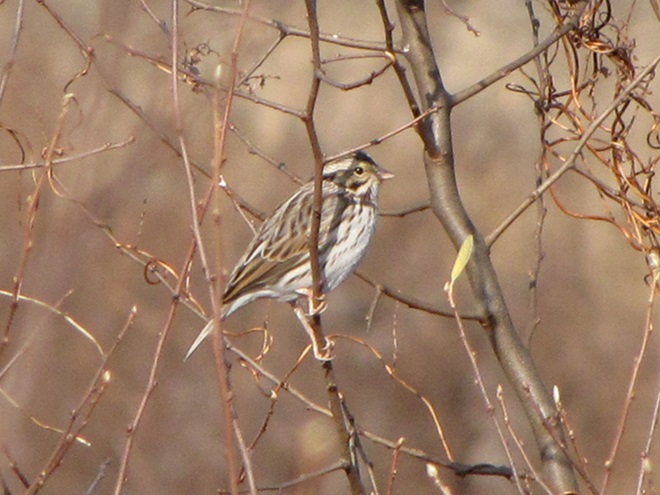
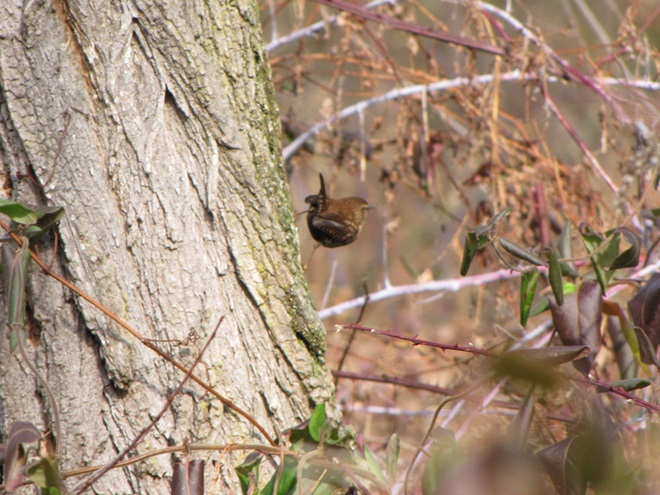
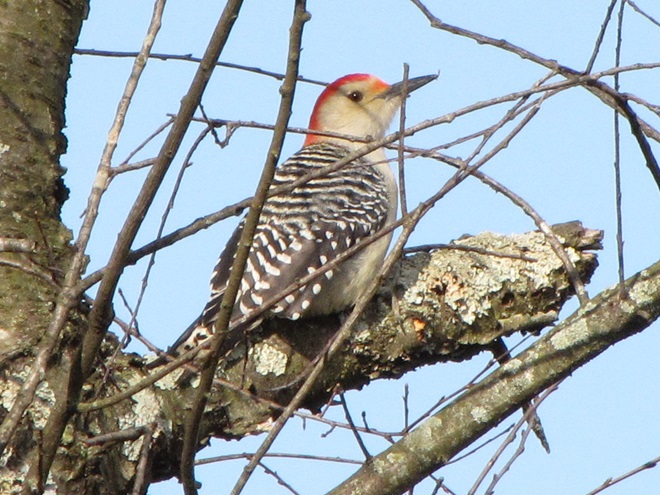
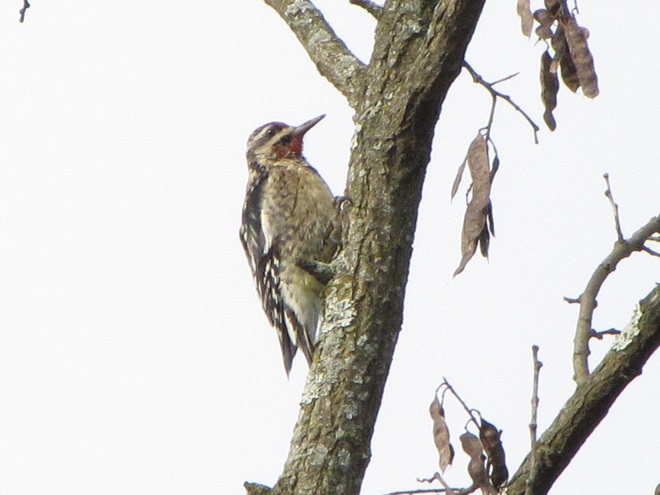
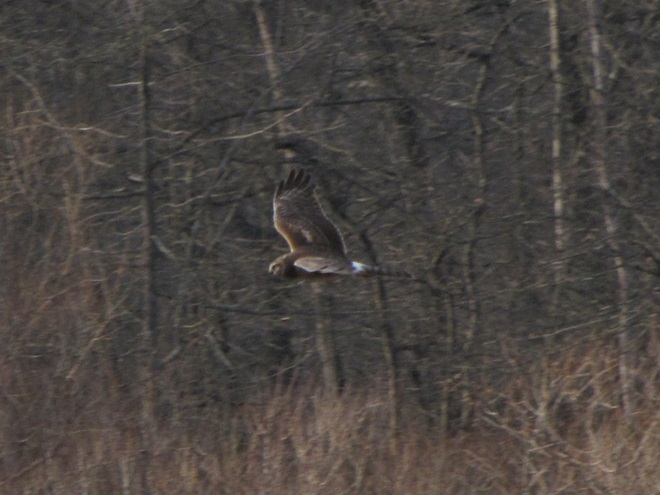
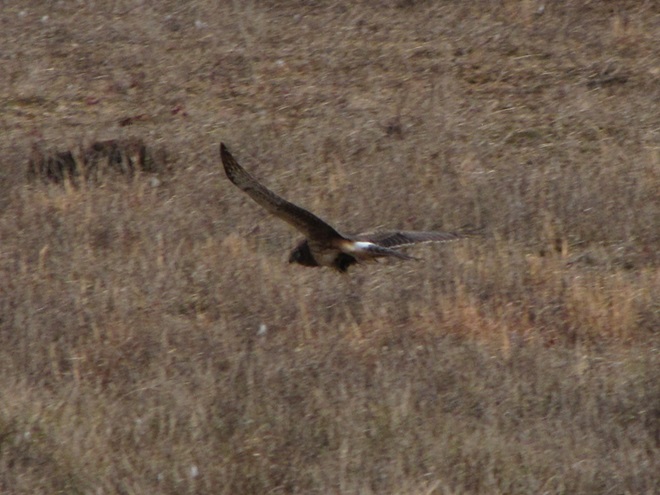



















I’m worried about the beaver. Here’s why.
Imagine a network of brooks and rivulets meandering through a mosaic of shrubby, sometimes boggy, marshland, purifying water and absorbing high volumes of flow during storm events. This was a typical low-gradient stream in the valleys of the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed in the days prior to the arrival of the trans-Atlantic human migrant. Then, a frenzy of trapping, tree chopping, mill building, and stream channelization accompanied the east to west waves of settlement across the region. The first casualty: the indispensable lowlands manager, the North American Beaver (Castor canadensis).

Without the widespread presence of beavers, stream ecology quickly collapsed. Pristine waterways were all at once gone, as were many of their floral and faunal inhabitants. It was a streams-to-sewers saga completed in just one generation. So, if we really want to restore our creeks and rivers, maybe we need to give the North American Beaver some space and respect. After all, we as a species have yet to build an environmentally friendly dam and have yet to fully restore a wetland to its natural state. The beaver is nature’s irreplaceable silt deposition engineer and could be called the 007 of wetland construction—doomed upon discovery, it must do its work without being noticed, but nobody does it better.
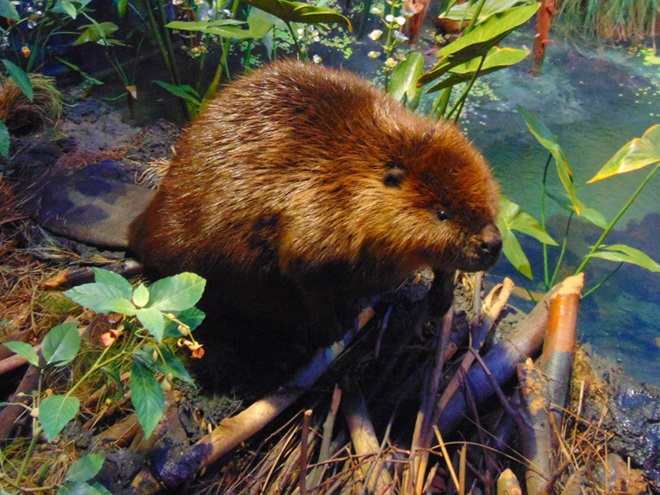
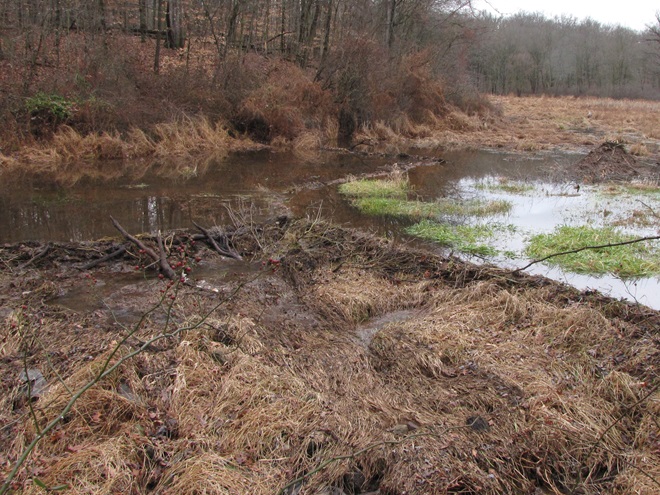
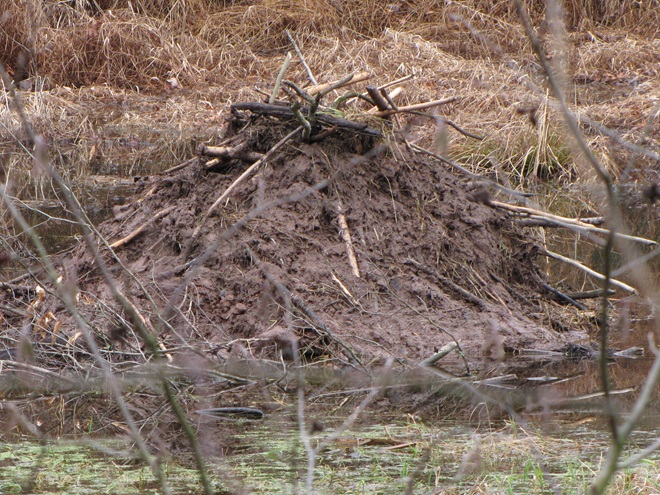
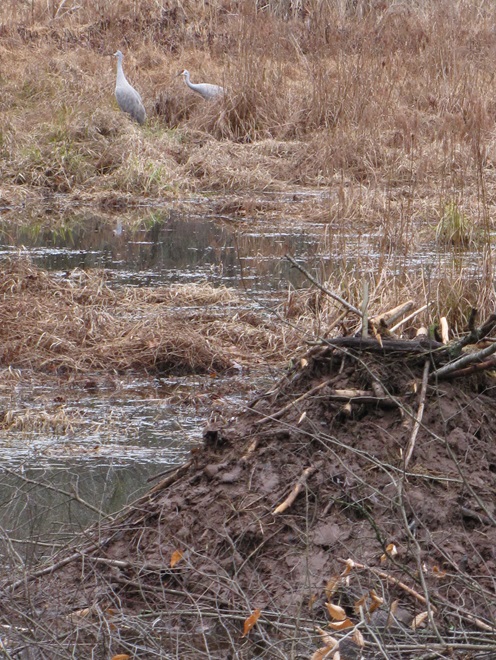










Few landowners are receptive to the arrival of North American Beavers as guests or neighbors. This is indeed unfortunate. Upon discovery, beavers, like wolves, coyotes, sharks, spiders, snakes, and so many other animals, evoke an irrational negative response from the majority of people. This too is quite unfortunate, and foolish.
North American Beavers spend their lives and construct their dams, ponds, and lodges exclusively within floodplains—lands that are going to flood. Their existence should create no conflict with the day to day business of human beings. But humans can’t resist encroachment into beaver territory. Because they lack any basic understanding of floodplain function, people look at these indispensable lowlands as something that must be eliminated in the name of progress. They’ll fill them with soil, stone, rock, asphalt, concrete, and all kinds of debris. You name it, they’ll dump it. It’s an ill-fated effort to eliminate these vital areas and the high waters that occasionally inundate them. Having the audacity to believe that the threat of flooding has been mitigated, buildings and poorly engineered roads and bridges are constructed in these “reclaimed lands”. Much of the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed has now been subjected to over three hundred years-worth of these “improvements” within spaces that are and will remain—floodplains. Face it folks, they’re going to flood, no matter what we do to try to stop it. And as a matter of fact, the more junk we put into them, the more we displace flood waters into areas that otherwise would not have been impacted! It’s absolute madness.
By now we should know that floodplains are going to flood. And by now we should know that the impacts of flooding are costly where poor municipal planning and negligent civil engineering have been the norm for decades and decades. So aren’t we tired of hearing the endless squawking that goes on every time we get more than an inch of rain? Imagine the difference it would make if we backed out and turned over just one quarter or, better yet, one half of the mileage along streams in the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed to North American Beavers. No more mowing, plowing, grazing, dumping, paving, spraying, or building—just leave it to the beavers. Think of the improvements they would make to floodplain function, water quality, and much-needed wildlife habitat. Could you do it? Could you overcome the typical emotional response to beavers arriving on your property and instead of issuing a death warrant, welcome them as the talented engineers they are? I’ll bet you could.

What was the attraction that prompted dozens of birders to hike more than a mile to a secluded field edge along the Northwest Lancaster County River Trail on this last full day of autumn? It must be something good.
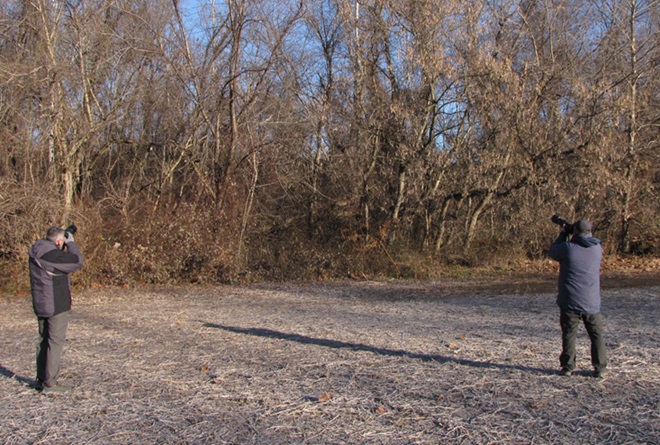

Indeed it was. A Western Flycatcher (Empidonax difficilis), first discovered late last week, has weathered the coastal storm that in recent days pummeled the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed with several inches of rain and blustery winds. Western Flycatchers nest in the Rocky Mountain and Pacific Coast regions of North America. They spend their winters in Mexico. There are several records of these tiny passerines in our area during December. The first, a bird found in an area known as Tanglewood during the Southern Lancaster County Christmas Bird Count (CBC) on December 16, 1990, was well documented—photographs were taken and its call was tape recorded. It constituted the first record of a member of the Western Flycatcher’s “Pacific-slope” subspecies group ever seen east of the Mississippi River. It was reported through December 26, 1990. The Tanglewood flycatcher and a bird sighted years later on a subsequent “Solanco CBC” were both found inhabiting wooded thickets in the shelter of a ravine created by one of the Susquehanna’s small tributaries.
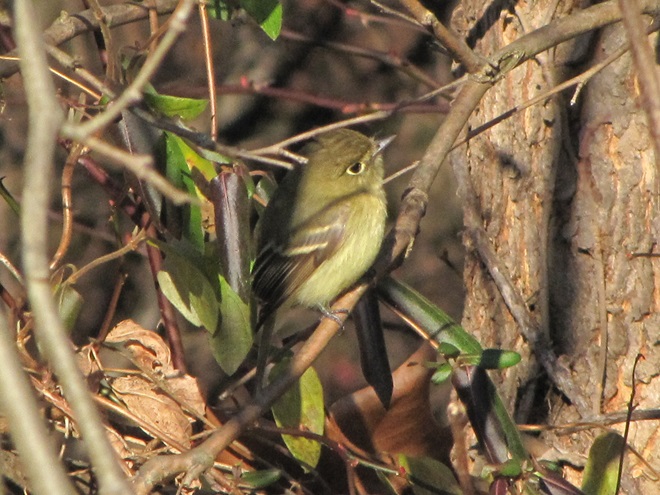
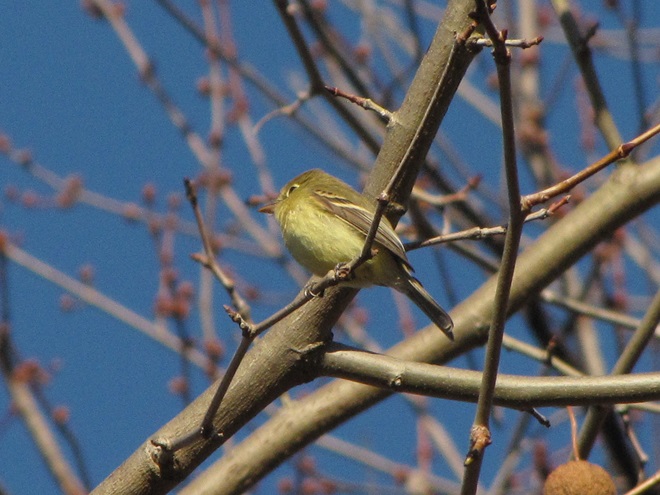
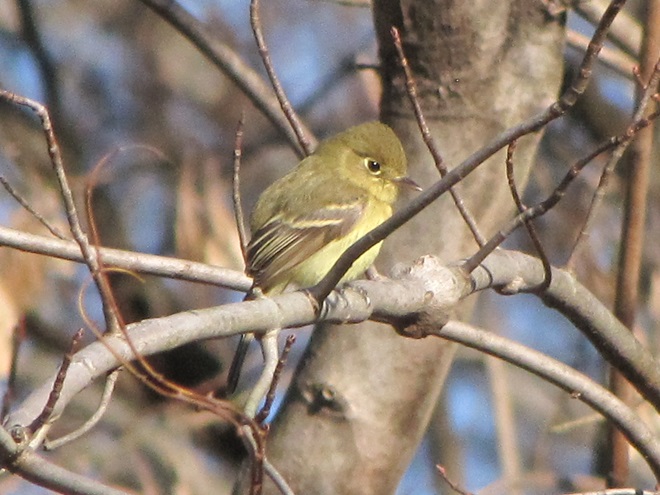



How long will this wandering rarity remain along the river trail? For added sustenance, sunny days throughout the coming winter offer ever-increasing chances of stonefly hatches on the adjacent river, particularly in the vicinity of the stone bridge piers. But ultimately, the severity of the weather and the bird’s response to it will determine its destiny.
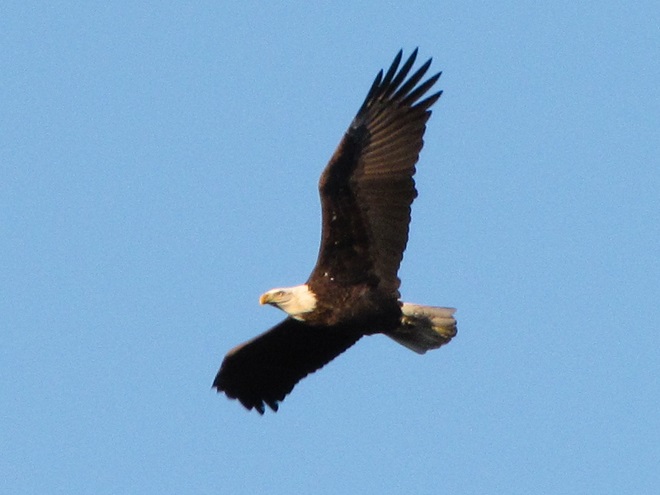


As the autumn raptor migration draws to a close in the Lower Susquehanna Valley Watershed, observers at the Second Mountain Hawk Watch in Lebanon County, Pennsylvania, were today treated to a flight of both Bald and Golden Eagles. Gliding on updrafts created by a brisk northwest breeze striking the slope of the ridge, seven of the former and three of the latter species were seen threading their way through numerous bands of snow as they made their way southwest toward favorable wintering grounds.
The best and final bird of the day, and possibly one of the highlights of the season at this counting station, was a “Barthelemyi Golden Eagle”, a rare Golden Eagle variant with conspicuous shoulder epaulets created by white scapular feathers.
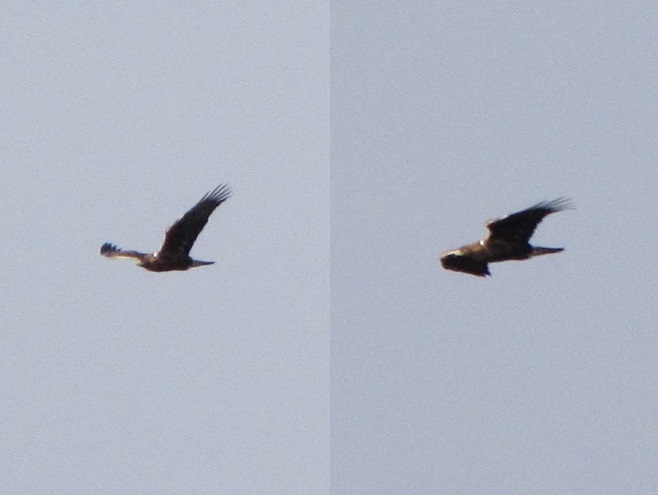
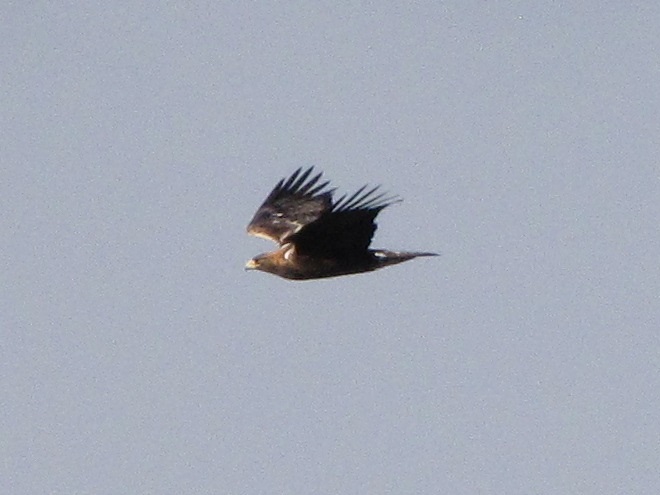


Today’s rarity is the second record of a “Barthelemyi Golden Eagle” at Second Mountain Hawk Watch—the first occurring on October 21, 2017.
SOURCES
Spofford, W. R. 1961. “White Epaulettes in Some Appalachian Golden Eagles”. Prothonotary. 27: 99.
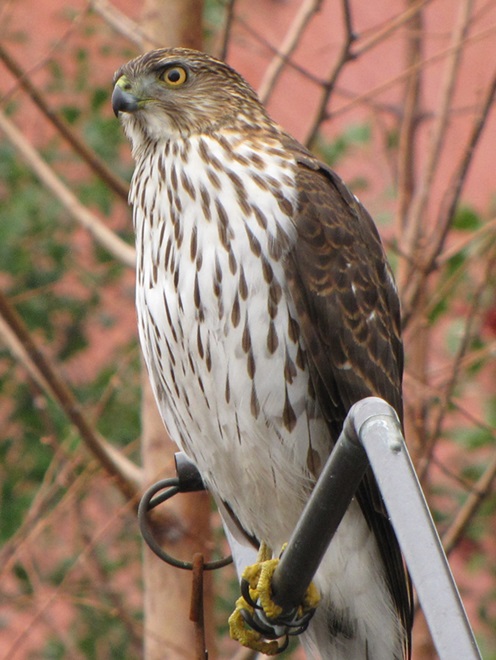
While trimming the trees and shrubs in the susquehannawildlife.net garden, it didn’t seem particularly unusual to hear the resident Carolina Chickadees and Carolina Wrens scolding our every move. But after a while, their persistence did seem a bit out of the ordinary, so we took a little break to have a look around…
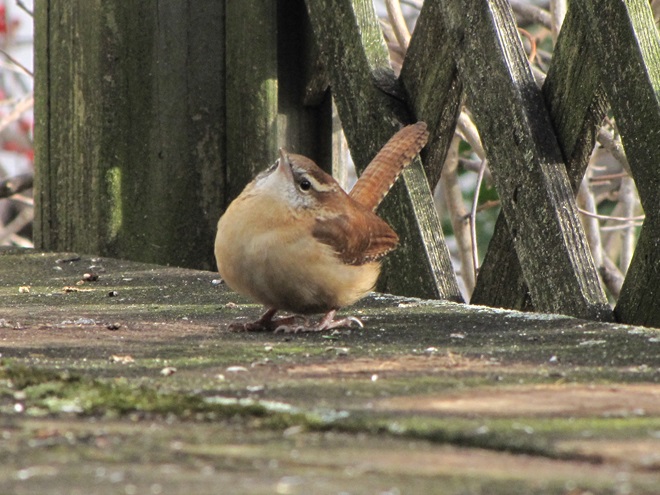
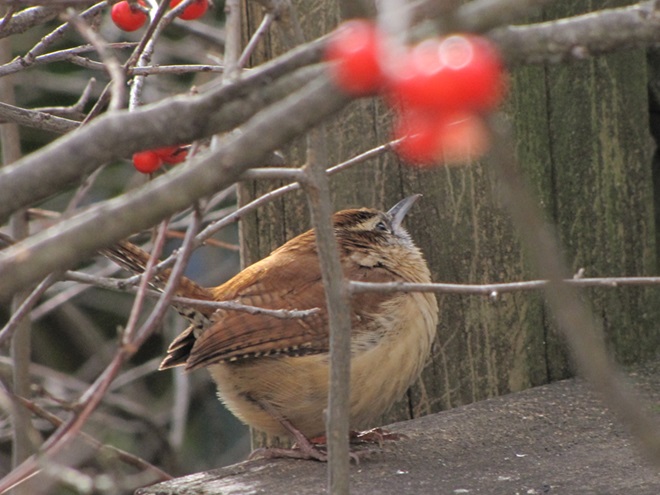
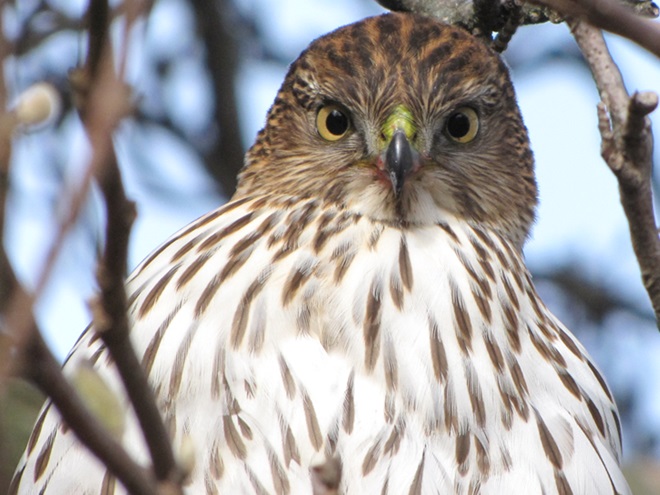
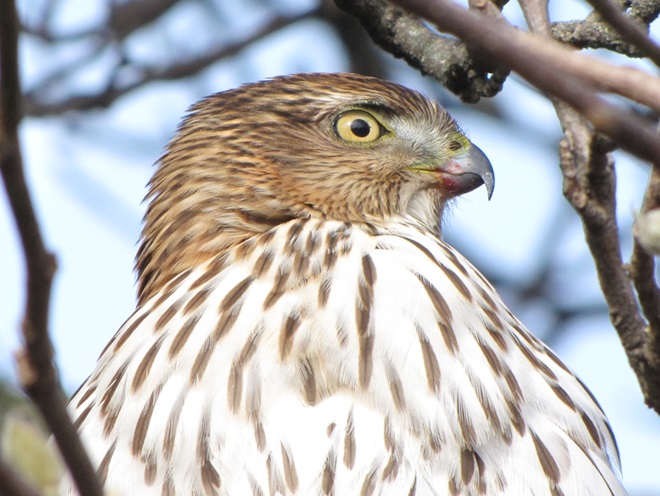
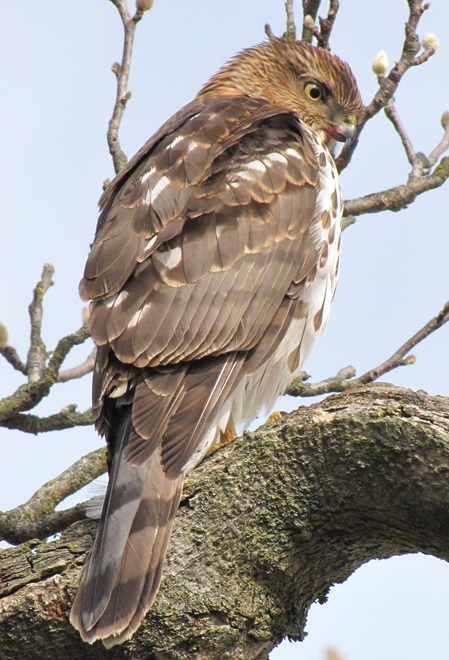






Here at susquehannawildlife.net headquarters, we are visited by Cooper’s Hawks for several days during the late fall and winter each year. The small birds that visit our feeders have plenty of trees, shrubs, vines, and other natural cover in which to hide from raptors and other native predators. We don’t create unnatural concentrations of birds by dumping food all over the place. We try to keep our small birds healthy by sparingly offering fresh seed and other provisions in clean receptacles to provide a supplement to the seeds, fruits, insects, and other foods that occur naturally in the garden. With only a few vulnerable small birds around, the Cooper’s Hawks visit just long enough to cull out our weakest individuals before moving elsewhere. While they’re in our garden, they too are our welcomed guests.
A glimpse of the rowdy guests crowding the Thanksgiving Day dinner table at susquehannawildlife.net headquarters…
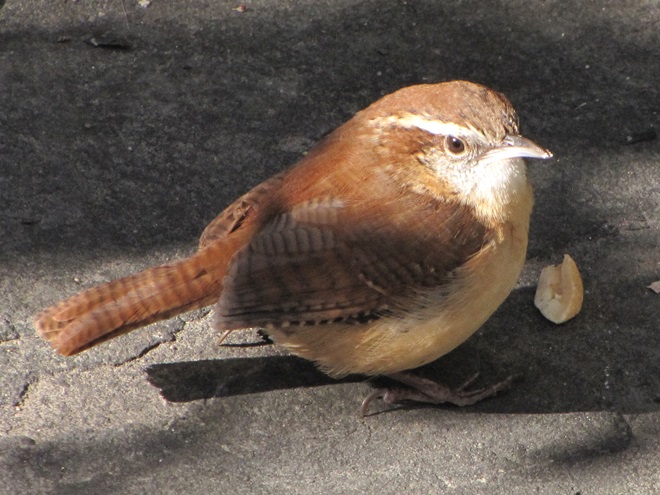
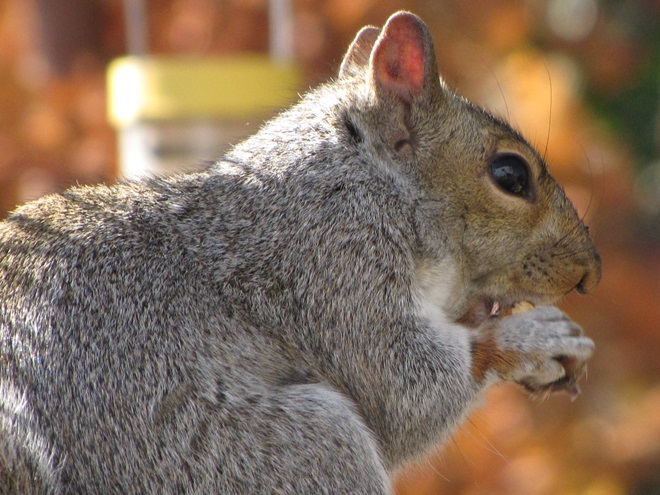
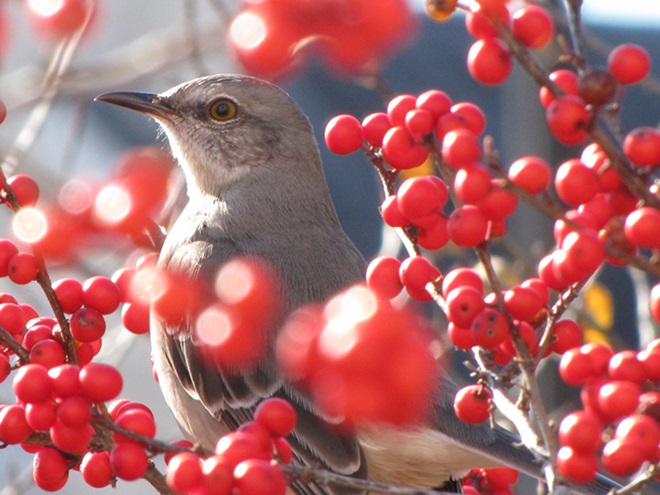
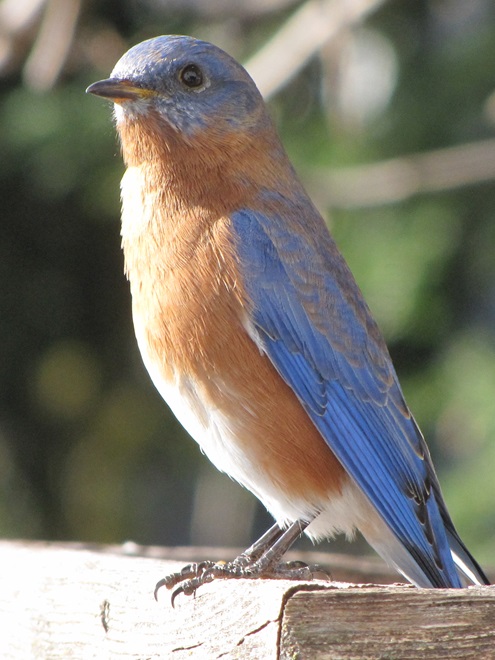
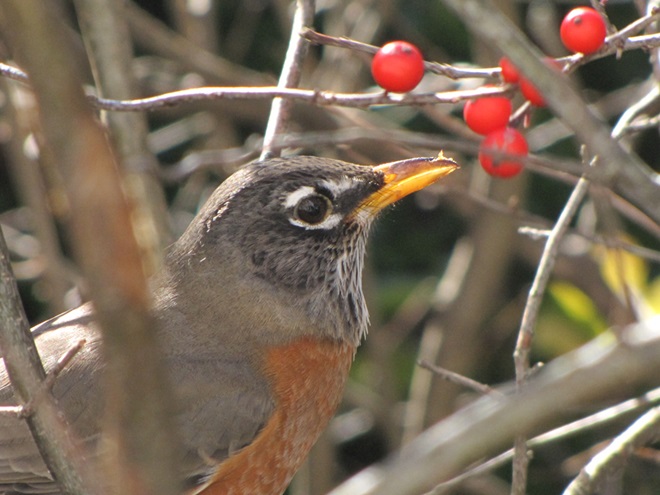
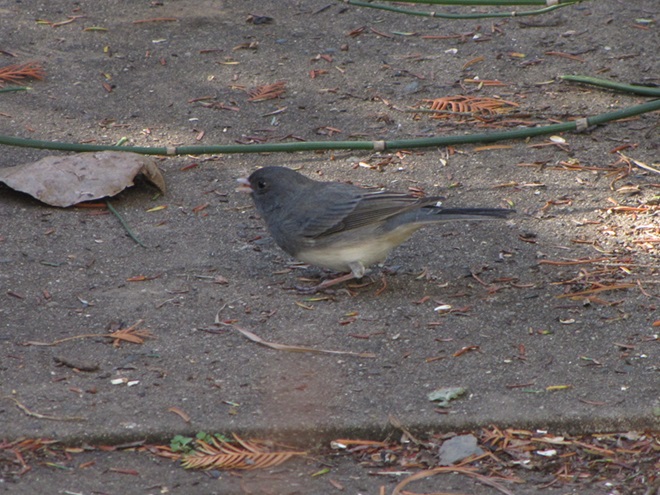









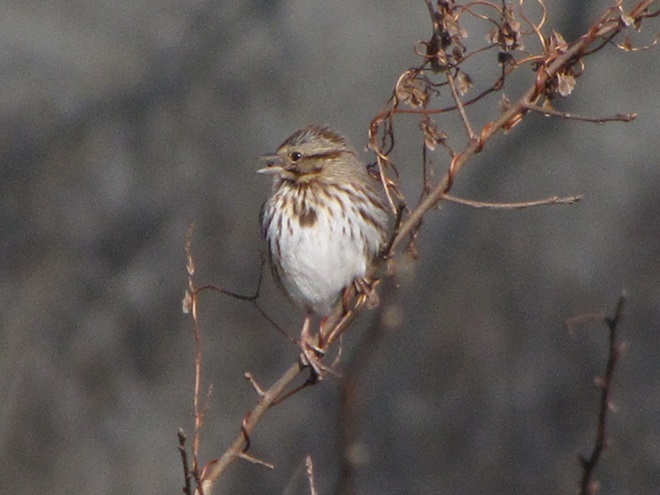
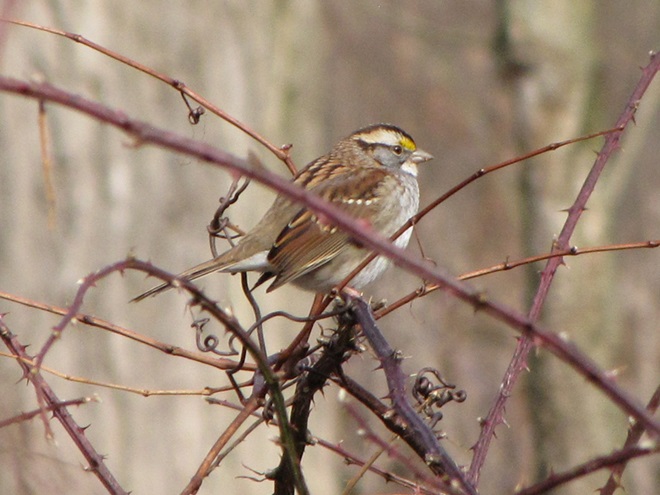
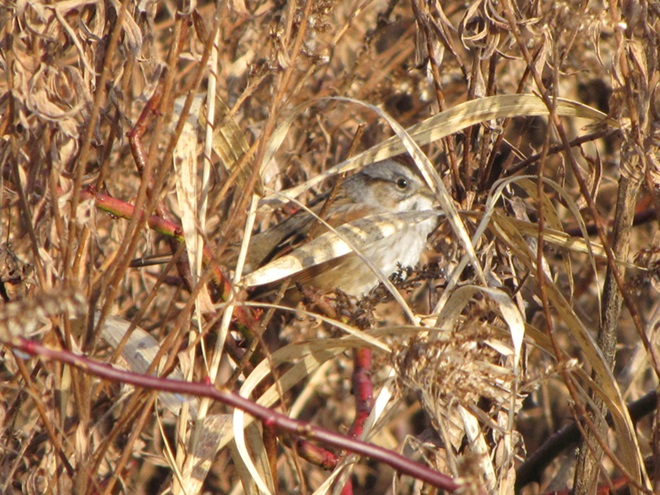
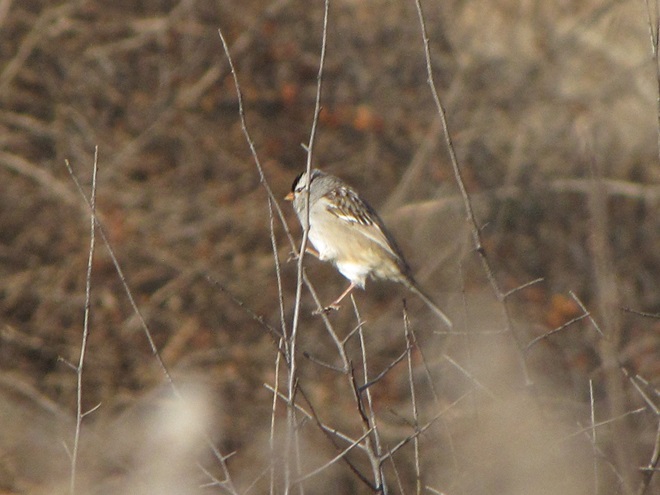
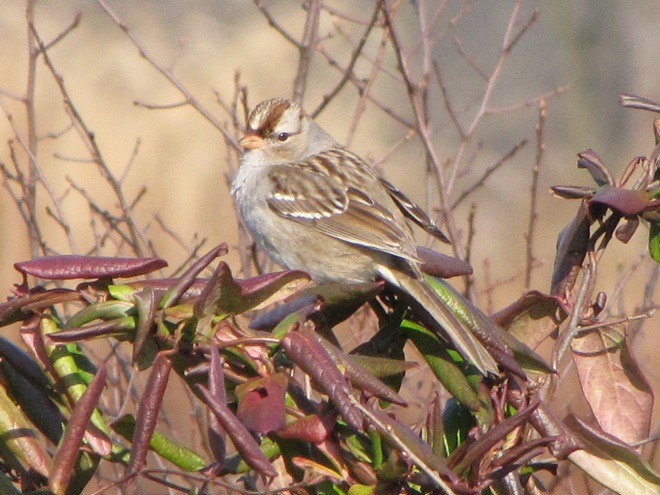
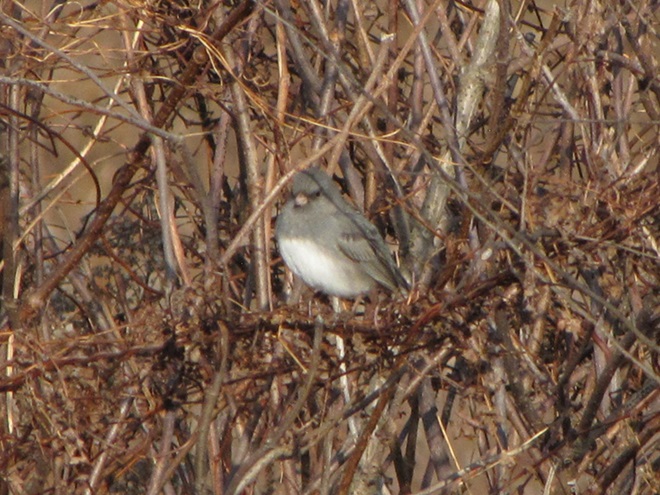
As the annual autumn songbird migration begins to reach its end, native sparrows can be found concentrating in fallow fields, early successional thickets, and brushy margins along forest edges throughout the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed.

Visit native sparrow habitat during mid-to-late November and you have a good chance of seeing these species and more…
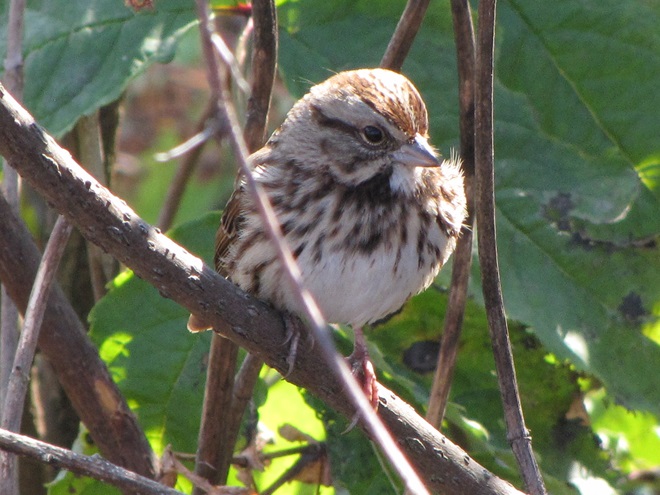
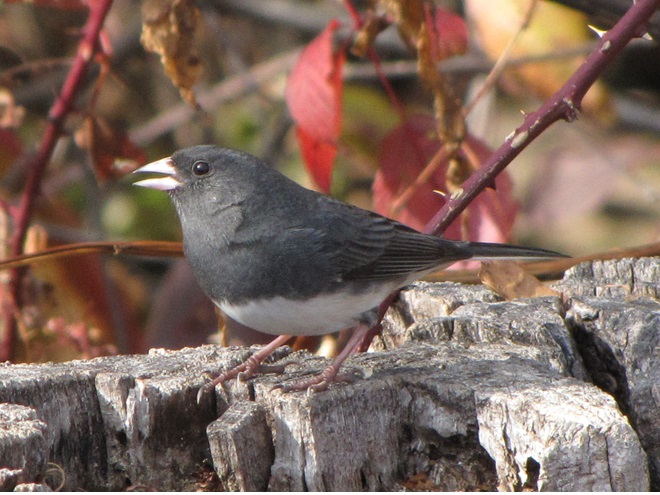
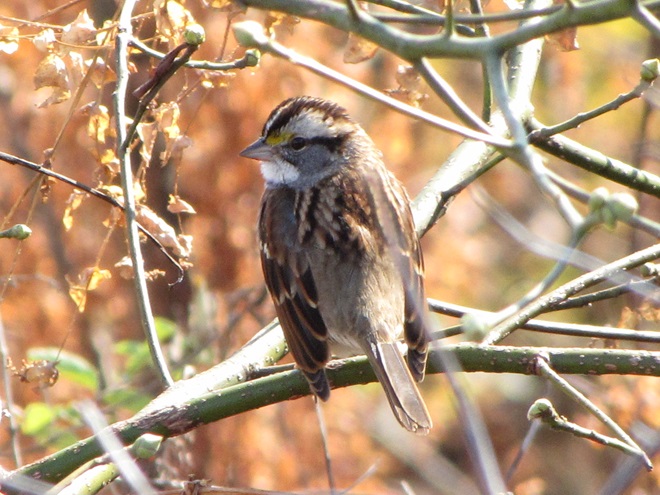
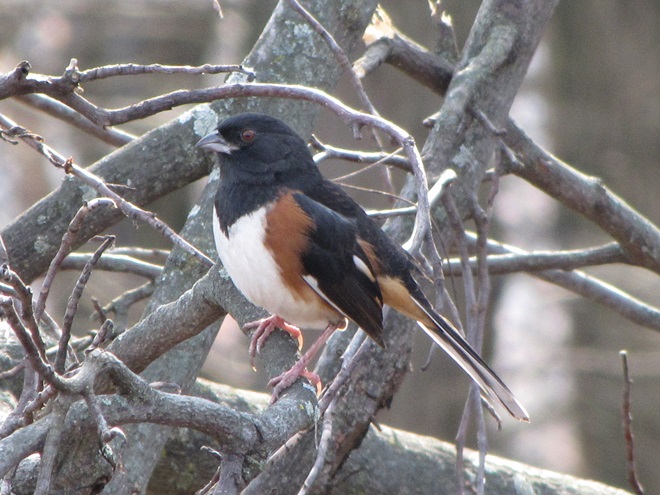
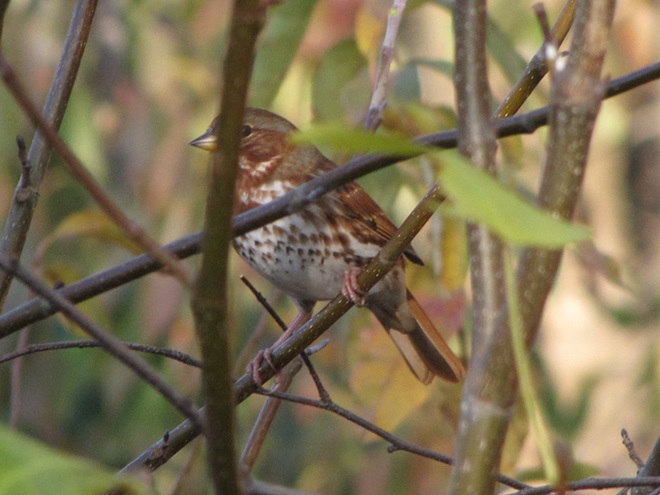





If you’re lucky enough to live where non-native House Sparrows won’t overrun your bird feeders, you can offer white millet as a supplement to the wild foods these beautiful sparrows might find in your garden sanctuary. Give it a try!
Recently, we found these Chestnut Oak acorns setting roots into the leaf litter to secure their place among the plants that will turn the forest understory green in the spring. Individual acorns that germinate soon after falling to the ground in autumn may avoid becoming food for squirrels, turkeys, deer, and other wildlife, thus increasing their chances of surviving to later become adult trees able to produce acorns that pass this quick-development trait to yet another generation of oaks.
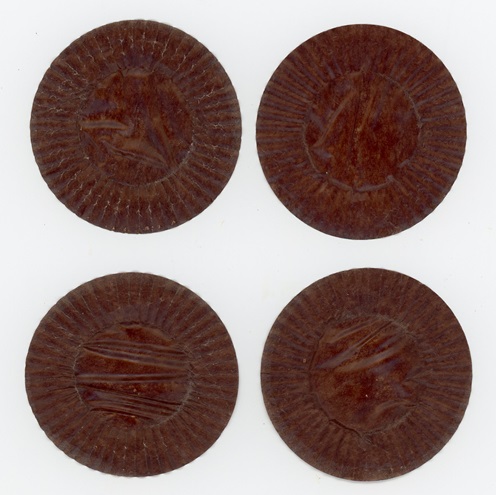

Colder temperatures and gusty northwest winds are prompting our largest migratory raptors to continue their southward movements. Here are some of the birds seen earlier today riding updrafts of air currents along one of the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed’s numerous ridges.
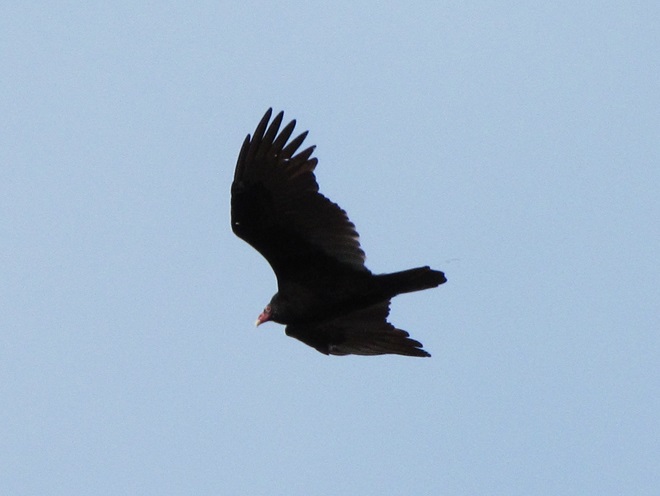
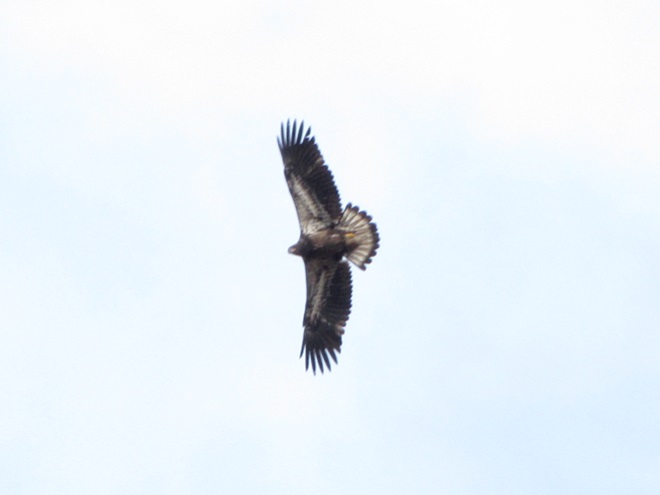
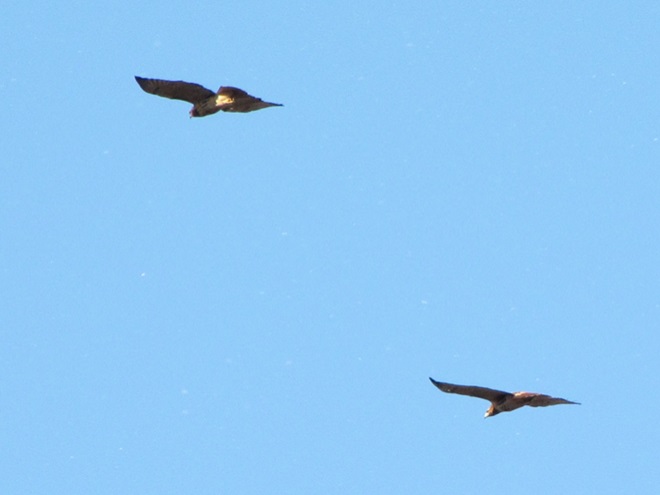
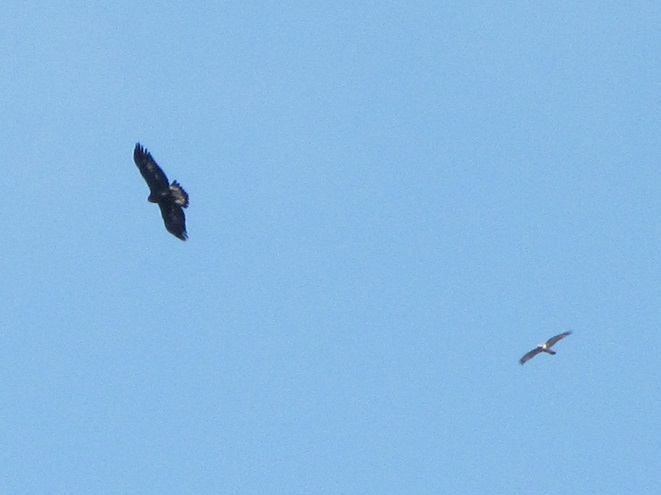
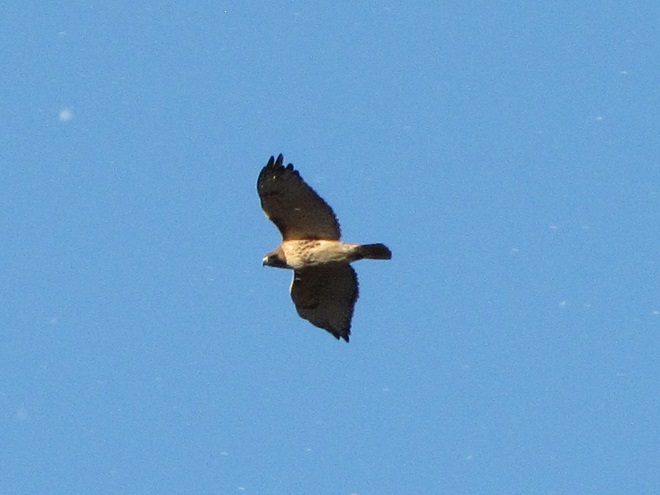





As winter begins clawing at the door, now is great time to visit a hawk watch near you to see these late-season specialties. Remember to dress in layers and to click the “Hawkwatcher’s Helper: Identifying Bald Eagles and other Diurnal Raptors” tab at the top of this page. Hawkwatcher’s Helper is your guide to regional hawk watching locations and raptor identification. Be sure to check it out. And remember, it’s cold on top of those ridges, so don’t forget your hat, your gloves, and your chap stick!
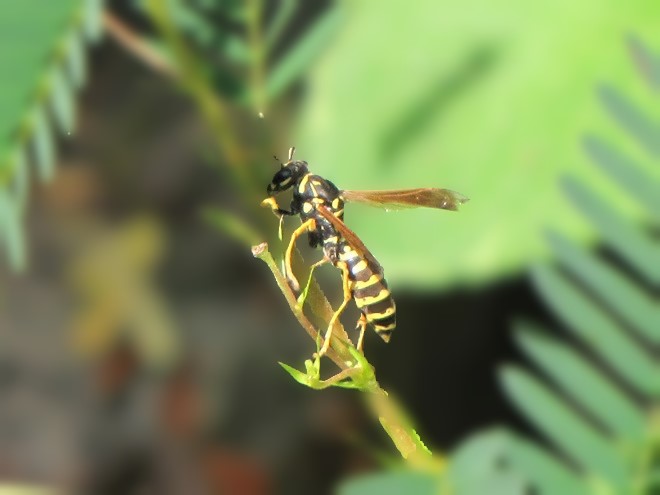
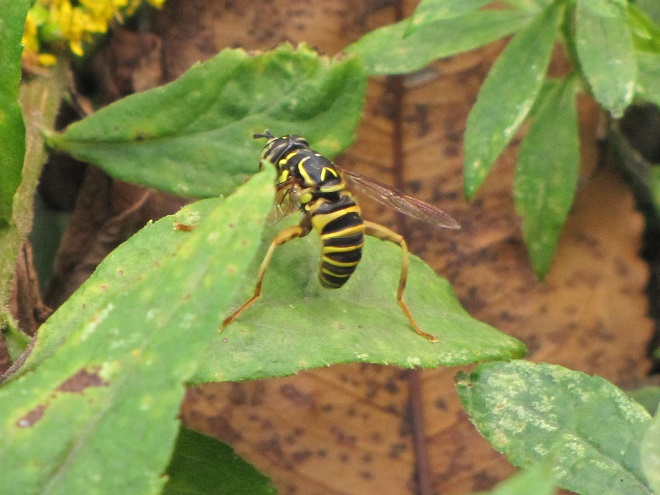
Only fools mess around with bees, wasps, and hornets as they collect nectar and go about their business while visiting flowering plants. Relentlessly curious predators and other trouble makers quickly learn that patterns of white, yellow, or orange contrasting with black are a warning that the pain and anguish of being zapped with a venomous sting awaits those who throw caution to the wind. Through the process of natural selection, many venomous and poisonous animals have developed conspicuously bright or contrasting color schemes to deter would-be predators and molesters from making such a big mistake.

Visual warnings enhance the effectiveness of the defensive measures possessed by venomous, poisonous, and distasteful creatures. Aggressors learn to associate the presence of these color patterns with the experience of pain and discomfort. Thereafter, they keep their distance to avoid any trouble. In return, the potential victims of this unsolicited aggression escape injury and retain their defenses for use against yet-to-be-enlightened pursuers. Thanks to their threatening appearance, the chances of survival are increased for these would-be victims without the need to risk death or injury while deploying their venomous stingers, poisonous compounds, or other defensive measures.

One shouldn’t be surprised to learn that over time, as these aforementioned venomous, poisonous, and foul-tasting critters developed their patterns of warning colors, there were numerous harmless animals living within close association with these species that, through the process of natural selection, acquired nearly identical color patterns for their own protection from predators. This form of defensive impersonation is known as Batesian mimicry.
Let’s take a look at some examples of Batesian mimicry right here in the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed.
Suppose for a moment that you were a fly. As you might expect, you would have plenty to fear while you spend your day visiting flowers in search of energy-rich nectar—hundreds of hungry birds and other animals want to eat you.
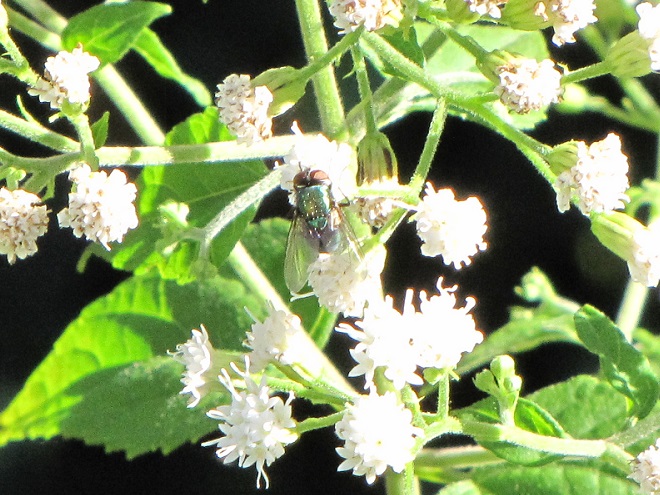
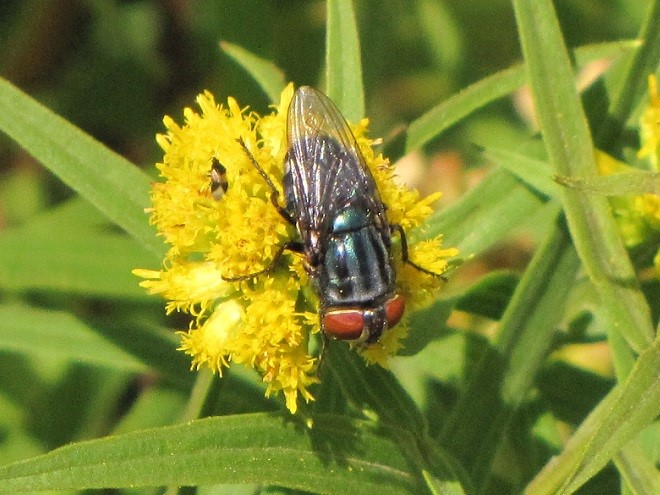


If you were a fly and you were headed out and about to call upon numerous nectar-producing flowers so you could round up some sweet treats, wouldn’t you feel a whole lot safer if you looked like those venomous bees, wasps, and hornets in your neighborhood? Wouldn’t it be a whole lot more fun to look scary—so scary that would-be aggressors fear that you might sting them if they gave you any trouble?
Suppose Mother Nature and Father Time dressed you up to look like a bee or a wasp instead of a helpless fly? Then maybe you could go out and collect sweets without always worrying about the bullies and the brutes, just like these flies of the lower Susquehanna do…
FLOWER FLIES/HOVER FLIES
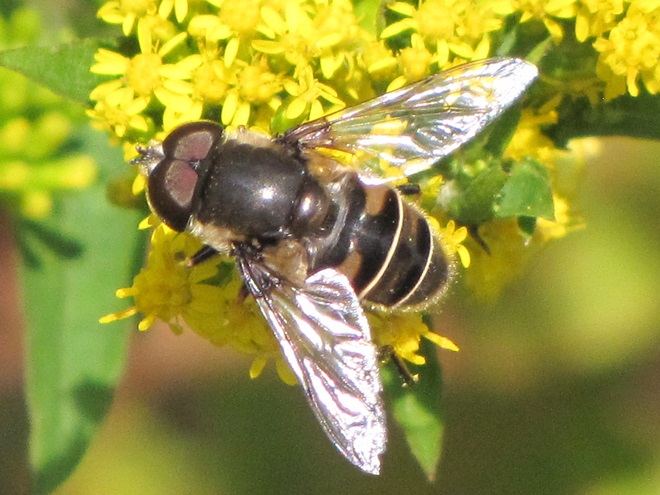
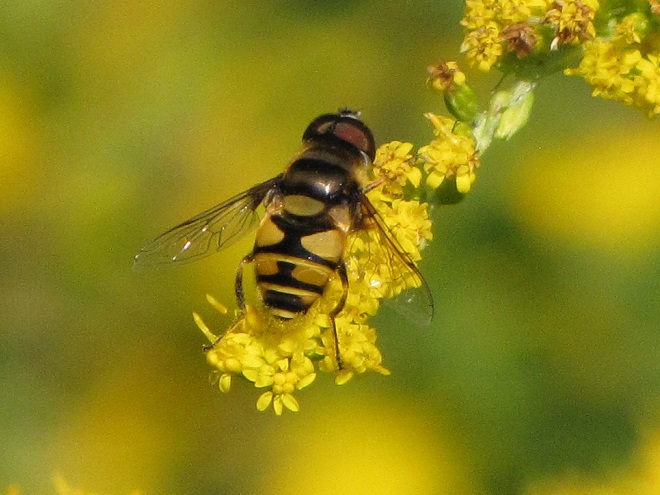
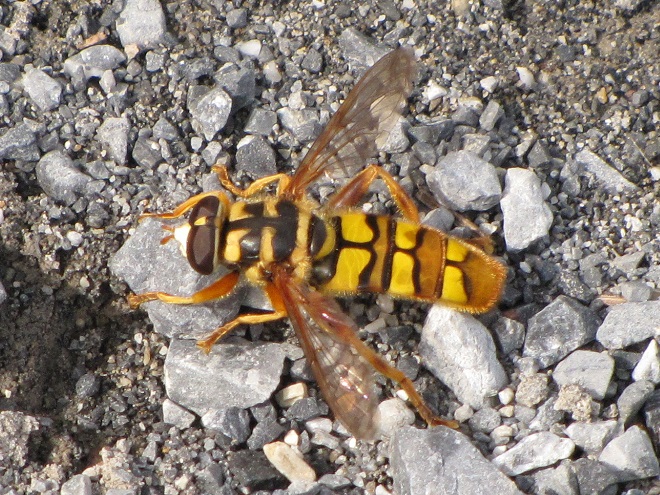
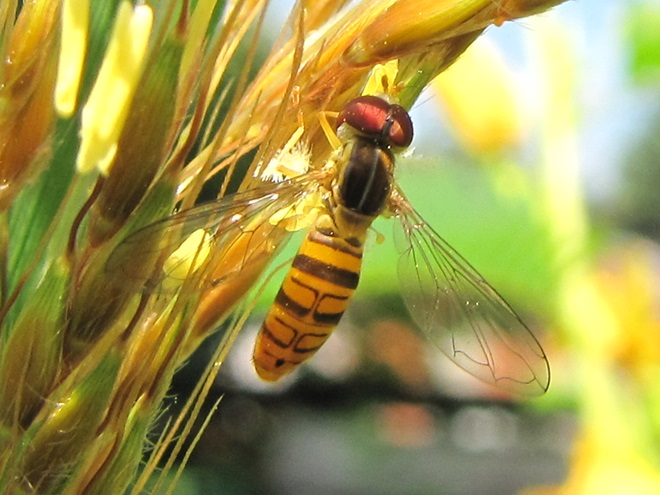
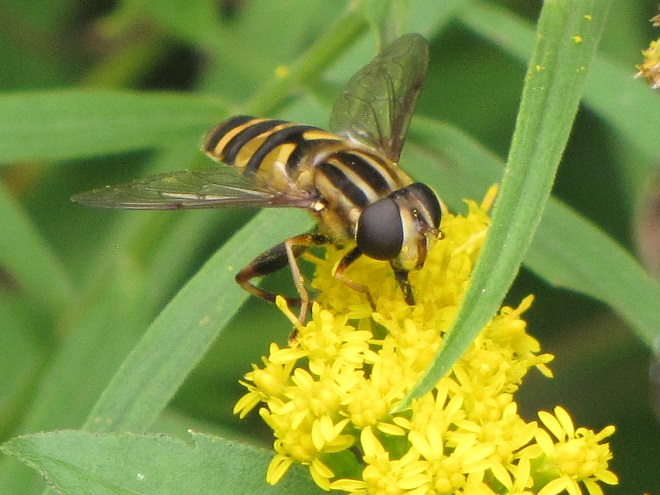
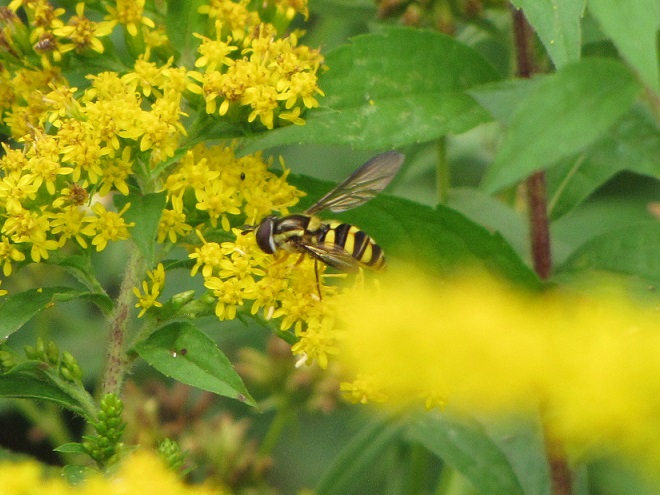







TACHINID FLIES
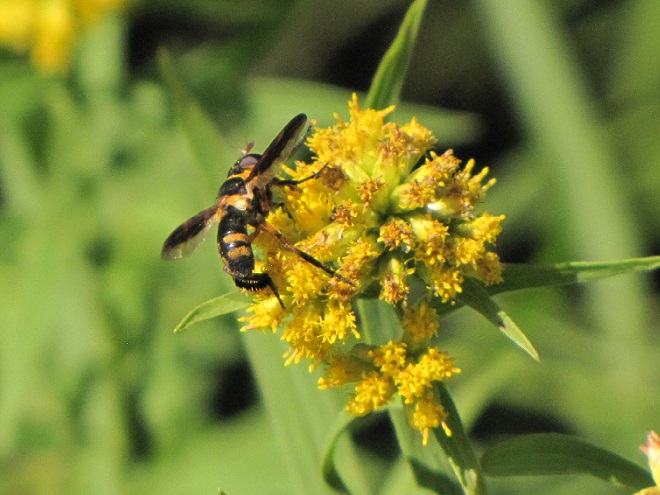

BEE FLIES
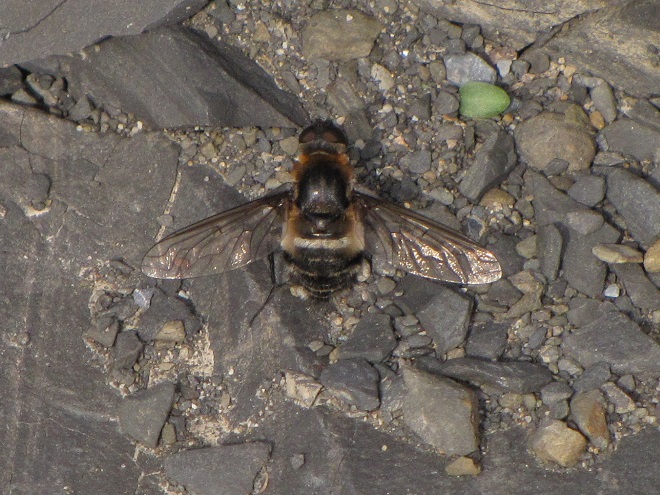
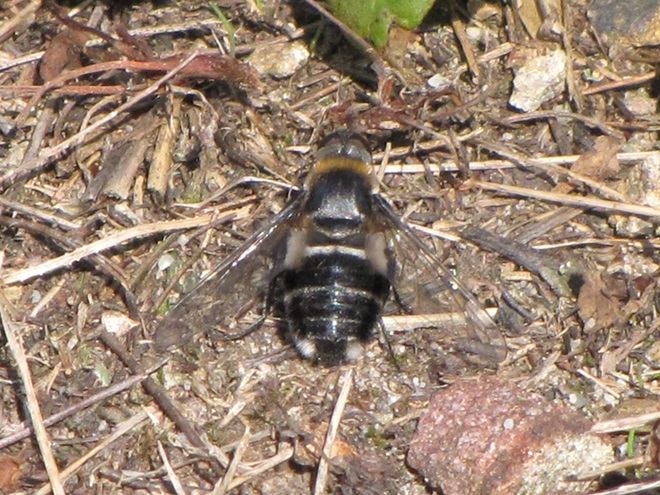


So let’s review. If you’re a poor defenseless fly and you want to get your fair share of sweets without being gobbled up by the beasts, then you’ve got to masquerade like a strongly armed member of a social colony—like a bee, wasp, or hornet. Now look scary and go get your treats. HAPPY HALLOWEEN!
Where should you go this weekend to see vibrantly colored foliage in our region? Where are there eye-popping displays of reds, oranges, yellows, and greens without so much brown and gray? The answer is Michaux State Forest on South Mountain in Adams, Cumberland, and Franklin Counties.
South Mountain is the northern extension of the Blue Ridge Section of the Ridge and Valley Province in Pennsylvania. Michaux State Forest includes much of the wooded land on South Mountain. Within or adjacent to its borders are located four state parks: King’s Gap Environmental Education Center, Pine Grove Furnace State Park, Caledonia State Park, and Mont Alto State Park. The vast network of trails on these state lands includes the Appalachian Trail, which remains in the mountainous Blue Ridge Section all the way to its southern terminus in Georgia.
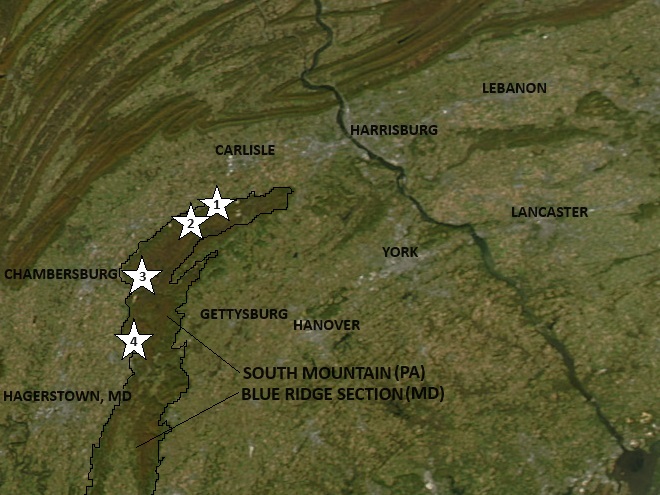
If you want a closeup look at the many species of trees found in Michaux State Forest, and you want them to be labeled so you know what they are, a stop at the Pennsylvania State University’s Mont Alto arboretum is a must. Located next door to Mont Alto State Park along PA 233, the Arboretum at Penn State Mont Alto covers the entire campus. Planting began on Arbor Day in 1905 shortly after establishment of the Pennsylvania State Forest Academy at the site in 1903. Back then, the state’s “forests” were in the process of regeneration after nineteenth-century clear cutting. These harvests balded the landscape and left behind the combustible waste which fueled the frequent wildfires that plagued reforestation efforts for more than half a century. The academy educated future foresters on the skills needed to regrow and manage the state’s woodlands.
Online resources can help you plan your visit to the Arboretum at Penn State Mont Alto. More than 800 trees on the campus are numbered with small blue tags. The “List of arboretum trees by Tag Number” can be downloaded to tell you the species or variety of each. The interactive map provides the locations of individual trees plotted by tag number while the Grove Map displays the locations of groups of trees on the campus categorized by region of origin. A Founder’s Tree Map will help you find some of the oldest specimens in the collection and a Commemorative Tree Map will help you find dedicated trees. There is also a species list of the common and scientific tree names.
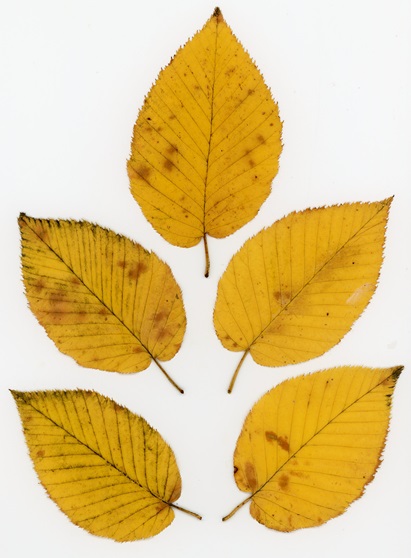
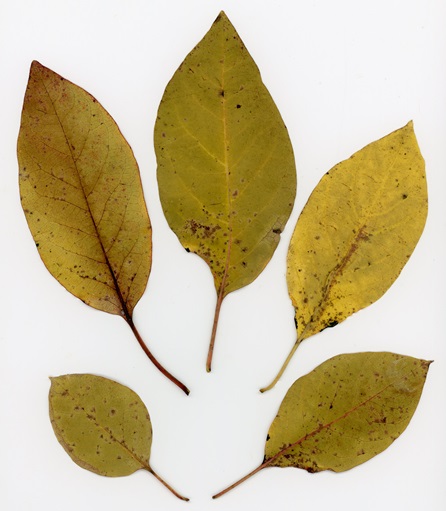






The autumn leaves will be falling fast, so make it a point this weekend to check out the show on South Mountain.
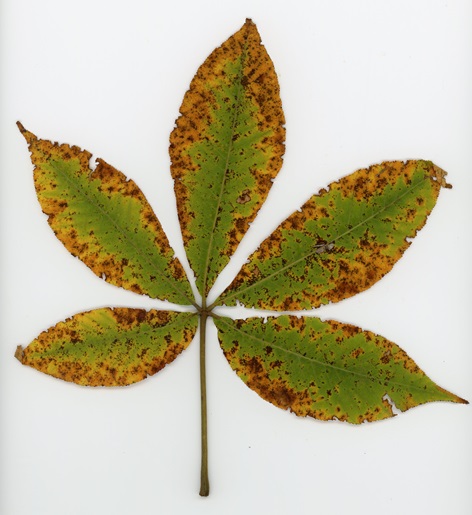
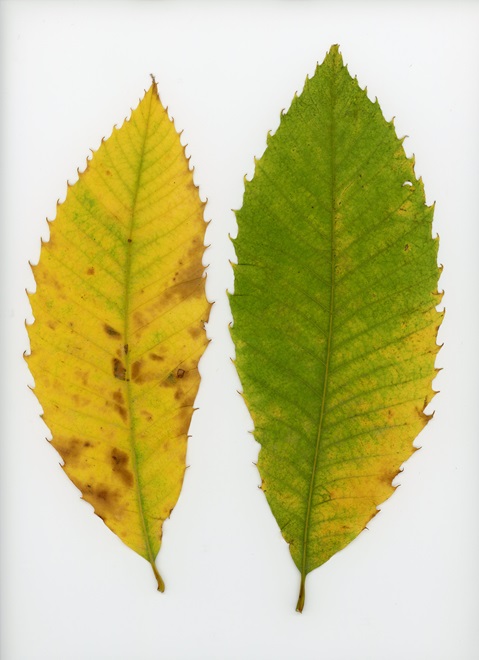
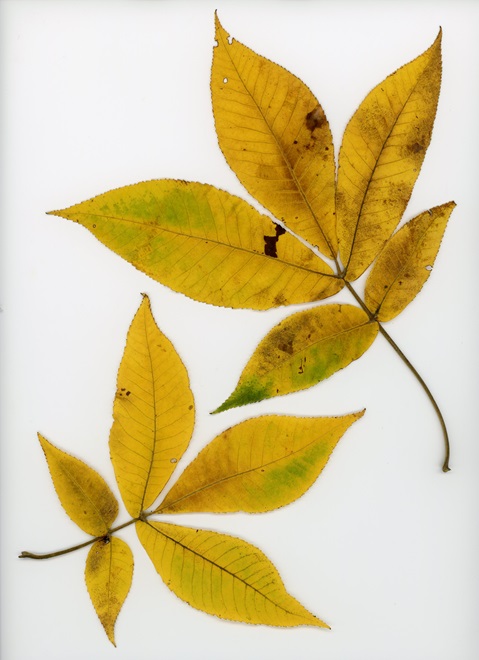
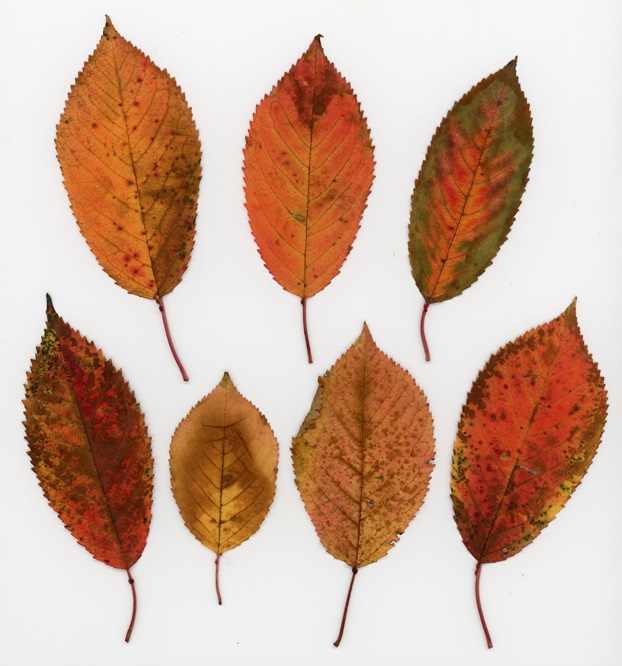
Have you noticed? Foliage throughout the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed has been painted with the brilliant colors of autumn, so now is the time to get out there and have a look. Why not make a collection? You can pick up an inexpensive scrap book or photo album at the craft store to press and label the varieties you find. Uncle Tyler Dyer is already busy adding to the project he assembled last year. You can use his exhibit as a reference for identifying and learning a little bit more about the leaves you find.


With nearly all of the Neotropical migrants including Broad-winged Hawks gone for the year, observers and counters at eastern hawk watches are busy tallying numbers of the more hardy species of diurnal raptors and other birds. The majority of species now coming through will spend the winter months in temperate and sub-tropical areas of the southern United States and Mexico.
Here is a quick look at the raptors seen this week at two regional counting stations: Kiptopeke Hawk Watch near Cape Charles, Virginia, and Second Mountain Hawk Watch at Fort Indiantown Gap, Pennsylvania.
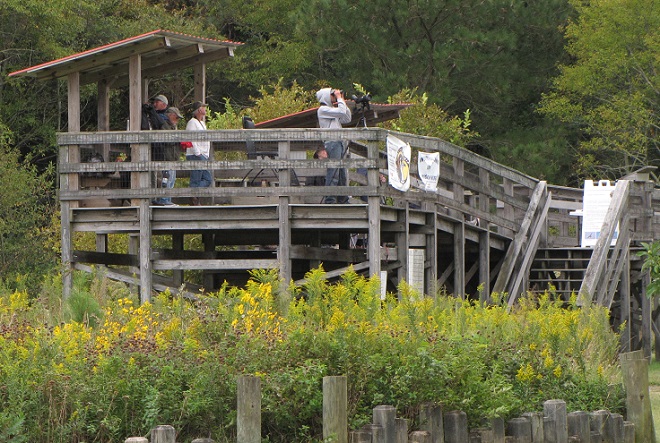
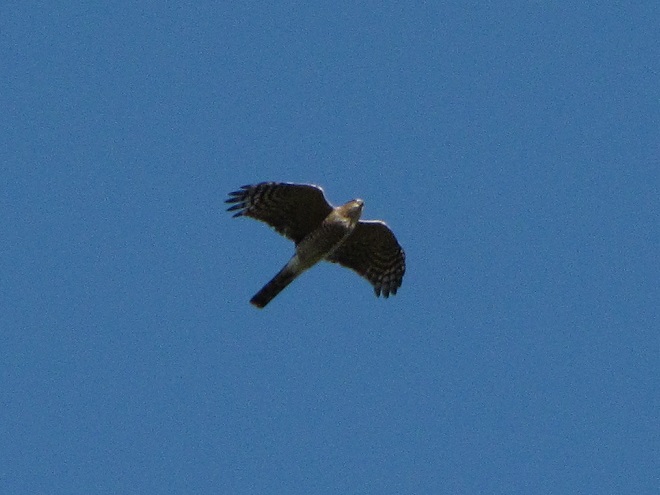
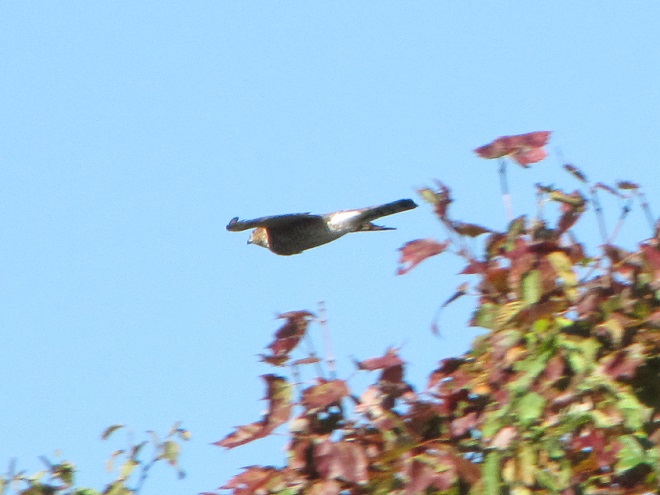
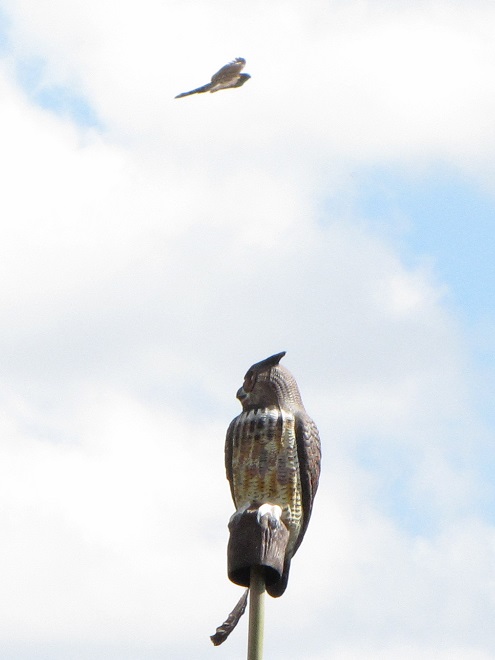
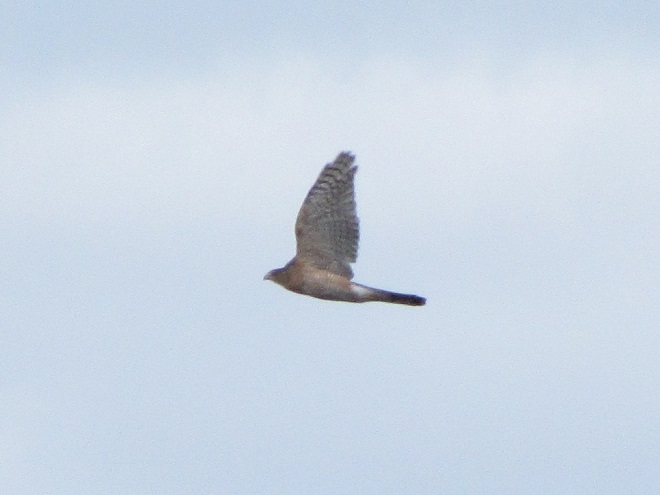
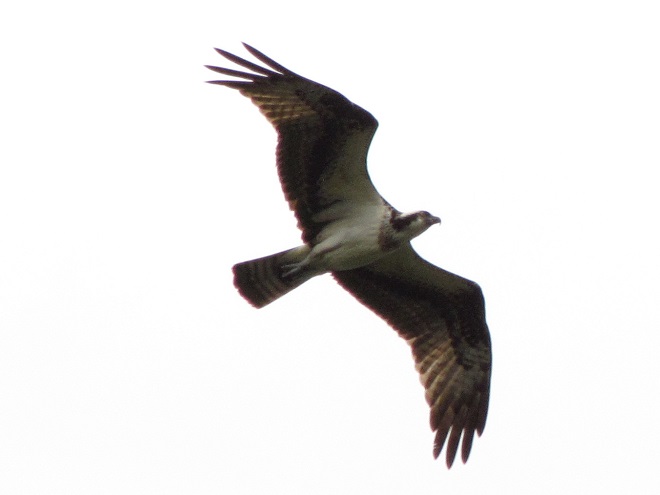
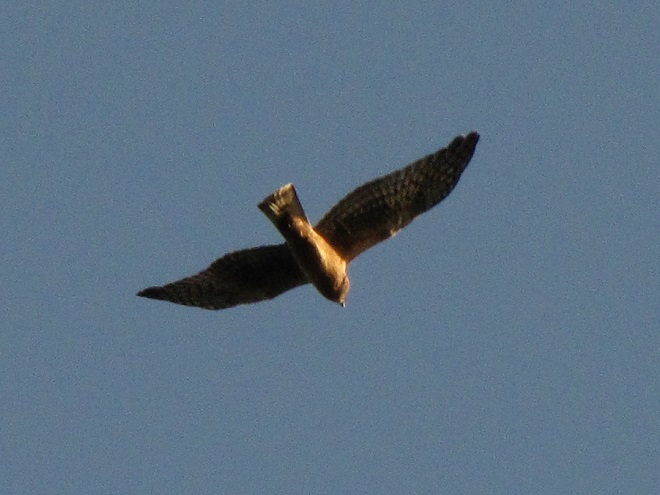
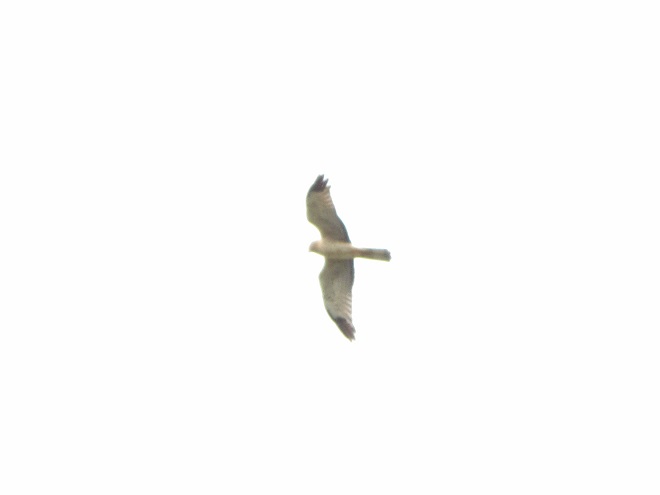
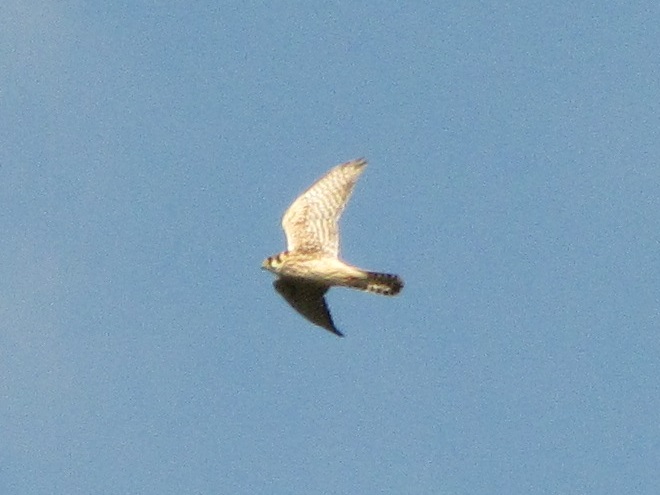
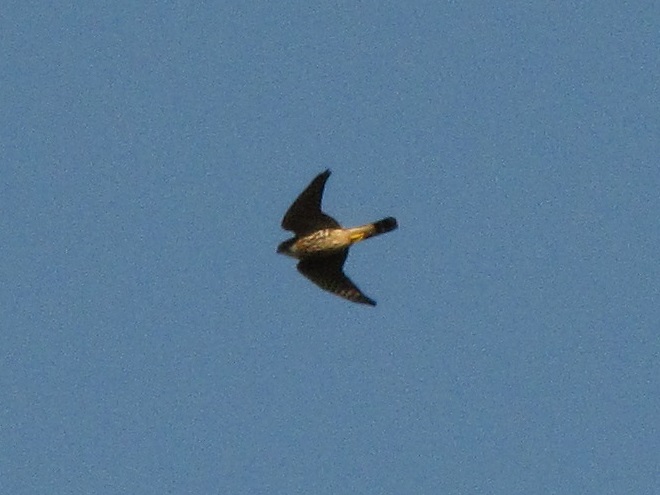
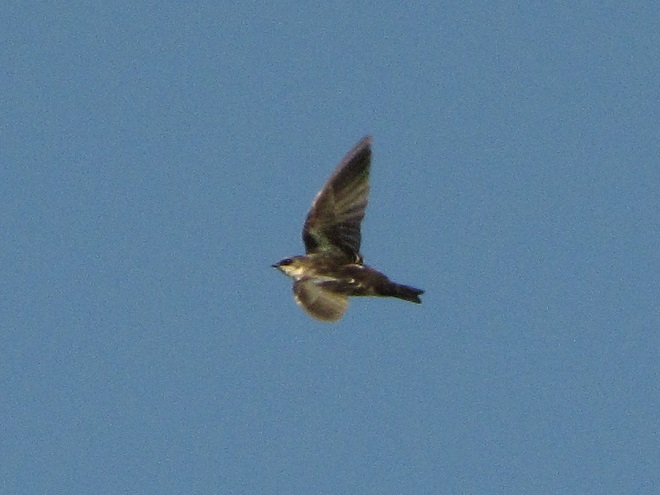
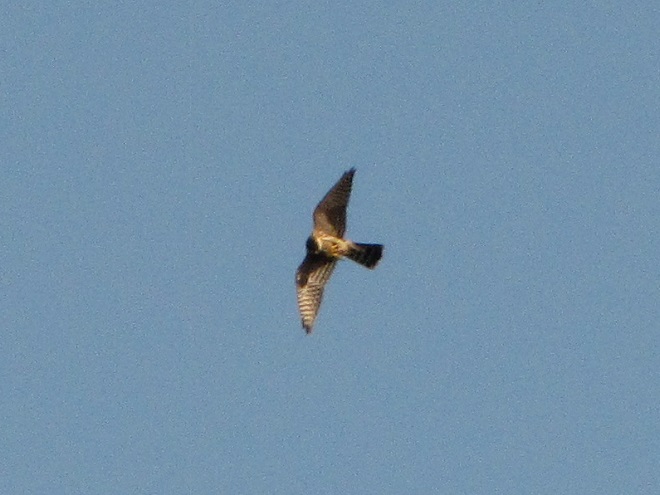
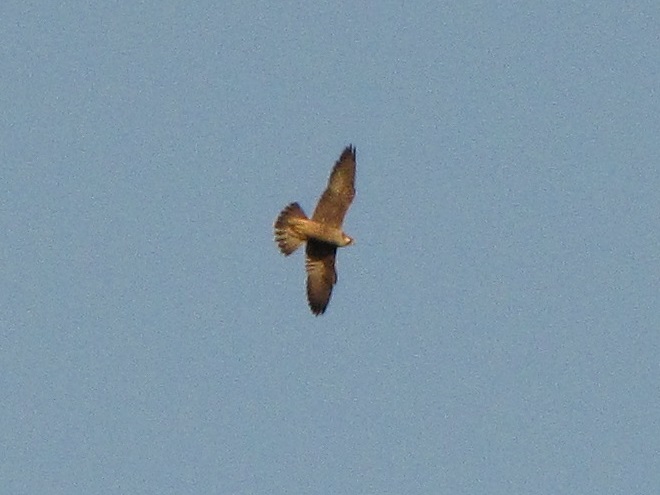















During coming days, fewer and fewer of these birds will be counted at our local hawk watches. Soon, the larger raptors—Red-tailed Hawks, Red-shouldered Hawks, and Golden Eagles—will be thrilling observers. Cooler weather will bring several flights of these spectacular species. Why not plan a visit to a lookout near you? Click on the “Hawkwatcher’s Helper: Identifying Bald Eagles and other Diurnal Raptors” tab at the top of this page for site information and a photo guide to identification. See you at the hawk watch!



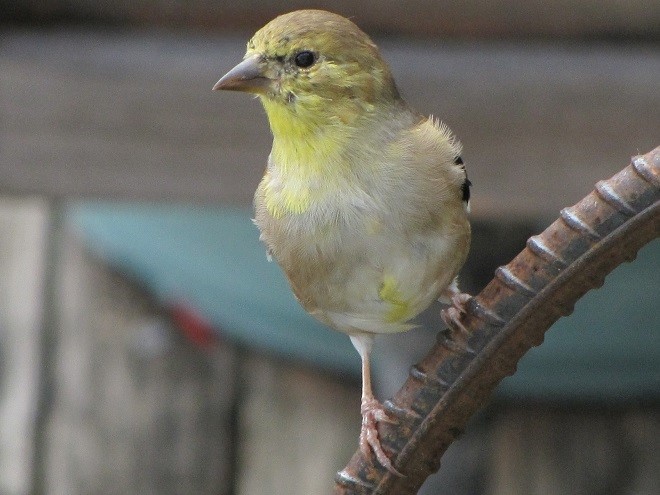
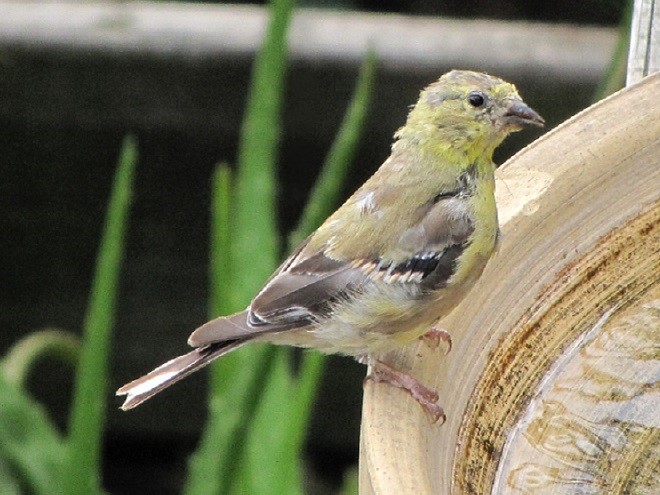
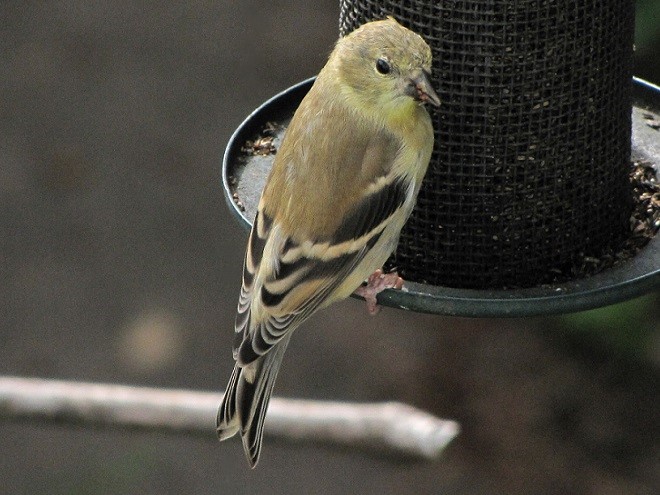
Say it isn’t so. Does summer really have to go?
Our brightly colored goldfinches are gone for the year. No more Pennsylvania distelfinks glowing like bright-yellow Easter peeps on our feeders. Oh, the birds are still here mind you, but their sunshine-gold feathers are falling away. Because winter time is no time to show off. One must blend in and maintain a low profile to conserve energy and avoid trouble as rough weather arrives. So our American Goldfinches have commenced to molting—shedding their breeding plumes and replacing them with drab earth-tone shades for winter.


