Homo sapiens owes much of its success as a species to an acquired knowledge of how to make, control, and utilize fire. Using fire to convert the energy stored in combustible materials into light and heat has enabled humankind to expand its range throughout the globe. Indeed, humans in their furless incomplete mammalian state may have never been able to expand their populations outside of tropical latitudes without mastery of fire. It is fire that has enabled man to exploit more of the earth’s resources than any other species. From cooking otherwise unpalatable foods to powering the modern industrial society, fire has set man apart from the rest of the natural world.
In our modern civilizations, we generally look at the unplanned outbreak of fire as a catastrophe requiring our immediate intercession. A building fire, for example, is extinguished as quickly as possible to save lives and property. And fires detected in fields, brush, and woodlands are promptly controlled to prevent their exponential growth. But has fire gone to our heads? Do we have an anthropocentric view of fire? Aren’t there naturally occurring fires that are essential to the health of some of the world’s ecosystems? And to our own safety? Indeed there are. And many species and the ecosystems they inhabit rely on the periodic occurrence of fire to maintain their health and vigor.

Man has been availed of the direct benefits of fire for possibly 40,000 years or more. Here in the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed, the earliest humans arrived as early as 12,000 years ago—already possessing skills for using fire. Native plants and animals on the other hand, have been part of the ever-changing mix of ecosystems found here for a much longer period of time—millions to tens of millions of years. Many terrestrial native species are adapted to the periodic occurrence of fire. Some, in fact, require it. Most upland ecosystems need an occasional dose of fire, usually ignited by lightning (though volcanism and incoming cosmic projectiles are rare possibilities), to regenerate vegetation, release nutrients, and maintain certain non-climax habitat types.
But much of our region has been deprived of natural-type fires since the time of the clearcutting of the virgin forests during the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries. This absence of a natural fire cycle has contributed to degradation and/or elimination of many forest and non-forest habitats. Without fire, a dangerous stockpile of combustible debris has been collecting, season after season, in some areas for a hundred years or more. Lacking periodic fires or sufficient moisture to sustain prompt decomposition of dead material, wildlands can accumulate enough leaf litter, thatch, dry brush, tinder, and fallen wood to fuel monumentally large forest fires—fires similar to those recently engulfing some areas of the American west. So elimination of natural fire isn’t just a problem for native plants and animals, its a potential problem for humans as well.
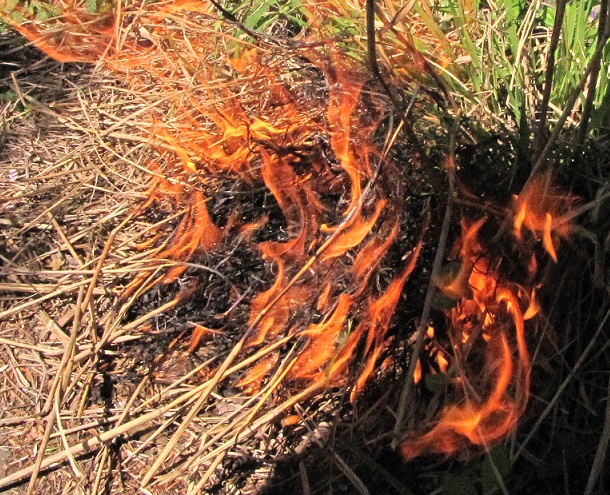

To address the habitat ailments caused by a lack of natural fires, federal, state, and local conservation agencies are adopting the practice of “prescribed fire” as a treatment to restore ecosystem health. A prescribed fire is a controlled burn specifically planned to correct one or more vegetative management problems on a given parcel of land. In the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed, prescribed fire is used to…
-
-
- Eliminate dangerous accumulations of combustible fuels in woodlands.
- Reduce accumulations of dead plant material that may harbor disease.
- Provide top kill to promote oak regeneration.
- Regenerate other targeted species of trees, wildflowers, grasses, and vegetation.
- Kill non-native plants and promote growth of native plants.
- Prevent succession.
- Remove woody growth and thatch from grasslands.
- Promote fire tolerant species of plants and animals.
- Create, enhance, and/or manage specialized habitats.
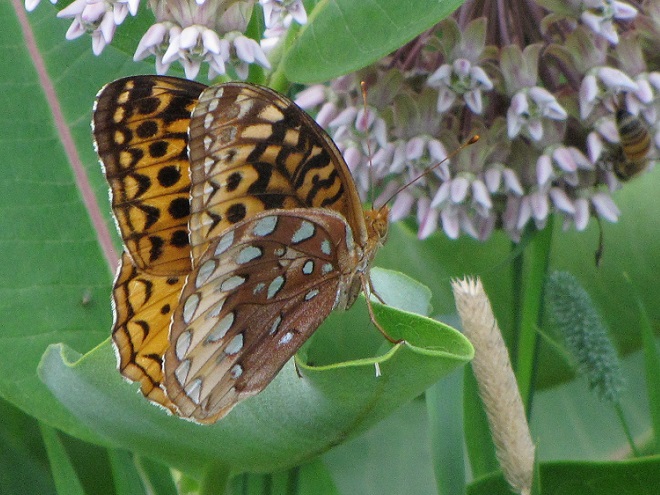
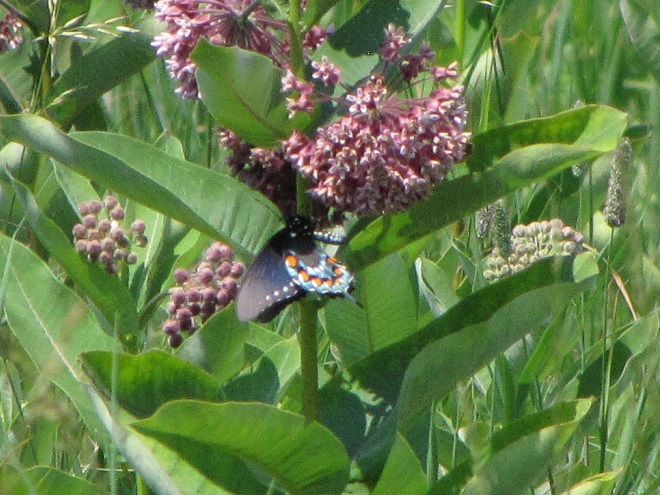
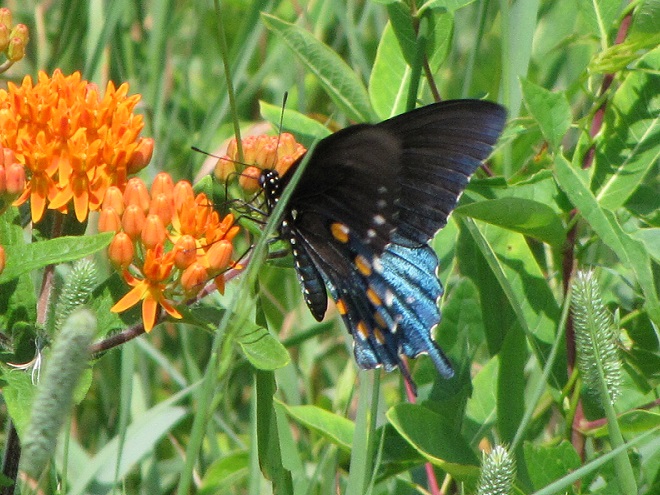
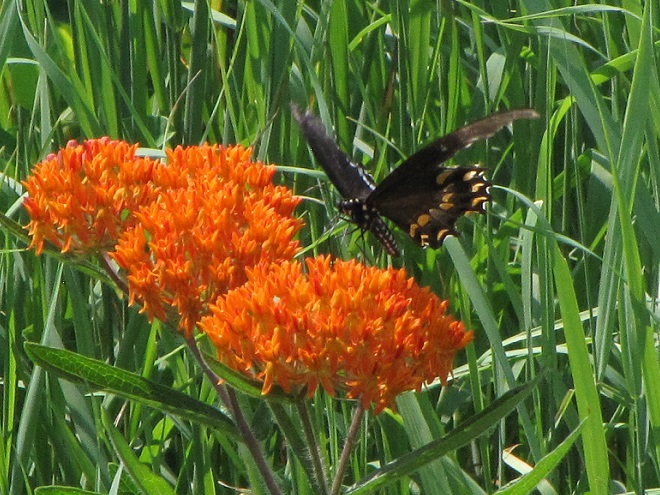
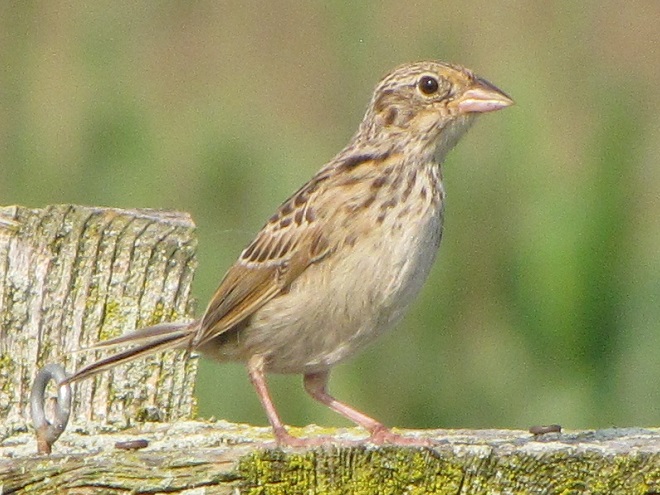
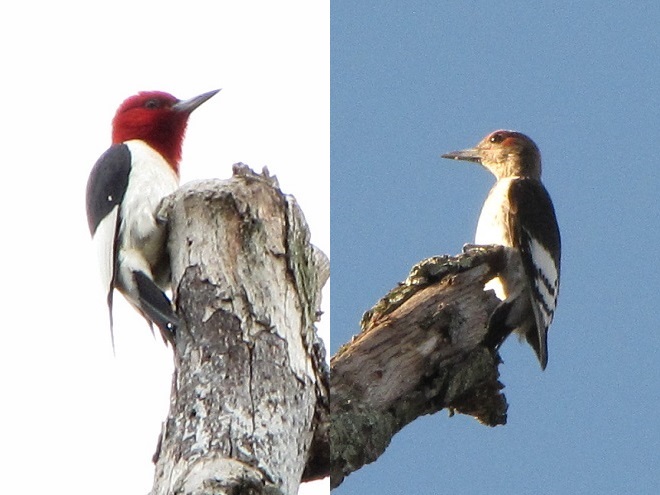
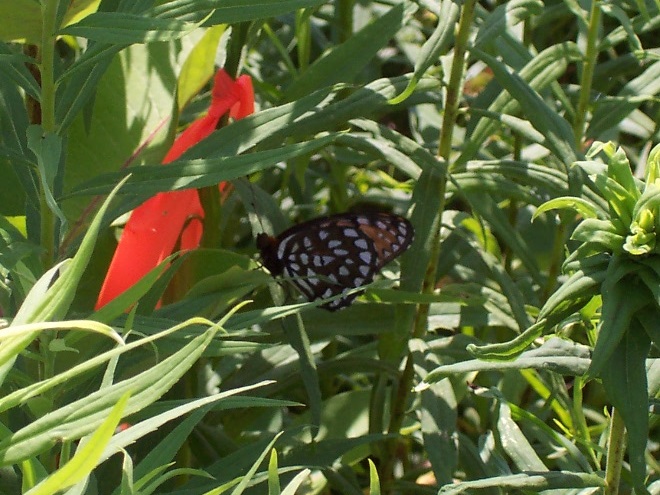
- Improve habitat for rare species (Regal Fritillary, etc.)
- Recycle nutrients and minerals contained in dead plant material.
-
Let’s look at some examples of prescribed fire being implemented right here in our own neighborhood…
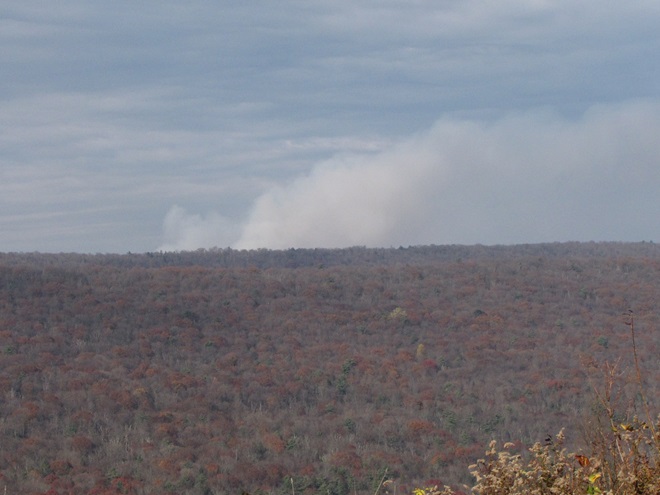
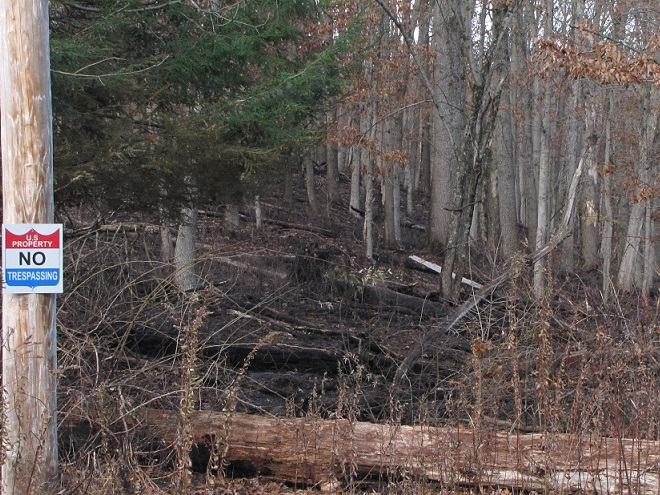
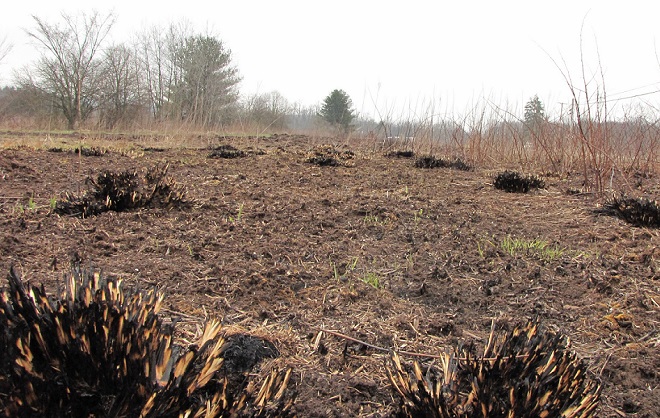
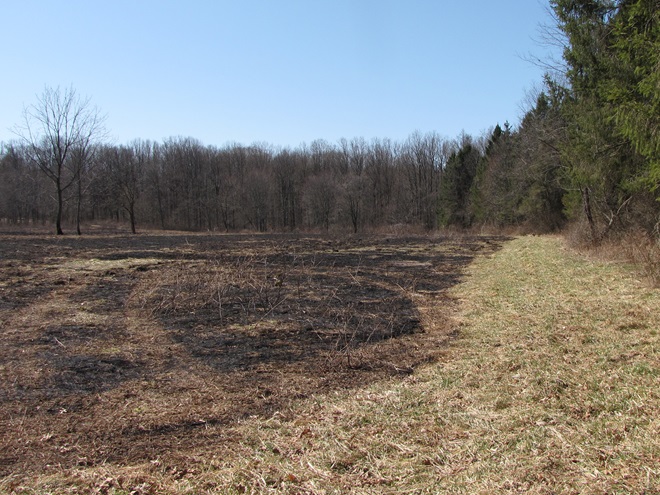
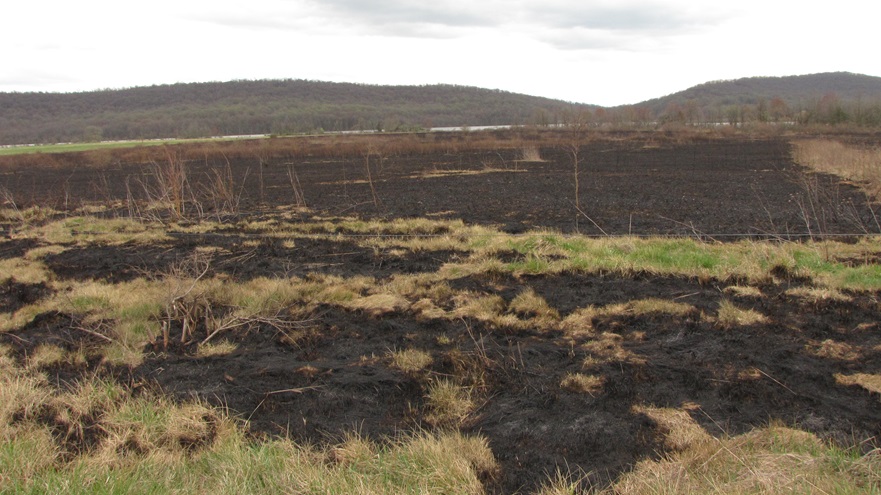

























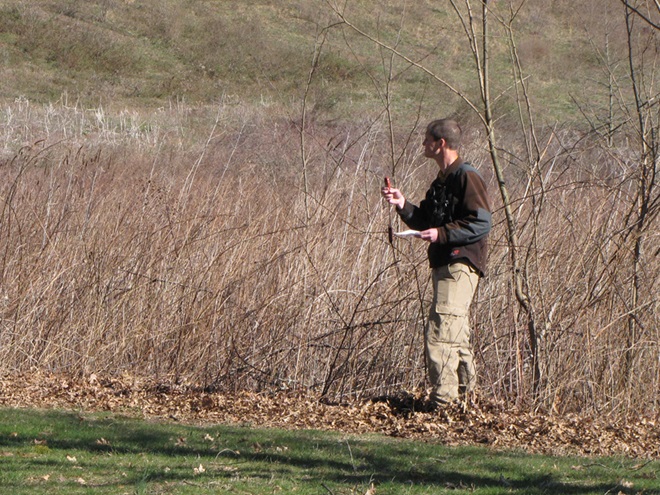
In Pennsylvania, state law provides landowners and crews conducting prescribed fire burns with reduced legal liability when the latter meet certain educational, planning, and operational requirements. This law may help encourage more widespread application of prescribed fire in the state’s forests and other ecosystems where essential periodic fire has been absent for so very long. Currently in the Lower Susquehanna River Watershed, prescribed fire is most frequently being employed by state agencies on state lands—in particular, the Department of Conservation and Natural Resources on State Forests and the Pennsylvania Game Commission on State Game Lands. Prescribed fire is also part of the vegetation management plan at Fort Indiantown Gap Military Reservation and on the land holdings of the Hershey Trust. Visitors to the nearby Gettysburg National Military Park will also notice prescribed fire being used to maintain the grassland restorations there.
For crews administering prescribed fire burns, late March and early April are a busy time. The relative humidity is often at its lowest level of the year, so the probability of ignition of previous years’ growth is generally at its best. We visited with a crew administering a prescribed fire at Middle Creek Wildlife Management Area last week. Have a look…
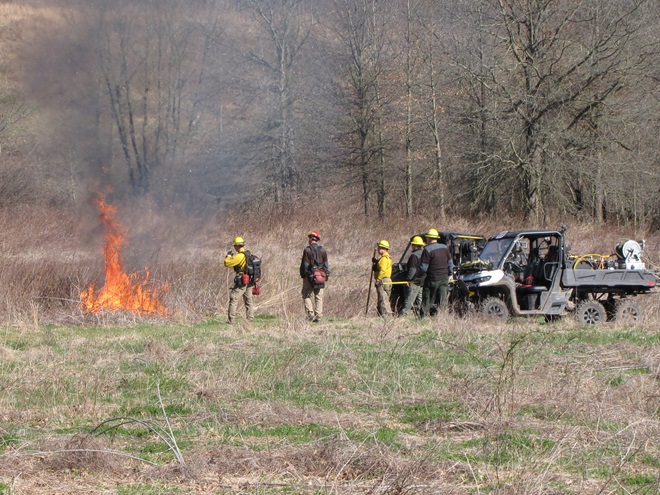
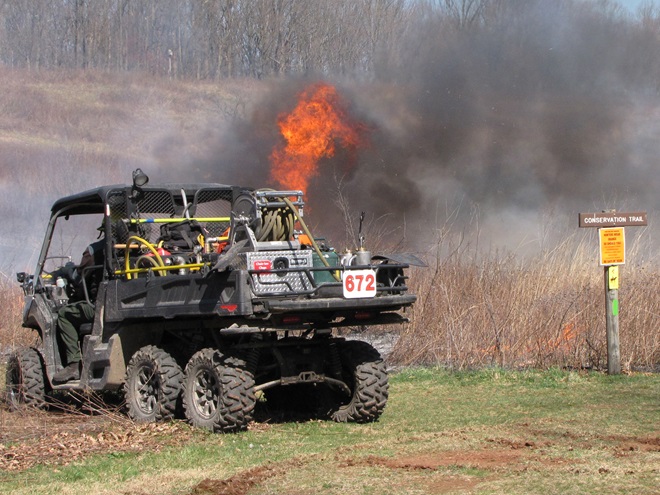
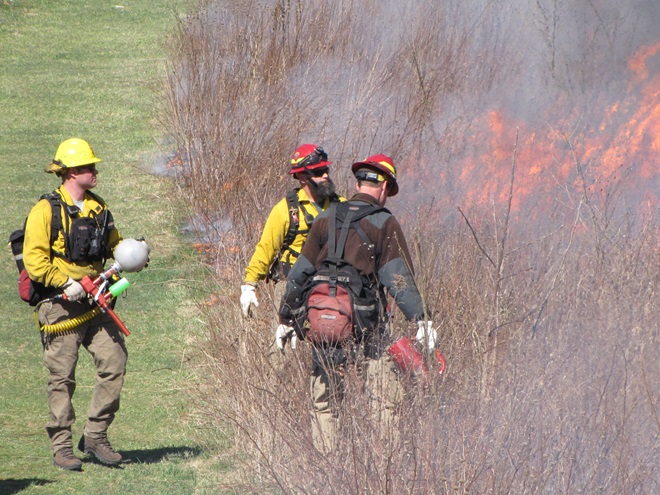
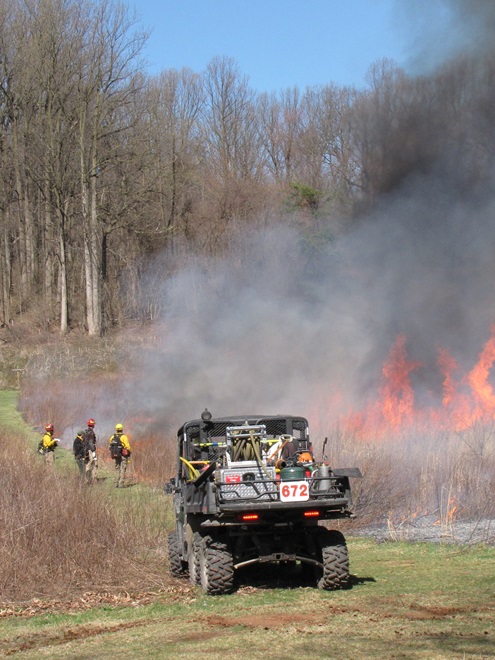
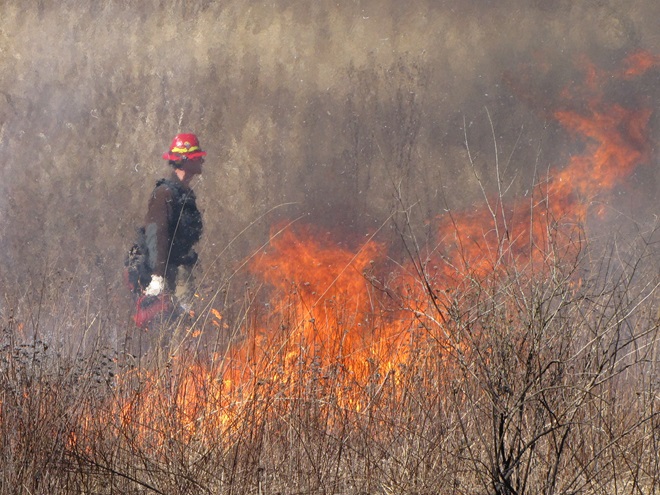
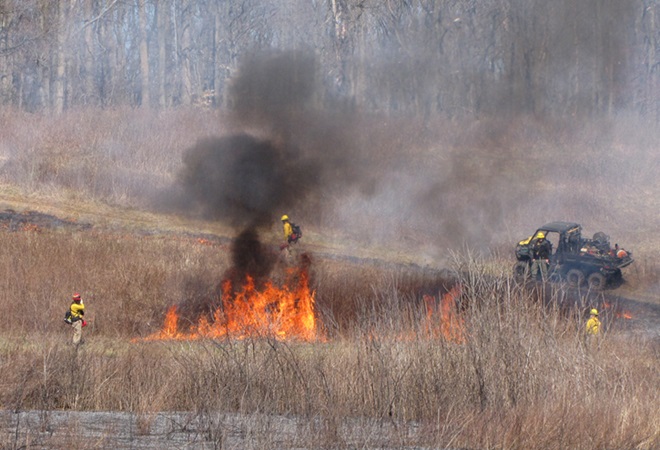
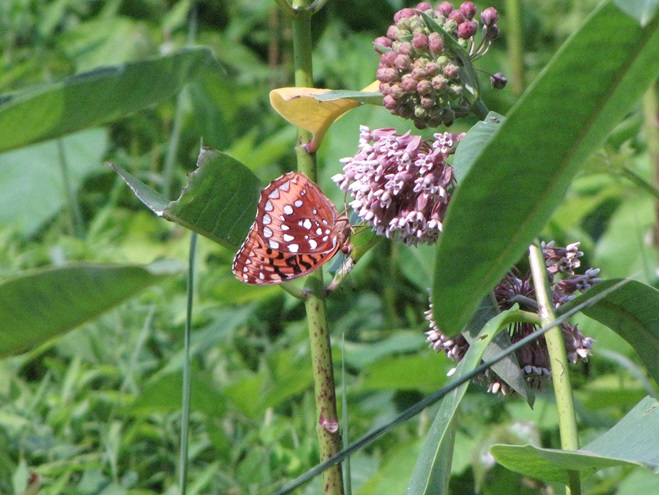

















Prescribed burns aren’t a cure-all for what ails a troubled forest or other ecosystem, but they can be an effective remedy for deficiencies caused by a lack of periodic episodes of naturally occurring fire. They are an important option for modern foresters, wildlife managers, and other conservationists.